Hydrocarbon generation characteristics and significance of accumulation of Upper Paleozoic source rocks in Dongpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin
-
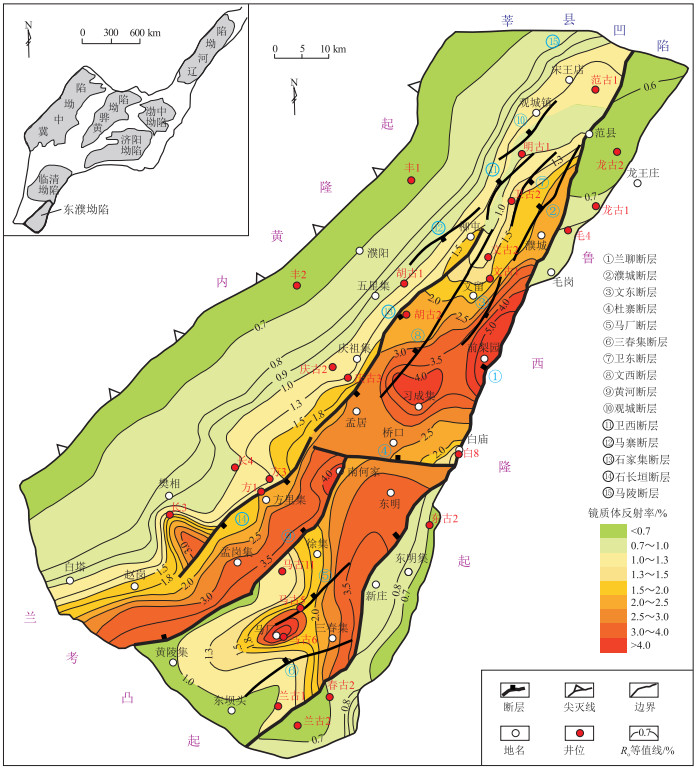
摘要: 为了明确渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷上古生界油气成藏条件和规律,采用烃源岩评价、生烃热模拟实验和盆地模拟相结合的研究方法,定量研究石炭系—二叠系烃源岩生烃历史和强度,并探讨其成藏意义。结果表明:东濮凹陷石炭系—二叠系烃源岩显微组成中富氢的壳质组、基质镜质体含量高(>10%),烃源岩具有较高生油潜力,成烃演化过程以多阶段性、生气带宽为特征;石炭系—二叠系在燕山期埋藏深度小,Ro在0.6%~0.8%,生气量较小,在喜马拉雅期呈差异化的热演化特征,凹陷西部至西斜坡地区生气强度整体较低,为(1~20)×108 m3/km2,东部深洼带烃源岩埋深大、演化程度高、生气量大,生气强度达(60~110)×108 m3/km2。已有勘探成果分析显示,生气强度大于40×108 m3/km2的区域才能形成天然气富集,前梨园洼陷带生气强度在(60~110)×108 m3/km2,具备形成原生煤成气藏和古生新储煤成气藏的有利条件,是下步有利勘探区带。Abstract: In order to clarify the conditions and rules of hydrocarbon accumulation of the Upper Paleozoic in the Dongpu Sag of Bohai Bay Basin, source rock evaluation, pyrolysis experiment and basin modelling were carried out in this paper, the history of hydrocarbon generation and intensity of source rocks have been quantitatively studied, consequently, the significance of hydrocarbon accumulation in this area has also been discussed. The micro-composition of the Carboniferous-Permian source rocks in the Dongpu Sag is featured by high contents of hydrogen-rich exinite and matrix vitrinite (>10%), and the source rocks have a high oil-generating potential. The hydrocarbon generation process is characterized by multiple stages and wide gas generation band. During the Yanshanian period, the Carboniferous-Permian source rocks were shallowly buried, the Ro value ranged between 0.6%-0.8%, and only a little gas has been generated. In the Himalayan period, due to the differential thermal evolution of the Paleogene deposits, from the western part of the sag to the western slope, gas generation was significantly decreased, with an average of (1-20)×108 m3/km2. While in deep sag of the eastern part, source rocks were deeply buried with a high thermal degree, and a large amount of gas was generated with an intensity of (60-110)×108 m3/km2. Past exploration results have shown that the area with a gas generation intensity greater than 40×108 m3/km2 is favorable for natural gas accumulation. The gas generation intensity of the Qianliyuan sub-sag ranges (60-110)×108 m3/km2, which has favorable conditions for the formation of primary as well as paleogenetic and new-storage coal-derived gas reservoirs, and is a favorable exploration zone for the future exploration.
