Control of Paleocene volcanic edifice on favorable reservoirs: a case study of the southwestern Huizhou Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要: 珠江口盆地惠西南地区发育古新世厚层火山岩,与上覆始新统文昌组湖相沉积岩连续充填于惠州凹陷内,构成裂陷盆地早、中期主体岩层,没有明显沉积间断导致火山岩表生暴露、风化淋滤作用不强,因此,火山岩有利储层分布主要受火山机构的影响。基于岩矿、测井、三维地震等资料,通过岩心及薄片观察,开展惠西南地区火山机构及岩相特征研究,分析火山机构对有利储层的控制作用。研究表明,研究区存在“喷发方式控制火山机构类型、火山机构控制优相展布、优相控制有利储层分布”的递进特征:(1)受火山喷发时期与方式控制,研究区发育层状火山机构与穹隆状火山机构,火山口外形表现为内凹与穹隆两种类型;(2)火山岩优势岩相展布于火山机构内幕中心部位,火山口、近火山口的火山通道相、爆发相、喷溢相是有利岩相组合;(3)有利储层分布受岩相组合及裂陷期断层活动影响,储集空间分为原生孔缝、次生孔缝两类,岩相控制原生孔缝富集程度,后期断裂活动起到激活、改造、连通作用,形成规模孔—缝型火山岩油气储集层;(4)穹隆状火山机构最顶部侵出相由于岩浆挥发分含量低,导致原生孔缝不发育,岩石致密且难以改造,含油气性较差。Abstract: Thickly developed Paleocene volcanic rocks in the southwestern Huizhou Sag of the Pearl River Mouth Basin are continuously filled with lacustrine sedimentary rocks of the overlying Eocene Wenchang Formation in the sag, forming the main rock formations in the early and middle stages of the rift basin. Absence of obvious sedimentary hiatus leads to poor supergene exposure as well as weathering and leaching effects of volcanic rocks. Therefore, the distribution of favorable reservoirs in volcanic rocks is mainly affected by volcanic edifices. Based on the latest drilling, logging and 3D seismic data, through the observation of cores and thin sections, the research on the volcanic edifice and lithofacies characteristics in the southwestern Huizhou Sag was carried out, and the controls of volcanic edifice on favorable reservoirs was analyzed. Results show that the study area has the progressive characteristics of "the eruption mode controls the type of volcanic edifice, the volcanic edifice controls the distribution of favorable facies, and the favorable facies controls the distribution of favorable reservoirs". (1) Controlled by the period and mode of volcanic eruption, stratovolcano and dome-like volcanic edifices developed in the study area, and the crater shape is of two types: subsidence caldera and dome. (2) The dominant lithofacies of volcanic rocks are distributed in the center of the volcanic edifice. The volcanic conduit facies, explosive facies and effusive facies in or near the crater are favorable combination of lithofacies. (3) The distribution of favorable reservoirs is affected by lithofacies assemblages and fault activities during the rifting period. The reservoir space is divided into primary and secondary pores and fractures. The lithofacies controls the enrichment degree of primary pores and fractures, while the later fault activities reform and connect the protogenetic pores and fractures, forming large-scale oil and gas reservoirs of pore-fracture type in volcanic rocks. (4) Extrusive facies, which is on the top of dome volcanic edifice, shows a poor oil-bearing property with hardly pores and fractures due to low volatiles content during the magma extruding.
