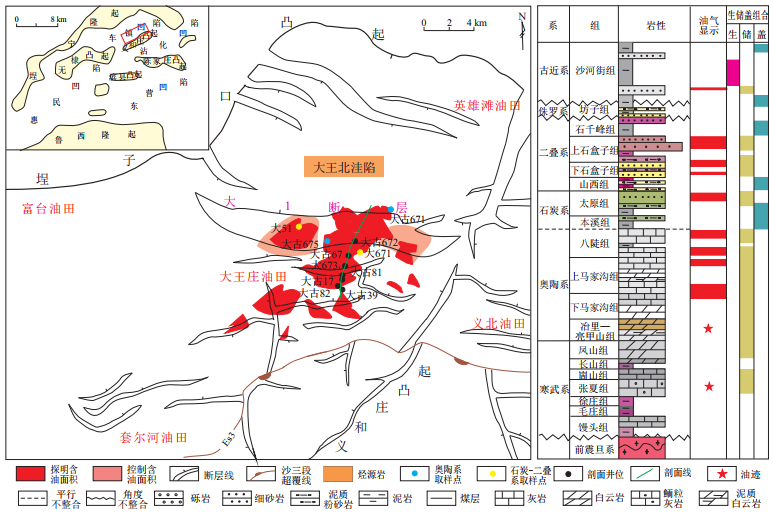
Characteristics of reservoir fluid inclusions and hydrocarbon charging process in the Dawangzhuang buried hill zone of Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
-
摘要: 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷古生界潜山油气藏储量巨大,但成藏过程复杂,制约了油气勘探进程。为了探明其油气充注与调整改造过程,以大王庄潜山带为例,利用包裹体岩相学、显微测温及烃包裹体丰度分析等技术,对古生界油气成藏进行了研究。研究区古生界储层烃包裹体发育,奥陶系烃包裹体呈淡黄色、蓝绿色荧光,沿方解石脉及颗粒愈合缝分布,沥青包裹体与油质沥青仅在大古671油藏少量分布,均一温度主峰为80~90℃和100~110℃;石炭—二叠系储层烃包裹体呈蓝绿色荧光,赋存于石英颗粒微裂隙及次生加大边,均一温度主峰为100~110℃。结合烃源岩生排烃期可以得出,研究区古生界存在两期油气充注:第一期发生在东营组沉积晚期(27~25 Ma),为古生界小规模成藏,以奥陶系为主;第二期发生在馆陶组沉积末期—明化镇组沉积末期(5~2 Ma),为奥陶系和石炭—二叠系大规模成藏。大古671井区附近沥青包裹体的发育以及含烃包裹体有效网格(EGOI)显示古油水界面低于现今油水界面的现象,与明化镇组沉积末期(2 Ma)大1断层的活动有关,导致油气藏发生了局部调整,范围变小。Abstract: The Dawangzhuang buried hill zone is a typical representative of Paleozoic oil and gas exploration in the Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, and has experienced a complicated accumulation process. Using petrographic observation, microthermometry and abundance of hydrocarbon inclusions, the Paleozoic hydrocarbon charging process in Dawangzhuang buried hill zone was discussed. The study shows that the Paleozoic reservoirs developed hydrocarbon inclusions in the study area. Ordovician hydrocarbon inclusions with pale yellow and blue-green fluorescence distributed along the calcite veins and particle healing joints. Asphalt inclusions and oleaginous are only distributed in Dagu 671 oil reservoir with a small scale. The main peaks of the homogenization temperature are from 80 ℃ to 90 ℃ and from 100 ℃ to 110 ℃; Carboniferous-Permian hydrocarbon inclusions with blue-green fluorescent distributed along the micro-cracks of quartz particles and secondary enlarged edges. The main peak of the homogenization temperature is from 100 ℃ to 110 ℃. Combining with the hydrocarbon generation and expulsion periods of source rocks, it can be concluded that there are two stages of hydrocarbon charging in the Paleozoic in the study area. The first stage of oil and gas charging occurred in the late Dongying period (27~25 Ma), which was a small-scale accumulation of Paleozoic, mainly in the Ordovician; the second stage of oil and gas charging occurred from the end of Guantao period to the end of Minghuazhen period (5~2 Ma), which was a large-scale accumulation of Ordovician and Carboniferous-Permian. The development of asphalt inclusions near the Dagu 671 well area and the fact shown by the Effective Grids containing Oil Inclusions (EGOI) that the ancient oil-water interface is lower than the current one are related to the activity of the Da 1 fault at the end of the Minghuazhen period (2 Ma), resulting in local adjustments and smaller scope of oil and gas reservoir.
