Effects of elemental sulfur and sulfur-bearing minerals on the thermal evolution of aromatic compounds in solid bitumen
-
摘要: 前人研究表明,部分芳烃化合物比值参数与有机质成熟度具有良好的线性关系。为了明确常用芳烃化合物比值参数在不同含硫地质条件下的适用性,通过对四川盆地低熟固体沥青样品开展在单质硫和含硫矿物(黄铁矿、硫酸亚铁、硫酸铁和硫酸钙)存在条件下的加水热模拟实验,进而探讨上述含硫物质在固体沥青热演化过程中对其中所赋存的芳烃化合物的影响。研究表明:各类含硫物质均不同程度影响了芳烃化合物甲基化、甲基重排及去甲基化的进程和强度,随之改变了常用芳烃化合物比值参数的适用性及适用范围。但也存在一些在含硫环境下仍能稳定表征有机质成熟度的参数,如萘系化合物的1,2,3-TMN/2,3,6-TMN、菲系化合物的P/(P+∑MP)和甲基菲指数MPI、二苯并噻吩系化合物的4,6-DMDBT/3,6-DMDBT等参数,能够应用于含硫地质体中有机质成熟度的表征。Abstract: Previous studies have shown that some of the aromatic compound parameters have good correlation with the maturity of organic matter. However, it is still unknown whether the widely used aromatic maturity-related parameters are available with the co-existence of sulfur (elemental and/or sulfur-bearing minerals). Artificial simulation experiments of solid bitumen together with elemental sulfur and/or sulfur-bearing minerals (e.g., pyrite, ferrous sulfate, iron sulfate, and calcium sulfate) were carried out to investigate the influence of elemental sulfur and sulfur-bearing minerals on the thermal evolution of aromatic compounds. Results illustrated that some reactions including methylation, alkyl rearrangement and demethylation of aromatic compounds were affected with various extents by the existence of elemental sulfur and sulfur-bearing minerals. Thus, the applicability of the aromatic index should be careful. This study also found some parameters that still can effectively evaluate the maturity of organic matter in the sulfur-bearing environment, such as 1,2,3-TMN/2,3,6-TMN, P/(P+∑MP), MPI and 4,6-DMDBT/3,6-DMDBT.
-
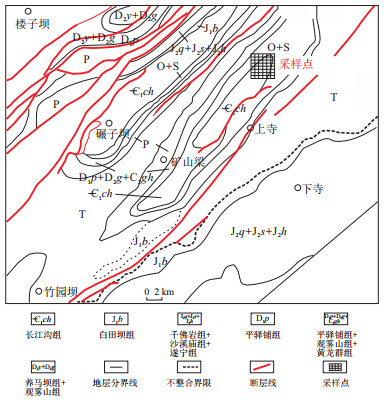
图 1 龙门山北段构造—地层区域分布及采样位置示意
据参考文献[40]修改。
Figure 1. Tectonic-stratigraphic belts and sampling wells in the northern section of Longmen Mountain
图 4 各系列样品中萘系化合物GC-MS谱图
a为未知物;1为2-甲基萘;2为1-甲基萘;3为2-乙基萘;4为1-乙基萘;5为2,6+2,7-二甲基萘;6为1,3+1,7-二甲基萘;7为1,6-二甲基萘;8为1,4+2,3-二甲基萘;9为1,5-二甲基萘;10为1,2-二甲基萘;11为1,3,7-三甲基萘;12为1,3,6-三甲基萘;13为1,3,5+1,4,6-三甲基萘;14为2,3,6-三甲基萘;15为1,2,7+1,6,7+2,3,5-三甲基萘;16为1,2,3-三甲基萘
Figure 4. GC-MS spectra of naphthalene compounds in different samples
图 6 各系列样品中萘系化合物常用比值柱状图及与Ro关系的折线图
DNR=[2(β), 6(β)-二甲基萘+2(β), 7(β)-二甲基萘]/1(α), 5(α)-二甲基萘;TNR2=[1(α), 3(β), 7(β)-三甲基萘+ 2(β), 3(β), 6(β)-三甲基萘]/[1(α), 3(β), 5(α)-三甲基萘+1(α), 3(β), 6(β)-三甲基萘+1(α), 4(α), 6(β)-三甲基萘]
Figure 6. Histograms of common ratios of naphthalene compounds in different samples and line graphs of the relationship with Ro
图 9 各系列样品中二苯并噻吩系列化合物GC-MS谱图
DBT为二苯并噻吩;MDBT为甲基二苯并噻吩;DMDBT为二甲基二苯并噻吩
b为未知物;30为二苯并噻吩;31为4-甲基二苯并噻吩;32为2,3-甲基二苯并噻吩;33为1-甲基二苯并噻吩;34为4-乙基二苯并噻吩;35为4,6-二甲基二苯并噻吩;36为2,4-二甲基二苯并噻吩;37为2,6-二甲基二苯并噻吩;38为3,6-二甲基二苯并噻吩;39为2,5-二甲基二苯并噻吩;40为2,7+3,7-二甲基二苯并噻吩;41为1,4-二甲基二苯并噻吩;42为1,3+3,4-二甲基二苯并噻吩;43为1,7-二甲基二苯并噻吩Figure 9. GC-MS spectra of dibenzothiophene compounds in different samples
图 12 部分系列样品中三芳甾类化合物相对丰度折线图
图中横坐标化合物代号名称见图 11中的图注。
Figure 12. Triaromatic steroids histogram in some series of samples
表 1 玻璃管热模拟实验条件
Table 1. Experimental conditions for glass tube thermal simulations
温度/℃ 编号 固体沥青/mg H2O/mg 添加剂/mg CaSO4 FeS2 FeSO4 Fe2(SO4)3 S 300 300-1 96.0 24.0 300-2 98.9 24.0 21.0 300-3 100.3 24.2 20.8 300-4 101.6 24.1 21.0 300-5 103.4 23.9 21.3 300-6 102.6 24.6 20.5 330 330-1 99.0 23.7 330-2 101.6 23.5 20.9 330-3 101.1 23.6 19.4 330-4 100.9 23.2 19.8 330-5 102.1 23.9 21.1 330-6 99.8 23.3 21.4 350 350-1 94.6 23.5 350-2 99.9 25.3 20.8 350-3 98.3 24.1 20.3 350-4 101.4 23.7 20.6 350-5 99.6 23.7 20.9 350-6 102.9 23.9 21.0 370 370-1 101.8 23.8 370-2 103.0 24.5 20.0 370-3 101.5 23.8 20.9 370-4 101.3 24.0 22.6 370-5 103.6 23.6 21.4 370-6 100.7 24.5 19.7 -
