Separation of steranes and hopanes by domestic X-type molecular sieves
-
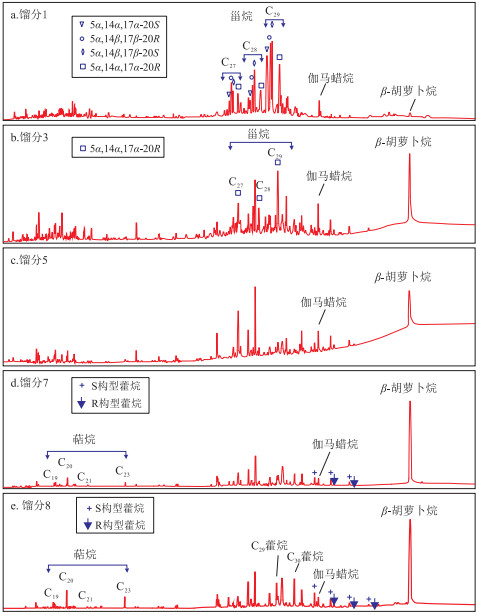
摘要: 采用国产10X和13X型分子筛对甾烷和藿烷类生物标志物进行吸附和脱附实验,探讨两种分子筛在制备甾烷和藿烷类化合物过程中的稳定碳同位素分馏效应,为甾烷和藿烷单体化合物的分离技术提供一种可靠方法。结果表明,两种分子筛对不同类型化合物的吸附作用不同,对甾烷化合物中的5α,14α,17α-20S、5α,14β,17β-20R、5α,14β,17β-20S三种构型吸附能力最弱,其次是5α,14α,17α-20R构型的甾烷系列、β-胡萝卜烷和伽马蜡烷。13X型分子筛对藿烷组分吸附能力强于10X型分子筛,可用于藿烷类化合物的分离;而10X型分子筛对甾烷组分吸附能力强于13X型分子筛。通过控制淋洗液的用量,能够分别分离不同构型的甾烷化合物。获得的甾烷和藿烷化合物单体烃稳定碳同位素分析结果显示,分离过程中无碳同位素分馏现象,重复性非常好,说明国产10X和13X型分子筛可用于甾烷和藿烷类化合物的分离富集及其单体烃碳同位素研究。Abstract: Domestic 10X-type and 13X-type molecular sieves were used for the adsorption and desorption experiments of steranes and hopanes, and their stable carbon isotopic fractionation by the two kinds of molecular sieves during separation process was discussed in detail. These two kinds of molecular sieves have various adsorption effects on different types of compounds. They both have the weakest adsorption capacities for 5α, 14α, 17α-20S steranes, 5α, 14β, 17β-20R steranes and 5α, 14β, 17β-20S steranes, followed by 5α, 14α, 17α-20R steranes, β-carotane, and gammacerane. The 13X-type molecular sieve has stronger adsorption capacity for hopanes than that of the 10X-type molecular sieve, which can be used for the separation of hopanes. The 10X-type molecular sieve has stronger adsorption capacity for steranes than that of the 13X-type molecular sieve. By controlling the amount of eluent, different configuration of steranes can be further separated. The stable carbon isotopes of steranes and hopanes showed that no carbon isotopic fractionation occurred during separation process and the repeatability was very good, indicating that domestic 10X-type and 13X-type molecular sieves can be used for steranes and hopanes separation.
