Existence and geological significance of pyrite in the organic-rich shale of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Upper Yangtze region
-
摘要: 黄铁矿的研究不仅为沉积、成岩环境的恢复提供依据,也为富有机质页岩的预测提供参考。以上扬子板块3个不同沉积位置钻井(宜昌EYY1井、威远W001-4井、汉中SNY1井)的下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩为例,通过X射线衍射全岩矿物分析(XRD)、显微镜、扫描电镜和碳硫分析等实验手段对样品及其黄铁矿进行对比研究。研究区样品中黄铁矿主要发育草莓状、立方体自形、条带状及不规则非自形等4种类型。其中草莓状黄铁矿发育最多,其粒径整体较小且变化范围较窄,反映以同沉积成因为主,一般与有机质含量有良好的正相关性,其他类型黄铁矿则可能为成岩成因。3口钻井页岩样品中黄铁矿形貌特征和粒径特征差异显示,SNY1井沉积水体安静、还原性最强,W001-4井和EYY1井沉积水体下部具有贫氧—厌氧环境的转变,其中W001-4井高丰度黄铁矿可能受绵阳—长宁拉张槽热液活动的影响。岩相对黄铁矿含量具有一定的控制作用,硅质页岩和硅质—钙质过渡型页岩比钙质页岩更有利于黄铁矿的形成。黄铁矿对有机孔的发育和保存具有积极影响,有利于页岩储层中天然气的富集和储存。Abstract: The existence of pyrite provides a basis for the restoration of sedimentary and diagenetic environment, also, it can be regarded as a reference for the prediction of organic-rich shale. Shales of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation drilled at three different sedimentary locations (wells Yichang EYY1, Weiyuan W001-4 and Hanzhong SNY1) in the Yangtze region have been taken as samples in this study. The pyrites founded within these samples have been analyzed with XRD, microscope, scanning electron microscope and carbon and sulfur contents. By the comparison of analytical results, it was indicated that there were four types of pyrite in these samples including framboidal, cubic automorphic, strip-shaped and irregular non-self-formed. The framboidal pyrite was mostly developed, and its particle size was relatively smaller and varied in a narrow range, reflecting the synsedimentary origin, generally has a good and positive correlation with the content of organic matter, while other types of pyrite may be diagenetically originated. The morphological differences of pyrite in shale samples from three wells indicated that the sedimentary water of well SNY1 is quiet and has the strongest reductivity. The lower part of the sedimentary water of wells W001-4 and EYY1 experienced a transformation from oxygen-poor to anaerobic, and the high-abundance pyrite in the shales of well W001-4 might be affected by hydrothermal activities in the Mianyang-Changning tension trough. Compared with calcareous shale, siliceous shale and silicic-calcareous transitional shale are more favorable for the formation of pyrite. Pyrite has a positive effect on the development and preservation of organic pores, which is beneficial to the enrichment and storage of natural gas in shale reservoirs.
