Distribution and genetic mechanisms of connected pore systems in continental shale reservoirs: a case study of Xujiahe Formation of Upper Triassic, Western Sichuan Depression
-
摘要: 为揭示陆相页岩储层连通孔隙系统的形成机制,指导页岩气高效开发,以川西坳陷上三叠统须家河组陆相页岩为例,综合运用X衍射、场发射扫描电镜、低温气体吸附、高压压汞和核磁共振冻融等分析测试方法,研究了样品的矿物组分、全孔径分布特征和孔隙连通特征,并分析了孔隙连通性的主控因素。川西坳陷研究区上三叠统须家河组陆相页岩黏土矿物含量最高,石英含量次之;页岩孔径分布复杂,其中中孔最为发育,是孔体积(占87.33%)和比表面积(占49.19%)的主要贡献者;20~50 nm孔隙连通性较好,是研究区须家河组主要的连通孔隙发育区间;须家河组陆相页岩主要发育黏土矿物晶间孔,粒内溶孔较少,基本不发育有机质孔,广泛发育微裂缝,其中黏土矿物晶间孔—微裂缝孔隙组合是研究区主要的连通孔隙类型;黏土矿物及石英等脆性矿物的含量及排列方式控制连通孔隙的发育及分布。基于以上结果总结了陆相页岩连通孔隙的3种潜在发育机制:发育在黏土矿物与脆性矿物基质上的黏土矿物晶间孔—微裂缝组合连通性最好;黏土矿物集合体内的黏土矿物晶间孔连通性次之;有机—黏土复合体内的有机孔—黏土矿物晶间孔连通性最差。Abstract: The distribution and genetic mechanisms of connected pore systems in continental shale reservoirs were analyzed in this paper to enhance the high-efficiency exploration of shale gas. A case study was made with the continental shale of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Western Sichuan Depression. Various experimental methods such as X-ray diffraction, field emission-scanning electron microscopy, low temperature gas adsorption, high-pressure mercury injection and nuclear magnetic resonance cryoporometry were applied to study its mineral composition, distribution of pore-size and pore connectivity, and the main constrains for pore connectivity were discussed. The continental shale of the Xujiahe Formation in the study area has a high content of clay minerals, followed by quartz. The pore-size distribution is complex, and the mesopores in the range of 4-50 nm is the main contributor to pore volume (87.33%) and specific surface area (49.19%). The pores having the size between 20-50 nm appeared to have better pore connectivity and are the major type of connected pores. The continental shale developed various types of pore, predominantly composed of clay intercrystalline pores, with minor dissolved pores and organic pores. Microfractures were widely developed and formed the dominant connective pore assemblage together with clay intercrystalline pores. The development and distribution of connected pores were controlled by the contents and arrangement of brittle minerals such as clay minerals and quartz. Based on the experimental results, some development mechanisms of connected pores in continental shale were concluded. The combination of intercrystalline pores and microfractures developed on the matrix of clay minerals and brittle minerals shows the best connectivity, followed by the clay intercrystalline pores in clay minerals, while the organic pores and clay intercrystalline pores in organic-clay complexes show the lowest connectivity.
