Fault systems and their relationships to oil and gas in Dabancheng subsag, Chaiwopu Sag, Junggar Basin
-
摘要: 准噶尔盆地柴窝堡凹陷于20世纪80年代末首次取得油气勘探重大突破,此后断裂复杂性以及油气分布不均制约了该区勘探效果。作为凹陷主体的达坂城次凹,二叠纪以来受博格达山逆冲带向南方向、依连哈比尔尕山(简称依山)冲断带向北东方向和黑山向西北方向的强烈挤压,形成了多应力场叠加的压性狭长的对冲构造体系,并导致盆地断裂特征及演化具有复杂性和特殊性。应用测井资料、地震资料以及野外踏勘资料,对达坂城次凹的断裂特征进行了对比研究,并将其划分为博格达南断裂系统、依山断裂系统和黑山断裂系统。其中博格达南断裂系统存在浅层滑脱面,属于含塑性滑脱层的造山楔构造;依山断裂系统为基底卷入式断裂系统。晚海西期、印支期、燕山期和喜马拉雅期构造运动在该区均有地质记录,分别形成了不同规模的断层,其中海西晚期为断裂雏形期,印支—燕山期为断裂定型期,喜马拉雅期为断裂调整期。博格达南断裂系统中滑脱带与中下二叠统烃源岩展布一致,结合构造运动时期、地层沉积特征以及断裂系统,综合分析认为博格达南断裂系统是潜在的油气聚集区。Abstract: The Chaiwopu Sag of Junggar Basin experienced a major breakthrough in oil and gas exploration for the first time in the late 1980s, however, the exploration effect in this area is still restricted by the complexity of faults and the uneven distribution of oil and gas. As the main body of the sag, the Dabancheng subsag has been strongly extruded by the Bogda Mountain thrust belt to the south, the Yilian Habirga Mountain (abbreviated as Yishan) thrust belt to the northeast, and the Heishan Mountain to the northwest since Permian. A compressive and narrow ramp structural system superimposed by multiple stress fields was developed, which led to the complexity and particularity of fault characteristics and evolution in the Dabancheng subsag. Approaches including logging, seismic and field geological survey data were applied to study the fault systems in the subsag, including the Southern Bogda Mountain fault system, the Yishan fault system and the Heishan fault system. The Southern Bogda Mountain fault system has a shallow detachment surface, which belongs to an orogenic wedge structure with plastic detachment layers. The Yishan fault system is a basement-involved structure. The Late Hercynian, Indosinian, Yanshanian and Himalayan tectonic movements have geological records in this area, forming different scales of faults. The late Hercynian period is a breakup stage, the Indosinian-Yanshanian period is a fault-shaping period, and the Himalayan period is a fault adjustment period. The distribution of detachment belt in the Southern Bogda Mountain fault system is consistent with that of the Middle-Lower Permian source rocks. Combined with the analyses of tectonic movement period, stratigraphic characteristics and fault systems, the Southern Bogda Mountain fault system is a potential oil and gas accumulation area.
