Flume simulation of response of deltaic sedimentary process to Paleogene flexural gentle slope belt in Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea
-
摘要: 南海北部陆缘深水区已发现数亿吨油气地质储量,而裂陷期古近系规模有效储层的分布是深水区勘探取得持续发现的关键。珠江口盆地白云凹陷深水区挠曲缓坡带裂陷期从文昌组到恩平组的地震资料上可观察到持续发育的大型辫状河三角洲。在无井或少井的情况下,为进一步认识该区构造沉降过程中大型辫状河三角洲的沉积单元组成、演化规律,开展了白云凹陷挠曲缓坡带三角洲沉积过程响应水槽模拟实验。实验设计了3期构造沉降,分别对应古近纪区域构造—沉积演化的3个时期,即均衡裂陷期、拆离裂陷期和断拗裂陷期,采用洪水、平水、枯水相间隔的方式模拟牵引流的水动力机制。实验表明,在3期构造沉降过程中,挠曲缓坡带均发育天然堤、泛滥平原、分流河道、废弃河道、支流间湾、水下分流河道、河口坝等三角洲沉积环境微相单元;辫状河三角洲以侧向进积作用为主,垂向加积作用为辅,沉积中心逐渐向洼陷中心迁移;裂陷期挠曲缓坡带三角洲形态及砂体分布主要受构造地貌、入湖河流流量、湖平面升降以及水体深度等因素控制。Abstract: Hundreds of millions of tons of oil and gas geological reserves have been discovered through exploration in the deep-water area of the northern continental margin of the South China Sea, and the distribution of large-scale effective reservoirs during the Paleogene rifting period is the key for continuous discovery in deep-water zone. Large braided fluvio-delta can be observed on seismic data from the Wenchang to Enping formations in the rifting period of the flexural gentle slope belt in the deep-water zone. Due to the absence of wells or few wells, for further understanding of the composition and evolution of large braided fluvio-deltaic sedimentary units in the process of tectonic subsidence in this region, a simulation experiment on the response of the deltaic sedimentation process in the flexural gentle slope zone to flume was carried out. Three phases of tectonic subsidence were designed for the simulation experiment, corresponding to the three phases of Paleogene regional tectonic-sedimentary evolution including balanced rifting period, detached rifting period, and faulted depression rifting period. The hydrodynamic mechanism of tractive flow was simulated by means of flood, flat water, and dry water. Simulation results showed that during the three stages of tectonic subsidence, the flexural gentle slope zone deve-loped distributary channels, natural dikes, floodplains, underwater distributary channels, estuaries, inter-tributary bays and other delta sedimentary microfacies units. The braided river delta was dominated by lateral proliferation, supplemented by vertical accretion, and the sedimentary center gradually migrated to the center of the depression, with almost no degeneration. The delta shape and sand body distribution in the flexural gentle slope zone during the rifting period were mainly controlled by factors such as structural geomorphology, river discharge amount into lake, lake level changes, and water depth.
-
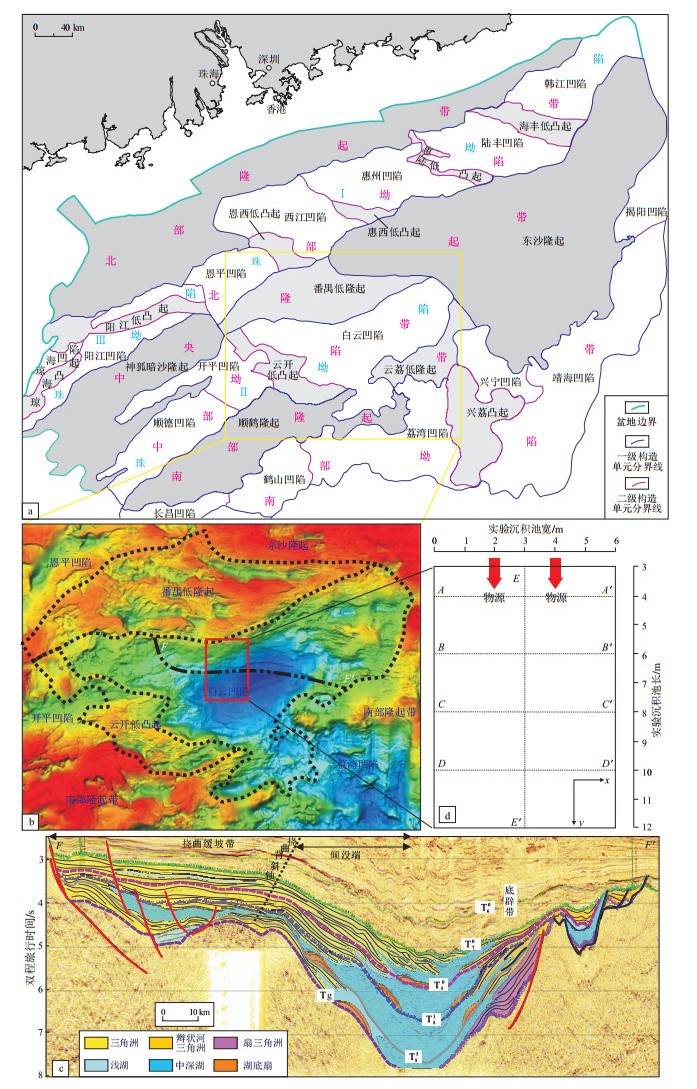
图 1 珠江口盆地构造单元划分(a)、白云凹陷地理位置(b)、白云凹陷三角洲—湖相沉积体系(c)及研究区模拟实验平面按比例对照示意(d)
图1a改自文献[22];图1c位置见图1b,引自文献[1];图1d中的x,y对应图 2中的x,y。
Figure 1. Division of tectonic units in Pearl River Mouth Basin (a), geographic location of Baiyun Sag (b), delta-lacustrine sedimentary system of Baiyun Sag (c), and schematic diagram of scale of study area (d)
图 6 水槽模拟实验不同位置横剖面3期砂体叠置特征
剖面位置见图 1d。
Figure 6. Superimposed characteristics of three stages of sand bodies on cross section at different positions in flume simulation
图 7 水槽模拟实验纵剖面3期砂体叠置特征
E-E’剖面位置见图 1d。
Figure 7. Superimposed characteristics of three stages of sand bodies on longitudinal section in flume simulation
表 1 挠曲坡折带模拟实验活动底板设计参数
Table 1. Design parameters of movable floor for flexural slope-break simulation experiment