-
图 2 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷大王庄潜山带典型包裹体观测样品手标本
a.大古671井,O2mx,3 087.6 m,深灰色灰岩见溶蚀孔与方解石脉;b.大古671井,O2mx,3 121.2 m,灰白色灰岩见垂直孔缝;c.大古675井,O2mx,3 403.4 m,深灰色灰岩见方解石脉;d.大古675井,O2ms,2 922.3 m,灰白色灰岩见方解石脉;e.大671井,C-P,2 970.2 m,深灰色含砾砂岩见油气显示;f.大671井,C-P,2 966.8 m,深灰色泥质粉砂岩见铁质侵染;g.大51井,C-P,2 941.0 m,灰色细砂岩孔隙发育;h.大51井,C-P,3 637.5 m,灰色碳质砂岩
Figure 2. Typical inclusion sample hand specimen of Dawangzhuang buried hill zone in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
图 3 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷大王庄潜山带奥陶系流体包裹体镜下分布特征
a.大古671井,O2ms,2 941.0 m,烃包裹体分布在方解石颗粒表面,透射光,×50;b.大古671井,O2ms,2 941.0 m,淡黄色荧光烃包裹体分布在方解石颗粒表面,荧光,×50;c.大古675井,O2ms,2 922.3 m,烃包裹体呈线状分布在方解石愈合缝及方解石脉,透射光,×50;d.大古675井,O2ms,2 922.3 m,蓝绿色荧光烃包裹体呈线状分布在方解石愈合缝及方解石脉,荧光,×50;e.大古675井,O2ms,2 922.3 m,烃包裹体成群分布在方解石脉,透射光,×20;f.大古675井,O2ms,2 922.3 m,蓝绿色荧光烃包裹体分布在方解石脉,荧光,×20;g.大古671井,O2ms,3 043.6 m,烃包裹体与沥青类包裹体呈带状分布在方解石颗粒表面,透射光,×50;h.大古671井,O2ms,3 043.6 m,淡黄色荧光、蓝绿色荧光烃包裹体与沥青类包裹体呈带状分布在方解石颗粒表面,荧光,×50
Figure 3. Microscopic characteristics of Ordovician fluid inclusions of Dawangzhuang buried hill zone in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
图 4 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷大王庄潜山带奥陶系储层沥青镜下特征
a.大古671井,O2ms,3 043.6 m,沥青充填于岩石基质溶孔内,透射光,×20;b.大古671井,O2ms,3 043.6 m,淡蓝色沥青充填于岩石基质溶孔内,荧光,×20;c.大古671井,O2ms,3 043.6 m,沥青充填于岩石微裂缝内,透射光,×20;d.大古671井,O2ms,3 043.6 m,淡蓝色沥青充填于岩石微裂缝内,荧光,×20
Figure 4. Microscopic characteristics of asphalt in Ordovician reservoir of Dawangzhuang buried hill zone in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
图 5 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷大王庄潜山带石炭—二叠系流体包裹体镜下分布特征
a.大671井,2 760.5 m,烃包裹体沿切及石英颗粒微裂隙分布,透射光,×50;b.大671井,2 760.5 m,蓝绿色荧光烃包裹体沿切及石英颗粒微裂隙分布,荧光,×50;c.大671井,2 567.4 m,烃包裹体沿石英加大边内侧成带分布,透射光,×50;d.大671井,2 567.4 m,蓝绿色荧光烃包裹体沿石英加大边内侧成带分布,荧光,×50;e.大671井,2 794.2 m,烃包裹体沿石英颗粒微裂隙分布,透射光,×50;f.大671井,2 794.2 m,蓝绿色荧光烃包裹体沿石英颗粒微裂隙分布,荧光,×50;g.大51井,3 867.0 m,盐水包裹体分布在石英颗粒表面,透射光,×20;h.大51井,3 867.0 m,无荧光盐水包裹体分布在石英颗粒表面,荧光,×20
Figure 5. Microscopic characteristics of Carboniferous-Permian fluid inclusions of Dawangzhuang buried hill zone in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
图 8 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷大王庄潜山带大古671井奥陶系上马家沟组储层烃包裹体EGOI分布
a.2 941 m,微裂缝及方解石愈合缝里总有效网格数12个,含烃包裹体有效网格数3个,EGOI值为3/12=25%,透射光,×20;b.2 941 m,淡黄色荧光烃包裹体沿微裂缝及方解石愈合缝分布,荧光,×20;c.2 982 m,方解石愈合缝里总有效网格数11个,含烃包裹体有效网格数2个,EGOI值为2/11=18.2%,透射光,×20;d.2 982 m,淡黄色荧光与蓝绿色荧光烃包裹体分布在方解石愈合缝,荧光,×20;e.3 043.6 m,沥青充填于岩石微裂缝中,透射光,×20;f.3 043.6 m,淡蓝色沥青充填于岩石微裂缝中,荧光,×20;g.3 043.6 m,方解石愈合缝里总有效网格数38个,含烃包裹体有效网格数10个,EGOI值为10/38=26.3%,透射光,×20;h.3 043.6 m,淡黄色荧光、蓝绿色荧光烃包裹体与沥青类包裹体沿方解石愈合缝分布,荧光,×20
Figure 8. Distribution of EGOI values of hydrocarbon inclusions in well Dagu 671 of Dawangzhuang buried hill zone in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
表 1 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷大王庄潜山带包裹体观测样品信息
Table 1. Data sheet of inclusion samples of Dawangzhuang buried hill zone in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
编号 井号 深度/m 层位 岩性描述 1 大古675 2 922.3 O2ms 灰白色灰岩 2 大古675 3 147.6 O2ms 灰色白云岩 3 大古675 3 403.4 O2mx 深灰色灰岩 4 大古671 2 941.0 O2ms 灰白色灰岩 5 大古671 2 969.0 O2ms 深灰色灰岩 6 大古671 2 982.0 O2ms 深灰色灰岩 7 大古671 3 000.8 O2ms 深灰色泥晶灰岩 8 大古671 3 043.6 O2ms 深灰色灰岩 9 大古671 3 087.6 O2mx 深灰色灰岩 10 大古671 3 121.2 O2mx 灰白色灰岩 11 大671 2 555.3 C-P 灰色细砂岩 12 大671 2 567.4 C-P 灰黄色粉细砂岩 13 大671 2 760.5 C-P 深灰色细砂岩 14 大671 2 794.2 C-P 深灰色细砂岩 15 大671 2 966.8 C-P 深灰色泥质粉砂岩 16 大671 2 970.2 C-P 深灰色含砾砂岩 17 大51 3 637.5 C-P 灰色泥质砂岩 18 大51 3 867.0 C-P 灰色细砂岩 -
