Multi-factor evaluation for fine grading of tight sandstone reservoirs: a case study from H3 sand group in the upper section of Oligocene Huagang Formation, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin
-
摘要: 东海盆地西湖凹陷西次凹渐新统花港组上段H3砂组为低孔低渗—低孔特低渗致密砂岩储层,优质储层分布成为制约开发产能的关键问题。基于岩心、测井及物性测试等资料,对该区进行了沉积微相刻画和储层物性分析,结合构造、沉积微相发育特征,对储层展开精细分级评价和优质储层预测。研究表明,H3砂组储层分布主要受构造特征、沉积微相、砂体厚度和孔渗条件四个因素影响。在综合分析各因素与含气饱和度关系的基础上,建立了受产能约束的四因子储层精细分级评价标准,把H3砂组储层划分为“甜点”储层(Ⅰ类)、中等储层(Ⅱ类)和无效储层(Ⅲ类)三种类型。优质储层预测研究区H3-3小层为可能的高产能潜力带,H3-1、H3-2和H3-4小层次之。Abstract: The H3 sand group of the upper section of the Oligocene Huagang Formation in the western sub-sag of the Xihu Sag of the East China Sea Continental Shelf Basin is a tight sandstone reservoir with low porosity and low or ultra-low permeability. The distribution of high-quality reservoirs has become a key factor restricting productivity. Based on coring, well logging and physical property test data, the sedimentary microfacies and physical properties of the H3 sand group were studied, and a fine grading evaluation and "sweet spot" prediction were carried out. The reservoir distribution in the H3 sand group was mainly affected by four factors: structural characteristics, sedimentary microfacies, sand thickness and conditions of porosity and permeability. Moreover, on the basis of comprehensive analysis of the relationship among these factors and gas saturation, a four-factor reservoir fine grading evaluation method was proposed. The H3 sand group reservoirs were divided into three types: "sweet spot" reservoirs (type Ⅰ), medium reservoirs (type Ⅱ) and ineffective reservoirs (type Ⅲ).The H3-3 single sand layer has a great exploration potential, followed by the H3-1, H3-2 and H3-4 single sand layers.
-
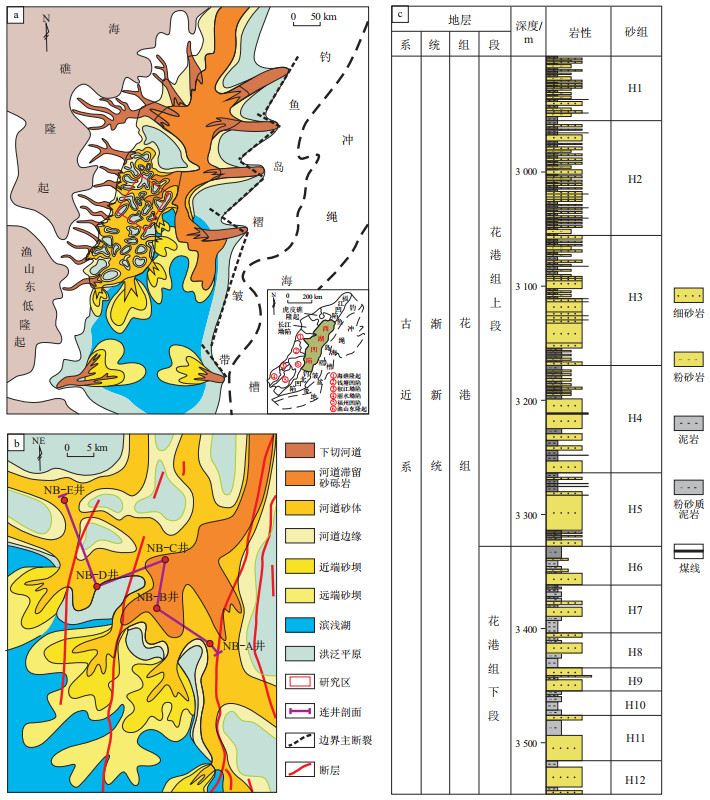
图 1 东海盆地西湖凹陷花港组构造区划(a)、古地理图(a,b)与地层柱状图(c)[32]
Figure 1. Tectonic division (a), paleogeographic map (a, b) and stratigraphic column (c) of Huagang Formation in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin
图 4 东海盆地西湖凹陷NB-1构造花港组上段H3砂组断层发育情况与产能关系连井对比
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 4. Well connection contrasts of the correlation of fault development and productivity in H3 sand group of Upper Huagang Formation in NB-1 structure of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin
图 5 东海盆地西湖凹陷NB-1构造花港组上段H3砂组沉积微相展布特征与产能关系连井对比
剖面位置见图 1。
Figure 5. Well connection contrasts of the correlation of sedimentary microfacies distribution characteristics and productivity in H3 sand group of Upper Huagang Formation in NB-1 structure of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin
表 1 东海盆地西湖凹陷NB-1构造花港组上段H3砂组储层孔渗条件与产能关系分类
Table 1. Grading table of relationship between porosity and permeability factors and productivity of H3 sand group of Upper Huagang Formation in NB-1 structure of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin
沉积微相 平均孔隙度/% 平均渗透率/10-3 μm2 含气饱和度/% 储层物性分类 河道滞留沉积 7.59 1.66 46,54,56 低孔低渗 心滩 7.52 1.07 64,68 低孔低渗 湖泛改造的心滩 7.08 0.53 48 低孔特低渗 滨浅湖砂质滩坝 6.52 0.13 0 非储层 表 2 储层精细分级评价标准
Table 2. Evaluation criteria for fine classification of reservoirs
储层分级 构造因子 沉积微相因子 砂厚因子 孔渗因子 Ⅰ级(甜点储层) A区 河道滞留沉积、心滩 累厚15~20 m,单层大于2 m,少夹层 低孔低渗 Ⅱ级(中等储层) B区 湖泛改造的心滩 累厚大于20 m,单层大于1 m,多夹层(洪泛层) 低孔特低渗 Ⅲ级(无效储层) C区 滨浅湖砂质滩坝 累厚小于15 m,单层小于1 m,多夹层(洪泛层) 非储层 -
[1] 蔡全升, 胡明毅, 胡忠贵, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷中央隆起带古近系花港组储层特征及成岩孔隙演化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(4): 733-740. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201304013.htmCAI Quansheng, HU Mingyi, HU Zhonggui, et al. Reservoir characteristics and evolution of diagenetic porosity of Huagang Formation of Paleogene in the central anticlinal belt of Xihu Sag, Donghai Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(4): 733-740. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201304013.htm [2] 刘勇, 徐国盛, 曾兵, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷花港组储层孔隙演化与油气充注关系[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(2): 168-176. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201802168LIU Yong, XU Guosheng, ZENG Bing, et al. Relationship between porosity evolution and hydrocarbon charging in tight sandstone reservoirs in Oligocene Huagang Formation, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(2): 168-176. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201802168 [3] 张武, 徐发, 徐国盛, 等. 