-
Key words:
- molecular sieve /
- steranes /
- hopanes /
- compound specific carbon isotope /
- biomarkers /
- petroleum geochemistry
-
表 1 国产10X型分子筛分离出的甾烷化合物单体烃碳同位素测定结果
Table 1. Carbon isotopic values of steranes separated by domestic 10X molecular sieve
样品 单体烃碳同位素δ13C/‰ α, α, α-C27S甾烷 α, β, β-C27R甾烷 α, β, β-C27 S甾烷 α, α, α-C27 R甾烷 C29 S重排甾烷 α, α, α-C28 S甾烷 α, β, β-C28 R甾烷 α, β, β-C28 S甾烷 α, α, α-C28 R甾烷 α, α, α-C29 S甾烷 α, β, β-C29 R甾烷 α, β, β-C29 S甾烷 α, α, α-C29 R甾烷 伽马蜡烷 β-胡萝卜烷 馏分1 - -36.19 -32.88 - - - -33.84 -31.31 - -32.66 -34.64 -33.12 - - - 馏分2 -31.41 -34.87 -32.53 - -33.93 -33.59 -33.19 -32.64 -33.00 -32.08 -33.50 -33.70 - - - 馏分3 -31.46 -34.75 -31.61 -31.95 -35.51 -34.98 - -34.56 -30.42 -31.19 -34.00 -32.86 -29.84 - -31.92 馏分4 - - - -30.79 - - - - -30.43 - - - -29.29 -36.38 -32.06 馏分5 - - - -30.52 - - - - -29.96 - - - -30.31 - -32.45 馏分6 - - - -29.11 - - - - -30.41 - - - -30.76 -37.24 -32.00 馏分7 - - - - - - - - - - - - - -36.77 -32.35 馏分8 - - - - - - - - - - - - - -36.53 -31.99 表 2 国产10X型分子筛分离出的甾烷化合物单体烃碳同位素测定结果与平均值的误差
Table 2. Error of carbon isotope measurement and average values of sterane compounds separated by domestic 10X molecular sieve
样品 单体烃碳同位素测定结果与平均值的误差/‰ α, α, α-C27S甾烷 α, β, β-C27R甾烷 α, β, β-C27 S甾烷 α, α, α-C27 R甾烷 C29 S重排甾烷 α, α, α-C28 S甾烷 α, β, β-C28 R甾烷 α, β, β-C28 S甾烷 α, α, α-C28 R甾烷 α, α, α-C29 S甾烷 α, β, β-C29 R甾烷 α, β, β-C29 S甾烷 α, α, α-C29 R甾烷 伽马蜡烷 β-胡萝卜烷 馏分1 - - 0.54 - - - -0.31 -1.60 - 0.66 0.54 -0.10 - - - 馏分2 -0.30 0.06 0.19 - -1.80 -0.79 0.31 -0.20 - 0.08 -0.60 0.53 - - - 馏分3 0.30 -0.06 -0.73 1.30 1.80 0.79 - -1.80 0.12 -0.74 0.06 -0.43 -0.20 - -0.21 馏分4 - - - 0.19 - - - - 0.13 - - - -0.71 -0.35 -0.07 馏分5 - - - -0.08 - - - - -0.36 - - - 0.31 - 0.34 馏分6 - - - -0.80 - - -0.11 - - - 0.60 0.51 -0.13 馏分7 - - - - - - - - - - - - 0.04 0.24 馏分8 - - - - - - - - - - - -0.20 -0.12 表 3 国产10X分子筛分离出的甾烷化合物单体烃碳同位素重复性分析
Table 3. Repeatability analysis of carbon isotope of sterane compounds by domestic 10X molecular sieve
平行实验 单体烃碳同位素δ13C/‰ α, α, α-C27S甾烷 α, β, β-C27R甾烷 α, β, β-C27 S甾烷 α, α, α-C27 R甾烷 C29 S重排甾烷 α, α, α-C28 S甾烷 α, β, β-C28 R甾烷 α, β, β-C28 S甾烷 α, α, α-C28 R甾烷 α, α, α-C29 S甾烷 α, β, β-C29 R甾烷 α, β, β-C29 S甾烷 α, α, α-C29 R甾烷 伽马蜡烷 β-胡萝卜烷 第一次 -31.46 -34.87 -33.96 30.79 -33.53 -32.98 -33.84 -33.31 -30.52 -32.34 -34.43 -33.34 -29.36 -36.45 -32.06 第二次 -32.28 -32.41 -34.43 30.85 -34.51 -33.69 -33.19 -32.64 -30.42 -32.98 -33.65 -32.89 -29.87 -35.87 -32.43 表 4 国产10X型和13X型分子筛分离出的藿烷化合物单体烃碳同位素测定结果
Table 4. Carbon isotope of hopane compounds separated by domestic 10X and 13X molecular sieves
分子筛 单体烃碳同位素δ13C/‰ C20三环萜烷 C21三环萜烷 C23三环萜烷 C24三环萜烷 C29藿烷 C30藿烷 C30莫烷 C31藿烷S构型 C31藿烷R构型 C32藿烷S构型 C32藿烷R构型 10X -33.7 -31.4 -32.6 -30.2 -60.7 -60.3 -60.1 -60.0 -60.1 -60.4 -60.8 13X -33.3 -31.4 -32.8 -30.3 -60.4 -60.3 -60.3 -60.7 -60.4 -60.7 -60.8 -
[1] LAUGHREY C D, BALDASSARE F J. Geochemistry and origin of some natural gases in the Plateau province, central Appalachian Basin, Pennsylvania and Ohio[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1998, 82(2): 317-335. [2] 王铁冠. 广西百色盆地州景矿第三系褐煤有机地球化学与煤岩学研究: Ⅳ. 单化合物碳稳定同位素推断生物标志物起源[J]. 沉积学报, 1995, 13(4): 73-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB504.007.htmWANG Tieguan. Organic geochemistry and coal petrology of the Tertiary brown coal in the Zhoujing Mine, Baise Basin, South China: Ⅳ Biomarker source inferred from stable carbon isotope compositions of individual compounds[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1995, 13(4): 73-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB504.007.htm [3] 李文奇, 刘小平, 关铭, 等. 渤海湾盆地沧东凹陷古近系孔二段页岩层系原油地球化学特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(2): 263-272. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202002263LI Wenqi, LIU Xiaoping, GUAN Ming, et al. Geochemical characte-ristics of crude oils in the second member of Kongdian Formation shale system, Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geo-logy & Experiment, 2020, 42(2): 263-272. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202002263 [4] 李二庭, 靳军, 曹剑, 等. 准噶尔盆地新光地区佳木河组天然气地球化学特征及成因[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(9): 1362-1369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201909013.htmLI Erting, JIN Jun, CAO Jian, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of natural gas in Jiamuhe Formation in Xinguang area, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(9): 1362-1369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201909013.htm [5] 刁帆, 王建伟, 陈晓娜, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷高尚堡地区油源对比及高蜡油成因[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(1): 117-125. