Influence of Permian basaltic volcanic activity on coal-bearing shale reservoirs, Southern Guizhou Depression
-
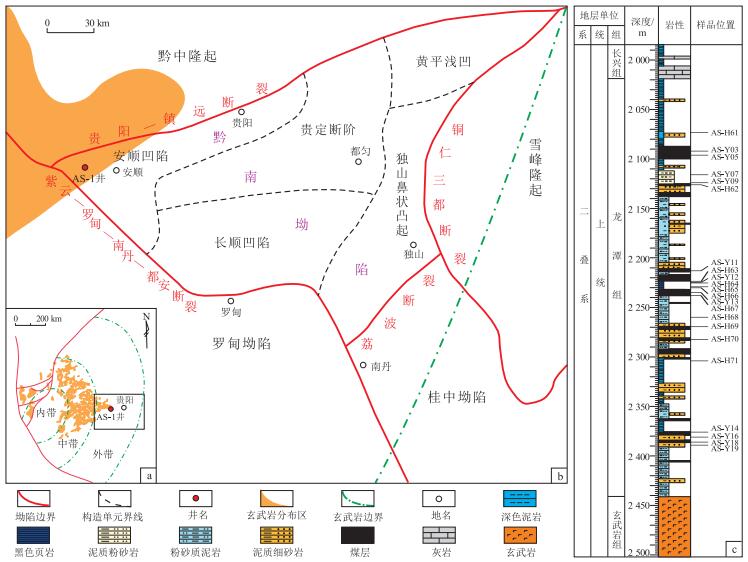
摘要: 为了研究火山活动对泥页岩储层的影响,以黔南坳陷二叠纪峨眉山玄武岩对龙潭组泥页岩储层的影响为例,通过总有机碳含量、XRD、镜质体反射率以及低温氮气及二氧化碳吸附等方法,研究了火山活动对含煤泥页岩生烃、矿物成分以及储层孔隙结构等方面的影响。研究表明:火山活动对含煤泥页岩的生烃、矿物组成和孔隙结构存在明显的影响;火山活动显著促进了泥页岩的有机质成熟演化,使其迅速进入到了过成熟阶段(Ro从2.0%增加到2.88%),加快了烃源岩的生排烃效率;随着与岩浆岩距离的减小,石英和碳酸盐矿物含量增加,黏土矿物含量减小,伊利石和绿泥石含量呈现规律变化,指示了泥页岩成岩演化也受到了一定的影响;火山活动带来的热源对泥页岩储层孔隙的形成演化产生了重要的影响,随着距离岩浆岩越近,含煤泥页岩储层中的微孔占比逐渐增高,介孔和宏孔含量呈下降趋势,推测火山活动的热作用促进了有机质孔隙的生成,同时也影响了无机孔隙的发育。Abstract: To investigate the influences of volcanic activities on shale reservoirs, a case study was carried out on the Permian Mount Emei basalt and coal-bearing shale of Longtan Formation in the Southern Guizhou Depression. Based on the analytical results of total organic carbon content, XRD, vitrinite reflectance and cryogenic nitrogen and carbon dioxide adsorptions, the effects of volcanic activities on the hydrocarbon generation, mineral composition and reservoir microstructure of coal-bearing shale were discussed. The results showed that volcanic activities had obvious effects on the hydrocarbon generation, mineral composition and pore structure of coal-bearing shale. They significantly promoted the evolution and maturation of organic matters in shale, which quickly entered the over-mature stage (Ro% increased from 2.0% to 2.88%), and accelerated the hydrocarbon generation and expulsion efficiency. With the decrease of the distance to the basalt, the contents of clastic minerals and carbonate minerals increased, the content of clay minerals decreased, and the contents of illite and chlorite changed regularly, which indicated that the evolution of shale diagenesis had also been affected to a certain extent. The heat brought by volcanic activities had an important influence on the pores of reservoirs. As it got closer to basalt, the proportion of micropores increased while the content of mesopores and macropores decreased. It was speculated that the thermal effects of volcanic activities promoted the formation of organic pores and also affected the development of inorganic pores.