-
Key words:
- thrusting fault /
- detachment belt /
- fault system /
- hydrocarbon distribution /
- Dabancheng subsag /
- Chaiwopu Sag /
- Junggar Basin
-
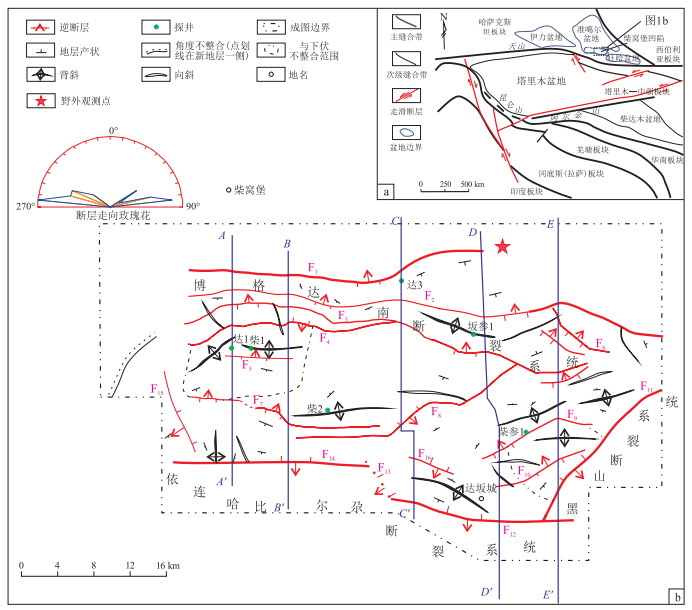
图 1 准噶尔盆地柴窝堡凹陷达坂城次凹及邻区构造格架(a)及达坂城次凹三叠系下仓房群底面断层分布(b)
博格达南断裂系统由F1—F7断层组成;依山断裂系统由F8、F12—F16等断层组成;黑山断裂系统由F9—F11等断层组成
Figure 1. Tectonic background of Dabancheng subsag of Chaiwopu Sag in Junggar Basin and adjacent areas (a) and distribution of faults on the underlying surface unconformity of Lower Triassic Xiacangfang group of Dabancheng subsag (b)
图 3 博格达山南侧二叠系井井子沟组出露点野外剖面
剖面位置见图 1;图b为a图中黑框线部分。
Figure 3. Field profile of Permian Jingjingzigou Formation, southern Bogda Mountain
图 4 准噶尔盆地柴窝堡凹陷达坂城次凹西部二维地震解释
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 4. Seismic interpretation of western Dabancheng subsag, Chaiwopu Sag, Junggar Basin
图 5 准噶尔盆地柴窝堡凹陷达坂城次凹东部二维地震解释
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 5. Seismic interpretation of eastern Dabancheng subsag, Chaiwopu Sag, Junggar Basin
表 1 准噶尔盆地柴窝堡凹陷达坂城次凹滑脱层深度
Table 1. Depth of detachment layer in Dabancheng subsag, Chaiwopu Sag, Junggar Basin
剖面 构造 地层原始长度/m 现今剖面长度/m 压缩量/m 溢出面积/m2 滑脱面深度/m D—D' 坂参1井背斜 3 527 3 201 326 887 775 4 080 D—D' F2下盘背斜 3 061 2 925 135 258 212 4 120 E—E' F6下盘背斜 6 076 5 880 196 277 392 4 000 -
[1] 任建业, 张俊霞, 阳怀忠, 等. 塔里木盆地中央隆起带断裂系统分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(1): 219-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201101015.htmREN Jianye, ZHANG Junxia, YANG Huaizhong, et al. Analysis of fault systems in the central uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(1): 219-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201101015.htm [2] 陈书平, 漆家福, 王德仁, 等. 东濮凹陷断裂系统及变换构造[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(1): 43-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200701007.htmCHEN Sheping, QI Jiafu, WANG Deren, et al. Fault systems and transfer structures in Dongpu Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(1) : 43-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200701007.htm [3] 柳永军, 赵弟江, 李正宇, 等. 走滑—伸展断裂叠合特征及其控藏作用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(2): 46-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201902008.htmLIU Yongjun, ZHAO Dijiang, LI Zhengyu, et al. The superposition patterns of strike-slip-extension faults and its effects on hydrocarbon accumulatuon[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(2): 46-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201902008.htm [4] 江志强, 明彦伯, 姚刚. 东海盆地丽水凹陷断裂系统划分方法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(1): 310-315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201901042.htmJIANG Zhiqiang, MING Yanbo, YAO Gang. Study on fault division of Lishui Sag in East China Sea Basin[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(1): 310-315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201901042.htm [5] 汤良杰, 金之钧, 戴俊生, 等. 柴达木盆地及相邻造山带区域断裂系统[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2002, 27(6): 676-682. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200206004.htmTANG Liangjie, JIN Zhijun, DAI Junsheng, et al. Regional fault systems of Qaidam Basin and adjacent orogenic belts[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2002, 27(6): 676-682. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200206004.htm [6] 魏国齐, 贾承造, 施央申, 等. 塔北隆起北部中新生界张扭性断裂系统特征[J]. 石油学报, 2001, 22(1): 19-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200101003.htmWEI Guoqi, JIA Chengzao, SHI Yangshen, et al. Tectonic characte-ristics and petroleum accumulation in extensional-shear fault system in Mesozoic-Cenozoic formations in the northern area of Tabei Uplift, Tarim[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2001, 22(1): 19-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200101003.htm [7] 李兵, 邓尚, 李王鹏, 等. 塔里木盆地塔河地区走滑断裂体系活动特征与油气地质意义[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(4): 45-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201904008.htmLI Bing, DENG Shang, LI Wangpeng, et al. Strike-slip fault system activity and hydrocarbon geology understanding in Tahe of Tarim Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(4): 45-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201904008.htm [8] 杨迪生, 肖立新, 阎桂华, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘四棵树凹陷构造特征与油气勘探[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(2): 138-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201902002.htmYANG Disheng, XIAO Lixin, YAN Guihua, et al. Structural characteristics and petroleum exploration in Sikeshu sag, southern margin of Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(2): 138-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201902002.htm [9] 俞仁连, 杨树生, 赵立群. 