-
图 3 珠江口盆地惠西南地区惠州75层状火山机构H3井岩性柱状图(a)、地震剖面图(b)、地质剖面图(c)
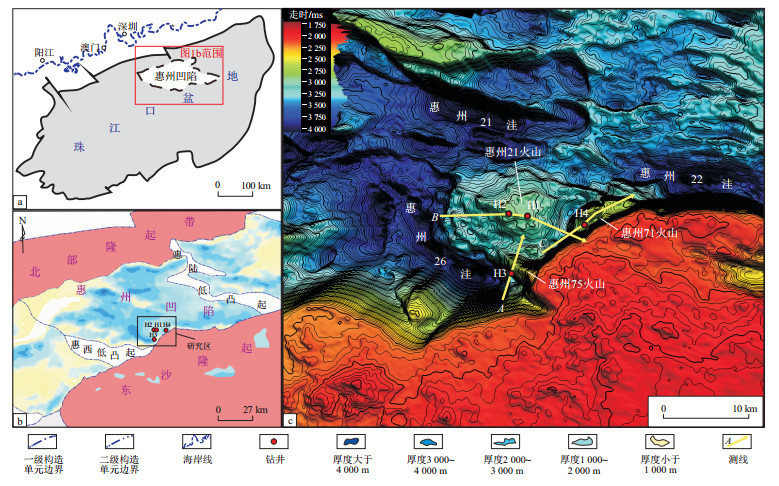
剖面位置见图 1的A测线。
Figure 3. Lithological column of well H3 (a), seismic section (b) and geological section (c) of Huizhou 75 stratovolcano edifice in southwestern Huizhou Sag, PRMB
图 4 珠江口盆地惠西南地区惠州21穹隆状火山机构H1、H2井岩性柱状图(a1、a2)、地震剖面图(b)、地质剖面图(c)
剖面位置见图 1的B测线。
Figure 4. Lithological column of well H1 & H2 (a1 & a2), seismic section (b) and geological section (c) of Huizhou 21 dome-like volcanic edifice in southwestern Huizhou Sag, PRMB
图 5 珠江口盆地惠西南地区惠州71穹隆状火山机构H4井岩性柱状图(a)、地震剖面图(b)、地质剖面图(c)
剖面位置见图 1的C测线。
Figure 5. Lithological column of well H4 (a), seismic section (b) and geological section (c) of Huizhou 71 dome-like volcanic edifice in southwestern Huizhou Sag, PRMB
图 6 珠江口盆地惠西南地区古新世火山岩岩性、岩相特征
a.粗安质火山角砾熔岩,火山角砾结构,堆砌构造,箭头指示角砾,火山通道相火山颈亚相(H1井,4 604.0 m);b.粗安岩,斑状结构,正交偏光(H1井,4 604.0 m);c.粗安岩,斑状结构,斑晶以长石为主,侵出相,正交偏光(H2井,4 430.99 m);d.安山岩,斑状结构,斑晶斜长石自形发育聚片双晶与环带,侵出相,正交偏光(H4井,4 003.8 m);e.安山质凝灰岩,角砾凝灰结构,爆发相热碎屑流亚相,正交偏光(H3井,4 745.8 m);f.辉石安山岩,斑状结构,斑晶单斜辉石,基质安山结构,流动定向构造,喷溢相中部亚相,正交偏光(H3井,4 780.0 m);g.辉石安山岩,斑状结构,基质安山结构,喷溢相中部亚相,正交偏光(H3井,4 842.5 m);h.安山岩,斑状结构,斑晶以斜长石为主,粒径最大2 mm,具环带结构,基质安山结构,喷溢相,正交偏光(H3井,5 052.7 m);i.安山岩,可见不规则杏仁体,充填绿泥石,喷溢相,正交偏光(H4井,4 246.7 m)
Figure 6. Characteristics and lithofacies of Paleocene volcanic rocks in southwestern Huizhou Sag, PRMB
图 7 珠江口盆地惠西南地区古新世火山岩储集空间类型
a.霏细结构,安山质凝灰岩,壁心实测孔隙度4.9%,正交偏光(H3井,4 759.0 m);b.晶洞,边缘霏细结构,中空为孔,安山质凝灰熔岩,正交偏光(H4井,4 223.2 m);c.溶蚀缝与斑晶炸裂缝,粗安岩,单偏光(H2井,4 604.0 m);d.杏仁体边缘为硅质,中部绿泥石,安山岩,正交偏光(H4井,4 154.8 m);e.基质溶孔,安山质凝灰岩,壁心实测孔隙度6.7%,单偏光(H3井,4 775.0 m);f.杏仁体与斑晶溶蚀孔,辉石安山岩,壁心实测孔隙度16.3%,单偏光(H3井,4 877.0 m)
Figure 7. Reservoir spaces types of Paleocene volcanic rocks in southwestern Huizhou Sag, PRMB
-
[1] 邹才能, 赵文智, 贾承造, 等. 中国沉积盆地火山岩油气藏形成与分布[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(3): 257-271. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200803002.htmZOU Caineng, ZHAO Wenzhi, JIA Chengzao, et al. Formation and distribution of volcanic hydrocarbon reservoirs in sedimentary basins of China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(3): 257-271. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200803002.htm [2] 王璞珺, 冯志强, 刘万洙, 等. 盆地火山岩[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008.WANG Pujun, FENG Zhiqiang, LIU Wanzhu, et al. Volcanic rocks in petroliferous basins[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008. [3] 杨双, 李忠博, 闫相宾, 等. 火山岩圈闭识别描述方法及其应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(3): 540-548. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103540YANG Shuang, LI Zhongbo, YAN Xiangbin, et al. Method of identi-fying and characterizing of volcanic traps and its application[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2021, 43(3): 540-548. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103540 [4] 高荣杰. 齐家火山岩油藏特征及勘探潜力分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(1): 37-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202105006.htmGAO Rongjie. Analysis of the characteristics and exploration potential of volcanic hydrocarbon reservoir in Qijia area[J]. Special Oil&Gas Reserviors, 2021, 28(1): 37-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202105006.htm [5] 王璞珺, 陈树民, 刘万洙, 等. 松辽盆地火山岩相与火山岩储层的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2003, 24(1): 18-23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2003.01.004WANG Pujun, CHEN Shumin, LIU Wanzhu, et al. Relationship between volcanic facies and volcanic reservoirs in Songliao Basin[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 2003, 24(1): 18-23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2003.01.004 [6] 王璞珺, 迟元林, 刘万洙, 等. 松辽盆地火山岩相: 类型、特征和储层意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2003, 33(4): 449-456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200706024.htmWANG Pujun, CHI Yuanlin, LIU Wanzhu, et al. Volcanic facies of the Songliao Basin: classification, characteristics and reservoir significance[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2003, 33(4): 449-456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200706024.htm [7] 匡立春, 吕焕通, 薛晶晶, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘五八开发区二叠系佳木河组火山岩储层特征[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14(2): 164-171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.02.005KUANG Lichun, LYU Huantong, XUE Jingjing, et al. Characteristics of volcanic reservoirs in Jiamuhe Formation of Permian in the 5th and 8th Districts, northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2008, 14(2): 164-171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.02.005 [8] 鲜本忠, 牛花朋, 朱筱敏, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘下二叠统火山岩岩性、岩相及其与储层的关系[J]. 