Origin and mixing ratio of crude oils in different charging episodes of Yangjiang Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
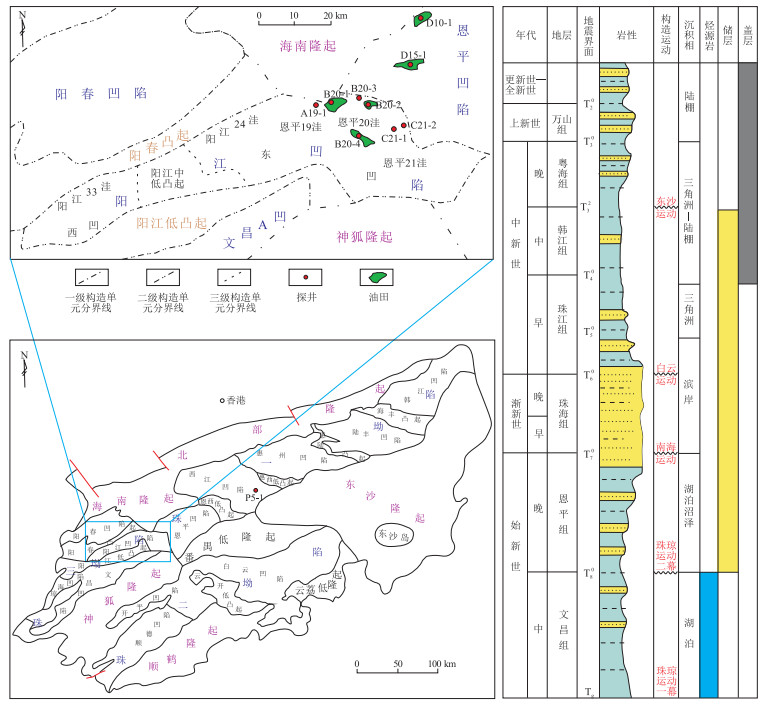
摘要: 阳江凹陷为珠江口盆地近两年来获得油气勘探重大突破的新区。采用饱和烃色谱—质谱实验、流体包裹体系统分析和全油气相色谱法混源油定量配比实验相结合,对阳江凹陷不同成藏期次原油成因进行系统分析,并对已获得混源油藏的混源比例进行了测算。阳江凹陷发生两期原油充注,充注时间分别为12.0~7.5 Ma和6.5~0 Ma。第一期原油来源于恩平20洼始新统文昌组文三段中浅湖相烃源岩,主要在中新统珠江组储层中聚集成藏;第二期原油来源于文一段和文二段中深湖相烃源岩,在中新统珠江组—韩江组储层中均有成藏。通过混源油定量配比实验建立混源比例测算模板,计算结果表明,B20-1、B20-2油田韩江组油藏均为第二期充注,B20-1油田珠江组油藏第一期和第二期充注量占比分别为39%和61%。关键成藏时期断裂活动强度、圈闭发育层段及有效烃源岩三者耦合关系共同控制着圈闭富集程度。Abstract: The oil and gas exploration in the Yangjiang Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin has successfully carried out and breakthroughs have been achieved in the past two years. The generation mechanisms of crude oils of multiple charging episodes were studied and the sources, mixing ratios were quantitatively calculated by the using of analytical results of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) for the saturated hydrocarbon fractions, fluid inclusion system analysis and whole-oil gas chromatography (GC-FID) for mixed-source oil proportion experiment. Results showed that there were two episodes of crude oil charging in the Yangjiang Sag, 12.0-7.5 Ma and 6.5-0 Ma. In the first stage, crude oils came from the medium-shallow deposited lacustrine source rocks in the third member of Wenchang Formation in the Enping 20 sub-sag, and mainly were accumulated in the Zhujiang Formation. In the second stage, crude oil came from the medium-deep deposited lacustrine source rocks of the first and second members of Wenchang Formation, and accumulated in the Zhujiang and Hanjiang formations. A template for the calculation of mixed propotion of oils was established through quantitative experiments. It was concluded that the Hanjiang reservoirs in the B20-1 and B20-2 oil fields were mainly charged during the second episode, while the Zhujiang reservoirs in the B20-1 oil field were charged during both the first and the second episodes, accounting for 39% and 61%, respectively. The coupling relationship among fault activity intensity, trap development interval and effective source rock controlled the degree of enrichment.