-
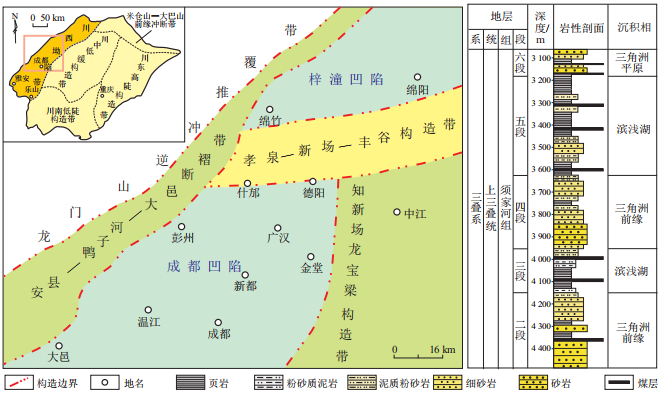
图 1 川西坳陷研究区区域位置及地层柱状图[21]
Figure 1. Location and stratigraphic column of study area in Western Sichuan Depression
表 1 川西坳陷研究区三叠系须家河组陆相页岩孔体积统计
Table 1. Statistics of pore volume of continental shale of Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Western Sichuan Depression
样品编号 深度/m 孔体积/(mL·g-1) 孔体积比例/% 微孔 中孔 宏孔 总孔体积 微孔 中孔 宏孔 LD-1 1 346.1 0.008 2 0.072 4 0.001 7 0.082 3 9.96 87.97 2.07 LD-2 1 367.3 0.007 8 0.072 8 0.001 4 0.082 0 9.51 88.78 1.71 LD-3 1 376.1 0.006 9 0.055 2 0.001 9 0.064 0 10.78 86.25 2.97 LD-4 1 385.5 0.006 9 0.063 2 0.002 0 0.072 1 9.57 87.66 2.77 LD-5 1 402.4 0.005 4 0.052 8 0.003 2 0.061 4 8.79 85.99 5.21 平均 0.007 0 0.063 3 0.002 0 0.072 4 9.72 87.33 2.95 表 2 川西坳陷研究区三叠系须家河组陆相页岩比表面积统计
Table 2. Statistics of pore specific surface area of continental shale of Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Western Sichuan Depression
样品编号 深度/m 比表面积/(m2·g-1) 比表面积比例/% 微孔 中孔 宏孔 总比表面积 微孔 中孔 宏孔 LD-1 1 346.1 24.077 8 25.204 0.037 8 49.319 6 48.82 51.10 0.08 LD-2 1 367.3 22.369 8 23.086 0.172 7 45.628 5 49.03 50.60 0.38 LD-3 1 376.1 21.703 4 19.752 0.215 4 41.670 8 52.08 47.40 0.52 LD-4 1 385.5 21.946 7 20.129 0.217 6 42.293 3 51.89 47.59 0.52 LD-5 1 402.4 16.218 6 15.942 0.217 6 32.378 2 50.09 49.24 0.67 平均 21.263 3 20.823 0.172 2 42.258 1 50.38 49.19 0.43 -
[1] 黄金亮, 董大忠, 李建忠, 等. 陆相页岩储层特征及其影响因素: 以四川盆地上三叠统须家河组页岩为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(2): 158-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602019.htmHUANG Jinliang, DONG Dazhong, LI Jianzhong, et al. Reservoir characteristics and its influence on continental shale: an example from Triassic Xujiahe Formation shale, Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2): 158-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602019.htm [2] 张洪, 李靖, 郑庆龙, 等. 页岩孔缝结构及海相与陆相储层特征差异研究[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2017, 39(1): 1-6.ZHANG Hong, LI Jing, ZHENG Qinglong, et al. Studies on the structures of pores and fractures in shale reservoirs and the characteristic differences between marine and continental shale reservoirs[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2017, 39(1): 1-6. [3] 庞铭, 陈华兴, 唐洪明, 等. 海相页岩与陆相页岩微观孔隙结构差异: 以川南龙马溪组、鄂尔多斯延长组为例[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2018, 41(2): 29-36.PANG Ming, CHEN Huaxing, TANG Hongming, et al. Differences of micropore structure between marine shale and continental shale: examples from Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin and Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2018, 41(2): 29-36. [4] 李廷微, 姜振学, 宋国奇, 等. 陆相和海相页岩储层孔隙结构差异性分析[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(1): 65-71.LI Tingwei, JIANG Zhenxue, SONG Guoqi, et al. Analysis of differences in pore structure between continental and marine shale reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(1): 65-71. [5] 周道容, 李延钧, 陈义才, 等. 川西南部地区须家河组页岩气资源潜力研究[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 10(10): 43-45.ZHOU Daorong, LI Yanjun, CHEN Yicai, et al. Research of shale resource potential of Xujiahe Formation in the southwest of Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 10(10): 43-45. [6] 郑定业, 庞雄奇, 张可, 等. 四川盆地上三叠系须家河组油气资源评价[J]. 特种油气藏, 2017, 24(4): 67-72.ZHENG Dingye, PANG Xiongqi, ZHANG Ke, et al. Oil & gas resource evaluation for Xujiahe Formation in Upper Triassic series in Sichuan Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2017, 24(4): 67-72. [7] 张慧, 林伯伟, 卞建玲, 等. 富有机质海相与陆相页岩的对比研究: 以南方早古生代和华北石炭—二叠纪页岩为例[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(6): 88-95.ZHANG Hui, LIN Bowei, BIAN Jianling, et al. Comparative study on organic-rich marine and continental shale: the case of Lower Paleozoic in South China and Carboniferous-Permian shale in North China[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(6): 88-95. [8] 黄金亮, 董大忠, 李建忠, 等. 陆相页岩储层孔隙分形特征: 以四川盆地三叠系须家河组为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(9): 1611-1618.HUANG Jinliang, DONG Dazhong, LI Jianzhong, et al. Reservoir fractal characteristics of continental shale: an example from Triassic Xujiahe Formation shale, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(9): 1611-1618. [9] 高凤琳, 宋岩, 梁志凯, 等. 