Normal fault evolution in Lishu Fault Depression, southern Songliao Basin
-
摘要: 松辽盆地的形成受周缘构造带多方向、不同性质构造应力的影响,具有复杂的地质结构和盆地演化过程,位于松辽盆地南部的梨树断陷具有多种构造活动叠加复合演化的特征,是揭示周缘构造带活动过程及盆地构造—沉积响应的良好窗口,走滑构造活动是否控制了盆地沉积过程是长期以来未能解决的问题。利用三维地震数据开展精细解释,结合断距统计、构造模式分析等研究手段,对梨树断陷内桑树台断裂和秦家屯断裂早白垩世早期的伸展活动开展了研究。桑树台断裂演化过程受近东—西向伸展构造应力控制,断裂初始形成时规模较大,因而桑树台断裂受伸展方向调整影响较小;秦家屯断裂在下白垩统火石岭组沉积期受北东东—南西西伸展方向控制,下白垩统沙河子组沉积期受北东—南西伸展方向控制。梨树断陷早白垩世早期伸展活动和区域性走滑活动引起了伸展方向的变化。Abstract: The formation of the Songliao Basin was affected by multidirectional tectonic stress and various peripheral structural belts, and has a complicated geological structure and basin evolution process. The Lishu Fault Depression in the southern Songliao Basin has the characteristics of superimposed and complex evolution of multiple tectonic activities, and is a good window to reveal the impacts of the peripheral structural belts and basin tectonic-sedimentary response. Whether strike-slip tectonic activity controls the sedimentary process of the basin is an unsolved problem. Using three-dimensional seismic data to carry out detailed interpretation, combined with fault distance statistics, structural model analysis and other research methods, the extension activities of the Sangshutai and Qinjiatun faults in the Lishu Fault Depression during the Early Cretaceous were studied. The evolution process of the Sangshutai fault was controlled by the nearly east-west extensional tectonic stress. The initial scale of the fault was large, so the Sangshutai fault was less affected by the adjustment of the extension direction. The Qinjiatun fault was controlled by the NEE-SWW extension during the Early Cretaceous Huoshiling period, and by the NE-SW extension during the Early Cretaceous Shahezi period. The regional strike-slip activity in the Early Cretaceous extension in the Lishu Fault Depression caused a change in the extension direction.
-
Key words:
- extension structure /
- Early Cretaceous /
- Lishu Fault Depression /
- Songliao Basin
-
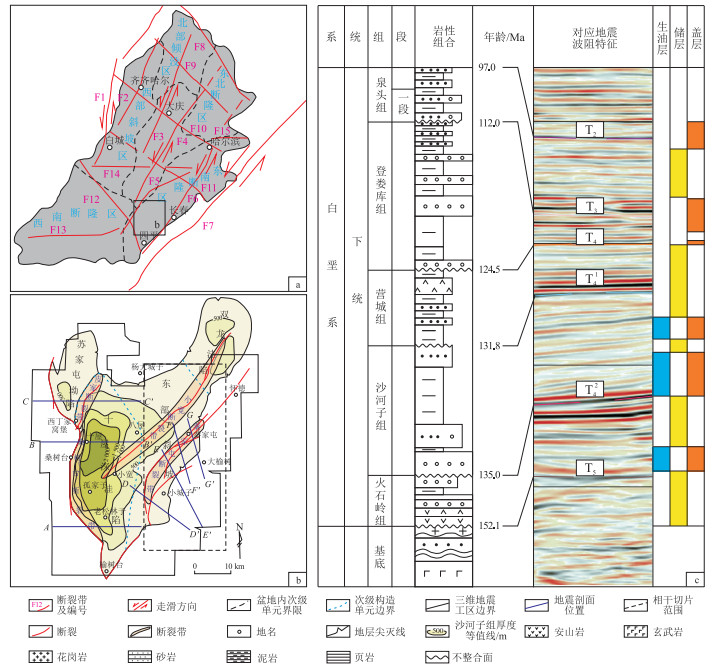
图 1 松辽盆地南部梨树断陷地质背景
a.松辽盆地内主要断裂构造示意,修改自文献[26];b.梨树断陷基本结构及主要地震剖面位置;c.梨树断陷地层岩性柱状图及对应波组特征;F1.嫩江—白城断裂;F2.富裕—泰来断裂;F3.德都—大安断裂;F4.青冈—乾安断裂;F5.双辽—扶余断裂;F6.四平—德惠断裂;F7.依兰—伊通断裂;F8.塔溪—林口断裂;F9.讷河—绥化断裂;F10.滨州断裂;F11.大安—扶余断裂;F12.突泉—四平断裂;F13.卧虎屯断裂;F14.洮安—扶余断裂;F15.松花江断裂
Figure 1. Geological setting of Lishu Fault Depression, southern Songliao Basin
图 2 松辽盆地梨树断陷桑树台断裂地震剖面解释方案
剖面位置见图 1b。
Figure 2. Interpretation of seismic profiles of Sangshutai Fault, Lishu Fault Depression, Songliao Basin
图 3 松辽盆地梨树断陷秦家屯断裂地震解释方案
剖面位置见图 1b。
Figure 3. Interpretation of seismic profiles of Qinjiatun Fault, Lishu Fault Depression, Songliao Basin
图 4 松辽盆地梨树断陷秦家屯断裂在不同深度的平面展布形态
切片范围见图 1b。
Figure 4. Distribution patterns of Qinjiatun Fault at different time depths, Lishu Fault Depression, Songliao Basin
-
[1] 李思田. 沉积盆地动力学研究的进展、发展趋向与面临的挑战[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501002.htmLI Sitian. Advancement, trend and new challenges in basin geodynamics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501002.htm [2] 琚宜文, 孙盈, 王国昌, 等. 盆地形成与演化的动力学类型及其地球动力学机制[J]. 地质科学, 2015, 50(2): 503-523. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201502010.htmJU Yiwen, SUN Ying, WANG Guochang, et al. Dynamic types of basin formation and evolution and its geodynamic mechanisms[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2015, 50(2): 503-523. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201502010.htm [3] 解习农, 林畅松, 李忠, 等. 中国盆地动力学研究现状及展望[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(5): 877-887. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201705002.htmXIE Xinong, LIN Changsong, LI Zhong, et al. Research reviews and prospects of sedimentary basin geodynamics in China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(5): 877-887. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201705002.htm [4] ZHOU Jianbo, WILDE S A, ZHANG Xingzhou, et al. The onset of Pacific margin accretion in NE China: evidence from the Heilongjiang high-pressure metamorphic belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 478(3/4): 230-246. [5] 李三忠, 张国伟, 周立宏, 等. 