-
图 3 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷以及珠一坳陷典型原油及烃源岩生物标志化合物特征
C27.20R-5α(H), 14α(H), 17α(H)-胆甾烷;C28.20R-24-甲基-5α(H), 14α(H), 17α(H)-胆甾烷;C29.20R-24-乙基-5α(H), 14α(H), 17α(H)-胆甾烷;Ts.18α(H)-22, 29, 30-三降藿烷;Tm.17α(H)-22, 29, 30-三降藿烷;C30Dia-H.C30-重排藿烷;OL.奥利烷;C30H.17α(H), 21β(H)-藿烷;T.树脂化合物T
Figure 3. Typical biomarker distributions of crude oils and source rocks in Yangjiang Sag and Zhu Ⅰ Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin
图 5 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷油气包裹体特征
TR表示偏光,UV表示荧光,×10表示显微镜物镜放大倍数
a-b.B20-1,1 761.2 m,切穿石英颗粒成岩裂纹中检测到大量发黄绿色荧光油包裹体;c-d.B20-1,1 541.4 m,石英颗粒内裂纹中检测到大量发蓝绿色荧光油包裹体,粒间孔隙中检测到大量发黄绿色荧光油浸染;e-f.B20-1,2 080.0 m,石英颗粒粒间孔隙及微裂隙中检测到大量褐色沥青;g-h.B20-1,2 308.0 m,早期基底式方解石胶结物中可见发蓝绿色荧光单一液相油包裹体,石英颗粒内裂纹中检测到大量发蓝绿色荧光油包裹体,粒间孔隙中检测到大量发蓝绿色荧光油浸染Figure 5. Characteristics of oil and gas inclusions in Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin
表 1 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷B20-1井与油包裹体同期盐水包裹体均一温度及充注时间数据
Table 1. Homogenization temperatures of aqueous inclusions accompanied with oil inclusions and charging time in well B20-1 of Yangjiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin
深度/m 层位 样品个数 盐水包裹体均一温度/℃ 产状 时间/Ma 共生类型 1 541.4 韩江组 8 59.6~66.5 石英颗粒成岩裂纹 6.7~4.4 油包裹体(黄绿色) 1 627.0 韩江组 9 66.3~71.5 石英颗粒成岩裂纹 5.2~3.0 油包裹体(黄绿色) 1 761.2 珠江组 12 65.6/79.6~91.6 石英颗粒成岩裂纹 7.5/2.4~0 油包裹体(黄绿+蓝绿色) 1 870.7 珠江组 7 73.1~85.1 石英颗粒成岩裂纹 5.8~0 油包裹体(黄绿色) 2 080.0 珠江组 14 60/85.5~93.3 石英颗粒成岩裂纹 12.0/3.5~0 油包裹体(黄绿+蓝绿色) 2 162.0 珠江组 9 88.3~96.6 石英颗粒成岩裂纹 3.0~0 油包裹体(黄绿色) 2 308.0 珠江组 10 86.7~97.7 石英颗粒成岩裂纹 6.1~0 油包裹体(黄绿色) 2 380.0 珠江组 5 92.8~103.5 石英颗粒成岩裂纹 4.3~0 油包裹体(黄绿色) 注:样品个数表示与油包裹体共生的盐水包裹体均一温度数据点个数。 -
[1] 李平鲁. 南海北部陆缘盆地构造单元划分命名建议[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1999, 13(6): 460-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199906018.htmLI Pinglu. Suggestions on the division and nomenclature of structural units in the continental margin basins in the northern South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1999, 13(6): 460-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199906018.htm [2] 田立新, 张向涛, 彭光荣, 等. 珠江口盆地阳江凹陷石油地质特征及成藏主控因素[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(1): 13-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202001002.htmTIAN Lixin, ZHANG Xiangtao, PENG Guangrong, et al. Petroleum geological characteristics and main controlling factors of the Yangjiang Sag in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(1): 13-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202001002.htm [3] 彭光荣, 张向涛, 许新明, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地阳江凹陷油气勘探重要发现与认识[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(3): 267-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201903001.htmPENG Guangrong, ZHANG Xiangtao, XU Xinming, et al. Important discoveries and understandings of oil and gas exploration in Yangjiang Sag of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(3): 267-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201903001.htm [4] 杨海长, 徐建永, 武爱俊, 等. 珠三坳陷阳江凹陷构造特征及其对油气成藏的影响[J]. 海洋石油, 2011, 31(2): 20-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201102006.htmYANG Haichang, XU Jianyong, WU Aijun, et al. Structural features and impact on hydrocarbon accumulation in Yangjiang Sag of ZHU Ⅲ Depression[J]. Offshore Oil, 2011, 31(2): 20-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201102006.htm [5] 刘志峰, 王升兰, 印斌浩, 等. 珠江口盆地珠Ⅰ、珠Ⅲ坳陷裂陷期湖相分布差异及其控制因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(5): 523-527. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201305523LIU Zhifeng, WANG Shenglan, YIN Binhao, et al. Different distribution of lacustrine facies and its controlling factors during rifting stage, Zhu Ⅰ and Zhu Ⅲ Depressions, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2013, 35(5): 523-527. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201305523 [6] 陈长民, 施和生, 许仕策, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)第三系油气藏形成条件[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.CHEN Changmin, SHI Hesheng, XU Shice, et al. Formation conditions of third series of petroleum reservoirs in the Pearl River Mouth Basin (Eastern)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003. [7] 鲁宝亮, 王璞珺, 张功成, 等. 