-
Key words:
- pyrite /
- shale /
- Niutitang Formation /
- Lower Cambrian /
- Upper Yangtz region
-
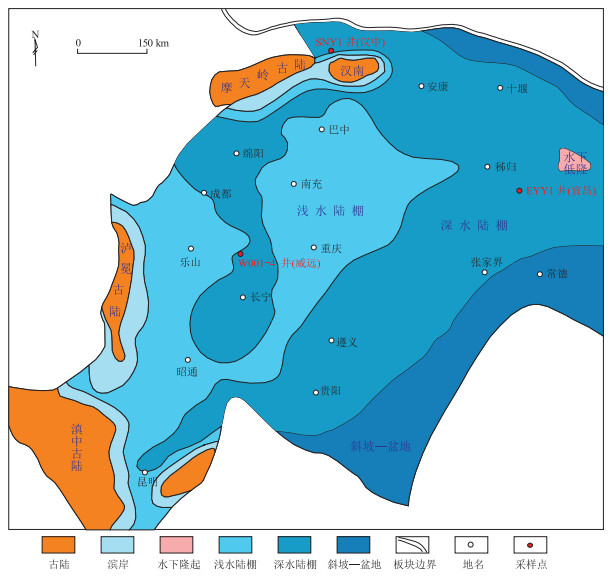
图 1 上扬子地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组沉积相平面分布及取样位置
修改自参考文献[1]。
Figure 1. Sedimentary facies of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation and sampling locations in Upper Yangtze region
图 4 上扬子地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组黄铁矿类型
a.SNY1-4,草莓状黄铁矿,硅质页岩,2 224.79 m;b.SNY1-1,草莓状黄铁矿,硅质页岩,2 162.15 m;c.SNY1-1,立方体自形黄铁矿,硅质页岩,2 162.15 m;d.W001-4-6,立方体自形黄铁矿,硅质页岩,2 973.56 m;e.EYY1-2,立方体自形黄铁矿,钙质页岩,2 943.65 m;f.EYY1-16,条带状黄铁矿,钙质页岩,3 066.47 m;g.W001-4-18,条带状黄铁矿,硅质页岩,3 083.88 m;h.EYY1-13,不规则非自形黄铁矿,硅质页岩,3 044.7 m;i.W001-4-17,不规则非自形黄铁矿,硅质页岩,3 084.58 m
Figure 4. Pyrite types of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, Upper Yangtze region
图 5 上扬子地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组黄铁矿分布特征
a.SNY1-2,黄铁矿分布在有机质富集地带,硅质页岩,2 187.46 m;b.W001-4-4,黄铁矿分布在有机质和黏土矿物附近,硅质页岩,2 950.58 m;c.SNY1-8,黄铁矿分布在矿物颗粒间,硅质页岩,2 369.55 m;d.W001-4-3,黄铁矿分布在矿物颗粒内,硅质页岩,2 898.64 m;e.EYY1-4,黄铁矿零星分布,钙质页岩,2 978.94 m;f.SNY1-10,黄铁矿顺层分布,硅质页岩,2 385.81 m
Figure 5. Distribution features of pyrites of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, Upper Yangtze region
图 8 上扬子地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩镜下照片
a.EYY1-7,硅质页岩,可见海绵骨针,3 004.85 m;b.EYY1-8,硅质页岩,可见矿物水平纹层,3 010.96 m;c.EYY1-14,钙质页岩,3 054.70 m;d.EYY1-16, 钙质页岩,3 066.47 m;e.EYY1-6,过渡型页岩,2 998.60 m;f.EYY1-9,过渡型页岩,3 023.58 m;g.W001-4-18,硅质页岩,3 084.58 m;h.SNY1-1,硅质页岩,2 162.15 m;i.SNY1-4,硅质页岩,2 224.79 m
Figure 8. Microscope pictures of shale of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, Upper Yangtze region
图 11 上扬子地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组有机孔发育情况
a.SNY1-4,黄铁矿伴生在运移有机质旁边,硅质页岩,2 224.79 m;b.SNY1-3,黄铁矿颗粒间运移有机质及孔隙特征,硅质页岩,2 205.04 m;c.SNY1-2,黄铁矿颗粒内运移有机质及孔隙特征,硅质页岩,2 187.46 m;d.W001-4-19,运移有机质孔,硅质页岩,3 084.8 m;e.W001-4-13,运移有机质孔,硅质页岩,3 065.54 m;f.EYY1-8,运移有机质孔,硅质页岩,3 010.96 m
Figure 11. Development of organic pores of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, Upper Yangtze region
表 1 上扬子地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组样品采集信息
Table 1. Sample information of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Upper Yangtze region
采样点 取样井 样品数/块 沉积亚相 岩性特征 宜昌 EYY1井 16 深水陆棚 主要为灰黑色—黑色页岩及灰质页岩 威远 W001-4井 20 深水陆棚 主要为浅灰色—灰黑色页岩,底部发育有Mo-Ni矿层 汉中 SNY1井 10 深水陆棚 主要为碳质页岩、硅质页岩和泥岩 表 2 上扬子地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组草莓状黄铁矿粒径统计
Table 2. Statistics of particle size of strawberry pyrites of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, Upper Yangtze region
样品号 统计个数 最大值/μm 最小值/μm 平均粒径/μm 标准偏差/μm 样品号 统计个数 最大值/μm 最小值/μm 平均粒径/μm 标准偏差/μm EYY1-1 5 7.7 2.1 4.0 2.0 W001-4-3 7 10.3 0.6 6.3 3.1 EYY1-2 9 12.6 3.1 6.2 3.0 W001-4-4 13 11.2 1.1 5.3 2.7 EYY1-3 11 10.2 0.5 3.5 2.8 W001-4-6 13 8.9 1.2 4.2 2.2 EYY1-4 17 8.8 1.4 3.7 1.9 W001-4-10 5 10.9 2.3 5.8 3.1 EYY1-5 39 6.5 1.8 4.1 1.3 W001-4-13 11 4.9 1.0 2.7 1.2 EYY1-6 21 8.0 2.7 5.1 1.4 W001-4-14 9 8.1 1.2 3.6 2.1 EYY1-7 9 6.8 0.9 4.0 1.9 W001-4-19 3 4.2 3.5 3.9 0.3 EYY1-8 10 5.5 1.4 3.2 1.6 SNY1-1 28 6.7 1.3 3.6 1.4 EYY1-9 14 19.7 4.6 8.4 4.5 SNY1-2 27 6.4 0.8 3.1 1.5 EYY1-10 24 8.1 1.4 4.4 1.7 SNY1-3 9 6.9 2.5 4.3 1.4 EYY1-11 9 13.5 1.7 6.9 3.9 SNY1-4 13 9.5 1.8 5.3 2.8 EYY1-12 3 6.5 3.0 5.0 1.5 SNY1-5 11 7.1 2.6 5.1 1.5 EYY1-13 10 4.6 1.4 2.8 1.1 NY1-6 17 8.9 2.0 4.6 1.6 EYY1-14 2 7.8 4.6 6.2 1.6 SNY1-7 11 5.6 1.9 3.6 1.1 EYY1-15 7 3.9 1.0 3.1 0.9 SNY1-8 13 7.9 1.4 3.5 1.7 EYY1-16 9 10.1 2.7 6.1 2.5 SNY1-9 12 4.7 1.3 2.8 1.2 W001-4-1 17 11.6 1.6 4.9 2.3 SNY1-10 10 6.3 1.7 3.2 1.3 W001-4-2 14 10.4 1.2 4.5 2.4 表 3 海相页岩岩相类型划分方案[18]