陆相页岩有机质孔隙发育特征及成因: 以松辽盆地长岭断陷沙河子组页岩为例[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(9): 1030-1044. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201909002.htmGAO Fenglin, SONG Yan, LIANG Zhikai, et al. Development characteristics of organic pore in the continental shale and its genetic mechanism: a case study of Shahezi Formation shale in the Changling Fault Depression of Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(9): 1030-1044. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201909002.htm [10] 左如斯, 杨威, 王乾右, 等. 川西坳陷须家河组陆相页岩岩相控制下的微观储集特征[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(6): 22-28.ZUO Rusi, YANG Wei, WANG Qianyou, et al. Lithofacies-control microscopic reservoir characterization of the continental shale in the Xujiahe Formation of Western Sichuan Depression[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(6): 22-28. [11] 董大忠, 邹才能, 戴金星, 等. 中国页岩气发展战略对策建议[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(3): 397-406.DONG Dazhong, ZOU Caineng, DAI Jinxing, et al. Suggestions on the development strategy of shale gas in China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(3): 397-406. [12] 申颍浩, 葛洪魁, 王小琼, 等. 陆相页岩气储层微观结构及其对气体产出的影响[C]//2014年中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国地球物理学会, 2014.SHEN Yinghao, GE Hongkui, WANG Xiaoqiong, et al. The microstructure of continental shale gas reservoir and its influence on gas production[C]//Annual Meeting of Chinese Geoscience Union. Beijing: China Geophysics Society, 2014. [13] 肖佃师, 卢双舫, 房大志, 等. 海相高成熟页岩气储层孔隙连通关系: 以彭水地区龙马溪组为例[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2019, 9(5): 45-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ201905006.htmXIAO Dianshi, LU Shuangfang, FANG Dazhi, et al. Pore connectivity of marine high-maturity shale gas reservoirs: a case study in Longmaxi Formation, Pengshui area[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2019, 9(5): 45-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ201905006.htm [14] GAO Fenglin, SONG Yan, LI Zhuo, et al. Quantitative characte-rization of pore connectivity using NMR and MIP: a case study of the Wangyinpu and Guanyintang shales in the Xiuwu Basin, Southern China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 197: 53-65. [15] 宁传祥, 姜振学, 高之业, 等. 用核磁共振和高压压汞定量评价储层孔隙连通性: 以沾化凹陷沙三下亚段为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(3): 578-585.NING Chuanxiang, JIANG Zhenxue, GAO Zhiye, et al. Quantitative evaluation of pore connectivity with nuclear magnetic resonance and high pressure mercury injection: a case study of the lower section of Es3 in Zhanhua Sag[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2017, 46(3): 578-585. [16] SUN Mengdi, YU Bingsong, HU Qinhong, et al. Pore connectivity and tracer migration of typical shales in South China[J]. Fuel, 2017, 203: 32-46. [17] 陈冬霞, 刘雨晨, 庞雄奇, 等. 川西坳陷须五段陆相页岩层系储层特征及对含气性的控制作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(1): 174-184.CHEN Dongxia, LIU Yuchen, PANG Xiongqi, et al. Reservoir characteristics and its control on gas-bearing properties of the 5th member of the Triassic Xujiahe Formation continental shale in the Sichuan Basin of China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(1): 174-184. [18] 刘君龙, 纪友亮, 杨克明, 等. 川西须家河组前陆盆地构造层序及沉积充填响应特征[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 39(6): 11-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201506002.htmLIU Junlong, JI Youliang, YANG Keming, et al. Tectono-stratigraphy and sedimentary infill characteristics of Xujiahe Formation in western Sichuan Foreland Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2015, 39(6): 11-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX201506002.htm [19] 陈果, 刘哿行, 李洪玺, 等. 四川盆地上三叠统须家河组陆相页岩气资源潜力分析[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2019, 13(5): 21-29.CHEN Guo, LIU Gehang, LI Hongxi, et al. Resource potential of continental shale gas in Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Technology, 2019, 13(5): 21-29. [20] 侯强, 李延飞, 周瑶, 等. 川西坳陷须家河组须三段烃源岩地化特征[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2014, 8(2): 5-8.HOU Qiang, LI Yanfei, ZHOU Yao, et al. Geochemical characteristics of source rock in Xujiahe 3 member, Western Sichuan Depression[J]. Natural Gas Technology, 2014, 8(2): 5-8. [21] 左如斯. 