Multi-scale characterization of the spatial distribution of movable hydrocarbon in intersalt shale of Qianjiang Formation, Qianjiang Sag, Jianghan Basin
-
摘要: 为更精细地刻画可动页岩油赋存的孔隙空间特征,通过对比抽提前后样品在低温氮气吸附实验的吸附量变化、高压压汞实验的进汞量变化以及场发射扫描电镜中的孔径变化特征,来表征可动页岩油赋存的孔隙空间。研究表明,江汉盆地潜江凹陷古近系潜江组Eq34-10韵律可动页岩油主要赋存在微、纳米级的白云石晶间孔、粒间孔以及黏土矿物层间孔中,纹层状发育的页岩可动页岩油较为富集。以孔径80 nm为界拼接低温氮吸附和高压压汞测试孔径,结果表明,可动页岩油主要赋存在孔径小于200 nm的范围内,微米级孔隙内也有赋存,90~200 nm孔径范围内可动页岩油赋存相对较多。黏土矿物含量较低的样品,在孔径小于等于5 nm的范围内抽提出可动页岩油。孔隙度越高,平均孔径越大,可动页岩油越富集。Abstract: Pore space containing mobile shale oil was more precisely characterized by comparing the change of adsorption volume of low-temperature nitrogen experiments and the change of mercury intake volume in high-pressure mercury injection experiments and the change of pore diameter using field emission scanning electron microscopy. The Eq34-10 rhythmic mobile hydrocarbon mainly occurs in dolomitic intercrystalline/intergranular pores and clay mineral interbedded pores, and movable hydrocarbon is relatively rich in lamellar shale. Low temperature nitrogen adsorption and high-pressure mercury injection measurements of pore size were spliced with pore size of 80 nm, and the results showed that movable hydrocarbon mainly occurs in the range of pore size less than 200 nm, and also occurs in the micron sized pores. Relatively more movable shale oil occurs in pores from 90 nm to 200 nm. The samples with low clay mineral content can yield movable hydrocarbon within the pores of ≤5 nm. The higher the porosity, the larger the average pore size, and the richer the movable shale oil.
-
Key words:
- movable shale oil /
- multi-scale /
- occurrence spatial /
- Qianjiang Formation /
- Qianjiang Sag /
- Jianghan Basin
-
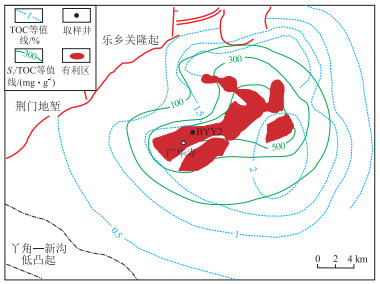
图 1 江汉盆地潜江凹陷潜江组Eq34-10韵律有利区分布及取样位置[28]
Figure 1. Advantageous reservoir distribution and sampling location of Eq34-10 rhythm of Qianjiang Formation
表 1 江汉盆地潜江凹陷潜江组页岩样品地化特征及矿物组成
Table 1. Geochemical characteristics and mineral composition of shale samples from Qianjiang Formation in Qianjiang Sag, Jianghan Basin
样品号 深度/m 岩性 S1/(mg·g-1) w(TOC)/% 矿物成分/% 黏土 石英 长石 方解石 白云石 黄铁矿 石盐 硬石膏 透闪石 石膏 BYY2-21 2 814.45 褐色灰质泥岩 4.24 1.83 9.13 13.87 21.37 36.25 15.17 1.94 2.27 - - - BYY2-28 2 814.67 深灰色云质页岩 7.25 2.40 - 7.09 7.68 13.50 64.42 4.28 3.03 - - - BYY2-90 2 817.11 褐色页岩 9.85 2.44 19.96 8.60 28.35 5.17 29.71 2.68 1.95 3.59 - - BYY2-101 2 817.51 深灰色页岩 7.91 2.05 19.64 8.4 30.39 13.49 22.13 1.68 0.85 - 3.43 - BYY2-161 2 820.23 褐色云质泥岩 7.18 1.15 15.50 9.52 20.54 1.60 44.38 1.70 2.22 2.11 - 2.43 表 2 江汉盆地潜江凹陷潜江组Eq34-10韵律页岩样品抽提物族组分含量
Table 2. Component content of extract group in shale samples of Eq34-10 rhythm of Qianjiang Formation in Qianjiang Sag, Jianghan Basin
样品号 饱和烃 芳香烃 胶质 沥青质 BYY2-21 0.42 0.23 0.12 0.23 BYY2-28 0.37 0.19 0.11 0.33 BYY2-90 0.46 0.23 0.13 0.18 BYY2-101 0.39 0.21 0.13 0.27 BYY2-161 0.36 0.24 0.16 0.24 -
[1] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望: 以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2): 173-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201202002.htmZOU Caineng, ZHU Rukai, WU Songtao, et al. Types, characteristics, genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations: taking tight oil and tight gas in China as an instance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 173-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201202002.htm [2] CURTIS M E, CARDOTT B J, SONDERGELD C H, et al. Development of organic porosity in the Woodford shale with increasing thermal maturity[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2012, 103: 26-31. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2012.08.004 [3] GUO Huijuan, JIA Wanglu, PENG Ping'an, et al. Evolution of organic matter and nanometer-scale pores in an artificially matured shale undergoing two distinct types of pyrolysis: a study of the Yanchang shale with type Ⅱ kerogen[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 105: 56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2017.01.004 [4] MASTALERZ M, SCHIMMELMANN A, DROBNIAK A, et al. Porosity of Devonian and Mississippian New Albany shale across a maturation gradient: insights from organic petrology, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(10): 1621-1643. doi: 10.1306/04011312194 [5] 张琴, 朱筱敏, 李晨溪, 等. 渤海湾盆地沾化凹陷沙河街组富有机质页岩孔隙分类及孔径定量表征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(3): 422-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201603017.htmZHANG Qin, ZHU Xiaomin, LI Chenxi, et al. Classification and quantitative characterization of microscopic pores in organic-rich shale of the Shahejie Formation in the Zhanhua Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(3): 422-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201603017.htm [6] 包友书. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷古近系页岩油主要赋存空间探索[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(4): 479-484. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201804479BAO Youshu. Effective reservoir spaces of Paleogene shale oil in the Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geo-logy & Experiment, 2018, 40(4): 479-484. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201804479 [7] 雷浩, 何建华, 胡振国. 