-
表 1 渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷上古生界烃源岩显微组分含量
Table 1. Maceral contents of source rocks of Upper Paleozoic, Dongpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin
岩性 层位 显微组分含量/% 镜质组 壳质组 惰质组 矿物沥青基质 煤岩 山西组 55.0~79.0/71.8(26) 4.3~15.6/7.9(26) 6.2~29.0/13.9(26) 1.5~14.0/6.4(26) 太原组 66.7~80.2/72.6(14) 6.3~20.5/14.1(14) 7.5~11.5/9.7(14) 3.1~5.0/3.6(14) 泥岩 山西组 45.8~85.0/76.3(23) 5.0~16.1/7.0(23) 4.0~19.0/12.5(23) 0~29.17/4.2(23) 太原组 30.1~82.5/67.7(27) 3.2~13.5/8.6(27) 8.9~34.0/15.9(27) 4.0~48.7/7.8(27) 注:表中分式含义为:最小值~最大值/平均值(样品数)。 -
[1] 朱家蔚, 戚厚发, 廖永胜. 文留煤成气藏的发现及其对华北盆地找气的意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1983(1): 4-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK198301001.htmZHU Jiawei, QI Houfa, LIAO Yongsheng. Discovery of Wenliu gas pool generating from coal measures and its significance of prospecting gas in North China Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1983(1): 4-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK198301001.htm [2] 李继东, 许书堂, 杨玉娥, 等. 东濮凹陷胡古2气藏成藏条件分析[J]. 断块油气田, 2015, 22(4): 450-453. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201504009.htmLI Jidong, XU Shutang, YANG Yu'e, et al. Forming condition ana-lysis of Hugu 2 gas reservoir in Dongpu Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas field, 2015, 22(4): 450-453. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201504009.htm [3] 常俊合, 岳玉山, 吕红玉, 等. 东濮凹陷上古生界热演化史与生烃期关系[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(2): 32-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200402007.htmCHANG Junhe, YUE Yushan, LÜ Hongyu, et al. Relationship between thermal evolution history and stage of hydrocarbon generation of Upper Paleozoic in the Dongpu Sag[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(2): 32-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200402007.htm [4] 何锋, 刘锋, 郑旭. 东濮凹陷上古生界生烃史及二次生烃时空差异性研究[J]. 断块油气田, 2010, 17(3): 296-299.HE Feng, LIU Feng, ZHENG Xu. Study on hydrocarbon generation history and space-time distribution variation of secondary hydrocarbon generation in Upper Palaeozoic formation of Dongpu Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2010, 17(3): 296-299. [5] 徐进军, 金强, 程付启, 等. 渤海湾盆地石炭系-二叠系煤系烃源岩二次生烃研究进展与关键问题[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2017, 24(1): 43-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201701007.htmXU Jinjun, JIN Qiang, CHENG Fuqi, et al. Advances and crucial issues on secondary hydrocarbon generation of the Carboniferous-Permian coal-measure source rocks in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2017, 24(1): 43-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201701007.htm [6] 刘丽, 任战利. 东濮凹陷热演化史研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2007, 34(4): 419-423, 444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200704007.htmLIU Li, REN Zhanli. Thermal evolution of Dongpu Sag[J]. Petro-leum Exploration and Development, 2007, 34(4): 419-423, 444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200704007.htm [7] 马文璞. 大别山北麓的石炭系及其大地构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 1991(1): 17-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199101001.htmMA Wenpu. The Carboniferous at the northern foot of the Dabie Mountains and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 1991(1): 17-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199101001.htm [8] 程克明, 王铁冠, 钟宁宁, 等. 烃源岩地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1995.CHENG Keming, WANG Tieguan, ZHONG Ningning, et al. Geochemistry of source rocks[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1995. [9] 邬立言, 顾信章, 盛志伟, 等. 生油岩热解快速定量评价[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986.WU Liyan, GU Xinzhang, SHENG Zhiwei, et al. Rapid quantitative evaluation of oil source rocks with pyrolysis method[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1986. [10] 彭君, 张云献, 刘阳, 等. 东濮凹陷及其周缘地区上古生界煤系沉积有机相及煤成烃潜力[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(5): 107-116, 112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT201805017.htmPENG Jun, ZHANG Yunxian, LIU Yang, et al. Sedimentary organic facies and hydrocarbon-forming potential of coal in Upper Paleozoic coal measures in Dongpu Depression and its peripheral areas[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(5): 107-116, 112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MDKT201805017.htm [11] 张洪安, 张爽, 张云献, 等. 渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷古生界煤成烃特征模拟实验研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(4): 527-534. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201704527ZHANG Hong'an, ZHANG Shuang, ZHANG Yunxian, et al. Simulation of hydrocarbon generation of the Paleozoic coals in the Dongpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(4): 527-534. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201704527 [12] 王兆云, 何海清, 程克明. 华北区古生界原生油气藏勘探前景[J]. 石油学报, 1999, 20(2): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB902.000.htmWANG Zhaoyun, HE Haiqing, CHENG Keming. Exploration prospect of Paleozoic primary oil and gas pools in Huabei area[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1999, 20(2): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB902.000.htm [13] 安作相, 马纪. 华北克拉通上古生界含气性[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2004, 25(1): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200401002.htmAN Zuoxiang, MA Ji. Gas property of Upper Paleozoic of craton blocks in North China Platform[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geo-logy, 2004, 25(1): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200401002.htm [14] 胡维强, 赵靖舟, 李军, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部上古生界烃源岩特征及其对天然气藏形成与分布的控制作用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(6): 1068-1075. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201506008.htmHU Weiqiang, ZHAO Jingzhou, LI Jun, et al. Characteristics of source rocks and its controls on the formation and distribution of gas from Upper Paleozoic in southwest Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(6): 1068-1075. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201506008.htm [15] 郑和荣, 胡宗全. 渤海湾盆地及鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界天然气成藏条件分析[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(3): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200603000.htmZHENG Herong, HU Zongquan. Gas pool-forming conditions for Bohai Bay Basin and Ordos Basin in the Upper Paleozoic[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(3): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200603000.htm [16] 曾秋楠, 张交东, 于炳松, 等. 太康隆起上古生界海陆交互相页岩气地质条件分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(3): 49-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201903009.htmZENG Qiunan, ZHANG Jiaodong, YU Bingsong, et al. Shale gas geology analysis of the Upper Paleozoic marine-continental interaction facies in Taikang Uplift[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(3): 49-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201903009.htm [17] 曹青, 赵靖舟, 付金华, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界准连续型气藏气源条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(5): 584-591. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201305003.htmCAO Qing, ZHAO Jingzhou, FU Jinhua, et al. Gas source conditions of quasi-continuous accumulation of the Upper Paleozoic in Ordos Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2013, 34(5): 584-591. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201305003.htm [18] 宋平, 郭明强, 赵靖舟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴地区上古生界烃源岩特征及其对天然气成藏的控制作用[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 34(1): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201901003.htmSONG Ping, GUO Mingqiang, ZHAO Jingzhou, et al. Characte-ristics of Upper Paleozoic source rocks in Linxing area, eastern margin of Ordos Basin and their controlling effect on accumulation of natural gas[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 34(1): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY201901003.htm [19] 付金华, 魏新善, 罗顺社, 等. 庆阳深层煤成气大气田发现与地质认识[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(6): 1047-1061. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201906005.htmFU Jinhua, WEI Xinshan, LUO Shunshe, et al. Discovery and geological knowledge of the large deep coal-formed Qingyang gas field, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(6): 1047-1061. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201906005.htm [20] 吴小奇, 倪春华, 陈迎宾, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地定北地区上古生界天然气来源[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(6): 819-827. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201906006.htmWU Xiaoqi, NI Chunhua, CHEN Yingbin, et al. Source of the Upper Paleozoic natural gas in Dingbei area in the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(6): 819-827. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201906006.htm [21] 孙晓, 王杰, 陶成, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地大牛地下古生界天然气地球化学特征及其来源综合判识[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(2): 307-314. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102307SUN Xiao, WANG Jie, TAO Cheng, et al. Evaluation of geochemical characteristics and source of natural gas in Lower Paleozoic, Daniudi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(2): 307-314. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102307 [22] 赖生华, 白璞, 叶超, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地高家河地区山西组二段下部地震沉积学研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(1): 79-87. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001079LAI Shenghua, BAI Pu, YE Chao, et al. Seismic sedimentology of lower part of second member of Shanxi Formation in Gaojiahe area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(1): 79-87. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001079 [23] 刘玲, 汤达祯, 王烽. 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴区块太原组致密砂岩黏土矿物特征及其对储层物性的影响[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(6): 28-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201906004.htmLIU Ling, TANG Dazhen, WANG Feng. Clay minerals characteristics of tight sandstone and its impact on reservoir physical properties in Taiyuan Formation of block Linxing in Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(6): 28-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201906004.htm [24] 胡华蕊, 邢凤存, 齐荣, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区晚古生代盆缘古地貌控砂及油气勘探意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(4): 491-497. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904491HU Huarui, XING Fengcun, QI Rong, et al. Paleogeomorphologic features and their controls on sandbody distribution on basin margin during Late Paleozoic era and significance for petroleum exploration, Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(4): 491-497. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904491 [25] 康东雅, 向芳, 邹佐元, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界砂岩岩石学特征及岩性差异[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(3): 299-303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201903007.htmKANG Dongya, XIANG Fang, ZOU Zuoyuan, et al. Petrological characteristics and lithological differences of Upper Paleozoic sandstone of Ordos Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2019, 26(3): 299-303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201903007.htm [26] 王子龙, 郭少斌. 鄂尔多斯盆地延安地区山西组泥页岩孔隙表征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(1): 99-107. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901099WANG Zilong, GUO Shaobin. Pore characterization of shale in Shanxi Formation, Yan'an area, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(1): 99-107. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201901099 [27] 周立宏, 滑双君, 孙超囡, 等. 大港油田上古生界煤系烃源岩地球化学特征与二次成烃[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(6): 1043-1051. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201706006.htmZHOU Lihong, HUA Shuangjun, SUN Chaonan, et al. Geochemical characteristics and secondary hydrocarbon generation of coal-measure source rocks in Upper Paleozoic of Dagang oilfield[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2017, 38(6): 1043-1051. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201706006.htm [28] 赵长毅, 李永新, 王居峰, 等. 渤海湾盆地天然气成因类型与勘探潜力分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(6): 783-789. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201906002.htmZHAO Changyi, LI Yongxin, WANG Jufeng, et al. Genetic types and exploration potential of natural gas in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(6): 783-789. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201906002.htm [29] 金凤鸣, 王鑫, 李宏军, 等. 渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷乌马营潜山内幕原生油气藏形成特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(3): 521-529. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201903011.htmJIN Fengming, WANG Xing, LI Hongjun, et al. Formation of the primary petroleum reservoir in Wumaying inner buried-hill of Huanghua Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(3): 521-529. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201903011.htm [30] 张成富. 渤海湾盆地莘县凹陷原油来源及成藏主控因素[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(5): 575-579. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201905008.htmZHANG Chengfu. Oil source and hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics of Shenxian Sag of Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2019, 26(5): 575-579. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201905008.htm -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号