-
Key words:
- maturity /
- mineral composition /
- pore structure /
- shale reservoir /
- volcanic activity /
- Permian /
- Southern Guizhou Depression
-
表 1 黔南坳陷AS-1井二叠系龙潭组含煤泥页岩样品N2和CO2气体吸附测试结果
Table 1. Test results of N2 and CO2 adsorptions of coal-bearing shale in Permian Longtan Formation, well AS-1, Southern Guizhou Depression
样品编号 体积/(cm3·g-1) 比表面积/(m2·g-1) 微孔 介孔 宏孔 微孔 介孔 宏孔 AS-Y03 0.056 0.002 0.008 190.268 0.410 0.261 AS-Y05 0.055 0.002 0.007 182.937 0.279 0.217 AS-Y07 0.037 0.002 0.007 125.215 0.223 0.221 AS-Y09 0.049 0.002 0.009 165.33 0.305 0.293 AS-Y11 0.055 0.001 0.006 184.311 0.276 0.184 AS-Y12 0.061 0.001 0.004 207.66 0.225 0.124 AS-Y13 0.060 0.001 0.002 209.959 0.142 0.055 AS-Y14 0.059 0.001 0.002 203.882 0.135 0.079 AS-Y16 0.061 0.002 0.001 212.138 0.161 0.083 AS-Y19 0.059 0.001 0.003 204.052 0.222 0.090 -
[1] CURTIS M E, CARDOTT B J, SONDERGELD C H, et al. Deve-lopment of organic porosity in the Woodford shale with increasing thermal maturity[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2012, 103: 26-31. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2012.08.004 [2] CURTIS M E, SONDERGELD C H, AMBROSE R J, et al. Microstructural investigation of gas shales in two and three dimensions using nanometer-scale resolution imaging[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(4): 665-677. doi: 10.1306/08151110188 [3] 张金川, 金之钧, 袁明生. 页岩气成藏机理和分布[J]. 天然气工业, 2004, 24(7): 15-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200407004.htmZHANG Jinchuan, JIN Zhijun, YUAN Mingsheng. Reservoiring mechanism of shale gas and its distribution[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2004, 24(7): 15-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200407004.htm [4] 张金川, 徐波, 聂海宽, 等. 中国页岩气资源勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2008, 28(6): 136-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200806048.htmZHANG Jinchuan, XU Bo, NIE Haikuan, et al. Exploration potential of shale gas resources in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2008, 28(6): 136-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200806048.htm [5] SLATT R M, O'BRIEN N R. Pore types in the Barnett and Woodford gas shales: contribution to understanding gas storage and migration pathways in fine-grained rocks[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2011, 95(12): 2017-2030. doi: 10.1306/03301110145 [6] LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett shale[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2009, 79(12): 848-861. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2009.092 [7] 田华, 张水昌, 柳少波, 等. 压汞法和气体吸附法研究富有机质页岩孔隙特征[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(3): 419-427. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201203011.htmTIAN Hua, ZHANG Shuichang, LIU Shaobo, et al. Determination of organic-rich shale pore features by mercury injection and gas adsorption methods[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(3): 419-427. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201203011.htm [8] MASTALERZ M, SCHIMMELMANN A, DROBNIAK A, et al. Porosity of Devonian and Mississippian New Albany shale across a maturation gradient: insights from organic petrology, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(10): 1621-1643. doi: 10.1306/04011312194 [9] MILLIKEN K L, RUDNICKI M, AWWILLER D N, et al. Organic matter-hosted pore system, Marcellus Formation (Devonian), Pennsylvania[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(2): 177-200. doi: 10.1306/07231212048 [10] 吉利明, 吴远东, 贺聪, 等. 富有机质泥页岩高压生烃模拟与孔隙演化特征[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(2): 172-181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201602003.htmJI Liming, WU Yuandong, HE Cong, et al. High-pressure hydrocarbon-generation simulation and pore evolution characteristics of organic-rich mudstone and shale[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(2): 172-181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201602003.htm [11] 马中良, 郑伦举, 徐旭辉, 等. 富有机质页岩有机孔隙形成与演化的热模拟实验[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(1): 23-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201701003.htmMA Zhongliang, ZHENG Lunju, XU Xuhui, et al. Thermal simulation experiment on the formation and evolution of organic pores in organic-rich shale[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(1): 23-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201701003.htm [12] 王民, 卢双舫, 薛海涛, 等. 岩浆侵入体对有机质生烃(成熟)作用的影响及数值模拟[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(1): 177-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201001022.htmWANG Min, LU Shuangfang, XUE Haitao, et al. The effects of magmatic intrusions on the maturation of organic matter and its numerical simualtion[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(1): 177-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201001022.htm [13] CHEN Ji, XIAO Xianming. Evolution of nanoporosity in organic-rich shales during thermal maturation[J]. Fuel, 2014, 129: 173-181. [14] 徐政语, 姚根顺, 郭庆新, 等. 黔南坳陷构造变形特征及其成因解析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2010, 34(1): 20-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201001001.htmXU Zhengyu, YAO Genshun, GUO Qingxin, et al. Genetic interpretation about geotectonics and structural transfiguration of the Southern Guizhou Depression[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2010, 34(1): 20-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201001001.htm [15] 张江江. 黔南坳陷构造演化研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学, 2010.ZHANG Jiangjiang. The research of tectonic evolution in Southern Guizhou Depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum, 2010. [16] 王民, 王岩, 卢双舫, 等. 岩浆侵入体热作用对烃源岩生烃影响的定量表征: 以松辽盆地南部英台断陷为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2014, 21(2): 171-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201402009.htmWANG Min, WANG Yan, LU Shuangfang, et al. Thermal influence of magma intrusion on hydrocarbon generation of source rock: taking south Yingtai Fault Depression of Songliao Basin as an example[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2014, 21(2): 171-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201402009.htm [17] 聂爱国, 秦德先, 管代云, 等. 