Tectonic evolution characteristics of Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin
-
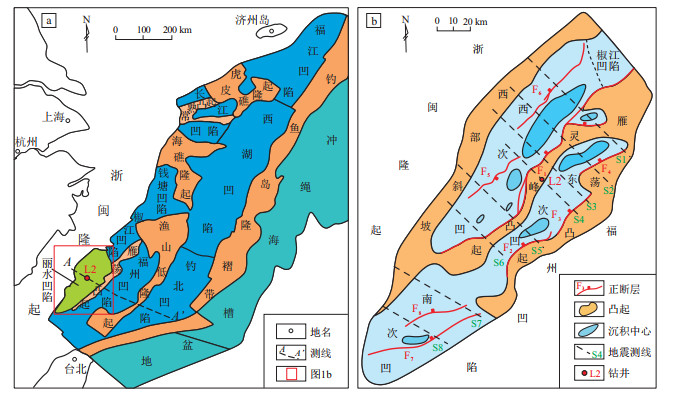
摘要: 为了精细刻画东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷构造演化历史,从北至南选取了丽水凹陷8条骨干地震测线剖面,运用平衡剖面技术,对其进行了构造演化剖面的恢复,测定了伸缩量、伸缩率、伸缩速率等参数,对丽水凹陷10个地质时期的伸缩特征进行了定量化、精细化研究,探讨了其阶段性、空间性伸缩特征。丽水凹陷构造演化阶划可分为断陷初期、断陷早期、断陷晚期、拗陷期、反转期和稳定沉降期6个阶段,古新统灵峰组下段沉积期(T90—T88)是断陷作用最强烈、断层活动性最强阶段,而不同演化阶段的伸缩特征在空间上存在差异。丽水凹陷的构造演化反映了东海陆架盆地晚中生代以来从早到晚、自西向东发生构造与沉积迁移的规律,其受控于(古)太平洋板块向欧亚板块后撤式俯冲的动力学背景,并与东海陆架盆地周围各大汇聚板块的相互作用息息相关。Abstract: To detailly describe the tectonic evolution history of Lishui Sag of the East China Sea Shelf Basin, eight seismic sections from north to south were selected. The balanced section technology was used to restore structural evolution section, and some parameters such as extension amount, ratio and rate were measured. The extension characteristics of the sag during ten geological periods were described quantitatively and finely, moreover, the stage and spatial extension characteristics were also discussed. The structural evolution of the sag were classified into six stages: the initial, early and late stages of fault depression, the depression stage, the inversion stage and the stable subsidence stage. It was considered that the most intense stage for fault depression and fault activity in the sag was the deposition stage of the lower Lingfeng Formation (T90-T88), and the extension and contraction characteristics of different evolution stages were different in space. The tectonic evolution of the Lishui Sag, controlled by the geodynamic background of retrogressive subduction of the (paleo) Pacific plate to the Eurasian plate, reflects the rule of tectonic and sedimentary migration from west to east in the East China Sea Shelf Basin since the Late Mesozoic, and is closely related to the interaction of the convergence plates around the East China Sea shelf Basin.