中、新生代超级汇聚背景下的陆内差异变形: 华北伸展裂解和华南挤压逆冲[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(3): 79-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201103012.htmLI Sanzhong, ZHANG Guowei, ZHOU Lihong, et al. The opposite Meso-Cenozoic intracontinental deformations under the superconvergence: Rifting and extension in the North China Craton and shortening and thrusting in the South China Craton[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(3): 79-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201103012.htm [6] 索艳慧, 李三忠, 曹现志, 等. 中国东部中新生代反转构造及其记录的大洋板块俯冲过程[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4): 249-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201704031.htmSUO Yanhui, LI Sanzhong, CAO Xianzhi, et al. Mesozoic-Cenozoic inversion tectonics of East China and its implications for the subduction process of the oceanic plate[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(4): 249-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201704031.htm [7] 黄磊, 童亨茂, 杨东辉, 等. 松辽盆地大庆长垣中浅层断层形成演化的新模式[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(3): 597-605. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201903006.htmHUANG Lei, TONG Hengmao, YANG Donghui, et al. A new model for the formation and evolution of middle-shallow faults in the Daqing placanticline, Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(3): 597-605. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201903006.htm [8] 孙永河, 陈艺博, 孙继刚, 等. 松辽盆地北部断裂演化序列与反转构造带形成机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(3): 275-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201303005.htmSUN Yonghe, CHEN Yibo, SUN Jigang, et al. Evolutionary sequence of faults and the formation of inversion structural belts in the northern Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(3): 275-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201303005.htm [9] 单伟. 松辽盆地南部长岭、十屋断陷层构造演化与沉积响应研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2009: 1-161.SHAN Wei. Research of the structural evolution and its sedimental response in Chinaling, Shiwu faulted depression of the southern Songliao Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2009: 1-161. [10] 葛荣峰, 张庆龙, 徐士银, 等. 松辽盆地长岭断陷构造演化及其动力学背景[J]. 地质学刊, 2009, 33(4): 346-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ200904006.htmGE Rongfeng, ZHANG Qinglong, XU Shiyin, et al. Structure evolution and its kinetic setting of Changling fault depression in Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Geology, 2009, 33(4): 346-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSDZ200904006.htm [11] 葛荣峰, 张庆龙, 王良书, 等. 松辽盆地构造演化与中国东部构造体制转换[J]. 地质论评, 2010, 56(2): 180-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201002005.htmGE Rongfeng, ZHANG Qinglong, WANG Liangshu, et al. Tectonic evolution of Songliao Basin and the prominent tectonic regime transition in Eastern China[J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56(2): 180-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201002005.htm [12] 葛肖虹, 任收麦, 刘永江, 等. 中国大型走滑断裂的复位研究与油气资源战略选区预测[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(9/10): 1022-1027. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2006Z2004.htmGE Xiaohong, REN Shoumai, LIU Yongjiang, et al. Restoration of the large-scale strike-slip faults and prediction of related oil and gas exploration strategic target area in China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2006, 25(9/10): 1022-1027. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2006Z2004.htm [13] 左宗鑫, 陆建林, 王苗, 等. 松辽盆地长岭断陷断层特征及其控油气作用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(2): 200-206. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201902200ZUO Zongxin, LU Jianlin, WANG Miao, et al. Fault characteristics and controls on hydrocarbon accumulation in Changling Faulted Depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(2): 200-206. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201902200 [14] 张庆龙, 王良书, 解国爱, 等. 郯庐断裂带北延及中新生代构造体制转换问题的探讨[J]. 高校地质学报, 2005, 11(4): 577-584. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200504014.htmZHANG Qinglong, WANG Liangshu, XIE Guoai, et al. Discussion on northward extension of the Tanlu fault zone and its tectonic regime transformation[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2005, 11(4): 577-584. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200504014.htm [15] 曲少东. 松辽盆地梨树断陷构造演化及区域动力学背景[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2013: 1-165.QU Shaodong. Tectonic evolution and regional dynamics background of Lishu subbasin, Songliao Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2013: 1-165. [16] 曲少东, 刘池阳, 宋立军, 等. 梨树断陷小宽断裂带构造特征及演化[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 43(4): 612-616. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201304031.htmQU Shaodong, LIU Chiyang, SONG Lijun, et al. The structural characteristics and evolution of Xiaokuan Fracture Zone in Lishu Rift[J]. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2013, 43(4): 612-616. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201304031.htm [17] 陈孔全, 徐言岗, 唐黎明, 等. 松辽盆地十屋断陷油气成藏条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1995, 16(4): 337-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT504.006.htmCHEN Kongquan, XU Yangang, TANG Liming, et al. Hydrocarbon pool forming condition of Shiwu fault-depression in Songliao Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1995, 16(4): 337-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT504.006.htm [18] 龙胜祥, 陈发景. 松辽盆地十屋—德惠地区断裂特征及其与油气的关系[J]. 现代地质, 1997, 11(4): 501-509. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ704.010.htmLONG Shengxiang, CHEN Fajing. Characteristics of faults in Shiwu-Dehui area of Songliao Basin and its relationship to petroleum[J]. Geoscince, 1997, 11(4): 501-509. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ704.010.htm [19] 解国爱, 张庆龙, 王良书, 等. 松辽盆地南缘十屋断陷构造物理模拟研究[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(4): 420-430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200904005.htmXIE Guoai, ZHANG Qinglong, WANG Liangshu, et al. Physical simulating model of Shiwu faulted depression structure in Songliao Basin, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(4): 420-430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200904005.htm [20] 杨立英, 李瑞磊, 张江涛, 等. 松辽盆地南部十屋断陷构造特征研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2005, 20(3): 775-779. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200503031.htmYANG Liying, LI Ruilei, ZHANG Jiangtao, et al. Study of structure character with seismic data in Shiwu Fault Depression in south of Songliao Basin[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 20(3): 775-779. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200503031.htm [21] 宋立军, 刘池洋, 郭召杰, 等. 桑树台断裂构造带结构构造特征及其形成演化[J]. 地质科学, 2013, 48(3): 665-676. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201303007.htmSONG Lijun, LIU Chiyang, GUO Zhaojie, et al. Textures and structures of Sangshutal fault belt in Lishu Fault Depression it's genetic mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2013, 48(3): 665-676. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201303007.htm [22] 曲少东, 刘池洋, 宋立军, 等. 梨树断陷秦家屯—秦东断裂带构造特征及形成演化[J]. 地质科学, 2013, 48(1): 245-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201301016.htmQU Shaodong, LIU Chiyang, SONG Lijun, et al. The structural characteristics and formation evolution of Qinjiatun-Qindong fracture zone in Lishu Fault Depression[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2013, 48(1): 245-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201301016.htm [23] 王秀林. 梨树断陷隐蔽油气藏分布规律与勘探目标评价[R]. 长春: 中石化东北油气分公司, 2015: 1-175.WANG Xiulin. Distribution of the subtle rservoris and evaluation of the exploration target in Lishu Fault Depression[R]. Changchun: Northeast Petroleum and Gas Branch of SINOPEC, 2015: 1-175. [24] 闫相宾, 周小进, 周卓明, 等. 