Accumulation factor matching and model of Bozhong 19-6 buried hill gas reservoir, Bohai Sea area
-
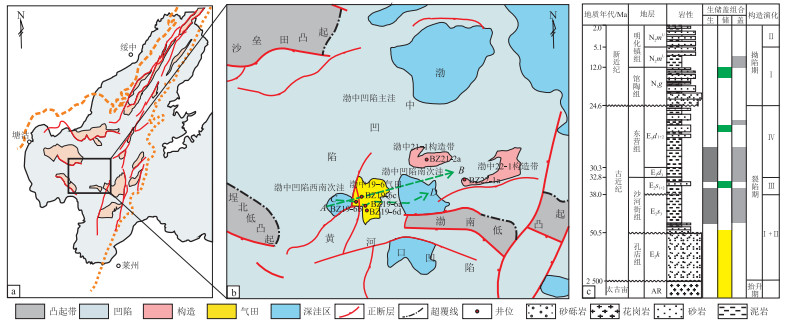
摘要: 为了明确渤海海域渤中19-6潜山千亿立方米气藏的形成过程,基于大量岩心、薄片、测井及地球化学数据,在地质分析的基础上,利用地球化学分析方法和盆地模拟的手段,对其成藏要素及成藏规律进行了系统分析。研究表明:(1)渤中凹陷沙三段烃源岩生气强度普遍超过50×108 m3/km2,晚期持续供烃为渤中19-6潜山气藏的形成提供了充足的物质基础;(2)印支期和燕山期构造运动是渤中19-6潜山构造裂缝型储层和潜山圈闭形成的关键时期,并形成了近源断裂输导体系和远源不整合面输导体系;(3)东营组厚层超压泥岩盖层和潜山较弱的晚期构造活动有利于渤中19-6潜山气藏的保存;(4)“生、储、盖、圈、运、保”六大成藏要素的时空匹配,最终导致了渤中19-6潜山千亿立方米大气田的形成。建立了渤中19-6潜山多洼供烃、多向充注、断裂和不整合联合输导的晚期成藏模式。
-
关键词:
- 渤中19-6潜山气田 /
- 成藏要素耦合 /
- 成藏模式 /
- 渤中凹陷 /
- 渤海海域
Abstract: The accumulation factors and mechanism of the 100 billion cubic meters gas reservoir in the Bozhong 19-6 buried hill of the Bohai Sea area were studied using geochemical analyses and basin modelling based on a large amount of core, cast thin section, well logging and geochemical data. The results showed the following. (1) The gas generated by the source rocks of the third member of the Shahejie Formation in the Bozhong Sag generally exceeds 5×109 m3/km2. The continuous hydrocarbon supply in the late period provided sufficient material for the formation of the Bozhong 19-6 buried hill gas reservoir. (2) The Indosinian and Yanshanian tectonic movements were the key periods for the formation of structural fractured reservoirs and buried-hill traps, and formed a near-source fault transport system and a far-source unconformity transport system. (3) The thick overpressure mudstone cap rocks of the Dongying Formation and the weak tectonic activity in the late period were beneficial to the preservation of the Bozhong 19-6 buried hill gas reservoir. (4) The time-space matching of the six major accumulation factors of "generation, storage, cap rock, trap, migration, and preservation" ultimately led to the formation of a large gas field of 100 billion cubic meters in the Bozhong 19-6 buried hill. A late accumulation model of multi-depression hydrocarbon supply, multi-directional charging, combined fault and unconformity transport was established in the Bozhong 19-6 buried hill. -
图 7 渤海海域渤中19-6潜山输导体系
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 7. Transport system of Bozhong 19-6 buried hill, Bohai Sea area
图 12 渤海海域渤中19-6潜山气藏成藏模式
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 12. Hydrocarbon accumulation pattern in Bozhong 19-6 buried hill, Bohai Sea area
-
[1] 高长海, 查明, 赵贤正, 等. 渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷深层古潜山油气成藏模式及其主控因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(4): 52-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201704009.htmGAO Changhai, ZHA Ming, ZHAO Xianzheng, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation models and their main controlling factors in the deep buried hills of the Jizhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(4): 52-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201704009.htm [2] 陈昭年. 石油与天然气地质学[M]. 2版. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013.CHEN Zhaonian. Oil and gas geology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Geolo-gical Publishing House, 2013. [3] 马立驰, 王永诗, 景安语. 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷隐蔽潜山油藏新发现及其意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(1): 13-18. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001013MA Lichi, WANG Yongshi, JING Anyu. Discovery and significance of subtle buried hills in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(1): 13-18. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001013 [4] 金强, 毛晶晶, 杜玉山, 等. 渤海湾盆地富台油田碳酸盐岩潜山裂缝充填机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(4): 454-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201504007.htmJIN Qiang, MAO Jingjing, DU Yushan, et al. Fracture filling mechanisms in the carbonate buried-hill of Futai Oilfield in Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(4): 454-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201504007.htm [5] 姜平. 千米桥潜山构造油气藏成藏分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(3): 14-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200003003.htmJIANG Ping. A pool formation analysis for Qianmiqiao buried hill structure[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(3): 14-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200003003.htm [6] 杨克绳. 