Restoration of Neogene paleo-geomorphology of Yinggehai Basin
-
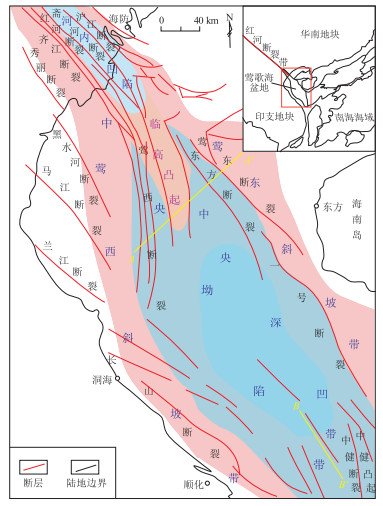
摘要: 新近系三亚组和梅山组是莺歌海盆地烃源岩发育的重要层系,研究其古构造地貌是预测烃源岩分布和油气资源潜力的基础。应用“构造应力体制保持不变的情况下,盆地内古构造地貌继承性发育”的思想,在确定莺歌海盆地新近纪构造变形应力体制及其演化的基础上,应用“将今论古”和“比例补偿”的思想和方法,分别以盆地现今地貌特征和地层厚度分布为基础资料,并以单井资料确定局部古海水深度作为约束条件,恢复莺歌海盆地新近纪的古构造地貌(古海水深度)。指出莺歌海盆地在三亚组和梅山组沉积时期是半封闭的局限海湾环境,有利于烃源岩的发育;提出古构造地貌研究的新方法——比例补偿法,可应用于其他盆地古构造地貌的恢复。Abstract: The Neogene Sanya and Meishan formations are important sequences of source rocks in the Yinggehai Basin. Understanding the paleo-tectonic geomorphology is an important basis for predicting the distribution of source rocks and the potential of oil and gas resources. Based on the rule that "the paleo-tectonic environment develops in the inherited way when tectonic stress system remains unchanged", we applied the idea and method of "the present is the key to the past" and "proportional compensation" to interpret the Neogene tectonic deformation system and its evolution in the Yinggehai Basin. The current geomorphological features and stratigraphic thickness distribution were used with the paleo-sea depth determined from single well data as a constraint to restore the Neogene paleo-geomorphology of the Yinggehai Basin. The Yinggehai Basin was a semi-enclosed confined bay during the deposition of the Sanya and Meishan formations, which was conducive to the development of source rocks. The "proportional compensation" method, which is a new way for paleo-geomorphology restoration, can be applied in other basins.
-
表 1 莺歌海盆地构造演化阶段
Table 1. Tectonic evolution of the Yinggehai Basin

表 2 莺歌海盆地中新世时期古海水深度与地层厚度的关系
Table 2. Relationship between paleo-seawater depth and stratigraphic thickness in Yinggehai Basin during Miocene
地层 水深范围/m 水深平均值/m 地层厚度/m 比例补偿系数 黄流组 25~148 78 600 15/17 梅山组 25~154 51 900 18/19 三亚组 25~50 32 200 10/11 -
[1] 何将启, 王彦. 莺歌海盆地盆地结构及天然气成藏模式研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2001, 23(4): 373-377. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200104373HE Jiangqi, WANG Yan. Study on the natural gas accumulation models and structure of the Yinggehai Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2001, 23(4): 373-377. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200104373 [2] 范彩伟. 莺-琼盆地高压成因输导体系特征、识别及其成藏过程[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(2): 254-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201802006.htmFAN Caiwei. The identification and characteristics of migration system induced by high pressure, and its hydrocarbon accumulation process in the Yingqiong Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(2): 254-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201802006.htm [3] 黄保家, 肖贤明, 董伟良. 莺歌海盆地烃源岩特征及天然气生成演化模式[J]. 天然气工业, 2002, 22(1): 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200201006.htmHUANG Baojia, XIAO Xianming, DONG Weiliang. Characteristics of hydrocarbon source rocks and generation & evolution model of natural gas in Yinggehai Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2002, 22(1): 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200201006.htm [4] 何家雄, 施小斌, 阎贫, 等. 南海北部边缘盆地油气地质特征与勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2007, 28(2): 129-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200702000.htmHE Jiaxiong, SHI Xiaobin, YAN Pin, et al. Petroleum geology and exploratory targets in marginal basins, northern South China Sea[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2007, 28(2): 129-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200702000.htm [5] 何卫军, 谢金有, 刘新宇, 等. 莺歌海盆地DF1-1-11井有孔虫生物地层与沉积环境研究[J]. 地层学杂志, 2011, 35(1): 81-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201101015.htmHE Weijun, XIE Jinyou, LIU Xinyu, et al. Foraminiferal biostrati-graphy and sedimentary environment reconstruction based on paleontological data from bore hole DF1-1-11, Yinggehai Basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2011, 35(1): 81-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201101015.htm [6] 何卫军, 张建新, 左倩媚, 等. 