潜江凹陷页岩油藏渗流特征物理模拟及影响因素分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(3): 94-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2019.03.017LEI Hao, HE Jianhua, HU Zhenguo. Physical simulation and influencing factor analysis of the flow characteristics in the shale oil reservoir of Qianjiang Depression[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(3): 94-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2019.03.017 [8] 马海洋, 夏遵义, 温庆志, 等. 渤海湾盆地沾化凹陷页岩微观孔隙特征实验研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(1): 149-156. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901149MA Haiyang, XIA Zunyi, WEN Qingzhi, et al. Micro-pore characte-ristics of shale in Zhanhua Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(1): 149-156. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901149 [9] 申浩冉, 丁文龙, 谷阳, 等. 黔北凤冈地区龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构特征[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(4): 480-485. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201904016.htmSHEN Haoran, DING Wenlong, GU Yang, et al. Pore structure characteristics of Longmaxi Formation shale in Fenggang area, northern Guizhou[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2019, 26(4): 480-485. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201904016.htm [10] 彭钰洁, 刘鹏, 吴佩津. 页岩有机质热演化过程中孔隙结构特征研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2018, 25(5): 141-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201805027.htmPENG Yujie, LIU Peng, WU Peijin. Pore structure characterization of shale organic matter during thermal evolution[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2018, 25(5): 141-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201805027.htm [11] 公言杰, 柳少波, 赵孟军, 等. 核磁共振与高压压汞实验联合表征致密油储层微观孔喉分布特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(3): 389-394. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201603389GONG Yanjie, LIU Shaobo, ZHAO Mengjun, et al. Characterization of micro pore throat radius distribution in tight oil reservoirs by NMR and high pressure mercury injection[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(3): 389-394. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201603389 [12] 杨峰, 宁正福, 孔德涛, 等. 高压压汞法和氮气吸附法分析页岩孔隙结构[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(3): 450-455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201303002.htmYANG Feng, NING Zhengfu, KONG Detao, et al. Pore structure of shales from high pressure mercury injection and nitrogen adsorption method[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(3): 450-455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201303002.htm [13] 宁方兴, 王学军, 郝雪峰, 等. 济阳坳陷页岩油赋存状态和可动性分析[J]. 新疆石油天然气, 2015, 11(3): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY201503001.htmNING Fangxing, WANG Xuejun, HAO Xuefeng, et al. An analysis on occurrence state and mobility of shale oil in Jiyang Depression[J]. Xinjiang Oil & Gas, 2015, 11(3): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY201503001.htm [14] 宋国奇, 张林晔, 卢双舫, 等. 页岩油资源评价技术方法及其应用[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(4): 221-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304021.htmSONG Guoqi, ZHANG Linye, LU Shuangfang, et al. Resource evaluation method for shale oil and its application[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4): 221-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304021.htm [15] 蒋启贵, 黎茂稳, 钱门辉, 等. 不同赋存状态页岩油定量表征技术与应用研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(6): 842-849. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201606842JIANG Qigui, LI Maowen, QIAN Menhui, et al. Quantitative characterization of shale oil in different occurrence states and its application[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(6): 842-849. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201606842 [16] 郭小波, 黄志龙, 陈旋, 等. 马朗凹陷芦草沟组泥页岩储层含油性特征与评价[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(1): 166-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201401019.htmGUO Xiaobo, HUANG Zhilong, CHEN Xuan, et al. The oil-bearing property characteristics and evaluation of Lucaogou Formation shale reservoirs in Malang Sag[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(1): 166-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201401019.htm [17] JARVIE D M. Components and processes affecting producibility and commerciality of shale resource systems[J]. Geologica Acta, 2014, 12(4): 307-325. [18] LI Jinbu, HUANG Wenbiao, LU Shuangfang, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance T1-T2 map division method for hydrogen-bearing components in continental shale[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(9): 9043-9054. [19] LI Zheng, ZOU Yanrong, XU Xingyou, et al. Adsorption of mudstone source rock for shale oil: experiments, model and a case study[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2016, 92: 55-62. [20] SANEI H, WOOD J M, ARDAKANI O H, et al. Characterization of organic matter fractions in an unconventional tight gas siltstone reservoir[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2015, 150-151: 296-305. [21] 肖枫. 