任丘古潜山油田的发现与地质特点[J]. 断块油气田, 2010, 17(5): 525-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201005003.htmYANG Kesheng. Discovery and geologic characteristics of Renqiu Oilfield with buried hill[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2010, 17(5): 525-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201005003.htm [7] 冯渊, 柳广弟, 杨伟伟, 等. 辽河坳陷兴隆台油田成藏特征与成藏模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(1): 137-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201401021.htmFENG Yuan, LIU Guangdi, YANG Weiwei, et al. Characteristics and models of hydrocarbon accumulation in Xinglongtai Oilfield, Liaohe Depression[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geo-logy, 2014, 34(1): 137-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201401021.htm [8] 薛永安. 渤海海域深层天然气勘探的突破与启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(1): 11-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201901003.htmXUE Yong'an. The breakthrough of the deep-buried gas exploration in the Bohai Sea area and its enlightenment[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(1): 11-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201901003.htm [9] 施和生, 王清斌, 王军, 等. 渤中凹陷深层渤中19-6构造大型凝析气田的发现及勘探意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(1): 36-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201901006.htmSHI Hesheng, WANG Qingbin, WANG Jun, et al. Discovery and exploration significance of large condensate gas fields in BZ19-6 structure in deep Bozhong Sag[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(1): 36-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201901006.htm [10] 李慧勇, 徐云龙, 王飞龙, 等. 渤海海域深层潜山油气地球化学特征及油气来源[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(1): 45-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201901006.htmLI Huiyong, XU Yunlong, WANG Feilong, et al. Geochemical characteristics and sources of oil and gas in deep buried hills, Bohai Sea area[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(1): 45-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201901006.htm [11] 谢玉洪. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷太古界潜山气藏BZ19-6的气源条件与成藏模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 858-866. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005858XIE Yuhong. Gas resources and accumulation model of BZ19-6 Archean buried-hill large-scale gas reservoir in Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 858-866. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005858 [12] 薛永安, 王奇, 牛成民, 等. 渤海海域渤中凹陷渤中19-6深层潜山凝析气藏的充注成藏过程[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(5): 891-902. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202005002.htmXUE Yong'an, WANG Qi, NIU Chengmin, et al. Hydrocarbon charging and accumulation of BZ 19-6 gas condensate field in deep buried hills of Bozhong Depression, Bohai Sea[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(5): 891-902. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202005002.htm [13] 徐长贵, 于海波, 王军, 等. 渤海海域渤中19-6大型凝析气田形成条件与成藏特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1): 25-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901003.htmXU Changgui, YU Haibo, WANG Jun, et al. Formation conditions and accumulation characteristics of Bozhong 19-6 large condensate gas field in offshore Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1): 25-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901003.htm [14] 朱伟林, 米立军, 龚再升, 等. 渤海海域油气成藏与勘探[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.ZHU Weilin, MI Lijun, GONG Zaisheng, et al. Oil and gas accumulation and exploration in Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009. [15] 戴金星, 邹才能, 陶士振, 等. 中国大气田形成条件和主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2007, 18(4): 473-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200704001.htmDAI Jinxing, ZOU Caineng, TAO Shizhen, et al. Formation conditions and main controlling factors of large gas fields in China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2007, 18(4): 473-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200704001.htm [16] 卢欢, 牛成民, 李慧勇, 等. 