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001117DIAO Fan, WANG Jianwei, CHEN Xiaona, et al. Correlation of oils and source rocks and genesis of high wax oils in Gaoshangpu area, Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(1): 117-125. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001117 [6] 朱心健, 陈践发, 伍建军, 等. 塔里木盆地台盆区古生界原油碳同位素组成及油源探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(6): 997-1004. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201706020.htmZHU Xinjian, CHEN Jianfa, WU Jianjun, et al. Carbon isotopic compositions and origin of Paleozoic crude oil in the platform region of Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(6): 997-1004. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201706020.htm [7] 何龙, 王云鹏, 陈多福. 川南地区晚奥陶-早志留世沉积环境与古气候的地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2019, 48(6): 555-566. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201906005.htmHE Long, WANG Yunpeng, CHEN Duofu. Geochemical features of sedimentary environment and paleoclimate during Late Ordovician to Early Silurian in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geochi-mica, 2019, 48(6): 555-566. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201906005.htm [8] 王圣柱, 王千军, 张关龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地石炭系烃源岩发育模式及地球化学特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(4): 13-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202004003.htmWANG Shengzhu, WANG Qianjun, ZHANG Guanlong, et al. Deve-lopment mode and geochemical characteristics of Carboniferous source rocks in Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Reco-very Efficiency, 2020, 27(4): 13-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202004003.htm [9] 李二庭, 靳军, 陈俊, 等. 生物降解稠油沥青质热解产物中生物标志化合物与单体烃碳同位素组成研究[J]. 地球化学, 2019, 48(3): 284-292. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201903006.htmLI Erting, JIN Jun, CHEN Jun, et al. Study on biomarkers and carbon isotopic compositions of monomer hydrocarbons in asphal-tene pyrolysis products from biodegraded heavy oil[J]. Geochi-mica, 2019, 48(3): 284-292. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201903006.htm [10] 綦艳丽. 正构烷烃单体烃的氢同位素分析方法及应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(2): 319-324. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202002319QI Yanli. Method and application of hydrogen isotope analysis of n-alkanes[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(2): 319-324. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202002319 [11] 包建平, 倪春华, 朱翠山, 等. 黔北坳陷高演化烃源岩中正构烷烃单体烃碳同位素组成[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(6): 838-848. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906838BAO Jianping, NI Chunhua, ZHU Cuishan, et al. Carbon isotope compositions of individual alkanes in highly mature source rocks from Northern Guizhou Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(6): 838-848. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906838 [12] 熊永强, 耿安松, 潘长春, 等. 陆相有机质中单体烃的氢同位素组成特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(1): 60-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200401018.htmXIONG Yongqiang, GENG Ansong, PAN Changchun, et al. Hydrogen isotopic compositions of individual n-alkanes in terrestrial source rocks[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(1): 60-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200401018.htm [13] SPOONER N, RIELEY G, COLLISTER J W, et al. Stable carbon isotopic correlation of individual biolipids in aquatic organisms and a lake bottom sediment[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1994, 21(6/7): 823-827. [14] 王丽, 曹新星, 李艳, 等. 松辽盆地湖相烃源岩中生物标志物的单体烃碳同位素组成特征及其意义[J]. 地球化学, 2015, 44(4): 337-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201504003.htmWANG Li, CAO Xinxing, LI Yan, et al. The carbon isotopic composition of individual biomarkers in lacustrine source rocks from Songliao Basin and its biogeochemical implication[J]. Geochimica, 2015, 44(4): 337-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201504003.htm [15] DENIRO M J, EPSTEIN S. Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1978, 42(5): 495-506. [16] BIDIGARE R R, KENNICUTT M C, KEENEY-KENNICUTT W L, et al. Isolation and purification of chlorophylls a and b for the determination of stable carbon and nitrogen isotope compositions[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1991, 63(2): 130-133. [17] HAYES J M, FREEMAN K H, POPP B N, et al. Compound-specific isotopic analyses: a novel tool for reconstruction of ancient biogeochemical processes[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1990, 16(4/6): 1115-1128. [18] 周友平, 史继扬, 向明菊, 等. 沉积有机质中藿烯的成因研究: 碳稳定同位素证据[J]. 沉积学报, 1998, 16(2): 14-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB802.003.htmZHOU Youping, SHI Jiyang, XIANG Mingju, et al. Origin study of geohopenes from different depositional environments: stable carbon isotopic evidences[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1998, 16(2): 14-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB802.003.htm [19] 史继扬, 向明菊, 周友平. 生物标志物藿烷类的单体碳稳定同位素研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, 18(2): 310-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200002023.htmSHI Jiyang, XIANG Mingju, ZHOU Youping. Study on carbon isotopic ratio of individual compound in hopanes[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2000, 18(2): 310-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200002023.htm [20] 董爱正, 张林晔, 黄第藩, 等. 饱和烃单体化合物稳定碳同位素测定方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1996, 23(2): 98-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK602.025.htmDONG Aizheng, ZHANG Linye, HUANG Difan, et al. Saturated hydrocarbon monomer compound stable carbon isotope determination method[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1996, 23(2): 98-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK602.025.htm [21] WHITEHEAD E. The structure of petroleum pentacyclanes[J]. Advances in Organic Geochemistry, 1974: 225-243. [22] 陈小慧, 张敏. 地质体中藿烷类单体化合物的分离与稳定碳同位素分析研究进展[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(26): 94-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201526016.htmCHEN Xiaohui, ZHANG Min. Research progress in separation and analysis of stable carbon isotope of monomer hydrocarbon compounds of hopanes in geological bodies[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(26): 94-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201526016.htm [23] KENIG F, POPP B N, SUMMONS R E. Preparative HPLC with ultrastable-Y zeolite for compound-specific carbon isotopic analyses[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(11): 1087-1094. [24] ARMANIOS C, ALEXANDER R, KAGI R I, et al. Fractionation of sedimentary higher-plant derived pentacyclic triterpanes using molecular sieves[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1994, 21(5): 531-543. [25] 王汇彤, 魏彩云, 张水昌, 等. 国产Y型分子筛对甾烷、藿烷的吸附和脱附研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(1): 71-75. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201001071WANG Huitong, WEI Caiyun, ZHANG Shuichang, et al. The study on adsorption and de-adsorption behavior of some biomarkers on different type-Y Chinese molecular sieves[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32(1): 71-75. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201001071 [26] 王汇彤, 魏彩云, 张水昌, 等. MOY分子筛对生物标志化合物的分离及其单体烃同位素测定研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(5): 513-516. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201005513WANG Huitong, WEI Caiyun, ZHANG Shuichang, et al. The study on biomarkers separation and its Csia by MOY molecular sieve[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32(5): 513-516. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201005513 [27] 王燕, 葛喜慧, 张敏卿, 等. 费托合成高温油相产品中正构烃的分离[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(11): 2894-2898. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJZ201411012.htmWANG Yan, GE Xihui, ZHANG Minqing, et al. Separation of n-hydrocarbons from high temperature oil phase products of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Chemical Industry and Enginee-ring Progress, 2014, 33(11): 2894-2898. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJZ201411012.htm [28] MOHAMMAD S A, GHANEMI K, LARKI A. Simultaneous extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons through the complete dissolution of solid biological samples in sodium hydroxide/urea/thiourea aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2016, 1476: 9-18. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/27887698 -





 下载:
下载:




 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号