潜江凹陷潜江组盐间页岩储层特征研究: 以潜3410韵律和潜40中5韵律为例[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2017.XIAO Feng. Study on the characteristics of salt shale reservoir in Qianjiang Formation in Qianjiang Sag: a case study of the 10th rhythm of Eq34 and the 5th rhythm of middle Eq40[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University, 2017. [22] 龙玉梅, 陈曼菲, 陈风玲, 等. 潜江凹陷潜江组盐间页岩油储层发育特征及影响因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(1): 59-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201901006.htmLONG Yumei, CHEN Manfei, CHEN Fengling, et al. Characte-ristics and influencing factors of inter-salt shale oil reservoirs in Qianjiang Formation, Qianjiang Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(1): 59-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201901006.htm [23] 孙中良, 王芙蓉, 何生, 等. 潜江凹陷古近系盐间典型韵律层页岩孔隙结构[J]. 深圳大学学报(理工版), 2019, 36(3): 289-297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZDL201903010.htmSUN Zhongliang, WANG Furong, HE Sheng, et al. The pore structures of the shale about typical inter-salt rhythm in the Paleogene of Qianjiang Depression[J]. Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering, 2019, 36(3): 289-297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZDL201903010.htm [24] 王民, 马睿, 李进步, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系沙河街组湖相页岩油赋存机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(4): 789-802. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201904020.htmWANG Min, MA Rui, LI Jinbu, et al. Occurrence mechanism of lacustrine shale oil in the Paleogene Shahejie Formation of Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(4): 789-802. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201904020.htm [25] 李卓, 姜振学, 唐相路, 等. 渝东南下志留统龙马溪组页岩岩相特征及其对孔隙结构的控制[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2017, 42(7): 1116-1123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707007.htmLI Zhuo, JIANG Zhenxue, TANG Xianglu, et al. Lithofacies characteristics and its effect on pore structure of the marine shale in the Low Silurian Longmaxi Formation, southeastern Chongqing[J]. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2017, 42(7): 1116-1123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707007.htm [26] 吴世强, 唐小山, 杜小娟, 等. 江汉盆地潜江凹陷陆相页岩油地质特征[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 36(3): 282-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ201303006.htmWU Shiqiang, TANG Xiaoshan, DU Xiaojuan, et al. Geologic characteristics of continental shale oil in the Qianjiang Depression, Jianghan Salt Lake Basin[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology (Natural Science), 2013, 36(3): 282-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ201303006.htm [27] 熊智勇, 吴世强, 王洋, 等. 江汉盐湖盆地盐间泥质白云岩油藏地质特征与实践[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2): 181-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502027.htmXIONG Zhiyong, WU Shiqiang, WANG Yang, et al. Geological characteristics and practice for intersalt argillaceous dolomites reservoir in the Qianjiang Depression of Jianghan Salt Lake Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(2): 181-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502027.htm [28] 吴严冬. 潜江凹陷潜34-10韵律页岩油储层录井评价[J]. 江汉石油职工大学学报, 2019, 32(5): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSZD201905001.htmWU Yandong. Logging evaluation on Qian 34-10 rhythm shale oil reservoir in Qianjiang Sag[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum University of Staff and Workers, 2019, 32(5): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSZD201905001.htm [29] 孙中良, 王芙蓉, 侯宇光, 等. 潜江凹陷潜江组页岩中可溶有机质赋存空间表征及影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 81-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906011.htmSUN Zhongliang, WANG Furong, HOU Yuguang, et al. Spatial characterization and influencing factors of soluble organic matter in shale of Qianjiang Formation in Qianjiang Depression[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 81-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906011.htm [30] 赵悦, 蔡进功, 雷天柱, 等. 泥质烃源岩中不同赋存状态有机质定量表征: 以东营凹陷沙河街组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(4): 416-423. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201804006.htmZHAO Yue, CAI Jingong, LEI Tianzhu, et al. Quantitative characte-rization of organic matters with different occurrences in argillaceous source rocks: a case of Shahejie Formation, Dongying Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(4): 416-423. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201804006.htm [31] WANG Guochang, JU Yiwen, YAN Zhifeng, et al. Pore structure characteristics of coal-bearing shale using fluid invasion methods: a case study in the Huainan-Huaibei Coalfield in China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 62: 1-13. [32] 钱门辉, 蒋启贵, 黎茂稳, 等. 湖相页岩不同赋存状态的可溶有机质定量表征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2): 278-286. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702278QIAN Menhui, JIANG Qigui, LI Maowen, et al. Quantitative characterization of extractable organic matter in lacustrine shale with different occurrences[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(2): 278-286. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702278 -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号