[1] HO T Y, ROGERS M A, DRUSHEL H V, et al. Evolution of sulfur compounds in crude oils[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1974, 58(11): 2338-2348. [2] RADKE M, WELTE D H, WILLSCH H. Geochemical study on a well in the Western Canada Basin: relation of the aromatic distribution pattern to maturity of organic matter[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1982, 46(1): 1-10. [3] RADKE M, WILLSCH H, LEYTHAEUSER D, et al. Aromatic components of coal: relation of distribution pattern to rank[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1982, 46(10): 1831-1848. [4] HUGHES W B. Use of thiophenic organosulfur compounds in characterizing crude oils derived from carbonate versus siliciclastic sources[M]//PALACAS J B. Petroleum geochemistry and source rock potential of carbonate rocks. Oklahoma: AAPG Press, 1984, 18: 181-196. [5] ALEXANDER R, KAGI R I, ROWLAND S J, et al. The effects of thermal maturity on distributions of dimethylnaphthalenes and trimethylnaphthalenes in some ancient sediments and petroleums[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1985, 49(2): 385-395. [6] RADKE M. Application of aromatic compounds as maturity indicators in source rocks and crude oils[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1988, 5(3): 224-236. [7] BUDZINSKI H, GARRIGUES P, CONNAN J, et al. Determination of maturity indicators in alkylated aromatic series by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)[M]//MANNING D. Organic geochemistry: advances and applications in energy and the natural environment. Manchester: Manchester University Press, 1991: 619-623. [8] GOLOVKO A K, KONTOROVICH A E, PEVNEVA G S, et al. Composition and distribution of alkylnaphthalenes in West Siberian oils[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2014, 55(5/6): 737-744. [9] 卢双舫, 赵锡嘏, 王子文, 等. 煤成烃生成和运移的模拟实验: 芳烃产物的特征及其意义[J]. 石油学报, 1996, 17(1): 47-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB601.006.htmLU Shuangfang, ZHAO Xigu, WANG Ziwen, et al. The characteristics of aromatic products of hydrocarbon generated from coal[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1996, 17(1): 47-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB601.006.htm [10] 罗斌杰, 李新宇. 原油中芳烃化合物特征[J]. 地球化学, 1993(2): 127-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199302002.htmLUO Binjie, LI Xinyu. Characteristics of aromatic hydrocarbons in crude oils[J]. Geochimica, 1993(2): 127-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX199302002.htm [11] 孟仟祥, 张松林, 崔明中, 等. 不同沉积环境湖相低熟原油的芳烃分布特征[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(1): 112-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB901.017.htmMENG Qianxiang, ZHANG Songlin, CUI Mingzhong, et al. Distribution features of aromatics in lacustrine low-mature crude oils from different environments[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(1): 112-120. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB901.017.htm [12] LI Maowen, YOU Huanxin, FOWLER M G, et al. Geochemical constraints on models for secondary petroleum migration along the Upper Devonian Rimbey-Meadowbrook reef trend in central Alberta, Canada[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1998, 29(1/3): 163-182. [13] HORSFIELD B, CLEGG H, WILKES H, et al. Maturity control of carbazole distributions in petroleum systems[J]. Naturwissenschaften, 1998, 85: 233-237. [14] RICHARD L. Calculation of the standard molal thermodynamic properties as a function of temperature and pressure of some geoche-mically important organic sulfur compounds[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(21): 3827-3877. [15] 卞良樵, 童箴言. 碳酸盐岩与泥(页)岩有机质演化的差异及成因探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1989(2): 7-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK198902001.htmBIAN Liangqiao, TONG Zhenyan. Difference in the evolution of organic matters between carbonates and mudstones (shales) and its origin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1989(2): 7-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK198902001.htm [16] 房玄, 雷怀彦. 粘土矿物对生物-热催化过渡带有机质热解影响的研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 1993, 4(6): 80-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX199306008.htmFANG Xuan, LEI Huaiyan. Effect of clay minerals on pyrolysis of organic matter in bio-thermal catalytic transition zone[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 1993, 4(6): 80-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX199306008.htm [17] 潘长春, 耿安松, 钟宁宁, 等. 矿物和水对干酪根热解生烃作用的影响: Ⅲ. 甾、藿烷(烯)的形成与热演化[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(3): 446-453. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200603018.htmPAN Changchun, GENG Ansong, ZHONG Ningning, et al. The effects of minerals and water on hydrocarbon generation from kerogen: Ⅲ. Steranes and triterpane generation and maturation[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(3): 446-453. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200603018.htm [18] WU Liangliang, FANG Xinyan, JI Shuhuan, et al. Thermal alteration of biomarkers in the presence of elemental sulfur and sulfur-bearing minerals during hydrous and anhydrous pyrolysis[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2018, 123: 74-89. [19] 黄第藩, 王兰生. 川西北矿山梁地区沥青脉地球化学特征及其意义[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(1): 23-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200801005.htmHUANG Difan, WANG Lansheng. Geochemical characteristics of bituminous dike in Kuangshanliang area of the northwestern Sichuan Basin and its significance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2008, 29(1): 23-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200801005.htm [20] 程斌, 廖泽文, 田彦宽, 等. 川西北侏罗系沙溪庙组固体沥青包裹烃的释放及其地球化学意义[J]. 地球化学, 2012, 41(5): 425-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201205004.htmCHENG Bin, LIAO Zewen, TIAN Yankuan, et al. Release of the hydrocarbons occluded inside solid bitumen in Jurassic Shaximiao Formation of northwestern Sichuan Basin and its geochemical significance[J]. Geochimica, 2012, 41(5): 425-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201205004.htm [21] 王广利, 王铁冠, 韩克猷, 等. 川西北地区固体沥青和油砂的有机地球化学特征与成因[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(6): 731-735. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201406731WANG Guangli, WANG Tieguan, HAN Keyou, et al. Organic geochemical characteristics and origin of solid bitumen and oil sands in northwestern Sichuan[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(6): 731-735. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201406731 [22] 黄士鹏, 廖凤蓉, 吴小奇, 等. 四川盆地含硫化氢气藏分布特征及硫化氢成因探讨[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2010, 21(5): 705-714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201005002.htmHUANG Shipeng, LIAO Fengrong, WU Xiaoqi, et al. Distribution characteristics of hydrogen sulphide-bearing gas pools and the genesis of hydrogen sulphide in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2010, 21(5): 705-714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201005002.htm [23] ORR W L. Geologic and geochemical controls on the distribution of hydrogen sulfide in natural gas[C]//CAMPOS R, GONI I. Advances in Organic Geochemistry. Oxford: Pergamon, 1977: 571-601. [24] 朱光有, 张水昌, 梁英波, 等. 四川盆地高含H2S天然气的分布与TSR成因证据[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(8): 1208-1218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200608030.htmZHU Guangyou, ZHANG Shuichang, LIANG Yingbo, et al. Distribution of high H2S-bearing natural gas and evidence of TSR origin in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(8): 1208-1218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200608030.htm [25] 胡守志, 付晓文, 王廷栋, 等. 储层中的沥青沉淀带及其对油气勘探的意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2007, 18(1): 99-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200701020.htmHU Shouzhi, FU Xiaowen, WANG Tingdong, et al. Bitumen-sealed belt in reservoirs and its implication to petroleum exploration[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2007, 18(1): 99-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200701020.htm [26] ALEXANDER R, BASTOW T P, FISHER S J, et al. Geosynthesis of organic compounds: Ⅱ. Methylation of phenanthrene and alkylphenanthrenes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(20): 4259-4266. [27] BASTOW T P, ALEXANDER R, KAGI R I. Geosynthesis of organic compounds IV. Methylation of 1,2,7-trimethylnaphthalene[J]. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 1996, 9(1/4): 177-183. [28] BASTOW T P, ALEXANDER R, FISHER S J, et al. Geosynthesis of organic compounds. Part Ⅴ-Methylation of alkylnaphthalenes[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(6): 523-534. [29] 马军, 李水福, 胡守志, 等. 