微体古生物在高精度层序地层及古环境研究中的应用: 以莺-琼盆地为例[J]. 地层学杂志, 2013, 37(4): 410-416. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201304003.htmHE Weijun, ZHANG Jianxin, ZUO Qianmei, et al. The application of micropaleontology in high-resolution sequence stratigraphy and paleoenvironmental reconstruction: a case study of the Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2013, 37(4): 410-416. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201304003.htm [7] 谢金有, 祝幼华, 麦文, 等. 南海北部莺琼盆地钙质超微化石年代地层研究[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2010, 27(4): 289-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT201004001.htmXIE Jinyou, ZHU Youhua, MAI Wen, et al. Chronostratigraphy of calcareous nannofossils in the Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2010, 27(4): 289-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT201004001.htm [8] 王随继, 黄杏珍, 妥进才, 等. 泌阳凹陷核桃园组微量元素演化特征及其古气候意义[J]. 沉积学报, 1997, 15(1): 65-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB701.011.htmWANG Suiji, HUANG Xingzhen, TUO Jincai, et al. Evolutional characteristics and their paleoclimate significance of trace elements in the Hetaoyuan Formation, Biyang Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1997, 15(1): 65-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB701.011.htm [9] 许淑梅, 吴鹏, 张威, 等. 南海关键地质历史时期的古海岸线变化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201301003.htmXU Shumei, WU Peng, ZHANG Wei, et al. Paleo-coastline changes in South China Sea in some critical times[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201301003.htm [10] VAIL P R, HARDENBOL J, TODD R G. Jurassic unconfor-mities, chronostratigraphy, and sea-level changes from seismic stratigraphy and biostratigraphy[J]. AAPG Special Volumes, 1984, 36: 129-144. [11] HARRIS P M, FROST S H, SEIGLIE G A, et al. Regional unconformities and depositional cycles, Cretaceous of the Arabian Peninsula[J]. AAPG Special Volumes, 1984, 36: 67-80. [12] 杨平, 陈晔, 刘泽纯. 柴达木盆地自然伽玛曲线在古气候及沉积环境研究中的应用[J]. 古地理学报, 2003, 5(1): 94-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200301008.htmYANG Ping, CHEN Ye, LIU Zechun. Application of gamma ray log to study on palaeoclimate and sedimentary environments of the Jurassic in Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2003, 5(1): 94-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200301008.htm [13] 万锦峰, 鲜本忠, 佘源琦, 等. 基于伽马能谱测井信息的古水深恢复方法: 以塔河油田4区巴楚组为例[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2011, 33(6): 98-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201106021.htmWAN Jinfeng, XIAN Benzhong, SHE Yuanqi, et al. Palaeobathymetric reconstruction based on natural gamma ray spectrometry logging data: by taking Bachu Formation in region 4 of Tahe oilfield for example[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2011, 33(6): 98-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201106021.htm [14] 郭秋麟, 倪丙荣. 利用化石群分异度探讨古水深[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 1990, 14(2): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX199002000.htmGUO Qiulin, NI Bingrong. Determination of palaeodepth with diversity of fossil community[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 1990, 14(2): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX199002000.htm [15] VAIL P R, AUDEMART F, BOWMAN S A, et al. The stratigraphic signatures of tectonics, eustasy and sedimentation: an overview[M]//EINSELE G, RICKEN W, SEILACHER A. Cyclic stratigraphy. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1991: 617-659. [16] LIN C S, ERIKSSON K, LI S T, et al. Sequence architecture, depositional systems, and controls on development of lacustrine basin fills in part of the Erlian Basin, Northeast China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2001, 85(11): 2017-2043. [17] TONY J T. Reservoir characterization, paleoenvironment, and paleo-geomorphology of the Mississippian Redwall limestone paleokarst, Hualapai Indian Reservation, Grand Canyon area, Arizona[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(11): 1875. [18] 辛云路, 任建业, 李建平. 