[1] 马立驰, 王永诗, 景安语. 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷下古生界潜山勘探新认识与新发现[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28(1): 10-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202101003.htmMA Lichi, WANG Yongshi, JING Anyu. New understanding and discovery in exploration of Lower Paleozoic buried hills in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2021, 28(1): 10-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202101003.htm [2] 马立驰, 王永诗, 景安语. 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷隐蔽潜山油藏新发现及其意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(1): 13-18. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001013MA Lichi, WANG Yongshi, JING Anyu. Discovery and significance of subtle buried hills in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(1): 13-18. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202001013 [3] 林会喜, 熊伟, 王勇济, 等. 济阳坳陷埕岛潜山油气成藏特征[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202101002.htmLIN Huixi, XIONG Wei, WANG Yong, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation in Chengdao buried hill of Jiyang Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2021, 28(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202101002.htm [4] 李丕龙, 张善文, 王永诗, 等. 多样性潜山成因、成藏与勘探: 以济阳坳陷为例[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003.LI Pilong, ZHANG Shanwen, WANG Yongshi, et al. Thegenesis, accumulation and exploration of diversity buried hills: taking Jiyang Depression as an example[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2003. [5] 孟卫工, 陈振岩, 李湃, 等. 潜山油气藏勘探理论与实践: 以辽河坳陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2009, 36(2): 136-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200902001.htmMENG Weigong, CHEN Zhenyan, LI Pai, et al. Exploration theories and practices of buried-hill reservoirs: a case from Liaohe depressions[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2009, 36(2): 136-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200902001.htm [6] 史长林, 纪友亮, 廖前进, 等. 黄骅坳陷奥陶系碳酸盐岩潜山成藏模式[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2009, 16(6): 29-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200906012.htmSHI Changlin, JI Youliang, LIAO Qianjin, et al. Accumulation patterns of Ordovician carbonate buried hill in Huanghua Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology & Recovery Efficiency, 2009, 16(6): 29-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200906012.htm [7] 季玉新, 王立歆, 王军, 等. 综合地球物理技术在济阳坳陷潜山油藏勘探开发中的应用[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2004, 27(3): 157-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ200403000.htmJI Yuxin, WANG Lixin, WANG Jun, et al. Application of integrated geophysical technology in the exploration of buried-hill reservoirs in Jiyang Sag[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 2004, 27(3): 157-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ200403000.htm [8] 谢玉洪, 罗小平, 王德英, 等. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷西次洼中生界古潜山油气成藏过程[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(5): 15-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201905002.htmXIE Yuhong, LUO Xiaoping, WANG Deying, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation of composite-buried hill reservoirs in the western subsag of Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(5): 15-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201905002.htm [9] 刘可禹, BOURDET J, 张宝收, 等. 应用流体包裹体研究油气成藏: 以塔中奥陶系储集层为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(2): 171-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201302004.htmLIU Keyu, BOURDET J, ZHANG Baoshou, et al. Hydrocarbon charge history of the Tazhong Ordovician reservoirs, Tarim Basin as revealed from an integrated fluid inclusion study[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(2): 171-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201302004.htm [10] 金强, 毛晶晶, 杜玉山, 等. 渤海湾盆地富台油田碳酸盐岩潜山裂缝充填机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(4): 454-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201504007.htmJIN Qiang, MAO Jingjing, DU Yushan, et al. Fracture filling mechanisms in the carbonate buried-hill of Futai Oilfield in Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(4): 454-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201504007.htm [11] 朱海龙, 杜威, 李晓庆. 