西湖凹陷某构造花港组致密砂岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 39(2): 122-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201202003.htmZHANG Wu, XU Fa, XU Guosheng, et al. Diagenesis and pore evolution of Huagang Formation tight sandstone reservoirs in a structure of Xihu Depression in East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2012, 39(2): 122-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201202003.htm [4] 彭伟欣. 中国东海西湖凹陷天然气资源及开发利用[J]. 天然气工业, 2002, 22(2): 76-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200202022.htmPENG Weixin. Natural gas resources in Xihu Depression of East China Sea in China and their development and utilization[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2002, 22(2): 76-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200202022.htm [5] 高伟中, 杨彩虹, 赵洪. 东海盆地西湖凹陷热事件对储层的改造及其机理探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2015, 37(5): 548-554. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201505548GAO Weizhong, YANG Caihong, ZHAO Hong. Reservoir formation and modification controlled by thermal events in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2015, 37(5): 548-554. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201505548 [6] 王伟明, 卢双舫, 陈旋, 等. 致密砂岩气资源分级评价新方法: 以吐哈盆地下侏罗统水西沟群为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(1): 60-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201501008.htmWANG Weiming, LU Shuangfang, CHEN Xuan, et al. A new method for grading and assessing the potential of tight sand gas resources: a case study of the Lower Jurassic Shuixigou Group in the Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Deve-lopment, 2015, 42(1): 60-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201501008.htm [7] 张安达, 王成, 乔睿. 致密砂岩储层物性下限确定新方法及系统分类[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(5): 5-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201405002.htmZHANG Anda, WANG Cheng, QIAO Rui. A new method for determining physical property lower limit of tight sandstone reservoir and reservoir system classification[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2014, 26(5): 5-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201405002.htm [8] 林潼, 魏红兴, 谢亚妮. 以喉道为参数的致密砂岩气储层评价方法: 以库车坳陷迪北地区致密砂岩气为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(5): 983-990. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201605017.htmLIN Tong, WEI Hongxing, XIE Yani. Using throat parametre to assess tight sandstone gas reservoir: a case study of Dibei tight sandstone gas in the east of Kuqa Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(5): 983-990. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201605017.htm [9] 李海燕, 岳大力, 张秀娟. 苏里格气田低渗透储层微观孔隙结构特征及其分类评价方法[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(2): 133-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201202020.htmLI Haiyan, QIU Dali, ZHANG Xiujuan. Characteristics of pore structure and reservoir evaluation of low permeability reservoir in Sulige gas field[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(2): 133-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201202020.htm [10] 吴浩, 刘锐娥, 纪友亮, 等. 典型致密砂岩气储层孔隙结构分类及其意义: 以鄂尔多斯盆地盒8段为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(5): 835-843. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201605010.htmWU Hao, LIU Ruie, JI Youliang, et al. Classification of pore structures in typical tight sandstone gas reservoir and its significance: a case study of the He8 Member of Upper Palaeozoic Shihezi Formation in Ordos Basin, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(5): 835-843. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201605010.htm [11] 陈林, 李珊珊, 游君君, 等. 文昌B凹陷古近系低渗储层物性影响因素定量评价与应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 165-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903017.htmCHEN Lin, LI Shanshan, YOU Junjun, et al. Quantitative evaluation and application of factors affecting the properties of low permeability reservoirs from the Paleogene in Wenchang B Sag[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 165-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903017.htm [12] 白松涛, 程道解, 万金彬, 等. 砂岩岩石核磁共振T2谱定量表征[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(3): 382-391. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201603011.htmBAI Songtao, CHENG Daojie, WAN Jinbin, et al. Quantitative characterization of sandstone NMR T2 spectrum[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(3): 382-391. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201603011.htm [13] 代全齐, 罗群, 张晨, 等. 基于核磁共振新参数的致密油砂岩储层孔隙结构特征: 以鄂尔多斯盆地延长组7段为例[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(7): 887-897. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201607007.htmDAI Quanqi, LUO Qun, ZHANG Chen, et al. Pore structure characteristics of tight-oil sandstone reservoir based on a new parameter measured by NMR experiment: a case study of seventh member in Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(7): 887-897. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201607007.htm [14] 肖佃师, 卢双舫, 姜微微, 等. 基于粒间孔贡献量的致密砂岩储层分类: 以徐家围子断陷为例[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(10): 1123-1134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201710003.htmXIAO Dianshi, LU Shuangfang, JIANG Weiwei, et al. Classification of tight sandstone reservoirs based on the contribution of intergra-nular pores: a case study of Xujiaweizi Fault Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(10): 1123-1134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201710003.htm [15] 武法东, 陆永潮, 陈平, 等. 东海西湖凹陷渐新统花港组海绿石的发现及其意义[J]. 沉积学报, 1997, 15(3): 160-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB703.028.htmWU Fadong, LU Yongchao, CHEN Ping, et al. The discovery and significance of glauconites in the Huagong Formation of the Oligocene, Xihu Depression, East China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1997, 15(3): 160-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB703.028.htm [16] 王丽顺, 陈琳琳. 东海西湖凹陷下第三系层序地层学分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1994, 14(3): 33-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ403.003.htmWANG Lishun, CHRN Linlin. Sequence stratigraphic analysis of Eogene system, Xihu Sag, East China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1994, 14(3): 33-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ403.003.htm [17] 刘书会, 王宝言, 刘成鑫. 西湖凹陷平湖地区平湖组沉积相的再认识[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2009, 16(3): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200903004.htmLIU Shuhui, WANG Baoyan, LIU Chengxin. The recognition about sedimentary facies in Pinghu Formation of Pinghu region[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2009, 16(3): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200903004.htm [18] 苏奥, 贺聪, 陈红汉, 等. 构造反转对西湖凹陷中部油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2016, 23(3): 75-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201603017.htmSU Ao, HE Cong, CHEN Honghan, et al. Effect of tectonic inversion on hydrocarbon accumulation in the central area of Xihu Depression[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2016, 23(3): 75-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201603017.htm [19] 李祥权, 刘金水, 陆永潮, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷花港组原型盆地性质厘定[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(2): 502-513. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201802012.htmLI Xiangquan, LIU Jinshui, LU Yongchao, et al. Prototype basin characterization of Huagang Formation of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(2): 502-513. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201802012.htm [20] 陈智远, 徐志星, 陈飞, 等. 异常高压与油气充注的耦合性: 以东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷花港组和平湖组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2): 186-194. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702186CHEN Zhiyuan, XU Zhixing, CHEN Fei. Coupling of abnormal overpressure and hydrocarbon charging: a case from the Huagang and Pinghu formations of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(2): 186-194. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702186 [21] ABBAS A, ZHU Hongtao, ZENG Zhiwei, et al. Sedimentary facies analysis using sequence stratigraphy and seismic sedimentology in the Paleogene Pinghu Formation, Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 93: 287-297. [22] 侯志强, 于浩, 刘云, 等. 西湖凹陷M气田区块低孔渗致密砂岩储层高精度三维孔隙压力场地震预测[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 267-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902032.htmHOU Zhiqiang, YU Hao, LIU Yun, et al. High-precision seismic prediction of 3D pore-pressure in tight sandstone gas reservoirs with low porosity and permeability at M gas field in Xihu Sag[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 267-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902032.htm [23] 陈哲, 张昌民, 侯国伟, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组断层组合样式及其控砂机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(4): 824-837. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004016.htmCHEN Zhe, ZHANG Changmin, HOU Guowei, et al. Fault distribution patterns and their control on sand bodies in Pinghu Formation of Xihu Sag in East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 824-837. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004016.htm [24] 王健伟, 吕鹏, 曾联波, 等. 