Table 3. Classification scheme of marine shale
岩相类型 岩石矿物组分质量分数/% 石英+长石 方解石+白云石 黏土 硅质页岩相 50~75 <30 10~50 黏土质页岩相 25~50 <30 50~75 钙质页岩相 <30 50~75 25~50 黏土质硅质混合页岩相 30~50 <33 30~50 黏土质钙质混合页岩相 <33 30~50 30~50 钙质硅质混合页岩相 30~50 30~50 <33 表 4 上扬子地区不同地区、不同岩相黄铁矿含量
Table 4. Pyrite contents in different regions and litho-facies, Upper Yangtze region
井位 岩相 ω(TOC)/% 黄铁矿平均含量/% 黄铁矿的形貌及分类 EYY1井 硅质页岩 4.27 2.30 草莓状和自形单晶为主,发现不规则非自形和少量条带状 EYY1井 钙质页岩 2.15 1.96 自形单晶、不规则非自形、草莓状较少,有少量条带状 EYY1井 过渡型页岩 2.85 3.45 草莓状、自形单晶、不规则非自形为主 W001-4井 硅质页岩 1.78 6.80 自形和不规则非自形为主,草莓状发育较少,偶尔可见条带状 SNY1井 硅质页岩 1.57 2.00 草莓状为主,自形单晶发育较多、少量不规则非自形 -
[1] 赵建华, 金之钧, 林畅松, 等. 上扬子地区下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩沉积环境[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(4): 701-715. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201904003.htmZHAO Jianhua, JIN Zhijun, LIN Changsong, et al. Sedimentary environment of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation shale in the Upper Yangtze region[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2019, 40(4): 701-715. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201904003.htm [2] 黄正清, 周道容, 李建青, 等. 下扬子地区寒武系页岩气成藏条件分析与资源潜力评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(1): 94-98. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901094HUANG Zhengqing, ZHOU Daorong, LI Jianqing, et al. Shale gas accumulation conditions and resource potential evaluation of the Cambrian in the Lower Yangtze area[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(1): 94-98. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901094 [3] 郑和荣, 彭勇民, 唐建信, 等. 中、上扬子地区常压页岩气勘探前景: 以湘中坳陷下寒武统为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(6): 1155-1167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201906001.htmZHENG Herong, PENG Yongmin, TANG Jianxin, et al. Exploration prospect of normal pressure shale gas in Middle and Upper Yangtze regions: a case study of the Lower Cambrian shale in Xiangzhong Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(6): 1155-1167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201906001.htm [4] 余宽宏, 金振奎, 苏奎, 等. 中、上扬子地台北缘寒武纪沉积特征及油气勘探意义[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2013, 43(9): 1418-1435. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201309004.htmYU Kuanhong, JIN Zhenkui, SU Kui, et al. The Cambrian sedimentary characteristics and their implications for oil and gas exploration in north margin of Middle-Upper Yangtze Plate[J]. Science China(Earth Sciences), 2013, 56(6): 1014-1028. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201309004.htm [5] 张君峰, 许浩, 周志, 等. 鄂西宜昌地区页岩气成藏地质特征[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(8): 887-899. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201908001.htmZHANG Junfeng, XU Hao, ZHOU Zhi, et al. Geological characteristics of shale gas reservoir in Yichang area, western Hubei[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(8): 887-899. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201908001.htm [6] 张焱林, 段轲, 刘早学, 等. 鄂西下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩特征及页岩气富集主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(5): 691-698. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201905691ZHANG Yanlin, DUAN Ke, LIU Zaoxue, et al. Characteristics of shale and main controlling factors of shale gas enrichment of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in western Hubei[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(5): 691-698. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201905691 [7] 许露露, 刘早学, 温雅茹, 等. 中扬子鄂西地区牛蹄塘组页岩储层特征及含气性研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2020, 27(4): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202004001.htmXU Lulu, LIU Zaoxie, WEN Yaru, et al. Shale gas reservoir and gas bearing properties of Middle Yangtze Niutitang Formation in western Hubei[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reserviors, 2020, 27(4): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202004001.htm [8] 高波, 刘忠宝, 舒志国, 等. 中上扬子地区下寒武统页岩气储层特征及勘探方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(2): 284-294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202002006.htmGAO Bo, LIU Zhongbao, SHU Zhiguo, et al. Reservoir characte-ristics and exploration of the Lower Cambrian shale gas in the Middle-Upper Yangtze area[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(2): 284-294. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202002006.htm [9] 田兴旺, 胡国艺, 苏桂萍, 等. 川南威远地区W201井古生界海相页岩矿物特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(4): 409-415. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201804005.htmTIAN Xingwang, HU Guoyi, SU Guiping, et al. Mineralogical characteristics of Paleozoic marine shales in well W201 of Weiyuan area, southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(4): 409-415. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201804005.htm [10] 任东超, 陈义才, 孙超亚, 等. 威远地区筇竹寺组页岩气成藏条件分析[J]. 石油化工应用, 2016, 35(8): 99-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXSH201608027.htmREN Dongchao, CHEN Yicai, SUN Chaoya, et al. Shale gas reservoir-forming conditions and predicting favorable exploration area in Qiongzhusi Formation, Vying region[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application, 2016, 35(8): 99-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXSH201608027.htm [11] 李延钧, 赵圣贤, 黄勇斌, 等. 四川盆地南部下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩沉积微相研究[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(8): 1136-1148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201308009.htmLI Yanjun, ZHAO Shengxian, HUANG Yongbin, et al. The sedimentary micro-facies study of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(8): 1136-1148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201308009.htm [12] 黄金亮, 邹才能, 李建忠, 等. 川南下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩气形成条件及资源潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(1): 69-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201201009.htmHUANG Jinliang, ZOU Caineng, LI Jianzhong, et al. Shale gas generation and potential of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(1): 69-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201201009.htm [13] 韩雨樾, 冉波, 李智武, 等. 四川盆地北缘下寒武统页岩生物标志化合物特征及其地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(3): 435-442. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903435HAN Yuyue, RAN Bo, LI Zhiwu, et al. Characteristics of biomarker compounds and their implications for Lower Cambrian black shale on the northern margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2019, 41(3): 435-442. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903435 [14] 陈相霖, 郭天旭, 石砥石, 等. 陕南地区牛蹄塘组页岩孔隙结构特征及吸附能力[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(5): 52-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201905006.htmCHEN Xianglin, GUO Tianxu, SHI Dishi, et al. Pore structure characteristics and adsorption capacity of Niutitang Formation shale in southern Shaanxi[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(5): 52-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201905006.htm [15] 王宁, 许锋. 