Key structural periods and Permian tight gas accumulation response in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
-
摘要: 关键构造期是大型叠合盆地中表征构造作用与油气成藏之间成因联系和因果关系(成藏响应)的关键时间点,是分析油气成藏演化和油气聚集规律的重要“窗口”。基于鄂尔多斯盆地构造演化史,通过磷灰石裂变径迹等热年代学指标的约束,分析了鄂尔多斯盆地北部杭锦旗地区中生代以来构造演化及变形序列,厘定了该区J3-K1、K2-E1两个关键构造期,并结合石炭系—二叠系成烃—成藏史,认为J3-K1是杭锦旗地区现今“北东高、南西低”NE向构造格局的定型期,对应于烃源岩大量生排烃和砂岩致密化期,主要形成三眼井—乌兰吉林庙—泊尔江海子断层南部(简称南部)的石炭系太原组、二叠系山西组及石盒子组盒一段岩性气藏;K2-E1是主干断裂活化、北部NE向构造圈闭和NW向断裂形成期,导致南部先期岩性气藏调整和北部构造或构造—岩性气藏的形成;主干断裂两侧成藏差异明显,南部成藏早于北部,南部以岩性气藏为主,北部以构造—岩性气藏为主,南部含气层系以深层为主,北部深浅层均有,古近纪北部的隆升导致天然气散失。关键成藏期和关键改造期在空间和时间上转化,通过对成藏要素的差异化改造最终控制天然气的富集和贫化。Abstract: Critical tectonic period is a critical time point that characterizes the genetic connection and causal relation (accumulation response) between tectonic effect and oil/gas accumulation in large superposition basins, it is also an important "window" for analyzing accumulation evolution and accumulation regularity of oil/gas. Based on the systematic review of the tectonic evolution history of the Ordos Basin, the tectonic evolution and deformation sequence since the Mesozoic in Hangjinqi area in the northern part of Ordos Basin were studied through the constraints of apatite fission tracks and other thermal chronological indicators. Two key structural periods including J3-K1 and K2-E1 were proposed. It was believed by combining with the understanding of the Carboniferous-Permian hydrocarbon-generating and reservoir-forming histories that the J3-K1 was the period of design finalization in the Hangjinqi area which formed a currant NE-trending structural framework "high in the northeast and low in the southwest" during which, lithologic gas reservoirs including the Carboniferous Taiyuan and the Permian Shanxi formations, first member of the Permian Shihezi Formation to the north of the Sanyanjing-Wulan Jilin Temple-Bo'erjiang Haizi fault were formed and corresponding to the period of great amount of hydrocarbon generated and expulsed from source rocks as well as the densification of sandstones. On the other hand, the K2-E1 period was the major stage for fault reactivation and the formation of NE-trending tectonic trap and NW-trending fault that led to the adjustment of early lithologic gas reser-voirs in the south and the formation of structural or structural-lithologic gas reservoirs in the north. The difference of accumulation on each sides of the main fault is obvious. The southern part was formed earlier than the northern part, and was dominated by lithologic gas reservoirs yet the northern part was dominated by structural-lithological gas reservoirs. The southern gas-bearing strata are dominated by deep strata, while those in the north are both shallow and deep ones. In Paleogene, lifting in the north caused loss of gas. The key accumulation and transformation periods transformed with space and time, which transformed accumulation factors differentially and finally constrained the enrichment and depletion of natural gas.
