Dissolution experiments and geological implications of tight sandstones in the Xujiahe Formation of Upper Triassic, Sichuan Basin
-
摘要: 四川盆地上三叠统须家河组为致密砂岩储层,溶蚀孔隙发育,但其形成机理仍不十分明确。选取须家河组长石岩屑砂岩、岩屑长石砂岩和长石石英砂岩等3块样品,通过配制与地层有机酸组分相近的反应液,设计5种温压条件进行溶蚀模拟实验,得到以下4点认识:(1)随温压条件升高,反应溶液中K、Na离子浓度不断增加,Ca、Mg离子浓度基本保持不变,Al离子浓度明显降低;(2)反应产生少量石英和大量高岭石等新矿物,长石颗粒和碳酸盐胶结物溶蚀产生大量溶蚀孔隙,增加孔隙度,改善了孔隙结构;(3)相同温压条件下,长石岩屑砂岩比长石石英砂岩溶蚀率高,高温压条件下(180 ℃,53 MPa),砂岩样品的溶蚀率大幅增加;(4)溶蚀实验结果为重建须家河组储层埋藏、成岩、孔隙演化序列,预测有利储层的分布提供了依据,长石等在高温压条件下快速溶蚀是深层碎屑岩有效储层的成因机理之一。Abstract: The Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan Basin is a tight sandstone reservoir with developed dissolution pores, but its formation mechanism is still unclear. In this paper, three samples, including feldspathic lithic, lithic arkose and feldspathic quartz sandstones of the Xujiahe Formation, were taken as examples. Some reaction fluid similar to the organic acid component of the formation was prepared. Five kinds of temperature and pressure conditions were applied in the corrosion simulation experiments, and four understandings were obtained. Firstly, with the increase of temperature and pressure, the concentrations of K+ and Na+ ions in the reaction solution increased, the concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions remained stable, but the concentration of Al3+ ions decreased significantly. Secondly, the reaction produced a small amount of quartz and a large number of kaolinite and other new minerals, and the dissolution of feldspar particles and carbonate cement produced a large number of dissolution pores, the porosity was increased and the pore structure was then improved. Thirdly, with the same temperature and pressure, the dissolution rate of feldspathic lithic sandstone was relatively higher than that of feldspathic quartz sandstone. With higher temperature and pressure (e.g. 180℃, 53 MPa), the dissolution rate of sandstone samples were significantly increased. Lastly, the results of dissolution experiments provided a reference for the reconstructing of burial sequence, diagenesis as well as pore evolution of the Xujiahe Formation and the distribution of favorable reservoirs can be predicted. The rapid dissolution of feldspar under higher temperature pressure is one of the genetic mechanisms of effective reservoir of deep clastic rock.
-
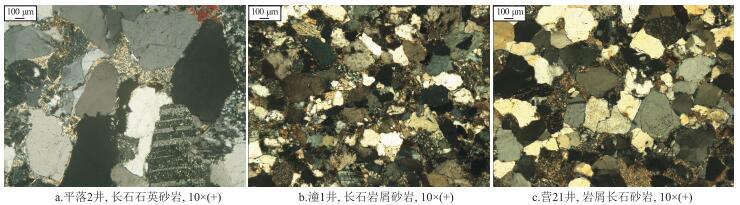
表 1 溶蚀模拟实验的样品岩石学特征
Table 1. Petrological characteristics of samples for dissolution simulation
样号 井号 层位 井深/m 岩性 石英/% 长石/% 岩屑/% 孔隙度/% 渗透率/(10-3μm2) 1 平落2 须二段 3 491.0 粗粒长石石英砂岩 84 11 5 5.22 0.07 2 潼1 须二段 2 208.5 中粒长石岩屑砂岩 74 11 15 8.68 0.55 3 营21 须四段 2 306.0 中粒岩屑长石砂岩 70 16 14 4.23 0.56 -
[1] 魏国齐, 杨威, 刘满仓, 等. 四川盆地大气田分布、主控因素与勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(6): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201906001.htmWEI Guoqi, YANG Wei, LIU Mancang, et al. Distribution rules, main controlling factors and exploration directions of giant gas fields in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(6): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201906001.htm [2] 杨威, 谢增业, 金惠, 等. 四川盆地上三叠统须家河组储层评价及天然气成藏机理[J]. 天然气工业, 2010, 30(12): 10-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201012002.htmYANG Wei, XIE Zengye, JIN Hui, et al. Reservoir evaluation and pooling mechanism of the Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(12): 10-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201012002.htm [3] 杜金虎, 徐春春, 魏国齐, 等. 四川盆地须家河组岩性大气区勘探[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011: 1-179.DU Jinhu, XU Chunchun, WEI Guoqi, et al. Large lithologic gas provinces exploration of Xujiahe Formation in Sichuan Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011: 1-179. [4] 杨威, 魏国齐, 李跃纲, 等. 川西地区须家河组二段储层发育的主控因素和致密化时间探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(6): 796-800. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200806010.htmYANG Wei, WEI Guoqi, LI Yuegang, et al. Main controlling factors and densification periods of the reservoir development of Xujiahe Formation second member, western Sichuan[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(6): 796-800. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200806010.htm [5] 谢武仁, 杨威, 赵杏媛, 等. 川中地区须家河组绿泥石对储集层物性的影响[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6): 674-679. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201006007.htmXIE Wuren, YANG Wei, ZHAO Xingyuan, et al. Influences of chlorite on reservoir physical properties of the Xujiahe Formation in the central part of Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(6): 674-679. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201006007.htm [6] 施振生, 杨威. 四川盆地上三叠统砂体大面积分布的成因[J]. 沉积学报, 2011, 29(6): 1058-1068. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201106006.htmSHI Zhensheng, YANG Wei. Genesis of widespread sandbodies of Upper Triassic in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(6): 1058-1068. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201106006.htm [7] 黄洁, 朱如凯, 侯读杰, 等. 深部碎屑岩储层次生孔隙发育机理研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2007, 26(6): 76-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200706014.htmHUANG Jie, ZHU Rukai, HOU Dujie, et al. The new advances of secondary porosity genesis mechanism in deep clastic reservoir[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2007, 26(6): 76-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200706014.htm [8] SURDAM R C, BOESE S W, CROSSEY L J. The chemistry of secondary porosity[M]//MCDONALD D A, SURDAM R C. Clastic Diagenesis. Tulsa: AAPG, 1984: 127-149. [9] CHARDON E S, LIVENS F R, VAUGHAN D J. Reactions of feldspar surfaces with aqueous solutions[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2006, 78(1/2): 1-26. [10] OELKERS E H, SCHOTT J. Experimental study of anorthite dissolution and the relative mechanism of feldspar hydrolysis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(24): 5039-5053. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00326-6 [11] STOESSELL R K, PITTMAN E D. Secondary porosity revisited: The chemistry of feldspar dissolution by carboxylicacids and anions[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(12): 1777-1794. [12] SURDAM R C, JIAO Z S, MACGOWAN D B. Redox reactions involving hydrocarbons and mineral oxidants: A mechanism for significant porosity enhancement in sandstones[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(9): 1509-1518. [13] 刘锐娥, 吴浩, 魏新善, 等. 酸溶蚀模拟实验与致密砂岩次生孔隙成因机理探讨: 以鄂尔多斯盆地盒8段为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 2015, 21(4): 758-766. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201504021.htmLIU Ruie, WU Hao, WEI Xinshan, et al. Experimental study on the genesis of secondary porosity in tight sandstone with the acid corrosion-model: a case from HE 8 member of upper Paleozoic in ordos basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2015, 21(4): 758-766. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201504021.htm [14] 杨俊杰, 黄月明, 张文正, 等. 乙酸对长石砂岩溶蚀作用的实验模拟[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1995, 22(4): 82-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK504.019.htmYANG Junjie, HUANG Yueming, ZHANG Wenzheng, et al. Experimental approach of dissolution of feldspar sand stone by acetic acid[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1995, 22(4): 82-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK504.019.htm [15] 黄思静, 杨俊杰, 张文正, 等. 不同温度条件下乙酸对长石溶蚀过程的实验研究[J]. 沉积学报, 1995, 13(1): 7-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB501.001.htmHUANG Sijing, YANG Junjie, ZHANG Wenzheng, et al. Experimental study of feldspar dissolution by acetic acid at different burial temperatures[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1995, 13(1): 7-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB501.001.htm [16] 向廷生, 蔡春芳, 付华娥. 不同温度、羧酸溶液中长石溶解模拟实验[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(4): 597-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200404006.htmXIANG Tingsheng, CAI Chunfang, FU Hua'e. Dissolution of microcline by carboxylic acids at different temperatures and complexing reaction of Al anion with carboxylic acid in aqueous solution[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(4): 597-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200404006.htm [17] 肖奕, 王汝成, 陆现彩, 等. 低温碱性溶液中微纹长石溶解性质研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2003, 23(4): 333-340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200304009.htmXIAO Yi, WANG Rucheng, LU Xiancai, et al. Experimental study on the low-temperature dissolution of microperthite in alkaline solution[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2003, 23(4): 333-340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200304009.htm [18] BLAKE R E, WALTER L M. Kinetics of feldspar and quartz dissolution at 70-80℃ and near-neutral pH: effects of organic acids and NaCl[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(13/14): 2043-2059. [19] DREVER J I, STILLINGS L L. The role of organic acids in mineral weathering[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 1997, 120(1/3): 167-181. [20] OELKERS E H, SCHOTT J. Experimental study of anorthite dissolution and the relative mechanism of feldspar hydrolysis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(24): 5039-5053. [21] ANJOS S M C D, DE ROS L F, DE SOUZA R S, et al. Depositional and diagenetic controls on the reservoir quality of Lower Cretaceous Pendencia sandstones, Potiguar rift basin, Brazil[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2000, 84(11): 1719-1742. [22] 林小兵, 田景春, 刘莉萍, 等. 四川盆地川西坳陷须家河组硅质碎屑颗粒溶蚀作用及机理[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(3): 404-410. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903404LIN Xiaobing, TIAN Jingchun, LIU Liping, et al. Dissolution mechanism of siliciclastic particles in Xujiahe Formation, West Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(6): 404-410. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903404 [23] 肖晖, 王浩男, 杨引弟, 等. 致密砂岩孔隙演化特征及其成岩作用对储层质量的影响: 以鄂尔多斯盆地马岭南延长组长8储层为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(6): 800-811. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906800XIAO Hui, WANG Haonan, YANG Yingdi, et al. Influence of diagenetic evolution on tight sandstone reservoir flow capacity: Chang 8 reservoir of Yanchang formation in southern Maling, ordos basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2019, 41(6): 800-811. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906800 [24] 王威, 黄曼宁. 元坝地区须家河组致密砂岩气藏富集主控因素[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 43(3): 266-273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201603002.htmWANG Wei, HUANG Manning. Main controlling factors of the tight sandstone gas reservoir of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Yuanba area, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2016, 43(3): 266-273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201603002.htm [25] 赵正望, 吴长江, 苑保国. 四川盆地西北部上三叠统须二段深层优质储层成因[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2016, 39(2): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT201602001.htmZHAO Zhengwang, WU Changjiang, YUAN Baoguo. Origin of deep and high-quality reservoir of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe 2 member northwestern Sichuan basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2016, 39(2): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRKT201602001.htm -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号