陕南镇巴地区牛蹄塘组页岩沉积环境分析[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(8): 1764-1774. . https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201908003.htmWANG Ning, XU Feng. Study of sedimentary environment of the Niutitang Formation shale in Xixiang-Zhenba area, Shaanxi[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2019, 10(8): 1764-1774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS201908003.htm [16] WILKIN R T, BARNES H L. Pyrite formation by reactions of iron monosulfides with dissolved inorganic and organic sulfur species[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(21): 4167-4179. [17] BUTLER I B, RICKARD D. Framboidal pyrite formation via the oxidation of iron (Ⅱ) monosulfide by hydrogen sulphide[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(15): 2665-2672. [18] 王玉满, 王淑芳, 董大忠, 等. 川南下志留统龙马溪组页岩岩相表征[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(1): 119-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601013.htmWANG Yuman, WANG Shufang, DONG Dazhong, et al. Lithofacies characterization of Longmaxi Formation of the Lower Silurian, southern Sichuan[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(1): 119-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601013.htm [19] 孙川翔, 聂海宽, 刘光祥, 等. 石英矿物类型及其对页岩气富集开采的控制: 以四川盆地及其周缘五峰组-龙马溪组为例[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(11): 3692-3704. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201911009.htmSUN Chuanxiang, NIE Haikuan, LIU Guangxiang, et al. Quartz type and its control on shale gas enrichment and production: a case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in the Sichuan Basin and its surrounding areas, China[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(11): 3692-3704. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201911009.htm [20] 张景廉, 张平中. 黄铁矿对有机质成烃的催化作用讨论[J]. 地球科学进展, 1996, 11(3): 282-287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ603.008.htmZHANG Jinglian, ZHANG Pingzhong. A discussion of pyrite catalysis on the hydrocarbon generation process[J]. Advances in Earth Sciences, 1996, 11(3): 282-287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ603.008.htm [21] 李丹, 欧成华, 马中高, 等. 黄铁矿与页岩的相互作用及其对页岩气富集与开发的意义[J]. 石油物探, 2018, 57(3): 332-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT201803003.htmLI Dan, OU Chenghua, MA Zhonggao, et al. Pyrite-shale interaction in shale gas enrichment and development[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2018, 57(3): 332-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT201803003.htm [22] 陈丽蓉, 石学法, 初凤友. 大西洋中脊热液黄铁矿的标型演化特征研究[J]. 科学通报, 1995, 40(12): 1119-1121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199512019.htmCHEN Lirong, SHI Xuefa, CHU Fengyou. Study on the morphological evolution characteristics of the Atlantic midridge hydrothermal pyrite[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(12): 1119-1121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199512019.htm [23] 刘开君, 黄菲, 高尚, 等. 北大西洋Logatchev热液区多形貌黄铁矿特征及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(5): 1562-1573.LIU Kaijun, HUANG Fei, GAO Shang, et al. Characteristics and research significance of polymorphic pyrite in Logatchev hydrothermal area, North Atlantic[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(5): 1562-1573. [24] LOVE L, AMSTUTZ G C. Review of microscopic pyrite from the Devonian Chattanooga shale and Rammelsberg Banderz[J]. Fortschrift Mineralogie, 1966, 43: 273-309. [25] 张光荣, 聂海宽, 唐玄, 等. 