峨眉山玄武岩浆喷发对贵州西部区域成矿贡献研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2007, 43(2): 50-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200702010.htmNIE Aiguo, QIN Dexian, GUAN Daiyun, et al. A research on regional metallogenic contribution to gushing Emeishan basalt magma in western of Guizhou province[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2007, 43(2): 50-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT200702010.htm [18] 何斌, 徐义刚, 肖龙, 等. 峨眉山大火成岩省的形成机制及空间展布: 来自沉积地层学的新证据[J]. 地质学报, 2003, 77(2): 194-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200302012.htmHE Bin, XU Yigang, XIAO Long, et al. Generation and spatial distribution of the Emeishan large igneous province: new evidence from stratigraphic records[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2003, 77(2): 194-202. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200302012.htm [19] 徐义刚, 何斌, 罗震宇, 等. 我国大火成岩省和地幔柱研究进展与展望[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(1): 25-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201301003.htmXU Yigang, HE Bin, LUO Zhenyu, et al. Study on mantle plume and large igneous provinces in China: an overview and perspectives[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2013, 32(1): 25-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201301003.htm [20] 陈荣书, 何生, 王青玲, 等. 岩浆活动对有机质成熟作用的影响初探: 以冀中葛渔城—文安地区为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1989, 16(1): 29-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK198901005.htmCHEN Rongshu, HE Sheng, WANG Qingling, et al. A preliminary discussion of magma activity on the maturation of organic matter: taking Geyucheng-Wenan area of Hebei province as an example[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1989, 16(1): 29-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK198901005.htm [21] 何生, 陈荣书, 兰廷泽. 冀中文安斜坡石炭—二叠纪煤系特征及岩浆热力成烃作用[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 1992, 17(6): 699-708. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199206008.htmHE Sheng, CHEN Rongshu, LAN Tingze. Coal formation characteristics of Carboniferous-Permian and magmatic thermal power hydrocarbon-generating in Wenan slope, Jizhong Depression[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 1992, 17(6): 699-708. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199206008.htm [22] 万从礼, 金强. 东营凹陷纯西辉长岩对烃源岩异常生排烃作用研究[J]. 长安大学学报(地球科学版), 2003, 25(1): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200301005.htmWAN Congli, JIN Qiang. Study on exceptional hydrocarbons generating and eliminating of Gabbros to source rocks in Chunxi area of Dongying Depression[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Earth Science Edition), 2003, 25(1): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200301005.htm [23] 宋颖睿, 侯宇光, 刘宇坤, 等. 黔南坳陷下石炭统摆佐组暗色页岩热演化与生烃史研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(2): 226-232. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201802226SONG Yingrui, HOU Yuguang, LIU Yukun, et al. Thermal evolution and hydrocarbon generation histories of black shale in Lower Carboniferous Baizuo Formation, Southern Guizhou Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(2): 226-232. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201802226 [24] 何治亮, 聂海宽, 张钰莹. 四川盆地及其周缘奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组页岩气富集主控因素分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(2): 8-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602004.htmHE Zhiliang, NIE Haikuan, ZHANG Yuying. The main factors of shale gas enrichment of Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2): 8-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602004.htm [25] 翟刚毅, 王玉芳, 包书景, 等. 我国南方海相页岩气富集高产主控因素及前景预测[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(7): 1057-1068. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707002.htmZHAI Gangyi, WANG Yufang, BAO Shujing, et al. Major factors controlling the accumulation and high productivity of marine shale gas and prospect forecast in southern China[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(7): 1057-1068. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707002.htm [26] 侯读杰, 冯子辉. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011.HOU Dujie, FENG Zihui. Petroleum geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011. [27] 李霞. 花岗岩侵入对页岩成分和孔隙结构的影响[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2016.LI Xia. Influence of granite intrusion on the mineralogy and pore structure of shales[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2016. [28] 邓恩德, 颜智华, 姜秉仁, 等. 黔西地区上二叠统龙潭组海陆交互相页岩气储层特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(3): 467-476. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003467DENG Ende, YAN Zhihua, JIANG Bingren, et al. Reservoir characteristics of marine-continental shale gas in Upper Permian Longtan Formation, western Guizhou province[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(3): 467-476. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003467 [29] LI Yingli, CAI Jingong, WANG Xuejun, et al. Smectite-illitization difference of source rocks developed in saline and fresh water environments and its influence on hydrocarbon generation: a study from the Shahejie Formation, Dongying Depression, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 80: 349-357. [30] 程璇, 徐尚, 郝芳, 等. 松辽盆地嫩江组富有机质页岩有机孔隙成因[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 62-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904008.htmCHENG Xuan, XU Shang, HAO Fang, et al. Origin of organic pores in the organic-rich shale of Nenjiang Formation, Songliao Basin, China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(4): 62-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904008.htm [31] 朱筱敏, 王英国, 钟大康, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系储层孔隙类型与次生孔隙成因[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(2): 197-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200702008.htmZHU Xiaomin, WANG Yingguo, ZHONG Dakang, et al. Pore types and secondary pore evolution of Paleogene reservoir in the Jiyang Sag[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(2): 197-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200702008.htm [32] ROSS D J K, BUSTIN R M. The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(6): 916-927. -





 下载:
下载:





 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号