-
Key words:
- critical tectonic period /
- accumulation factor /
- accumulation response /
- Permian /
- Hangjinqi area /
- Ordos Basin
-
图 6 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区关键构造期(J3-K1)末北西向构造剖面
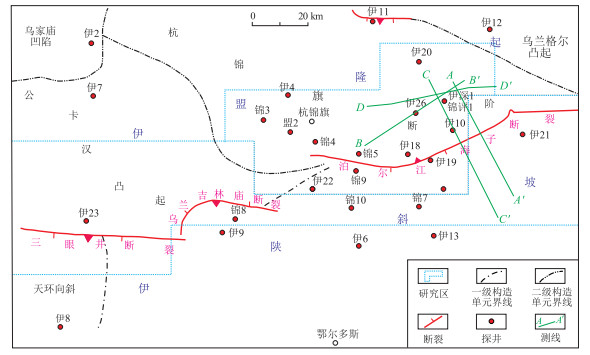
测线位置见图 1。
Figure 6. NW-trending structural profile at the end of key tectonic period (J3-K1) in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
图 7 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区关键构造期(K2-E1)末构造剖面
测线位置见图 1。
Figure 7. Structural profile at the end of key tectonic period (K2-E1) in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
图 8 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区喜马拉雅晚期(E2之后)北东向剖面
测线位置见图 1。
Figure 8. NE-trending section during the late Himalayan period (post E2) in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区构造关键期作用与成藏响应对比
Table 1. Comparison between key tectonic periods and hydrocarbon accumulation responses in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
-
[1] 刘池洋. 后期改造强烈: 中国沉积盆地的重要特点之一[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1996, 17(4): 255-261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200001001.htmLIU Chiyang. Strong late-reformation: one of the important characteristics of sedimentary basins in China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1996, 17(4): 255-261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200001001.htm [2] 赵文智, 胡素云, 刘伟, 等. 论叠合含油气盆地多勘探"黄金带"及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201501002.htmZHAO Wenzhi, HU Suyun, LIU Wei, et al. The multi-staged "golden zones" of hydrocarbon exploration in superimposed petroliferous basins of onshore China and its significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201501002.htm [3] 贾承造, 李本亮, 张兴阳, 等. 中国海相盆地的形成与演化[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(S1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2007S1001.htmJIA Chengzao, LI Benliang, ZHANG Xingyang, et al. Formation and evolution of the Chinese marine basins[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2007S1001.htm [4] 蔡勋育, 邱桂强, 孙冬胜, 等. 中国中西部大型盆地致密砂岩油气"甜点"类型与特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(4): 684-695. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004004.htmCAI Xunyu, QIU Guiqiang, SUN Dongsheng, et al. Types and characteristics of tight sandstone sweet spots in large basins of central-western China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 684-695. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004004.htm [5] 徐旭辉, 方成名, 刘金连, 等. 中国中西部山前构造变形结构分带模式与油气[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(6): 779-790. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906779XU Xuhui, FANG Chengming, LIU Jinlian, et al. Deformation zoning model of piedmont thrust, western China, and its petroleum response[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(6): 779-790. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906779 [6] 商丰凯. 叠合盆地凸起区多期复杂断裂特征及形成机制: 以准噶尔盆地车排子凸起为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(3): 278-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202003003.htmSHANG Fengkai. Characteristics and formation mechanism of multi-stage complex fault system of uplift in superimposed basin: a case study of Chepaizi Uplift, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(3): 278-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202003003.htm [7] MAGOON L B, DOW W G. The petroleum system: from source to trap[M]. Tulsa: AAPG, 1994: 3-24. [8] 汤良杰, 金文正, 何春波, 等. 叠合盆地关键构造变革期与分期差异构造变形[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2009, 30(2): 163-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200902008.htmTANG Liangjie, JIN Wenzheng, HE Chunbo, et al. Key tectonic changes and staging differential structural deformation in superimposed basins[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2009, 30(2): 163-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200902008.htm [9] 杨帆, 胡烨, 罗开平, 等. 中国中西部地区关键构造变革期次及变形特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(4): 475-481. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904475YANG Fan, HU Ye, LUO Kaiping, et al. Tectonic evolution stages and deformation characteristics in central and western China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(4): 475-481. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904475 [10] 刘昭茜, 罗开平, 唐永, 等. 四川盆地元坝—通南巴地区关键构造期构造特征及陆相致密砂岩天然气成藏响应[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3): 756-772. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903006.htmLIU Zhaoqian, LUO Kaiping, TANG Yong, et al. Critical tectonic periods and the response of gas accumulation in non-marine tight sandstone reservoir in Yuanba-Tongnanba area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(3): 756-772. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903006.htm [11] 胡华蕊, 邢凤存, 齐荣, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区晚古生代盆缘古地貌控砂及油气勘探意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(4): 491-497. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904491HU Huarui, XING Fengcun, QI Rong, et al. Paleogeomorphologic features and their controls on sandbody distribution on basin margin during Late Paleozoic Era and significance for petroleum exploration, Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(4): 491-497. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904491 [12] 齐荣. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗东部断裂特征及对天然气成藏的影响[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(4): 58-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201904010.htmQi Rong. Fault characterization and its influences on gas accumulation in the eastern Haggin Banner of Ordos Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(4): 58-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201904010.htm [13] 郑孟林, 金之钧, 王毅, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部中新生代构造特征及其演化[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2006, 28(3): 31-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200603006.htmZHENG Menglin, JIN Zhijun, WANG Yi, et al. Structural characte-ristics and evolution of north Ordos Basin in Late Mesozoic and Cenozoic[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2006, 28(3): 31-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200603006.htm [14] 张福礼, 黄舜兴, 杨昌贵, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地天然气地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994: 33-61.ZHANG Fuli, HUANG Shunxing, YANG Changgui, et al. Natural gas geology of Ordos Basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1994: 33-61. [15] 徐黎明, 周立发, 张义楷, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地构造应力场特征及其构造背景[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2006, 30(4): 455-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200604006.htmXU Liming, ZHOU Lifa, ZHANG Yikai, et al. Characteristics and tectonic setting of tectono-stress field of Ordos Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2006, 30(4): 455-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200604006.htm [16] 李江涛. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部加里东期后构造演化及其与古生界天然气的关系[J]. 现代地质, 1997, 11(4): 488-495. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ704.008.htmLI Jiangtao. Tectonic evolution and its relation to Paleozoic gas reservoirs since Caledonian Movement in northern Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 1997, 11(4): 488-495. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ704.008.htm [17] 薛会, 张金川, 王毅, 等. 鄂北杭锦旗探区构造演化与油气关系[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(2): 206-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200902003.htmXUE Hui, ZHANG Jinchuan, WANG Yi, et al. Relationship between tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon in Hangjinqi block of north Ordos Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2009, 33(2): 206-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200902003.htm [18] 邱隆伟, 穆相骥, 李浩, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区二叠系下石盒子组岩屑发育特征及其对储层物性的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(1): 24-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201901004.htmQIU Longwei, MU Xiangji, LI Hao, et al. Characteristics of detritus development in the Permian lower Shihezi Formation in Hangjinqi area and its influence on reservoir physical properties[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(1): 24-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201901004.htm [19] 邱隆伟, 穆相骥, 李浩, 等. 杭锦旗地区下石盒子组致密砂岩储层成岩作用对孔隙发育的影响[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(2): 42-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201902006.htmQIU Longwei, MU Xiangji, LI Hao, et al. Influence of diagenesis of tight sandstone reservoir on the porosity development of Lower Shihezi Formation in Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(2): 42-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201902006.htm [20] 赵明胜, 田景春, 张翔, 等. 鄂北杭锦旗地区山西组高分辨层序格架下沉积充填及砂体展布规律[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(6): 8-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201906002.htmZHAO Mingsheng, TIAN Jingchun, ZHANG Xiang, et al. Sedimentary filling and sandbody distribution patterns under high-resolution sequence framework of the Shanxi Formation in Hangjinqi area, northern Ordos Basin[J]. Special oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(6): 8-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201906002.htm [21] 易非凡, 田景春, 张翔, 等. 杭锦旗地区山西组沉积相及其演化特征[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(4): 439-443. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201904008.htmYI Feifan, TIAN Jingchun, ZHANG Xiang, et al. Sedimentary facies and its evolution characteristics of Shanxi Formation in Hangjinqi area[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2019, 26(4): 439-443. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201904008.htm [22] 付锁堂, 姚泾利, 李士祥, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中生界延长组陆相页岩油富集特征与资源潜力[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 698-710. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005698FU Suotang, YAO Jingli, LI Shixiang, et al. Enrichment characteristics and resource potential of continental shale oil in Mesozoic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 698-710. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005698 [23] 袁志祥. 鄂北塔巴庙、杭锦旗地区古生界天然气勘探前景分析[J]. 天然气工业, 2001, 21(S1): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG2001S1002.htmYUAN Zhixiang. An analysis of the natural gas exploration potential of Paleozoic at Tabamiao and Hangjin banner regions in north E'erduosi Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2001, 21(S1): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG2001S1002.htm [24] 张杰, 薛会, 王毅, 等. 鄂北杭锦旗探区上古生界天然气成藏类型[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 24(3): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200903000.htmZHANG Jie, XUE Hui, WANG Yi, et al. Accumulation types of Neopaleozoic gas in Hangjinqi block of north Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 2009, 24(3): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200903000.htm [25] 马静辉, 何登发. 贺兰山构造带及邻区中—新生代构造事件: 来自不整合面和裂变径迹的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(4): 1121-1142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201904010.htmMA Jinghui, HE Dengfa. Meso-Cenozoic tectonic events in the Helanshan tectonic belt and its adjacent areas: constraints from unconformity and fission track data[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(4): 1121-1142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201904010.htm [26] 高海龙. 华北北缘燕山褶断带早中生代地层年代学格架及其意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学, 2018.GAO Hailong. The Early Mesozoic chronostratigraphic framework of the Yanshan fold-thrust belt, North China and its implications[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2018. [27] 李建星, 岳乐平, 刘池洋, 等. 中新世以来吕梁山及邻区构造—沉积演化[J]. 地层学杂志, 2013, 37(1): 93-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201301015.htmLI Jianxing, YUE Leping, LIU Chiyang, et al. The tectonic-sedimentary evolution of the Lüliang mountains since the Miocene[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2013, 37(1): 93-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201301015.htm [28] 邹和平, 张珂, 刘玉亮, 等. 鄂尔多斯地块北部中、新生代玄武岩地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2010, 34(1): 92-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201001010.htmZHOU Heping, ZHANG Ke, LIU Yuliang, et al. Geochemical characteristics and their geological implications of Meso-Cenozoic basalts in the northern Ordos block, North China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2010, 34(1): 92-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201001010.htm [29] 邹和平, 张珂, 李刚. 鄂尔多斯地块早白垩世构造—热事件: 杭锦旗玄武岩的Ar-Ar年代学证据[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2008, 32(3): 360-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200803015.htmZHOU Heping, ZHANG Ke, LI Gang. Cretaceous tectono-thermal event in the Ordos block: an Ar-Ar chronological evidence from basalt at Hangjin banner, Inner Mongolia, North China Craton[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2008, 32(3): 360-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK200803015.htm [30] 丁超, 陈刚, 李振华, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东北部构造热演化史的磷灰石裂变径迹分析[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(3): 581-588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201103021.htmDING Chao, CHEN Gang, LI Zhenhua, et al. Apatite fission track analysis of tectono-thermal history in the northeast of Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2011, 25(3): 581-588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201103021.htm [31] 丁燕云. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部航磁反映的构造特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2000, 24(3): 197-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200003006.htmDING Yanyun. Structural characteristics of northern Ordos Basin reflected by aeromagnetic data[J]. Geophysical and Geoche-mical Exploration, 2000, 24(3): 197-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200003006.htm [32] 刘栋. 杭锦旗地区上古生界天然气富集规律与成藏机理研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016.LIU Dong. Research on gas enrichment regularity and accumulation mechanism of the Upper Paleozoic gas reservoir in Hangjinqi area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016. [33] 聂海宽, 张金川, 薛会, 等. 杭锦旗探区储层致密化与天然气成藏的关系[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 24(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200901003.htmNIE Haikuan, ZHANG Jinchuan, XUE Hui, et al. Relationship between the densification of reservoir and the accumulation of natural gas in Hangjinqi area of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 2009, 24(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200901003.htm -





 下载:
下载:








 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号