页岩中黄铁矿类型及其对页岩气富集的影响: 以四川盆地及其周缘五峰组-龙马溪组页岩为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(3): 459-466. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003459ZHANG Guangrong, NIE Haikuan, TANG Xuan, et al. Pyrite type and its effect on shale gas accumulation: a case study of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale in Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(3): 459-466. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003459 [26] RAISWELL R, BERNER R A. Pyrite formation in euxinic and semi-euxinic sediments[J]. American Journal of Science, 1985, 285(8): 710-724. [27] 王晓洁, 张世奇, 魏孟吉, 等. 东濮凹陷文东地区沙三段黄铁矿特征及形成模式[J]. 断块油气田, 2015, 22(2): 178-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201502009.htmWANG Xiaojie, ZHANG Shiqi, WEI Mengji, et al. Characteristics and formation mode of Es3 member pyrite in Wendong area of Dongpu Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2015, 22(2): 178-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201502009.htm [28] 常华进, 储雪蕾. 草莓状黄铁矿与古海洋环境恢复[J]. 地球科学进展, 2011, 26(5): 475-481. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201105002.htmCHANG Huajin, CHU Xuelei. Pyrite framboids and palaeo ocean redox condition reconstruction[J]. Advances in Earth Sciences, 2011, 26(5): 475-481. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201105002.htm [29] MERINERO R, LUNAR R, MARTÍNEZ-FRÍAS J, et al. Iron oxyhydroxide and sulphide mineralization in hydrocarbon seep-related carbonate submarine chimneys, Gulf of Cadiz (SW Iberian Peninsula)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2008, 25(8): 706-713. [30] WILKIN R T, BARNES H L, BRANTLEY S L. The size distribution of framboidal pyrite in modern sediments: an indicator of redox conditions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(20): 3897-3912. [31] 刘子驿. 湘鄂西五峰-龙马溪组黄铁矿成因及其页岩气意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.LIU Ziyi. Shale gas significance of pyrite in Wufeng-Longmaxi formations, case study in western Hunan and Hubei[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017. [32] 孙萌. 扬子地区牛蹄塘组矿物岩石学特征及黄铁矿的环境指示意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.SUN Meng. Mineralogical and petrological features and environmental significance of pyrite for the Niutitang Formation of the Cambrian in the Yangtze area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017. [33] WILKIN R T, ARTHUR M A, DEAN W E. History of water-column anoxia in the Black Sea indicated by pyrite framboid size distributions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1997, 148(3/4): 517-525. [34] RACKI G, PIECHOTA A, BOND D, et al. Geochemical and ecological aspects of Lower Frasnian pyrite-ammonoid level at Kostomłoty (Holy Cross Mountains, Poland)[J]. Geological Quarterly, 2004, 48(3): 267-282. [35] 王佳. 贵州桃映下寒武统牛蹄塘组黑色页岩中草莓状黄铁矿的粒径特征及其环境意义[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013.WANG Jia. Particle size characteristics of framboidal pyrite in black shale of Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Taoying, Guizhou and its environmental significance[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2013. [36] ZHOU Chuanming, JIANG Shaoyong. Palaeoceanographic redox environments for the Lower Cambrian Hetang Formation in South China: evidence from pyrite framboids, redox sensitive trace elements, and sponge biota occurrence[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2009, 