准噶尔盆地柴窝堡凹陷达坂城次凹构造特征及油气勘查方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 1996, 18(3): 237-243. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199603237YU Renlian, YANG Shusheng, ZHAO Liqun. Structural characteristics and oil/gas exploration targets of Dabancheng sub-depression of the Juggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 1996, 18(3): 237-243. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199603237 [10] 冯永宏, 吴妙娜, 准噶尔盆地南缘柴窝堡凹陷结构特征分析[J]. 河南石油, 2004, 18(5): 9-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN200405003.htmFENG Yonghong, WU Miaona. An analysis of structural characteristics of Chaiwopu Sag on southern border of Junggar Basin[J]. Henan Petroleum, 2004, 18(5): 9-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN200405003.htm [11] 旷理雄, 郭建华, 王英明, 等. 柴窝堡凹陷达坂城次凹油气成藏条件及勘探方向[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(1): 20-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200501005.htmKUANG Lixiong, GUO Jianhua, WANG Yingming. Studies on the oil & gas reservoir formation conditions and exploration bearing in Daban town sub-depression of Chaiwopu Depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(1): 20-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200501005.htm [12] 孙自明, 沈杰. 新疆博格达推覆构造及其与油气的关系[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(4) : 429-434. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201404429SUN Ziming, SHEN Jie. Bogda nappe structure and its relations to hydrocarbon in Xinjiang[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2014, 36(4) : 429-434. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201404429 [13] STAPLES RD, GIBSON H D, COLPRON M. An orogenic wedge model for diachronous deformation, metamorphism, and exhumation in the hinterland of the northern Canadian Cordillera[J]. Lithosphere, 2016, 8(2): 165-184. [14] SUPPE J. Geometry and kinematics of fault-bend folding[J]. American Journal of Science, 1983, 283(7): 684-721. [15] COSTA E, VENDEVILLE B C. Experimental insights on the geometry and kinematics of fold-and-thrust belts above weak, viscous evaporitic decollement[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2002, 24(11): 1729-1739. [16] 王宗秀, 李涛, 周高志, 等. 博格达山晚石炭纪造山活动的变形地质记录[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(1): 63-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200301011.htmWANG Zongxiu, LI Tao, ZHOU Gaozhi, et al. Geological record of the late-carboniferous orogeny in Bogedashan, northern Tianshan Mountains, Northwest China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(1): 63-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200301011.htm [17] 舒良树, 朱文斌, 王博, 等. 新疆博格达南缘后碰撞期陆内裂谷和水下滑塌构造[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(1): 25-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501003.htmSHU Liangshu, ZHU Wenbin, WANG Bo, et al. The post-collision intracontinental rifting and olistostrome on the southern slope of Bogda Mountains, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005, 21(1): 25-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200501003.htm [18] 朱明, 汪新, 肖立新. 准噶尔盆地南缘构造特征与演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(1): 9-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202001007.htmZHU Ming, WANG Xin, XIAO Lixin. Structural characteristics and evolution in the southern margin of Junggar basin[J]. Xingjiang Petroleum Geology, 2020, 41(1): 9-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202001007.htm [19] 刘慧, 张金亮, 赵乐强. 准南缘柴窝堡与吐哈西北缘大河沿早二叠世构造沉积特征及油气勘探启示[J]. 