高校地质学报, 2013, 19(1): 46-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2013.01.008XIAN Benzhong, NIU Huapeng, ZHU Xiaomin, et al. Early Permian volcanic lithology, lithofacies and their relations to reservoir in northwestern margin of the Junggar Basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2013, 19(1): 46-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2013.01.008 [9] 谢庆宾, 韩德馨, 朱筱敏, 等. 三塘湖盆地火成岩储集空间类型及特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2002, 29(1): 84-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200201020.htmXIE Qingbin, HAN Dexin, ZHU Xiaomin, et al. Reservoir space feature and evolution of the volcanic rocks in the Santanghu Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2002, 29(1): 84-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200201020.htm [10] 林潼, 焦贵浩, 孙平, 等. 三塘湖盆地石炭系火山岩储层特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(4): 513-517. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200904006.htmLIN Tong, JIAO Guihao, SUN Ping, et al. Characteristic and influencing factors of Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in Santanghu Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(4): 513-517. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200904006.htm [11] 周萍. 王府断陷火石岭组火山岩岩性及岩相识别[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(2): 188-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202002011.htmZHOU Ping. Identification of volcanics reservoir lithology and lithofacies in Huoshiling Formation of Wangfu Fault Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(2): 188-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202002011.htm [12] 江昱良, 秦启荣, 高瑞琪, 等. 蜀南地区二叠系火成岩特征及储集性研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(2): 11-19.JIANG Yuliang, QIN Qirong, GAO Ruiqi, et al. Study on the characteristics and reservoir quality of permian igneous rocks in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Special Oil&Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(2): 11-19. [13] 黄芸, 梁舒艺, 杨迪生, 等. 原生韵律型火山岩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(6): 54-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202106007.htmHUANG Yun, LIANG Shuyi, YANG Disheng, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of primary rhyolite volcanic reservoir[J]. Special Oil&Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(6): 54-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202106007.htm [14] 唐华风, 赵鹏九, 高有峰, 等. 盆地火山地层时空属性和岩石地层单位[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2017, 47(4): 949-973. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201704001.htmTANG Huafeng, ZHAO Pengjiu, GAO Youfeng, et al. Spatio-temporal attributes of volcano stratigraphy and its lithostratigraphic units in a basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2017, 47(4): 949-973. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201704001.htm [15] 代春萌, 曾庆才, 李波, 等. 准噶尔盆地滴南凸起石炭系古火山机构地震特征及有利区预测[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(6): 739-749. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201906006.htmDAI Chunmeng, ZENG Qingcai, LI Bo, et al. Seismic characte-ristics of Carboniferous ancient volcanic edifices and prediction of favorable zones in the Dinan bump of the Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(6): 739-749. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201906006.htm [16] 王立武, 刘智军, 刘殿密, 等. 松辽盆地德惠断陷营城组火山机构刻画及储层意义[J]. 世界地质, 2019, 38(1): 203-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ201901019.htmWANG Liwu, LIU Zhijun, LIU Dianmi, et al. Depiction on volcanic edifice of Yingcheng Formation in Dehui Fault Depression and its reservoir significance[J]. Global Geology, 2019, 38(1): 203-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ201901019.htm [17] 李平鲁, 梁慧娴, 戴一丁. 珠江口盆地基岩油气藏远景探讨[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 1998, 12(6): 361-369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199806000.htmLI Pinglu, LIANG Huixian, DAI Yiding. Exploration perspective of basement hydrocarbon accumulations in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 1998, 12(6): 361-369. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199806000.htm [18] 李思伟, 王璞珺, 丁琳, 等. 