变质岩潜山油气藏储层特征及评价[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(1): 28-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202001007.htmLU Huan, NIU Chengmin, LI Huiyong, et al. Reservoir feature and evaluation of metamorphic buried-hill reservoir[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(1): 28-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202001007.htm [17] 邓猛, 赵军寿, 金宝强, 等. 基于古地貌分析的中深层沉积储层质量评价: 以渤海X油田沙二段为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(2): 147-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201902004.htmDENG Meng, ZHAO Junshou, JIN Baoqiang, et al. Reservoir quality evaluation of middle-deep formations based on paleo-geomorphology analysis: a case study of Sha-2 Formation in X oilfield of Bohai Bay, China[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2019, 26(2): 147-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201902004.htm [18] 胡国艺, 汪晓波, 王义凤, 等. 中国大中型气田盖层特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(2): 162-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200902001.htmHU Guoyi, WANG Xiaobo, WANG Yifeng, et al. Cap rock characte-ristics of medium and large gas fields in China[J]. Natural gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(2): 162-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200902001.htm [19] 吕延防, 付广, 于丹. 中国大中型气田盖层封盖能力综合评价及其对成藏的贡献[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(6): 742-745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200506007.htmLV Yanfang, FU Guang, YU Dan. Comprehensive evaluation of sealing ability of cap rock in China's large and medium gas fields and their contribution to gas accumulation[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2005, 26(6): 742-745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200506007.htm [20] 吕延防, 张绍臣, 王亚明. 盖层封闭能力与盖层厚度的定量关系[J]. 石油学报, 2000, 21(2): 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200002005.htmLV Yanfang, ZHANG Shaochen, ZHANG Yaming. Research of quantitative relations between sealing ability and thickness of cap rock[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2000, 21(2): 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200002005.htm [21] 付广, 王彪, 史集建. 盖层封盖油气能力综合定量评价方法及应用[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2014, 48(1): 174-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC201401027.htmFU Guang, WANG Biao, SHI Jijian. Comprehensive quantitative evaluation method of sealing oil-gas ability of caprock and its application[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2000, 48(1): 174-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC201401027.htm [22] 谭明友, 刘福贵, 董臣强, 等. 埕北30潜山构造演化与油气富集规律研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2002, 37(2): 134-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ200202010.htmTAN Mingyou, LIU Fugui, DONG Chenqiang, et al. Study for evolution of CB30 buried hill structure and rule of oil-gas accumulation[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2002, 37(2): 134-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ200202010.htm [23] 付广, 王有功, 苏玉平. 超压泥岩盖层封闭性演化规律及其研究意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2006, 26(4): 453-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200604014.htmFU Guang, WANG Yougong, SU Yuping. Evoluation law for sealing of overpressured mudstone caprock and its research significance[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2006, 26(4): 453-459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200604014.htm [24] 彭波, 邹华耀. 渤海盆地现今岩石圈热结构及新生代构造—热演化史[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(6): 1399-1406. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201306018.htmPENG Bo, ZOU Huayao. Present-day geothermal structure of lithosphere and the Cenozoic tectono-thermal evolution of Bohai Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(6): 1399-1406. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201306018.htm [25] MAGARA K. Compaction and migration of fluids in Miocene mudstone, Nagaoka plain, Japan[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1968, 52(12): 2466-2501. [26] SMITH D A. Theoretical considerations of sealing and non-sealing faults[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1996, 50(2): 363-374. -





 下载:
下载:











 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号