南海北部陆缘盆地基底结构及其油气勘探意义[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(4): 580-587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201104005.htmLU Baoliang, WANG Pujun, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Basement structures of an epicontinental basin in the northern South China Sea and their significance in petroleum prospect[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(4): 580-587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201104005.htm [8] 易海, 张莉, 林珍. 南海北部中生代构造格局与盆地发育特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2012, 34(4): 388-394. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201204388YI Hai, ZHANG Li, LIN Zhen. Mesozoic tectonic framework and basin distribution characteristics of northern margin of South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2012, 34(4): 388-394. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201204388 [9] 朱伟林, 张功成, 高乐. 南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气地质特征与勘探方向[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200801002.htmZHU Weilin, ZHANG Gongcheng, GAO Le. Geological characteristics and exploration objectives of hydrocarbons in the northern continental margin basin of South China sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2008, 29(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200801002.htm [10] 施和生, 何敏, 张丽丽, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)油气地质特征、成藏规律及下一步勘探策略[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(3): 11-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201403002.htmSHI Hesheng, HE Min, ZHANG Lili, et al. Hydrocarbon geology, accumulation pattern and the next exploration strategy in the eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(3): 11-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201403002.htm [11] 傅宁, 李友川, 孙建新, 等. 珠三坳陷烃源岩及油源研究再认识[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(6): 1121-1130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201106010.htmFU Ning, LI Youchuan, SUN Jianxin, et al. Recognition of oil source and source rocks in Zhu Ⅲ Depression[J]. Geoscience, 2011, 25(6): 1121-1130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201106010.htm [12] 陆江, 周刚, 郑榕芬, 等. 珠江口盆地文昌A凹陷中深层原油来源及成藏特征[J]. 中国海上油气, 2016, 28(1): 20-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201601003.htmLU Jiang, ZHOU Gang, ZHENG Rongfen, et al. Oil origin and accumulation characteristics in middle-deep strata of Wenchang A Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2016, 28(1): 20-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201601003.htm [13] 张水昌, 龚再升, 梁狄刚, 等. 珠江口盆地东部油气系统地球化学Ⅰ: 油组划分、油源对比及混源油确定[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(S1): 15-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB2004S1003.htmZHANG Shuichang, GONG Zaisheng, LIANG Digang, et al. Geoche-mistry of petroleum systems in the eastern Pearl River Mouth BasinⅠ: oil family classification, oil-source correlation and mixed oil analysis[J]. Acta Sedimentary Sinica, 2004, 22(S1): 15-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB2004S1003.htm [14] 傅宁, 朱雷. 珠一坳陷惠州西凹混源油研究[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2007, 12(2): 20-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY200702003.htmFU Ning, ZHU Lei. Research on mixed oil in Western Huizhou Sag of Zhu Ⅰ Depression[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2007, 12(2): 20-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY200702003.htm [15] 李友川, 陶维祥, 孙玉梅, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷及其邻区原油分类和分布特征[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(6): 830-834. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200906007.htmLI Youchuan, TAO Weixiang, SUN Yumei, et al. Classification and distribution of oil in Huizhou Depression of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(6): 830-834. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200906007.htm [16] HU Yue, HAO Fang, ZHU Junzhang, et al. Origin and occurrence of crude oils in the Zhu1 sub-basin, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 24-37. [17] FU Jiamo, PEI Cunmin, SHENG Guoying, et al. A geochemical investigation of crude oils from Eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 1993, 8(1/4): 469-486. [18] 刁帆, 王建伟, 陈晓娜, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷高尚堡地区油源对比及高蜡油成因[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(1): 117-125. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001117DIAO Fan, WANG Jianwei, CHEN Xiaona, et al. Correlation of oils and source rocks and genesis of high wax oils in Gaoshangpu area, Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(1): 117-125. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001117 [19] 卢晓林, 石宁, 李美俊, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷原油双杜松烷分布特征及地球化学意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(4): 560-568. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904560LU Xiaolin, SHI Ning, LI Meijun, et al. Distribution patterns and geochemical implication of bicadinanes in crude oils from Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(4): 560-568. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904560 [20] 熊万林, 朱俊章, 施洋, 等. 珠江口盆地珠坳陷原油密度分布及其成因[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(1): 43-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201901005.htmXIONG Wanlin, ZHU Junzhang, SHI Yang, et al. Density distribution of crude oil in the Zhuyi Depression of Pearl River Mouth Basin and control factors[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(1): 43-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201901005.htm [21] WILHELMS A, LARTER S R. Origin of tar mats in petroleum reservoirs. Part Ⅰ: introduction and case studies[J]. Marine and Petro-leum Geology, 1994, 11(4): 418-441. [22] 陈红汉, 米立军, 刘妍鷨, 等. 珠江口盆地深水区CO2成因、分布规律与风险带预测[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(2): 119-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201702001.htmCHEN Honghan, MI Lijun, LIU Yanhua, et al. Genesis, distribution and risk belt prediction of CO2 in deep-water area in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(2): 119-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201702001.htm [23] 胡圣标, 龙祖烈, 朱俊章, 等. 珠江口盆地地温场特征及构造热演化[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(S1): 178-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2019S1015.htmHU Shengbiao, LONG Zulie, ZHU Junzhang, et al. Characteristics of geothermal field and the tectonic-thermal evolution in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(S1): 178-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2019S1015.htm [24] 王铁冠, 王春江, 何发岐, 等. 塔河油田奥陶系油藏两期成藏原油充注比率测算方法[J]. 石油实验地质, 2004, 26(1): 74-79. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200401074WANG Tieguan, WANG Chunjiang, HE Faqi, et al. Determination of double filling ratio of mixed crude oils in the Ordovician reservoir, Tahe Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2004, 26(1): 74-79. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200401074 [25] 肖瑶, 李小冬, 郑荣华, 等. 渤海湾盆地束鹿凹陷西曹固构造带断层圈闭成因机制及定量评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(5): 762-768. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201905762XIAO Yao, LI Xiaodong, ZHENG Ronghua, et al. Genetic mecha-nism and quantitative evaluation of fault traps in Xicaogu structural belt, Shulu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(5): 762-768. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201905762 [26] 刘峻桥, 王伟, 吕延防, 等. 渤海湾盆地廊固凹陷大柳泉地区油源断裂垂向输导能力定量评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(4): 606-613. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904606LIU Junqiao, WANG Wei, LV Yanfang, et al. Quantitative evaluation of vertical fault transport in Daliuquan area of Langgu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(4): 606-613. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904606 -





 下载:
下载:











 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号