西湖凹陷X气藏花港组H3段储层特征及影响因素[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(1): 22-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202001006.htmWANG Jianwei, LYU Peng, ZENG Lianbo, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of reservoir in H3 section of Huagang Formation, X gas reservoir, Xihu Sag[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(1): 22-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202001006.htm [25] 朱毅秀, 黄导武, 王欢, 等. 东海西湖凹陷A气田渐新统花港组三段厚层砂岩沉积环境[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(6): 1226-1235. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201906007.htmZHU Yixiu, HUANG Daowu, WANG Huan, et al. Sedimentary setting of thick sandstone in the 3rd member of the Oligocene Huagang Formation in A gas field in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(6): 1226-1235. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201906007.htm [26] 曹冰. 西湖凹陷中央反转构造带花港组致密砂岩储层埋藏史-热史[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 43(4): 405-414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201604003.htmCAO Bing. Study of burial and thermal history of Huagang Formation tight sandstone reservoir in central reversal structural belt, Xihu Depression, East China Sea[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2016, 43(4): 405-414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201604003.htm [27] 蒋玉波. 东海陆架盆地南部中生代地层展布及油气远景探讨[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013.JIANG Yubo. Discussion on the distribution characteristics and its hydrocarbon potential of Mesozoic stratum in southern East China Sea Shelf Basin[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2013. [28] 于兴河, 李顺利, 曹冰, 等. 西湖凹陷渐新世层序地层格架与沉积充填响应[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(2): 299-314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201702009.htmYU Xinghe, LI Shunli, CAO Bing, et al. Oligocene sequence framework and depositional response in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(2): 299-314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201702009.htm [29] 曹倩, 宋在超, 周小进, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷原油地化特征及来源分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(2): 251-259. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201902251CAO Qian, SONG Zaichao, ZHOU Xiaojin, et al. Geochemical characteristics and source of crude oil in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(2): 251-259. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201902251 [30] 张建培, 徐发, 钟韬, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组-花港组层序地层模式及沉积演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(1): 35-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201201009.htmZHANG Jianpei, XU Fa, ZHONG Tao, et al. Sequence stratigraphic models and sedimentary evolution of Pinghu and Huagang formations in Xihu Trough[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(1): 35-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201201009.htm [31] 苏奥, 陈红汉, 吴悠, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷中西部低渗近致密-致密砂岩气成因、来源及运聚成藏[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(1): 184-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201801013.htmSU Ao, CHEN Honghan, WU You, et al. Genesis, origin and migration-accumulation of low-permeable and nearly tight-tight sandstone gas in the central western part of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(1): 184-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201801013.htm [32] 刘金水, 陆永潮, 秦兰芝. 源-汇系统分析方法在大型储集体研究中的应用: 以西湖凹陷中央反转带花港组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(3): 303-310. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903303LIU Jinshui, LU Yongchao, QIN Lanzhi. Application of source to sink system analysis in large reservoir research: a case study of Huagang Formation, central inversion belt, Xihu Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(3): 303-310. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903303 [33] ZHANG Jingyu, LU Yongchao, KRIJGSMAN W, et al. Source to sink transport in the Oligocene Huagang Formation of the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 98: 733-745. [34] 吴逸豪. 冀中坳陷晋县凹陷中南部Es4-Ek1段致密储层特征及分级评价研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2016.WU Yihao. Research on characteristics and grading evaluation of tight reservoir in Es4-Ek1 section of south-central Jinxian Sag, Jizhong Depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum, 2016. -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号