-
图 7 过东海陆架盆地南部地震剖面
位置见图 1a的A-A’测线。
Figure 7. Seismic profile crossing the southern part of East China Sea Shelf Basin
表 1 东海陆架盆地构造演化简表
Table 1. Simplified structural evolution of East China Sea Shelf Basin

表 2 东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷8条骨干剖面各变形时期伸缩参数
Table 2. Extension and contraction parameters of eight key sections during each deformation period in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin
剖面 参数 时期 T20—T0 T40—T20 T50—T40 T80—T50 T83—T80 T85—T83 T88—T85 T90—T88 T100/Tg—T90 Tg—T100 S1 ΔL/m 123.8 -1410.9 899.6 333.3 563.5 689.9 1 978.9 2 327.1 1 673.9 4 092.1 r 0.001 4 -0.015 6 0.010 0 0.003 7 0.006 3 0.007 8 0.023 0 0.027 8 0.020 4 0.052 4 v/(m·Ma-1) 5.38 -77.52 136.30 40.65 375.67 405.82 1 522.23 2 115.55 380.43 232.51 S2 ΔL/m 73.3 -1 221.7 488.5 441.9 882.4 1 681 2 534.8 2 745.8 2 138 3 093.5 r 0.000 8 -0.013 2 0.005 3 0.004 8 0.009 7 0.018 9 0.029 3 0.032 8 0.026 2 0.039 4 v/(m·Ma-1) 3.19 -67.13 74.02 53.89 588.27 988.82 1 949.85 2 496.18 485.91 175.77 S3 ΔL/m 234.4 -2 605.6 180.3 247 193.3 969.1 1 218.9 1 947.3 2 359 2 375.3 r 0.002 6 -0.028 0 0.001 9 0.002 7 0.002 1 0.010 6 0.013 5 0.022 1 0.027 5 0.028 5 v/(m·Ma-1) 10.19 -143.16 27.32 30.12 128.87 570.06 937.62 1 770.27 536.14 134.96 S4 ΔL/m 4.3 -3 445.8 401.1 606.1 0.1 1 300.1 1 331 1 270.1 1 115.9 3 099.6 r 0.000 1 -0.040 1 0.004 7 0.007 1 0.000 0 0.015 5 0.016 2 0.015 7 0.014 0 0.040 4 v/(m·Ma-1) 0.19 -189.33 60.77 73.91 0.07 764.76 1 023.85 1 154.64 253.61 176.11 S5 ΔL/m 17.2 -3 140.5 333.9 364.8 311.3 846.9 1 770.2 2 350.3 1 269.7 3 371.6 r 0.000 2 -0.038 8 0.004 1 0.004 5 0.003 9 0.010 7 0.022 9 0.031 4 0.017 2 0.047 9 v/(m·Ma-1) 0.75 -172.55 50.59 44.49 207.53 498.18 1 361.69 2 136.64 288.57 191.57 S6 ΔL/m 99.4 -1 347.3 130.2 227.4 346.6 814.1 1 095.7 968.7 680.5 1 328.9 r 0.001 7 -0.023 1 0.002 2 0.003 9 0.006 0 0.014 3 0.019 6 0.017 7 0.012 6 0.025 1 v/(m·Ma-1) 4.32 -74.03 19.73 27.73 231.07 478.88 842.85 880.64 154.66 75.51 S7 ΔL/m 0 -1 098.9 70.7 84.8 538.9 450.2 755.2 1 500.7 2 416.8 r 0.000 0 -0.014 4 0.000 9 0.001 1 0.007 1 0.006 0 0.010 2 0.020 6 0.034 4 v/(m·Ma-1) 0.00 -60.38 10.71 10.34 359.27 264.82 580.92 1 364.27 109.85 S8 ΔL/m 18.9 -1 493.1 76 114.3 219.3 468 784.2 995.9 2 166.7 r 0.000 4 -0.030 8 0.001 6 0.002 4 0.004 6 0.009 8 0.016 8 0.021 7 0.049 6 v/(m·Ma-1) 0.82 -82.04 11.52 13.94 146.20 275.29 603.23 905.36 98.49 注:当Tg—T100存在数值时,T100/Tg—T90为T100—T90,否则为Tg—T90;Tg—T100的存在与否取决于T100反射层是否存在。 -
[1] 贾成业, 夏斌, 王核, 等. 东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷构造演化及油气地质分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2006, 17(3): 397-401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200603024.htmJIA Chengye, XIA Bin, WANG He, et al. Characteristic of tectonic evolution and petroleum geology in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2006, 17(3): 397-401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200603024.htm [2] 许薇龄, 乐俊英. 东海的构造运动及演化[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1988, 8(1): 11-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198801001.htmXU Weiling, LE Junying. Tectonic movement and evolution of the East China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1988, 8(1): 11-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ198801001.htm [3] 陈斯忠. 东海盆地主要地质特点及找气方向[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1): 6-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200301001.htmCHEN Sizhong. Main geological characteristics and gas exploration directions in East China Sea Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 6-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200301001.htm [4] 冯晓杰, 蔡东升, 王春修, 等. 东海陆架盆地中新生代构造演化特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1): 33-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200301006.htmFENG Xiaojie, CAI Dongsheng, WANG Chunxiu, et al. The Meso-Cenozoic tectonic evolution in East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 33-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200301006.htm [5] 杨长清, 杨传胜, 李刚, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部中生代构造演化与原型盆地性质[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3): 105-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201203017.htmYANG Changqing, YANG Chuansheng, LI Gang, et al. Mesozoic tectonic evolution and prototype basin characters in the southern East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3): 105-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201203017.htm [6] 张建培, 张田, 唐贤君. 东海陆架盆地类型及其形成的动力学环境[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(11): 2033-2043. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201411002.htmZHANG Jianpei, ZHANG Tian, TANG Xianjun. Basin type and dynamic environment in the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(11): 2033-2043. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201411002.htm [7] 张国华, 张建培. 东海陆架盆地构造反转特征及成因机制探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 260-270. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501025.htmZHANG Guohua, ZHANG Jianpei. A discussion on the tectonic inversion and its genetic mechanism in the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 260-270. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501025.htm [8] 刘金水, 许怀智, 蒋一鸣, 等. 东海盆地中、新生代盆架结构与构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3): 675-691. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202003001.htmLIU Jinshui, XU Huaizhi, JIANG Yiming, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic basin structure and tectonic evolution in the East China Sea Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(3): 675-691. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202003001.htm [9] 杨艳秋, 杨长清, 杨传胜, 等. 东海陆架盆地南部中生代断裂系统与盆地结构[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(6): 52-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201906004.htmYANG Yanqiu, YANG Changqing, YANG Chuansheng, et al. Mesozoic fault system in the southern East China Sea Shelf Basin and its bearing on basin structures[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(6): 52-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201906004.htm [10] 钟锴, 朱伟林, 高顺莉, 等. 东海陆架盆地形成演化及油气成藏关键地质问题[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(10): 3485-3497. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201810013.htmZHONG Kai, ZHU Weilin, GAO Shunli, et al. Key geological questions of the formation and evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation of the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(10): 3485-3497. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201810013.htm [11] 周荔青, 江东辉, 张尚虎, 等. 东海西湖凹陷大中型油气田形成条件及勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 803-812. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005803ZHOU Liqing, JIANG Donghui, ZHANG Shanghu, et al. Formation conditions and exploration direction of large and medium oil and gas reservoirs in Xihu Sag, East China Sea[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 803-812. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005803 [12] 丁道桂, 李凤丽. 下扬子区中-新生代变格构造运动[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 687-697. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005687DING Daogui, LI Fengli. Mesozoic and Cenozoic diktyogenese in the Lower Yangtze region[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 687-697. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005687 [13] 葛和平, 陈志勇, 方来富, 等. 丽水凹陷油气成藏期次探讨[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2003, 17(1): 44-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200301008.htmGE Heping, CHEN Zhiyong, FANG Laifu, et al. A discussion on hydrocarbon accumulation periods in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2003, 17(1): 44-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200301008.htm [14] 张胜利, 夏斌. 丽水-椒江凹陷构造演化特征与油气聚集[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(3): 324-328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200503014.htmZHANG Shengli, XIA Bin. Characters of tectonic evolution of the Lishui-Jiaojiang sag and oil accumulation[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(3): 324-328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200503014.htm [15] 张田, 张建培, 张绍亮, 等. 平衡剖面技术在东海丽水凹陷构造演化研究中的应用[J]. 上海国土资源, 2014, 35(1): 92-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD201401021.htmZHANG Tian, ZHANG Jianpei, ZHANG Shaoliang, et al. An application of the balanced cross-section technique: the tectonic evolution of Lishui Sag, the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 2014, 35(1): 92-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD201401021.htm [16] DAHLSTROM C D A. Balanced cross sections[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1969, 6(4): 743-757. [17] 张田, 张建培, 张绍亮, 等. 东海陆架盆地西部坳陷带构造特征及演化[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(5): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201505001.htmZHANG Tian, ZHANG Jianpei, ZHANG Shaoliang, et al. Tectonic characteristics and evolution of the west depression belt of the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(5): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201505001.htm [18] ZHANG Jinliang, GUO Jiaqi, LIU Jinshui, et al. 3D-basin modelling of the Lishui Sag: research of hydrocarbon potential, petroleum generation and migration[J]. Energies, 2019, 12(4): 650. [19] 葛和平, 高顺莉, 周平, 等. 