特种油气藏, 2020, 27(3): 14-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202003003.htmLIU Hui, ZHANG Jinliang, ZHAO Leqiang. Tectonic-sedimentary characterization and hydrocarbon exploration implication of Chaiwopu in the southern margin of Junggar Basin and Daheyan in the northwestern margin of Tuha Basin[J]. Specail Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2020, 27(3): 14-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202003003.htm [20] 关旭同, 吴朝东, 吴鉴, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗纪与白垩纪转折时期沉积序列与沉积环境演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(1): 67-79.GUAN Xutong, WU Chaodong, WU Jian, et al. Sedimentary sequence and depositional environment evolution of Upper Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous strata in the southern margin of Junggar basin[J]. Xingjiang Petroleum Geology, 2020, 41(1): 67-79. [21] 郭威. 新疆博格达山及其邻区板内构造作用研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2008.GUO Wei. Intraplate tectonics of Bogda Mountain in Xingjiang its adjacent plates[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2008. [22] 孙国智, 柳益群. 新疆博格达山隆升时间初步分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(3): 487-493. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200903013.htmSUN Guozhi, LIU Yiqun. The preliminary analysis of the uplift time of Bogda Mountain, Xinjiang, Northwest China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(3): 487-493. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200903013.htm [23] 汪新伟, 汪新文, 马永生. 新疆博格达山的构造演化及其与油气的关系[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(1): 116-124.WANG Xinwei, WANG Xinwen, MA Yongsheng. The tectonic evolution of Bogda Mountain, Xinjiang, Northwest China and its relationship to oil and gas accumulation[J]. Geoscience, 2007, 21(1): 116-124. [24] 沈传波, 梅廉夫, 刘麟, 等. 新疆博格达山中新生代隆升—热历史的裂变径迹记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(3): 87-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200603013.htmSHEN Chuanbo, MEI Lianfu, LIU Lin, et al. Evidence from apatite and Zircon fission track analysis for Mesozoic-Cenozoic uplift thermal history of Bogeda Mountain of Xinjiang, Northwest China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(3): 87-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ200603013.htm [25] CHEN Ke, LIN Wei, WANG Qingchen. The Bogeda Shan uplifting: evidence from multiple phases of deformation[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 99: 1-12. [26] HENDRIX M S, DUMITRU T A, GRAHAM S A. Late Oligocene-Early Miocene unroofing in the Chinese Tian Shan: an early effect of the India-Asia collision[J]. Geology, 1994, 22(6): 487-490. [27] 姚志刚, 周立发, 高璞, 等. 北天山中、新生代隆升和剥蚀史研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2010, 39(1): 121-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201001022.htmYAO Zhigang, ZHOU Lifa, GAO Pu, et al. Meso-Cenozoic uplift and exhumation history in the North Tianshan Mountains[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology. 2010, 39(1): 121-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201001022.htm [28] 徐学义, 马中平, 夏林圻, 等. 北天山巴音沟蛇绿岩斜长花岗岩锆石SHRIMP测年及其意义[J]. 地质论评, 2005, 51(5): 523-527. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200505007.htmXU Xueyi, MA Zhongping, XIA Linqi, et al. SHRIMP dating of Plagiogranite from Bayingou ophiolite in the Northern Tianshan Mountains[J]. Geological Review, 2005, 51(5): 532-527. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200505007.htm [29] 李向东. 新疆北天山晚古生代洋盆演化与推覆构造[J]. 新疆地质, 1993, 11(3): 207-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI199303003.htmLI Xiangdong. Evolution of the oceanic basin of Late Paleozoic and nappe structure of North Tianshan, Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 1993, 11(3): 207-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI199303003.htm [30] 郭建军, 陈践发, 朱忠云, 等. 柴窝堡凹陷达坂城次凹上二叠统烃源岩的地球化学特征及勘探方向[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(3): 446-455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200603018.htmGUO Jianjun, CHEN Jianfa, ZHU Zhongyun, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Upper Permian source rocks and exploration directions in Dabancheng sub-depression of Chaiwopu Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(3): 446-455. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200603018.htm [31] 吴光红, 巴秀娥, 冯永宏, 等. 柴窝堡凹陷石油地质特征及勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2003, 24(6): 523-526. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200306011.htmWU Guanghong, BA Xiue, FENG Yonghong, et al. Petroleum characteristics and prospecting target in Chaiwopu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2003, 24(6): 523-526. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200306011.htm [32] 张慧, 李琦, 林鹏, 等. 柴窝堡凹陷红雁池及芦草沟组储层特征及控制因素[J]. 现代矿业, 2013, 29(7): 52-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB201307018.htmZHANG Hui, LI Qi, LIN Peng, et al, Reservoir characteristics and controlling factors of Hongyanchi and Lucaogou formations in Chaiwopu Sag[J]. Morden Mining, 2013, 29(7): 52-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB201307018.htm [33] 周进松, 童小兰, 冯永宏. 柴窝堡背斜储层构造裂缝发育特征及控制因素[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(3): 53-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200603011.htmZHOU Jinsong, TONG Xiaolan, FENG Yonghong. Development characteristics and control factors for reservoir fracture in Chaiwopu anticline of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(3): 53-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200603011.htm [34] 陈嘉明, 吕宝凤, 段艳秋, 等. 新疆柴窝堡盆地构造样式及勘探思路[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2002, 25(2): 31-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200202006.htmCHEN Jiaming, LV Baofeng, DUAN Yanqiu, et al. Structural pattern and exploration idea of Chaiwopu Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Natural Gas Exploration & Development, 2002, 25(2): 31-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT200202006.htm [35] 臧明峰, 吴孔友. 准噶尔盆地南缘大龙口地区构造建模[J]. 断块油气田, 2009, 16(4): 11-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT200904006.htmZANG Mingfeng, WU Kongyou. Structure modeling of Dalongkou region in southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-Block oil and Gas Field. 2009, 16(4): 11-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT200904006.htm [36] 汤良杰, 杨克明, 金文正, 等. 龙门山冲断带多层次滑脱带与滑脱构造变形[J]. 中国科学(D辑地球科学), 2008, 38(S1): 30-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S1004.htmTANG Lingjie, YANG Kepeng, JIN Wenzheng, et al. Multi-level decollement zones and detachment deformation of Longmenshan thrust belt, Sichuan Basin, southwest China[J]. Science in China(Series D Earth Sciences), 2008, 51(S2): 32-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S1004.htm [37] 张迎朝, 汪伟, 甘军, 等. 伸展构造拉张量计算方法的适用性分析及在琼东南盆地的应用[J]. 高校地质学报, 2019, 25(5): 730-740. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201905010.htmZHANG Yingzhao, WANG Wei, GAN Jun et al. Applicability analysis of different methods for extensional displacement calculation in extensional structures with application in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Geolo-gical Journal of China Universities, 2019, 25(5): 730-740. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201905010.htm [38] 文凯, 李传新. 川东与大巴山褶皱冲断带交汇区构造几何学和运动学特征[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(2): 426-438. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202002005.htmWEN Kai, LI Chuanxin. The geometry and kinematics of the intersection area of eastern Sichuan and the Dabashan fold-thrust belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(2): 426-438. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202002005.htm [39] 赵利, 廖宗廷, 徐旭辉, 等. 陆内山前冲断结构分带的构造物理模拟实验[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(6): 871-878. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906871ZHAO Li, LIAO Zongting, XU Xuhui, et al. Physical modeling of thrusting structure zonation in front of an intracontinental orogen[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(6): 871-878. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906871 [40] 方成名, 赵利. 复合陆内山前冲断构造转换类型及其成因[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(6): 791-799. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906791FANG Chengming, ZHAO Li. Compound intracontinental piedmont thrust structure transformation and its formation mechanisms[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(6): 791-799. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906791 [41] 陈书平, 王春修, 肖华, 等. 尼日尔三角洲新生代褶皱作用及相关的油气圈闭[J]. 高校地质学报, 2013, 19(2): 355-363. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201302017.htmCHEN Shuping, WANG Chunxiu, XIAO Hua, et al. Folding of the Niger Delta in the Cenozoic and its related traps[J]. Geolo-gical Journal of China Universities, 2013, 19(2): 355-363. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201302017.htm -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号