梨树断陷构造演化及控油气作用研究[R]. 长春: 中石化东北油气分公司, 2013: 1-95.YAN Xiangbin, ZHOU Xiaojin, ZHOU Zhuoming, et al. Structural evolution and hydrocarbon control in Lishu Fault Depression[R]. Changchun: Northeast Petroleum and Gas Branch of Sinopec, 2013: 1-95. [25] 郭波, 潘红卫, 谢结来, 等. 梨树断陷连片地震资料解释及有利目标评价[R]. 涿州: 中国石油集团东方地球物理勘探有限责任公司, 2015: 1-164.GUO Bo, PAN Hongwei, XIE Jielai, et al. Interpretaiton of the seismic data and evaluation of favorable targets in Lishu Fault Depression[R]. Zhuozhou: China Petroleum Group Oriental Geophysical Exploration Co., Ltd, 2015: 1-164. [26] 李超, 刘少锋, 白玉. 松辽盆地南部白垩纪裂后期异常沉降分离[J], 现代地质, 2014, 28(6): 1213-1224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201406011.htmLI Chao, LIU Shaofeng, BAI Yu. Differentiation of anomalous cretaceous post-rift subsidence in the southern Songliao Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2014, 28(6): 1213-1224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201406011.htm [27] 梅啸寒, 吴欣松, 赵家宏, 等. 断裂密集带样式及其对油气成藏的控制作用: 以松辽盆地扶新隆起带杨大城子油层为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(1): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202001002.htmMEI Xiaohan, WU Xinsong, ZHAO Jiahong, et al. Types of fault-intensive belts and their control on hydrocarbon accumulation: a case study of Yangdachengzi oil layer in Fuxin Uplift, Songliao Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(1): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202001002.htm [28] 郭新军. 松辽盆地伏龙泉断陷断裂特征及控藏作用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(5): 657-662. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201905657GUO Xinjun. Fracture characteristics and controls on reservoirs in Fulongquan Fault Depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(5): 657-662. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201905657 [29] JACKSON C A L, ROTEVATN A. 3D seismic analysis of the structure and evolution of a salt-influenced normal fault zone: a test of competing fault growth models[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2013, 54: 215-234. [30] 王洪宇, 陈沫, 孟令东. 塔木察格盆地反向断层与反转断层控藏机理[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(2): 72-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202002010.htmWANG Hongyu, CHEN Mo, MENG Lingdong. Controlling mecha-nism of antithetic fault and reverse fault on hydrocarbon accumulations in Tamtsag Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(2): 72-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202002010.htm [31] 徐春华. 顺向断块断层及地层倾角与断层启闭性的关系: 以济阳坳陷勘探实践为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(6): 729-733. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202006012.htmXU Chunhua. Relationship between fault opening-closing and dip angles of fault and stratum in forward fault block: taking exploration practice of Jiyang Depression as an example[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(6): 729-733. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202006012.htm [32] 朱光, 王薇, 顾承串, 等. 郯庐断裂带晚中生代演化历史及其对华北克拉通破坏过程的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(4): 935-949. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201604001.htmZHU Guang, WANG Wei, GU Chengchuan, et al. Late Mesozoic evolution history of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone and its indication to destruction processes of the North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(4): 935-949. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201604001.htm [33] 朱光, 刘程, 顾承串, 等. 郯庐断裂带晚中生代演化对西太平洋俯冲历史的指示[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 48(4): 415-435. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201804003.htmZHU Guang, LIU Cheng, GU Chengchuan, et al. Oceanic plate subduction history in the western Pacific Ocean: constraint from late Mesozoic evolution of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(4): 386-405. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201804003.htm -





 下载:
下载:





 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号