南海北部陆缘古新世埃达克质岩的岩石成因[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(11): 4091-4117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202011015.htmLI Siwei, WANG Pujun, DING Lin, et al. Petrogenesis of Paleocene Adakite-like rocks in northern margin of the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(11): 4091-4117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202011015.htm [19] 陈长民, 施和生, 许士策, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)第三系油气藏形成条件[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.CHEN Changmin, SHI Hesheng, XU Shice, et al. Tertiary hydrocarbon accumulation condition in Pearl River Mouth Basin[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003. [20] 李平鲁, 梁慧娴. 珠江口盆地新生代岩浆活动与盆地演化、油气聚集的关系[J]. 广东地质, 1994, 9(2): 23-24.LI Pinglu, LIANG Huixian. Relation between Cenozoic igneous activity and basin evolution and oil-gas accumulation in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Guangdong Geology, 1994, 9(2): 23-34. [21] 张斌, 王璞珺, 张功成, 等. 珠-琼盆地新生界火山岩特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(6): 657-665.ZHANG Bin, WANG Pujun, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Cenozoic volcanic rocks in the Pearl River Mouth and Southeast Hainan Basins of South China Sea and their implications for petroleum geology[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(6): 657-665. [22] 施和生. 论油气资源不均匀分布与分带差异富集: 以珠江口盆地珠一坳陷为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2013, 25(5): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201505001.htmSHI Hesheng. On heterogeneous distribution and differential enrichment by zones of hydrocarbon resources: a case in Zhu I depre-ssion, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2013, 25(5): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201505001.htm [23] 施和生, 何敏, 张丽丽, 等. 珠江口盆地(东部)油气地质特征、成藏规律及下一步勘探策略[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(3): 11-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201403002.htmSHI Hesheng, HE Min, ZHANG Lili, et al. Hydrocarbon geology, accumulation pattern and the next exploration strategy in the eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(3): 11-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201403002.htm [24] 邱家骧, 陶奎元, 赵俊磊, 等. 火山岩[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996.QIU Jiaxiang, TAO Kuiyuan, ZHAO Junlei, et al. Extrusive rock[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996. [25] 赵澄林, 孟卫工, 金春爽, 等. 辽河盆地火山岩与油气[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1999.ZHAO Chenglin, MENG Weigong, JIN Chunshuang, et al. Volcanic rocks and hydrocarbon in Liaohe Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1999. [26] 赵澄林. 火山岩储层储集空间形成机理及含油气性[J]. 地质论评, 1996, 42(S1): 37-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP1996S1006.htmZHAO Chenglin. Formation mechanism of reservoir space and oil possibility of volcanic reservoirs[J]. Geological Review, 1996, 42(S1): 37-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP1996S1006.htm [27] 黄玉龙, 王璞珺, 舒萍, 等. 松辽盆地营城组中基性火山岩储层特征及成储机理[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(1): 82-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201001011.htmHUANG Yulong, WANG Pujun, SHU Ping, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the Cretaceous intermediate and mafic volcanic reservoirs in Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(1): 82-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201001011.htm [28] 张兴勇. 红山嘴油田石炭系火山岩储层裂缝发育特征及主控因素[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(3): 25-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202103004.htmZHANG Xingyong. Fracture development characteristics and main controlling factors of carboniferous volcanic reservoir in Hongshanzui Oilfield[J]. Special Oil&Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(3): 25-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202103004.htm [29] 王永卓, 周学民, 印长海, 等. 徐深气田成藏条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(7): 866-886. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201907014.htmWANG Yongzhuo, ZHOU Xuemin, YIN Changhai, et al. Gas accumulation conditions and key exploration&development technologies in Xushen gas field[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(7): 866-886. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201907014.htm [30] 常丽华, 曹林, 高福红. 火成岩鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009.CHANG Lihua, CAO Lin, GAO Fuhong. Introduction to lgneous rock[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009. -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号