Characterization of the length of structural fractures in low permeability reservoirs and its application: a case study of Longwangmiao Formation in Moxi-Gaoshiti areas, Sichuan Basin
-
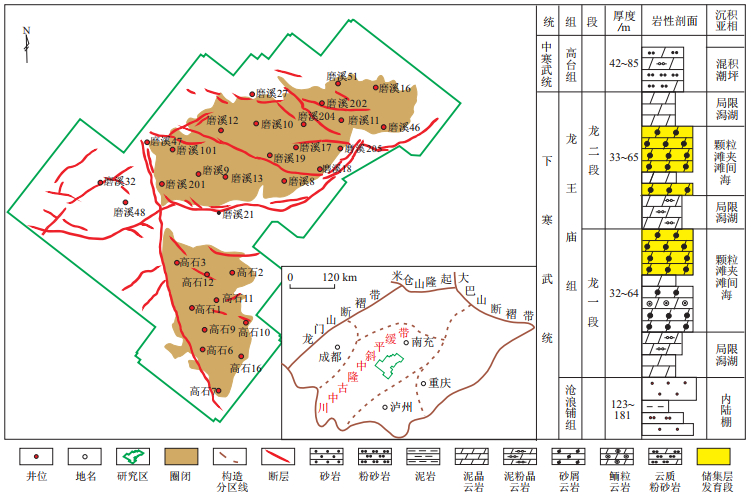
摘要: 为明确低渗透储层构造裂缝长度定量表征方法,以四川盆地磨溪—高石梯地区寒武系龙王庙组为例,综合采用岩心裂缝统计及岩石力学实验方法,从构造应力场的角度推导低渗透储层构造裂缝长度的关系式。该方法将裂缝长度与裂缝体密度、应变能密度及岩体应力状态联系起来,建立了裂缝长度与裂缝体密度之间的定量计算关系。结果表明:裂缝长度与裂缝数量呈负指数幂关系;裂缝体密度与应变能密度呈正比线性关系;裂缝长度与裂缝体密度呈负指数幂关系。将推导的裂缝长度公式应用于磨溪—高石梯地区龙王庙组,数值模拟结果显示:裂缝体密度值普遍介于1~5 m2/m3,最高为9 m2/m3,高值区主要分布于断层及周边地区;裂缝长度主要介于1~20 m,断层及周边区域裂缝密而短,长度普遍小于3 m。Abstract: In order to classify the quantitative characterization method of structural fracture length in low-permeability reservoirs, the Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation of Moxi-Gaoshiti areas in the Sichuan Basin is taken an example in this study. The relationship between structural fracture lengths of low-permeability reservoirs was derived from the perspective of structural stress field by the means of core fracture statistics and rock mechanical experiment. Quantitative relationships between fracture length and fracture volume density, strain energy density and rock mass stress state were established. Results showed a negative exponential power relationship between fracture length and number, a proportional linear relationship between fracture volume density and strain energy density, and a negative exponential power relationship between fracture length and volume density. The derived fracture length formula was applied to the Longwangmiao Formation in Moxi-Gaoshiti areas. Numerical simulation results showed that fracture density generally ranges from 1-5 m2/m3, and the highest value is 9 m2/m3, mainly distributed in fault and its surrounding areas. Fracture length is mainly between 1-20 m. The fractures in fault and surrounding areas are dense and short, usually less than 3 m.