构造-古地貌对沉积的控制作用: 以渤海南部莱州湾凹陷沙三段为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(3): 302-308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201303008.htmXIN Yunlu, REN Jianye, LI Jianping. Control of tectonic-paleogeomorphology on deposition: a case from the Shahejie Formation Sha 3 Member, Laizhouwan Sag, southern Bohai Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(3): 302-308. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201303008.htm [19] 刘峰, 裴健翔, 汪洋, 等. 古地貌对海底扇沉积过程的控制及与油气富集的关系: 以莺歌海盆地东方区黄流组一段为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2015, 27(4): 37-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201504005.htmLIU Feng, PEI Jianxiang, WANG Yang, et al. Palaeogeomorphologic control on sedimentary process of submarine fans and hydrocarbon accumulation: a case study of Member 1 of Huangliu Formation in DF area, Yinggehai Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2015, 27(4): 37-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201504005.htm [20] 童亨茂, 赵宝银, 曹哲, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷断裂系统成因的构造解析[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(11): 1647-1661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201311002.htmTONG Hengmao, ZHAO Baoyin, CAO Zhe, et al. Structural analysis of faulting system origin in the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. ACTA Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(11): 1647-1661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201311002.htm [21] 童亨茂, 范彩伟, 孟令箭, 等. 中国东-南部裂陷盆地断裂系统复杂性的表现形式及成因机制: 以南堡凹陷和涠西南凹陷为例[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(9): 1753-1765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201809001.htmTONG Hengmao, FAN Caiwei, MENG Lingjian, et al. Manifestation and origin mechanism of the fault system complexity in rift basins in eastern-southern China: case study of the Nanbu and Weixinan sags[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(9): 1753-1765. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201809001.htm [22] 朱伟林, 吴景富, 张功成, 等. 中国近海新生代盆地构造差异性演化及油气勘探方向[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 88-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501010.htmZHU Weilin, WU Jingfu, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Discrepancy tectonic evolution and petroleum exploration in China offshore Cenozoic basins[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 88-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501010.htm [23] 杨东辉, 童亨茂, 范彩伟, 等. 莺歌海盆地构造转折界面的确定及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2019, 43(3): 590-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201903015.htmYANG Donghui, TONG Hengmao, FAN Caiwei, et al. Determination of the tectonic transformation surface in Yinggehai Basin and its geological significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2019, 43(3): 590-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201903015.htm [24] 舒良树. 普通地质学[M]. 3版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010: 202.SHU Liangshu. Physical geology[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2010: 202. [25] 董刚, 何幼斌. 根据地层厚度恢复古水深的研究[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 7(3): 484-486. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201003176.htmDONG Gang, HE Youbin. Research of paleobathymetry recovery according to stratigraphic thickness[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 7(3): 484-486. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201003176.htm [26] 张辉, 胡望水, 李伟, 等. 关键层面古地貌演化剖面的建立及地质意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2018, 25(2): 8-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201802002.htmZHANG Hui, HU Wangshui, LI Wei, et al. Establishment of paleo-topography evolutionary section of key strata boundary and its geological implications[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2018, 25(2): 8-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201802002.htm -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号