川西坳陷须家河组陆相页岩发育模式及储层发育特征[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019.ZUO Rusi. The development model of Xujiiahe continental shale in Western Sichuan Depression and its reservoir characterisitics[D]. Beijing: China University of petroleum (Beijing), 2019. [22] 李晋宁. 泥页岩储层孔隙结构表征和连通方式研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2017.LI Jinning. Study on pore structure characterization and connectivity of shale reservoir[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2017. [23] 张倩, 董艳辉, 童少青, 等. 核磁共振冷冻测孔法及其在页岩纳米孔隙表征的应用[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(21): 2387-2394.ZHANG Qian, DONG Yanhui, TONG Shaoqing, et al. Nuclear magnetic resonance cryoporometry as a tool to measure pore size distribution of shale rock[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(21): 2387-2394. [24] KLAVER J, DESBOIS G, LITTKE R, et al. BIB-SEM characte-rization of pore space morphology and distribution in postmature to overmature samples from the Haynesville and Bossier shales[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 59: 451-466. [25] AL HINAI A, REZAEE R, ESTEBAN L, et al. Comparisons of pore size distribution: a case from the Western Australian gas shale formations[J]. Journal of Unconventional Oil and Gas Resources, 2014, 8: 1-13. [26] ROUQUEROL J, AVNIR D, FAIRBRIDGE C W, et al. Reco-mmendations for the characterization of porous solids[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1994, 66(8): 1739-1758. [27] WASHBURN E W. Note on a method of determining the distribution of pore sizes in a porous material[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1921, 7(4): 115-116. [28] 刘标. 低场核磁共振冻融法在非常规油气储层岩石孔径表征中的应用研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2018.LIU Biao. A nuclear magnetic resonance cryoporometry study on the pore size characterization of unconventional oil and gas reservoir rocks[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2018. [29] 孙梦迪. 中国南方海相页岩孔隙特征及其对气体储集与迁移的制约[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.SUN Mengdi. Characteristics of pore structure and its constrains on gas accumulation and migration in marine shale of South China[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2017. [30] 王朋飞, 吕鹏, 姜振学, 等. 中国海陆相页岩有机质孔隙发育特征对比: 基于聚焦离子束氦离子显微镜(FIB-HIM)技术[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(5): 739-748. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201805739WANG Pengfei, LV Peng, JIANG Zhenxue, et al. Comparison of organic matter pores of marine and continental facies shale in China: based on Focused Ion Beam Helium Ion Microscopy (FIB-HIM)[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(5): 739-748. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201805739 [31] 张文涛, 胡文瑄, 鲍芳, 等. 基于流体吸入实验的页岩纳米孔隙连通性分析方法[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(03): 415-421. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003415ZHANG Wentao, HU Wenxuan, BAO Xingfang, et al. A method for analyzing nanopore connectivity of shale using a fluid suction experiment[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(03): 415-421. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003415 [32] 胡钦红, 刘惠民, 黎茂稳, 等. 东营凹陷沙河街组页岩油储集层润湿性、孔隙连通性和流体—示踪剂运移[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(3): 278-289.HU Qinhong, LIU Huimin, LI Maowen, et al. Wettability, pore connectivity and fluid-tracer migration in shale oil reservoirs of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag of Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(3): 278-289. [33] THOMMES M, KANEKO K, NEIMARK A V, et al. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC technical report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2015, 87(9/10): 1051-1069. [34] LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6): 1071-1098. [35] ZHANG Luchan, XIAO Dianshi, LU Shuangfang, et al. Pore deve-lopment of the Lower Longmaxi shale in the southeastern Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas: insights from lithofacies identification and organic matter[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 122: 104662. -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号