沉积期 位置 下降时间/h 下降量/cm 第一列 第二列 第三列 第四列 第三期 第四排 24 2 2 4 8 第三排 24 2 2 4 8 第二排 24 2 2 4 8 第一排 24 2 2 4 8 第三期下降2次,合计下降 48 4 4 8 16 第二期 第四排 17 2 4 6 8 第三排 17 2 4 6 8 第二排 17 2 4 6 8 第一排 17 2 4 6 8 第二期下降3次,合计下降 51 6 12 18 24 第一期 第四排 20 2 4 4 6 第三排 20 2 4 4 6 第二排 20 2 4 4 6 第一排 20 2 4 4 6 第一期下降2次,合计下降 40 4 8 8 12 3期累计下降数值 139 14 24 34 52 -
[1] 柳保军, 庞雄, 王家豪, 等. 珠江口盆地深水区伸展陆缘地壳减薄背景下的沉积体系响应过程及油气勘探意义[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(S1): 124-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2019S1011.htmLIU Baojun, PANG Xiong, WANG Jiahao, et al. Sedimentary system response process and hydrocarbon exploration significance of crust thinning zone at extensional continental margin of deep-water area in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(S1): 124-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2019S1011.htm [2] 庞雄, 任建业, 郑金云, 等. 陆缘地壳强烈拆离薄化作用下的油气地质特征: 以南海北部陆缘深水区白云凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(1): 27-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201801004.htmPANG Xiong, REN Jianye, ZHENG Jinyun, et al. Petroleum geology controlled by extensive detachment thinning of continental margin crust: a case study of Baiyun Sag in the deep-water area of northern South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(1): 27-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201801004.htm [3] 李洪博, 郑金云, 庞雄, 等. 南海北部陆缘差异拆离作用结构样式与控制因素: 以珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(4): 24-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202004003.htmLI Hongbo, ZHENG Jinyun, PANG Xiong, et al. Structural patterns and controlling factors of differential detachment in the northern continental margin of the South China Sea: taking Baiyun-Liwan deep water area in the Pearl River Mouth Basin as an example[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(4): 24-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202004003.htm [4] 曾智伟, 杨香华, 朱红涛, 等. 白云凹陷恩平组沉积晚期大型三角洲发育特征及其意义[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2017, 42(1): 78-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201701007.htmZENG Zhiwei, YANG Xianghua, ZHU Hongtao, et al. Development characteristics and significance of large delta of upper Enping Formation, Baiyun Sag[J]. Earth Sciences (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2017, 42(1): 78-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201701007.htm [5] 韩银学, 陈莹, 杨海长, 等. 白云凹陷恩平组"源-汇"体系及其对油气勘探的影响[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2017, 22(2): 25-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201702003.htmHAN Yinxue, CHEN Ying, YANG Haichang, et al. "Source to sink" of Enping Formation and its effects on oil and gas exploration in Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(2): 25-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201702003.htm [6] 曹耀华, 赖志云, 刘怀波, 等. 沉积模拟实验的历史现状及发展趋势[J]. 沉积学报, 1990, 8(1): 143-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199001016.htmCAO Yaohua, LAI Zhiyun, LIU Huaibo, et al. Sedimentary simulation experiments: in the past, current states, and developing trend[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1990, 8(1): 143-147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199001016.htm [7] 张春生, 刘忠保, 施冬, 等. 