芳烃化合物组成及其在油气地球化学中的应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010, 29(6): 73-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201006012.htmMA Jun, LI Shuifu, HU Shouzhi, et al. The composition of aromatic hydrocarbon and its application in petroleum geochemistry[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(6): 73-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201006012.htm [30] RADKE M, WELTE D H. The methylphenanthrene index (MPI): a maturity parameter based on aromatic hydrocarbons[M]//BJORØY M. Advances in organic geochemistry 1981. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons Inc., 1983: 504-512. [31] LI Meijun, WANG T G, SHI Shengbao, et al. Oil maturity assessment using maturity indicators based on methylated dibenzothiophenes[J]. Petroleum Science, 2014, 11(2): 234-246. [32] LORANT F, BEHAR F, VANDENBROUCKE M, et al. Methane gene-ration from methylated aromatics: kinetic study and carbon isotope modeling[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2000, 14(6): 1143-1155. [33] FUSETTI L, BEHAR F, BOUNACEUR R, et al. New insights into secondary gas generation from the thermal cracking of oil: methylated monoaromatics. A kinetic approach using 1, 2, 4-trimethylbenzene. Part Ⅰ: a mechanistic kinetic model[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2010, 41(2): 146-167. [34] FUSETTI L, BEHAR F, GRICE K, et al. New insights into secondary gas generation from the thermal cracking of oil: methylated monoaromatics. A kinetic approach using 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene. Part Ⅱ: an empirical kinetic model[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2020, 41(2): 168-176. [35] 魏志彬, 张大江, 张传禄, 等. 甲基二苯并噻吩分布指数(MDBI)作为烃源岩成熟度标尺的探讨[J]. 地球化学, 2001, 30(3): 242-247. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200103006.htmWEI Zhibin, ZHANG Dajiang, ZHANG Chuanlu, et al. Methyldibenzothiophenes distribution index as a tool for maturity assessments of source rocks[J]. Geochimica, 2001, 30(3): 242-247. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200103006.htm [36] 李林强, 林壬子. 利用芳烃化合物研究东濮凹陷西斜坡地区原油成熟度[J]. 沉积学报, 2005, 23(2): 361-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200502025.htmLI Linqiang, LIN Renzi. Study on maturity of crude oil distributed in west slope of Dongpu Depression using aromatic compounds[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2005, 23(2): 361-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200502025.htm [37] 张刚庆, 李水福, 何生, 等. 板桥凹陷原油芳烃组成特征及地球化学意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(2): 367-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200902022.htmZHANG Gangqing, LI Shuifu, HE Sheng, et al. Composition characteristics and geochemical significance of aromatic hydrocarbons of crude oils from the Banqiao Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(2): 367-371. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200902022.htm [38] CHENG Bin, HU Shouzhi, SHEN Chuanbo, et al. The Geochemical characterization of adsorbed/occluded hydrocarbons inside solid bitumen in the Kuangshanliang area of the northwestern Sichuan Basin and its significance[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2014, 32(18): 2203-2211. [39] 刘德汉, 史继扬. 高演化碳酸盐烃源岩非常规评价方法探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1994, 21(3): 113-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK403.019.htmLIU Dehan, SHI Jiyang. Discussion on unconventional evaluation method of high evolution carbonate source rock[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1994, 21(3): 113-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK403.019.htm [40] 孙晓猛, 许强伟, 王英德, 等. 川西北龙门山冲断带北段油砂成藏特征及其主控因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(4): 886-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201004020.htmSUN Xiaomeng, XU Qiangwei, WANG Yingde, et al. Reservoir forming characteristics and main controlling factors of oil sandstones in the northern Longmen Mountain thurst zone of the northwest of Sichuan[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(4): 886-896. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201004020.htm [41] LEWAN M D. Sulphur-radical control on petroleum formation rates[J]. Nature, 1998, 391(6663): 164-166. [42] JENSEN H K B, CONNAN J, BJORØY M, et al. Geoelf sulphur analyser: quantification of thermally extractable and pyrolysable organic and mineral sulphur in source rocks[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1998, 28(1/2): 87-110. [43] SWEENEY J J, BURNHAM A K. Evaluation of a simple model of vitrinite reflectance based on chemical kinetics[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(10): 1559-1570. [44] 曾凡刚, 程克明. 华北地区下古生界海相烃源岩芳烃生物标志物地球化学特征: 兼论饱和烃、芳烃生源组合特征[J]. 地质地球化学, 1998, 26(3): 33-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ199803005.htmZENG Fangang, CHENG Keming. Characteristics of aromatic hydrocarbon biomarkers from Lower Palaeozoic marine carbonate rocks in north China[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 1998, 26(3): 33-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ199803005.htm [45] 彼得斯K E, 沃尔斯特C C, 莫尔多万J M. 生物标志化合物指南: 生物标志化合物和同位素在石油勘探与地史研究中的应用[M]. 2版. 张水昌, 李振西, 译. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011.PETERS K E, WALSTER C C, MORWAN J M. The biomarker guide Ⅱ: application of biomarker and isotopes in petroleum exploration and geohistory research[M]. 2nd ed. ZHANG Shuichang, LI Zhenxi, trans. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011. [46] 包建平, 王铁冠, 周玉琦, 等. 甲基菲比值与有机质热演化的关系[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 1992, 14(4): 8-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX199204001.htmBAO Jianping, WANG Tieguan, ZHOU Yuqi, et al. The relationship between methyl phenanthrene ratios and the evolution of organic matter[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute, 1992, 14(4): 8-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX199204001.htm [47] SCHOU L, MYHR M B. Sulfur aromatic compounds as maturity parameters[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1988, 13(1/3): 61-66. [48] 王崇敬, 张鹤, 李世宇, 等. 基于分子标志物的有机质成熟度评价参数选择及其适用范围分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(4): 208-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201804028.htmWANG Chongjing, ZHANG He, LI Shiyu, et al. Maturity parameters selection and applicable range analysis of organic matter based on molecular markers[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(4): 208-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201804028.htm [49] RADKE M, WELTE D H, WILLSCH H. Maturity parameters based on aromatic hydrocarbons: influence of the organic matter type[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10(1/3): 51-63. [50] YANG Sibo, LI Meijun, LIU Xiaoqiang, et al. Thermodynamic stability of methyldibenzothiophenes in sedimentary rock extracts: based on molecular simulation and geochemical data[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2019, 129: 24-41. [51] CHAKHMAKHCHEV A, SUZUKI M, TAKAYAMA K. Distribution of alkylated dibenzothiophenes in petroleum as a tool for maturity assessments[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1997, 26(7/8): 483-489. [52] MACKENZIE A S, LAMB N A, MAXWELL J R. Steroid hydrocarbons and the thermal history of sediments[J]. Nature, 1982, 295(5846): 223-226. [53] MCKENZIE D, MACKENZIE A S, MAXWELL J R, et al. Isomerization and aromatization of hydrocarbons in stretched sedimentary basins[J]. Nature, 1983, 301(5900): 504-506. [54] PICHA F J, PETERS K E. Biomarker oil-to-source rock correlation in the western Carpathians and their foreland, Czech Republic[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 1998, 4(4): 289-302. [55] 李水福, 何生. 原油芳烃中三芴系列化合物的环境指示作用[J]. 地球化学, 2008, 37(1): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200801006.htmLI Shuifu, HE Sheng. Geochemical characteristics of dibenzothiophene, dibenzofuran and fluorene and their homologues and their environmental indication[J]. Geochimica, 2008, 37(1): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200801006.htm [56] SEIFERT W K, MOLDOWAN J M. The effect of biodegradation on steranes and terpanes in crude oils[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(1): 111-126. [57] BEACH F, PEAKMAN T M, ABBOTT G D, et al. Laboratory thermal alteration of triaromatic steroid hydrocarbons[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1989, 14(1): 109-111. -





 下载:
下载:











 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号