-
表 1 四川盆地磨溪—高石梯地区不同应力承载比例下裂缝长度及数量
Table 1. Fracture length and quantity under different stress levels in Moxi-Gaoshiti areas, Sichuan Basin
承载比例(σ/σc) 裂缝长度/mm < 2 2~3 3~4 4~6 6~8 8~10 >10 长度平均值 0 72 16 2 0 0 0 0 1.32 0.50 133 40 7 1 0 0 0 1.45 0.65 142 42 7 4 0 0 0 1.49 0.85 188 43 8 8 2 1 0 1.52 1.00 232 52 18 16 5 4 4 1.90 1.18 286 73 23 18 6 5 5 1.88 裂缝条数均值 175.5 43.3 10.8 7.8 2.2 1.7 1.5 表 2 四川盆地磨溪—高石梯地区龙王庙组样品实验参数
Table 2. Experimental parameters of samples from Longwangmiao Formation in Moxi-Gaoshiti areas, Sichuan Basin
试样编号 实验应力σ/ MPa 实验应变ε/ 10-4 承载比例(σ/σc) 裂缝体密度Dvf/(m2·m-3) 应变能密度ω/(J·m-3) 样品状态 ② 165.8 53.0 1.18 44.0 439 370.0 完全破碎 ③ 70.3 17.7 0.50 3.2 62 215.5 发育微裂缝 ④ 91.3 24.3 0.65 6.6 110 929.5 发育微裂缝 ⑤ 119.4 31.7 0.85 13.4 189 249.0 产生宏观裂缝 ⑥ 140.5 42.5 1.00 40.6 298 562.5 宏观裂缝扩展 表 3 四川盆地磨溪—高石梯区块地质模型的岩石力学参数
Table 3. Rock mechanical parameters of geological model in Moxi-Gaoshiti areas, Sichuan Basin
岩体 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 密度/(kg·m-3) 断层(古) 85 0.30 2 780 断层(今) 50 0.19 2 200 储集体 79 0.29 2 744 夹层 65 0.31 2 600 围岩 80 0.28 2 750 -
[1] 赵思远, 贾自力, 吴长辉, 等. 低渗透油藏注水诱发裂缝实验研究: 以鄂尔多斯盆地吴起吴仓堡长9油藏为例[J]. 非常规油气, 2021, 8(3): 73-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FCYQ202103011.htmZHAO Siyuan, JIA Zili, WU Changhui, et al. Experimental study on waterflood induced fractures simulation in low permeability reservoir: a case study from Chang 9 reservoir in Wuqi Wucangbao, Ordos Basin[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2021, 8(3): 73-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FCYQ202103011.htm [2] OLSON J E, LAUBACH S E, LANDER R H. Natural fracture characterization in tight gas sandstones: integrating mechanics and diagenesis[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(11): 1535-1549. doi: 10.1306/08110909100 [3] 吕文雅, 曾联波, 张俊辉, 等. 川中地区中下侏罗统致密油储层裂缝发育特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2016, 38(2): 226-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201602008.htmLV Wenya, ZENG Lianbo, ZHANG Junhui, et al. Development characteristics of fractures in the Middle-Lower Jurassic tight oil reservoirs in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2016, 38(2): 226-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX201602008.htm [4] 霍健, 王星皓, 罗超, 等. 川南地区龙马溪组页岩储层裂缝特征[J]. 工程地质学报, 2021, 29(1): 171-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202101018.htmHUO Jian, WANG Xinghao, LUO Chao, et al. Fracture characte-ristics of Longmaxi shale in southern Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(1): 171-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202101018.htm [5] 黎静容, 朱桦, 冯晓明, 等. 川东北陆相储层裂缝特征差异性及对产能的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(6): 742-747. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201606742LI Jingrong, ZHU Hua, FENG Xiaoming, et al. Differences of fracture characteristics and the influence on productivity in the northeastern Sichuan continental basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(6): 742-747. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201606742 [6] 梅丹, 胡勇, 王倩. 裂缝对气藏储层渗透率及气井产能的贡献[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(5): 769-772. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201905769MEI Dan, HU Yong, WANG Qian. Experimental study on fracture contribution to gas reservoir permeability and well capacity[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(5): 769-772. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201905769 [7] 彭红利. 碳酸盐岩油气藏构造裂缝分布预测及定量参数场形成初步研究[D]. 南充: 西南石油大学, 2005.PENG Hongli. The preliminary research on carbonate gas reservoir structural fracture prediction and the quantitative parameter field formation[D]. Nanchong: Southwest Petroleum University, 2005. [8] 蒋有录, 李明阳, 王良军, 等. 川东北巴中—通南巴地区须家河组致密砂岩储层裂缝发育特征及控制因素[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(5): 1525-1537. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202005012.htmJIANG Youlu, LI Mingyang, WANG Liangjun, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of tight sandstone reservoir fractures of the Xujiahe Formation in the Bazhong-Tongnanba area, northeast Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(5): 1525-1537. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202005012.htm [9] 董少群, 吕文雅, 夏东领, 等. 致密砂岩储层多尺度裂缝三维地质建模方法[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(3): 627-637. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202003019.htmDONG Shaoqun, LU Wenya, XIA Dongling, et al. An approach to 3D geological modeling of multi-scaled fractures in tight sandstone reservoirs[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(3): 627-637. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202003019.htm [10] 鞠玮, 尤源, 冯胜斌, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7油层组致密砂岩储层层理缝特征及成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(3): 596-605.JU Wei, YOU Yuan, FENG Shengbin, et al. Characteristics and genesis of bedding-parallel fractures in tight sandstone reservoirs of Chang 7 oil layer, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(3): 596-605. [11] 季宗镇, 戴俊生, 汪必峰, 等. 构造裂缝多参数定量计算模型[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 34(1): 24-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201001007.htmJI Zongzhen, DAI Junsheng, WANG Bifeng, et al. Multi-parameter quantitative calculation model for tectonic fracture[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2010, 34(1): 24-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201001007.htm [12] 戴俊生, 冯建伟, 李明, 等. 砂泥岩间互地层裂缝延伸规律探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(2): 277-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201102031.htmDAI Junsheng, FENG Jianwei, LI Ming, et al. Discussion on the extension law of structural fracture in sand-mud interbed formation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(2): 277-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201102031.htm [13] 冯建伟, 戴俊生, 马占荣, 等. 低渗透砂岩裂缝参数与应力场关系理论模型[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(4): 664-671. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201104017.htmFENG Jianwei, DAI Junsheng, MA Zhanrong, et al. The theore-tical model between fracture parameters and stress field of low-permeability sandstones[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(4): 664-671. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201104017.htm [14] 丁中一, 钱祥麟, 霍红, 等. 构造裂缝定量预测的一种新方法: 二元法[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1998, 19(1): 1-7.DING Zhongyi, QIAN Xianglin, HUO Hong, et al. A new method for quantitative prediction of tectonic fractures: two-factor method[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1998, 19(1): 1-7. [15] 李辉, 林承焰, 任丽华, 等. 基于岩相—断层破碎带耦合约束的构造裂缝预测研究: 以博兴洼陷大芦湖油田沙三中亚段为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2020, 49(2): 305-317. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202002012.htmLI Hui, LIN Chengyan, REN Lihua, et al. Tectonic fracture prediction based on the coupling constraint of lithofacies and fault damage zone: a case study of the 2nd sand group of middle Es3 member in Daluhu Oilfield, Boxing Subsag[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2020, 49(2): 305-317. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202002012.htm [16] 李蒙, 商晓飞, 赵华伟, 等. 基于likelihood地震属性的致密气藏断裂预测: 以四川盆地川西坳陷新场地区须二段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(6): 1299-1309.LI Meng, SHANG Xiaofei, ZHAO Huawei, et al. Prediction of fractures in tight gas reservoirs based on likelihood attribute: a case study of the 2nd member of Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang area, Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(6): 1299-1309. [17] 任启强, 金强, 冯振东, 等. 和田河气田奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层关键期构造裂缝预测[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(6): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX202006002.htmREN Qiqiang, JIN Qiang, FENG Zhendong, et al. Prediction of key period fractures of Ordovician carbonate reservoir in Hetianhe Gas Field[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2020, 44(6): 1-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX202006002.htm [18] 穆龙新, 赵国良, 田中元, 等. 储层裂缝预测研究[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2009.MU Longxin, ZHAO Guoliang, TIAN Zhongyuan. The research of natural fracture for low permeability reservoirs[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2009. [19] 刘子雄, 常菁铉, 李新发, 等. 基于裂缝监测的致密储层压裂裂缝走向预测[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(6): 846-854. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202006011.htmLIU Zixiong, CHANG Jingxuan, LI Xinfa, et al. Fracturing direction prediction based on fracturing monitoring of tight gas reservoir[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(6): 846-854. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202006011.htm [20] 张林, 赵喜民, 刘池洋, 等. 沉积作用对水力压裂裂缝缝长的限制作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(2): 201-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200802012.htmZHANG Lin, ZHAO Ximin, LIU Chiyang, et al. Deposition confines hydraulic fracture length[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(2): 201-204. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200802012.htm [21] 尹丛彬, 李彦超, 王素兵, 等. 页岩压裂裂缝网络预测方法及其应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(4): 60-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201704011.htmYIN Congbin, LI Yanchao, WANG Subing, et al. Methodology of hydraulic fracture network prediction in shale reservoirs and its application[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(4): 60-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201704011.htm [22] 王翔. 川中高石梯—磨溪地区震旦系灯影组储层评价[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2017.WANG Xiang. Reservoir evaluation of Sinian Dengying Formation in the Gaoshiti-Moxi area, middle Sichuan Basin, China[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2017. [23] 刘树根, 孙玮, 罗志立, 等. 兴凯地裂运动与四川盆地下组合油气勘探[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(5): 511-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201305003.htmLIU Shugen, SUN Wei, LUO Zhili, et al. Xingkai taphrogenesis and petroleum exploration from Upper Sinian to Cambrian strata in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 40(5): 511-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201305003.htm [24] 钟勇, 李亚林, 张晓斌, 等. 川中古隆起构造演化特征及其与早寒武世绵阳—长宁拉张槽的关系[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 41(6): 703-712.ZHONG Yong, LI Yalin, ZHANG Xiaobin, et al. Evolution characteristics of central Sichuan palaeouplift and its relationship with Early Cambrian Mianyang-Changning intracratonic sag[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2014, 41(6): 703-712. [25] 李宗银, 姜华, 汪泽成, 等. 构造运动对四川盆地震旦系油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(3): 23-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201403006.htmLI Zongyin, JIANG Hua, WANG Zecheng, et al. Control of tectonic movement on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Sinian strata, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(3): 23-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201403006.htm [26] 魏国齐, 杨威, 杜金虎, 等. 四川盆地高石梯—磨溪古隆起构造特征及对特大型气田形成的控制作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(3): 257-265.WEI Guoqi, YANG Wei, DU Jinhu, et al. Tectonic features of Gaoshiti-Moxi paleo-uplift and its controls on the formation of a giant gas field, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(3): 257-265. [27] 田兴旺, 杨岱林, 钟佳倚, 等. 基于CT成像技术的白云岩储层微观表征: 以川中磨溪—龙女寺台内地区震旦系灯影组四段为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(5): 1264-1274.TIAN Xingwang, YANG Dailin, ZHONG Jiayi, et al. Microscopic characterization of dolomite reservoirs by CT imaging: a case study of the Dengsi Formation in Moxi-Longnvsi area, central Sichuan[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(5): 1264-1274. [28] 张志镇. 岩石变形破坏过程中的能量演化机制[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2013.ZHANG Zhizhen. Energy evolution mechanism during rock deformation and failure[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2013. [29] 谢和平, 鞠杨, 黎立云, 等. 岩体变形破坏过程的能量机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(9): 1729-1740.XIE Heping, JU Yang, LI Liyun, et al. Energy mechanism of deformation and failure of rock masses[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(9): 1729-1740. [30] 陈颙, 黄庭芳, 刘恩儒. 岩石物理学[M]. 北京: 中国科技大学出版社, 2009.CHEN Yong, HUANG Tingfang, LIU Enru. Rock physics[M]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology of China, 2009. [31] 赵建生. 断裂力学及断裂物理[M]. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2003.ZHAO Jiansheng. Fracture mechanics and fracture physics[M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 2003. [32] 孟庆彬, 王从凯, 黄炳香, 等. 三轴循环加卸载条件下岩石能量演化及分配规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(10): 2047-2059. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202010009.htmMENG Qingbin, WANG Congkai, HUANG Bingxiang, et al. Rock energy evolution and distribution law under triaxial cyclic loading and unloading conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(10): 2047-2059. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202010009.htm [33] 陈勉, 金衍, 张广清. 石油工程岩石力学基础[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011.CHEN Mian, JIN Yan, ZHANG Guangqing. Fundamentals of rock mechanics in petroleum engineering[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011. [34] 宋惠珍. 裂缝性储集层研究理论与方法[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2001.SONG Huizhen. Theory and method of fractured reservoir research[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2001. -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号