271(3/4): 279-286. [37] BERNER R A, DE LEEUW J W, SPIRO B, et al. Sulphate reduction, organic matter decomposition and pyrite formation[and discussion] [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1985, 315(1531): 25-38. [38] MACLEAN L C W, TYLISZCZAK T, GILBERT P U P A, et al. A high-resolution chemical and structural study of framboidal pyrite formed within a low-temperature bacterial biofilm[J]. Geobiology, 2008, 6(5): 471-480. [39] UFFMANN A K, LITTKE R, RIPPEN D. Mineralogy and geochemistry of Mississippian and Lower Pennsylvanian black shales at the northern margin of the Variscan Mountain belt (Germany and Belgium)[J]. International Journal of Coal Geo-logy, 2012, 103: 92-108. [40] WACEY D, KILBURN M R, SAUNDERS M, et al. Uncovering framboidal pyrite biogenicity using nano-scale CNorg mapping[J]. Geology, 2015, 43(1): 27-30. [41] 崔景伟, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 黄铁矿在页岩有机质富集、生排烃与页岩油聚集中的作用[C]//第一届全国青年地质大会论文集. 福州: 中国地质学会, 2013: 783-784.CUI Jingwei, ZHU Rukai, WU Songtao, et al. The role of pyrite in shale organic matter enrichment, hydrocarbon generation and expulsion, and shale oil accumulation[C]//Proceedings of the First National Youth Geological Conference. Fuzhou: Geological Society of China, 2013: 783-784. [42] MA Xiangxian, ZHENG Jianjing, ZHENG Guodong, et al. Influence of pyrite on hydrocarbon generation during pyrolysis of type-Ⅲ kerogen[J]. Fuel, 2016, 167: 329-336. [43] 蔡潇, 王亮, 靳雅夕, 等. 渝东南地区页岩有机孔隙类型及特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(3): 513-519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201603016.htmCAI Xiao, WANG Liang, JIN Yaxi, et al. Types and characteristics of organic pore in shale gas reservoir of southeastern Chongqing area[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(3): 513-519. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201603016.htm [44] 薛冰, 张金川, 唐玄, 等. 黔西北龙马溪组页岩微观孔隙结构及储气特征[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(2): 138-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201502002.htmXUE Bing, ZHANG Jinchuan, TANG Xuan, et al. Characteristics of microscopic pore and gas accumulation on shale in Longmaxi Formation, northwest Guizhou[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(2): 138-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201502002.htm [45] HUNT J M, LEWAN M D, HENNET R J C. Modeling oil generation with time-temperature index graphs based on the Arrhenius equation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1991, 75(4): 795-807. [46] 孙寅森, 郭少斌. 湘鄂西地区上震旦统陡山沱组页岩微观孔隙特征及主控因素[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2017, 39(1): 114-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201701009.htmSUN Yansen, GUO Shaobin. Characteristics of microscopic pores of shale from Upper Sinian Doushantuo Formation in the western of Hunan and Hubei, China and the main controlling factors[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2017, 39(1): 114-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201701009.htm [47] 马存飞, 董春梅, 栾国强, 等. 苏北盆地古近系泥页岩有机质孔发育特征及影响因素[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 41(3): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201703001.htmMA Cunfei, DONG Chunmei, LUAN Guoqiang, et al. Characte-ristics and influencing factors of organic-matter pores in Paleogene shale, Subei Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2017, 41(3): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201703001.htm -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号