济阳坳陷车镇凹陷大王庄缓坡带同生断层与油气聚集[J]. 贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 27(5): 29-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDI201005009.htmZHU Hailong, DU Wei, LI Xiaoqing. The contemporaneous faults and oil-gas accumulation in Dawangzhuang Gentle Slope in the Chezhen Sag, Jiyang Depression[J]. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Science), 2010, 27(5): 29-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDI201005009.htm [12] 范昆. 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷上古生界油气成藏主控因素研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2008.FAN Kun. The main controlling factors research of oil gas forming in Upper Paleozoic in Jiyang Depression in Bohaiwan Basin[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2008. [13] 任拥军, 杨景楠, 邱隆伟, 等. 大王北洼陷烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J]. 高校地质学报, 2010, 16(1): 63-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201001011.htmREN Yongjun, YANG Jingnan, QIU Longwei, et al. Organic geoche-mical characteristics of source rocks in Dawangbei Subsag[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2010, 16(1): 63-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201001011.htm [14] EADINGTON P J, HAMILTON P J, BAI G P. Fluid history analysis: a prospect evaluation[J]. The APPEA Journal, 1991, 31(1): 282-294. [15] 施继锡, 余孝颖. 碳酸盐岩中包裹体有机质特征与非常规油气评价[J]. 矿物学报, 1996, 16(2): 103-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB199602001.htmSHI Jixi, YU Xiaoying. Characteristics of organic matter in carbonate rocks and unconventional evaluation of oil and gas[J]. Acta Minera-logica Sinica, 1996, 16(2): 103-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB199602001.htm [16] ZHANG Yigang, FRANTZ J D. Determination of the homogenization temperatures and densities of supercritical fluids in the system NaCl-KCl-CaCl2-H2O using synthetic fluid inclusions[J]. Chemical Geology, 1987, 64(3/4): 335-350. [17] HALL D L, STERNER S M, BODNAR R J. Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O solutions[J]. Economic Geology, 1988, 83(1): 197-202. [18] EADINGTON P J, LISK M, KRIEGER F W. Identifying oil well sites: US, 5543616[P]. 1996-08-06. [19] LISK M, O'BRIEN G W, EADINGTON P J. Quantitative evaluation of the oil-leg potential in the Oliver Gas Field, Timor Sea, Australia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(9): 1531-1542. [20] PARNELL J. Potential of palaeofluid analysis for understanding oil charge history[J]. Geofluids, 2010, 10(1): 73-82. [21] ZHANG Nai, PAN Wenlong, TIAN Long, et al. Using a modified GOI index (effective grid containing oil inclusions) to indicate oil zones in carbonate reservoirs[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2015, 89(3): 902-910. [22] 张家震, 徐备. 车镇凹陷含油气系统划分及勘探方向[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 24(2): 13-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200902005.htmZHANG Jiazhen, XU Bei. Division of petroluem system and exploration direction in Chezhen Sag[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 24(2): 13-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200902005.htm [23] 王艳. 沾化、车镇凹陷盆地结构特征分析[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学, 2011.WANG Yan. Basin structure characteristics analysis of Zhanhua Sag and Chezhen Sag[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum, 2011. [24] 李大伟. 新构造运动与渤海湾盆地上第三系油气成藏[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(2): 170-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200402008.htmLI Dawei. Neotectonism and Neogene oil and gas pools in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2004, 25(2): 170-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200402008.htm -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号