Differential mechanisms of organic matter accumulation of source rocks in the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation and implications for gas exploration fields in Sichuan Basin
-
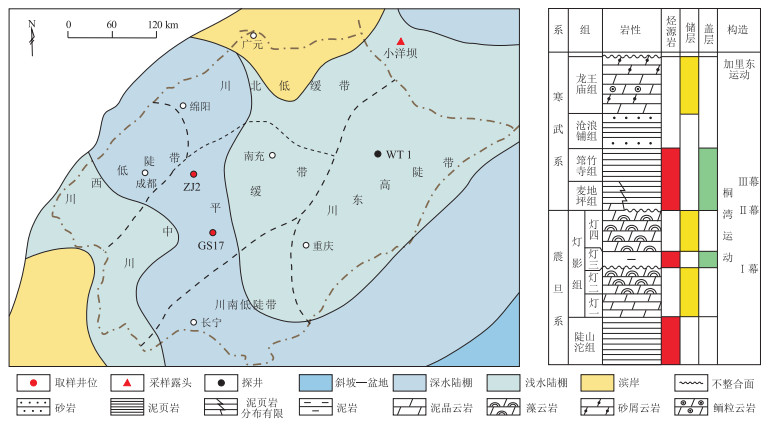
摘要: 四川盆地以下寒武统筇竹寺组为烃源岩的海相高演化天然气系统是全球这一领域的一个典范,为进一步深化地质理论认识,拓展勘探领域,针对当前川中、川东北2个热点勘探区块,通过地球化学方法,从古生产力、氧化还原条件、陆源输入三方面入手,对不同区域该套烃源岩质量及其有机质富集机制展开了差异对比研究,探讨了天然气勘探领域。结果表明:川中GS17井、ZJ2井所在的裂陷槽内深水陆棚相烃源岩有机碳含量整体高于川东北小洋坝浅水陆棚相烃源岩,两者有机质富集均主要受控于氧化还原环境;川中烃源岩形成于缺氧环境,相较于川东北烃源岩所形成的贫氧环境更有利于有机质的保存;川东北烃源岩形成过程中陆源输入对有机质的稀释作用尤为显著,烃源岩质量不如川中烃源岩。筇竹寺组天然气系统的勘探仍需围绕裂陷槽及周缘展开,同时盆地周缘的深水陆棚地区也值得加以重视,且常规与非常规天然气资源并重。Abstract: The marine facies highly mature natural gas system with the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation as the source rock in the Sichuan Basin is a global model in this field. To deepen the geological understanding of high quality source rocks and the natural gas exploration areas in the Sichuan Basin, taking two hot exploration blocks in the central and northeastern parts of Sichuan Basin as examples, the differential mechanisms of organic matter accumulation in source rocks of the Qiongzhusi Formation were studied, and some gas exploration areas were identified by the means of geochemical methods from three perspectives, including paleoproductivity, redox conditions and input of terristral organic matters. The TOC of source rocks within deep-water shelf in the intracratonic rift sampled from the Gaoshi 17 and Zhongjiang 2 wells in the central Sichuan were higher than that of source rocks within the shallow-water shelf sampled from the Xiaoyangba outcrop, northeastern Sichuan. The organic matter accumulations of both sample sets were mainly controlled by redox condition, but in comparison, the source rocks in the central Sichuan Basin were formed in relative anoxic environment, which was more conducive for the preservation of organic matter than the suboxic environment in northeastern Sichuan Basin. In addition, the dilution effection by terrestrial organic matter input was particularly significant during the formation of source rocks in the northeastern Sichuan Basin, leading to poorer source rock quality. The exploration of natural gas system in the Qiongzhusi Formation still needs to be carried out closely around the intracratonic rift and its surrounding margin in the future, and the deep-water shelf area around the basin also deserves attention. Both conventional and unconventional natural gas resources should be considered.