东海丽水凹陷断陷结构特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 地球科学前沿, 2019, 9(11): 1025-1035.GE Heping, GAO Shunli, ZHOU Ping, et al. Fault structural characteristics and its petroleum geological significance of Lishui Sag in Donghai Basin[J]. Advances in Geosciences, 2019, 9(11): 1025-1035. [20] 张世华. 川西拗陷须二段断裂演化特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 47(4): 385-394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG202004001.htmZHANG Shihua. Fault Evolution characteristics of the Member 2 of Xujiahe Formation in the Western Sichuan Depression, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science and Technology Edition), 2020, 47(4): 385-394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG202004001.htm [21] MARUYAMA S, SANTOSH M, ZHAO D. Superplume, supercontinent, and post-perovskite: mantle dynamics and anti-plate tectonics on the core-mantle boundary[J]. Gondwana Research, 2007, 11(1/2): 7-37. [22] 李三忠, 余珊, 赵淑娟, 等. 东亚大陆边缘的板块重建与构造转换[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(3): 65-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201303011.htmLI Sanzhong, YU Shan, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Tectonic transition and plate reconstructions of the East Asian continental magin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(3): 65-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201303011.htm [23] 葛肖虹, 任收麦, 马立祥, 等. 青藏高原多期次隆升的环境效应[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(6): 118-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200606017.htmGE Xiaohong, REN Shoumai, MA Lixiang, et al. Multi-stage uplifts of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau and their environmental effects[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(6): 118-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200606017.htm [24] LIU Mian, CUI Xiaojun, LIU Futian. Cenozoic rifting and volcanism in eastern China: a mantle dynamic link to the Indo-Asian collision?[J]. Tectonophysics, 2004, 393(1/4): 29-42. [25] 张建培. 东海西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带断裂系统特征及成因机制探讨[J]. 地质科学, 2013, 48(1): 291-303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201301020.htmZHANG Jianpei. Fault system and its genetic mechanism in the Pinghu slope of the Xihu Sag in the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2013, 48(1): 291-303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201301020.htm [26] VALER'EVNA D L, 王鹏程, 李三忠, 等. 东亚大汇聚与中-新生代地球表层系统演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(4): 33-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201704003.htmVALER'EVNA D L, WANG Pengcheng, LI Sanzhong, et al. Meso-Cenozoic evolution of earth surface system under the East Asian tectonic superconvergence[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(4): 33-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201704003.htm [27] 周蒂, 孙珍. 晚中生代以来太平洋域板块过程及其对东亚陆缘构造研究的启示[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(3): 1-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY201703001.htmZHOU Di, SUN Zhen. Plate evolution in the Pacific domain since Late Mesozoic and its inspiration to tectonic research of East Asia margin[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(3): 1-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDHY201703001.htm [28] 李三忠, 索艳慧, 李玺瑶, 等. 西太平洋中生代板块俯冲过程与东亚洋陆过渡带构造-岩浆响应[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(16): 1550-1593. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201816006.htmLI Sanzhong, SUO Yanhui, LI Xiyao, et al. Mesozoic plate subduction in West Pacific and tectono-magmatic response in the East Asian ocean-continent connection zone[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(16): 1550-1593. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201816006.htm [29] 李三忠, 曹现志, 王光增, 等. 太平洋板块中-新生代构造演化及板块重建[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(5): 642-677. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201905005.htmLI Sanzhong, CAO Xianzhi, WANG Guangzeng, et al. Meso-Cenozoic tectonic evolution and plate reconstruction of the Pacific Plate[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(5): 642-677. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201905005.htm [30] LIU Xin, ZHAO Dapeng, LI Sanzhong, et al. Age of the subducting Pacific slab beneath East Asia and its geodynamic implications[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 464: 166-174. [31] 祁江豪, 吴志强, 张训华, 等. 西太平洋弧后地区新生代构造迁移的深部地震证据[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(7): 2495-2507. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202007021.htmQI Jianghao, WU Zhiqiang, ZHANG Xunhua, et al. Deep seismic evidence of Cenozoic tectonic migration in the Western Pacific Back-Arc area[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(7): 2495-2507. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202007021.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号