-
图 4 四川盆地及周缘下寒武统筇竹寺组烃源岩U-Mo协变关系
底图修改自文献[26]。
Figure 4. Covariation of UEF and MoEF for Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in Sichuan Basin and its periphery
-
[1] 杜金虎, 邹才能, 徐春春, 等. 川中古隆起龙王庙组特大型气田战略发现与理论技术创新[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 268-277. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403005.htmDU Jinhu, ZOU Caineng, XU Chunchun, et al. Theoretical and technical innovations in strategic discovery of a giant gas field in Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation of central Sichuan paleo-uplift, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 268-277. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403005.htm [2] 邹才能, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 等. 四川盆地震旦系-寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 278-293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403006.htmZOU Caineng, DU Jinhu, XU Chunchun, et al. Formation, distribution, resource potential and discovery of the Sinian-Cambrian giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 278-293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403006.htm [3] 马新华, 杨雨, 文龙, 等. 四川盆地海相碳酸盐岩大中型气田分布规律及勘探方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901001.htmMA Xinhua, YANG Yu, WEN Long, et al. Distribution and exploration direction of medium- and large-sized marine carbonate gas fields in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901001.htm [4] SHI Chunhua, CAO Jian, TAN Xiucheng, et al. Hydrocarbon generation capability of Sinian-Lower Cambrian shale, mudstone, and carbonate rocks in the Sichuan Basin, southwestern China: implications for contributions to the giant Sinian Dengying natural gas accumulation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2018, 102(5): 817-853. doi: 10.1306/0711171417417019 [5] 金之钧, 胡宗全, 高波, 等. 川东南地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气富集与高产控制因素[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601002.htmJIN Zhijun, HU Zongquan, GAO Bo, et al. Controlling factors on the enrichment and high productivity of shale gas in the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601002.htm [6] 刘忠宝, 高波, 张钰莹, 等. 上扬子地区下寒武统页岩沉积相类型及分布特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(1): 21-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701004.htmLIU Zhongbao, GAO Bo, ZHANG Yuying, et al. Types and distribution of the shale sedimentary facies of the Lower Cambrian in Upper Yangtze area, South China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 21-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701004.htm [7] 魏国齐, 杨威, 杜金虎, 等. 四川盆地震旦纪-早寒武世克拉通内裂陷地质特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(1): 24-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201501004.htmWEI Guoqi, YANG Wei, DU Jinhu, et al. Geological characteristics of the Sinian-Early Cambrian intracratonic rift, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(1): 24-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201501004.htm [8] 杨跃明, 文龙, 罗冰, 等. 四川盆地达州-开江古隆起沉积构造演化及油气成藏条件分析[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(8): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201608002.htmYANG Yueming, WEN Long, LUO Bing, et al. Sedimentary tectonic evolution and reservoir-forming conditions of the Dazhou-Kaijiang paleo-uplift, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(8): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201608002.htm [9] 管树巍, 吴林, 任荣, 等. 中国主要克拉通前寒武纪裂谷分布与油气勘探前景[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(1): 9-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201701002.htmGUAN Shuwei, WU Lin, REN Rong, et al. Distribution and petro-leum prospect of Precambrian rifts in the main cratons, China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(1): 9-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201701002.htm [10] 武赛军, 魏国齐, 杨威, 等. 四川盆地桐湾运动及其油气地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(1): 60-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201601008.htmWU Saijun, WEI Guoqi, YANG Wei, et al. Tongwan Movement and its geologic significances in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(1): 60-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201601008.htm [11] 罗冰, 杨跃明, 罗文军, 等. 川中古隆起灯影组储层发育控制因素及展布[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(4): 416-426. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201504003.htmLUO Bing, YANG Yueming, LUO Wenjun, et al. Controlling factors and distribution of reservoir development in Dengying Formation of paleo-uplift in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(4): 416-426. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201504003.htm [12] 刘树根, 刘殊, 孙玮, 等. 绵阳-长宁拉张槽北段构造-沉积特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201801001.htmLIU Shugen, LIU Shu, SUN Wei, et al. Tectonic and sedimentary features of the northern Mianyang-Changning intracratonic sag, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2018, 45(1): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201801001.htm [13] 赵建华, 金之钧, 林畅松, 等. 上扬子地区下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩沉积环境[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(4): 701-715. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201904003.htmZHAO Jianhua, JIN Zhijun, LIN Changsong, et al. Sedimentary environment of the Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation shale in the Upper Yangtze region[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(4): 701-715. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201904003.htm [14] 杜金虎, 汪泽成, 邹才能, 等. 上扬子克拉通内裂陷的发现及对安岳特大型气田形成的控制作用[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(1): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201601002.htmDU Jinhu, WANG Zecheng, ZOU Caineng, et al. Discovery of intra-cratonic rift in the Upper Yangtze and its control effect on the formation of Anyue giant gas field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(1): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201601002.htm [15] 刘树根, 王一刚, 孙玮, 等. 拉张槽对四川盆地海相油气分布的控制作用[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 43(1): 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201601001.htmLIU Shugen, WANG Yigang, SUN Wei, et al. Control of intracratonic sags on the hydrocarbon accumulations in the marine strata across the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2016, 43(1): 1-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201601001.htm [16] 高剑峰, 陆建军, 赖鸣远, 等. 岩石样品中微量元素的高分辨率等离子质谱分析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 39(6): 844-850. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ200306013.htmGAO Jianfeng, LU Jianjun, LAI Minyuan, et al. Analysis of trace elements in rock samples using HR-ICPMS[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 2003, 39(6): 844-850. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJDZ200306013.htm [17] DYMOND J, SUESS E, LYLE M. Barium in deep-sea sediment: a geochemical proxy for paleoproductivity[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 1992, 7(2): 163-181. [18] PFEIFER K, KASTEN S, HENSEN C, et al. Reconstruction of primary productivity from the barium contents in surface sediments of the South Atlantic Ocean[J]. Marine Geology, 2001, 177(1/2): 13-24. [19] NAMEROFF T J, BALISTRIERI L S, MURRAY J W. Suboxic trace metal geochemistry in the eastern tropical north pacific[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66(7): 1139-1158. [20] PIPER D Z, PERKINS R B. A modern vs. Permian black shale: the hydrography, primary productivity, and water-column chemistry of deposition[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 206(3/4): 177-197. [21] TRIBOVILLARD N, ALGEO T J, LYONS T, et al. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: an update[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 232(1/2): 12-32. [22] CALVERT S E, PEDERSEN T F. Geochemistry of recent oxic and anoxic marine sediments: implications for the geological record[J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 113(1/2): 67-88. [23] MORFORD J L, EMERSON S R, BRECKEL E J, et al. Diagenesis of oxyanions (V, U, Re, and Mo) in pore waters and sediments from a continental margin[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(21): 5021-5032. [24] HELZ G R, MILLER C V, CHARNOCK J M, et al. Mechanism of molybdenum removal from the sea and its concentration in black shales: EXAFS evidence[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(19): 3631-3642. [25] CRUSIUS J, CALVERT S, PEDERSEN T, et al. Rhenium and molybdenum enrichments in sediments as indicators of oxic, suboxic and sulfidic conditions of deposition[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 145(1/4): 65-78. [26] ALGEO T J, TRIBOVILLARD N. Environmental analysis of paleoceanographic systems based on molybdenum-uranium covariation[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268(3/4): 211-225. [27] EINSELE G. Sedimentary basins: evolution, facies, and sediment budget[M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer, 2000: 463. [28] 兰才俊, 徐哲航, 马肖琳, 等. 四川盆地震旦系灯影组丘滩体发育分布及对储层的控制[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(9): 1069-1084. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201909005.htmLAN Juncai, XU Zhehang, MA Xiaolin, et al. Development and distribution of mound-shoal complex in the Sinian Dengying Formation, Sichuan Basin and its control on reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(9): 1069-1084. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201909005.htm [29] 冯明友, 强子同, 沈平, 等. 四川盆地高石梯-磨溪地区震旦系灯影组热液白云岩证据[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(5): 587-598. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201605003.htmFENG Mingyou, QIANG Zitong, SHEN Ping, et al. Evidences for hydrothermal dolomite of Sinian Dengying Formation in Gaoshiti-Moxi area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(5): 587-598. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201605003.htm [30] 金民东, 谭秀成, 童明胜, 等. 四川盆地高石梯-磨溪地区灯四段岩溶古地貌恢复及地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(1): 58-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701008.htmJIN Mindong, TAN Xiucheng, TONG Mingsheng, et al. Karst paleogeomorphology of the fourth member of Sinian Dengying Formation in Gaoshiti-Moxi area, Sichuan Basin, SW China: restoration and geological significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 58-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701008.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号