碎屑物理模拟研究的理论与方法[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2000, 21(4): 300-303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200004002.htmZHANG Chunsheng, LIU Zhongbao, SHI Dong, et al. Theory and method of physical simulation in clastic sedimentation[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 2000, 21(4): 300-303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200004002.htm [8] 张春生. 碎屑岩沉积模拟技术[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2003: 41-171.ZHANG Chunsheng. Clastic sedimentary simulation technology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2003: 41-171. [9] 张春生, 刘忠保, 施冬, 等. 三角洲分流河道及河口坝形成过程的物理模拟[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(3): 168-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200003022.htmZHANG Chunsheng, LIU Zhongbao, SHI Dong, et al. Physical simulation of formation process in distributary channels and debouch bars in delta[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2000, 7(3): 168-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200003022.htm [10] 王伟锋, 胡瑜, 于正军, 等. 东营三角洲前缘坡移扇储集体特征及成因研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(5): 600-608. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201605600WANG Weifeng, HU Yu, YU Zhengjun, et al. Reservoir characteristics and genesis of slope fans in Dongying delta front[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2016, 38(5): 600-608. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201605600 [11] 马晋文, 刘忠保, 尹太举, 等. 须家河组沉积模拟实验及大面积砂岩成因机理分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(1): 101-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201201011.htmMA Jinwen, LIU Zhongbao, YIN Taiju, et al. Sedimentary simulation of Xujiahe Formation and depositional mechanism of large area sandstone[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(1): 101-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201201011.htm [12] 王俊辉, 姜在兴, 张元福, 等. 三角洲沉积的物理模拟[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(6): 758-764. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201306008.htmWANG Junhui, JIANG Zaixing, ZHANG Yuanfu, et al. Physical simulation of deltaic deposits[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 2013, 34(6): 758-764. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201306008.htm [13] 关旭同, 李胜利, 马水平, 等. 湖盆小型细粒浅水三角洲沉积模式[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(1): 77-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202105011.htmGUAN Xutong, LI Shengli, MA Shuiping, et al. Sedimentary model of lacustrine small fine-grained shallow water delta[J]. Special Oil&Gas Reserviors, 2021, 28(1): 77-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202105011.htm [14] 吴穹螈, 穆朋飞, 孙广义, 等. 浅水三角洲分流砂坝精细刻画新方法[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(2): 176-181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202002009.htmWU Qiongyuan, MU Pengfei, SUN Guangyi, et al. New method for fine characterization of distributary bar in shallow water delta[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(2): 176-181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202002009.htm [15] 施和生, 舒誉, 杜家元, 等. 珠江口盆地古近系石油地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017: 1-4.SHI Hesheng, SHU Yu, DU Jiayuan, et al. Petroleum geology of the Paleogene in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[M]. Beijing: China Geology Press, 2017: 1-4. [16] 吴宇翔, 柳保军, 丁琳, 等. 珠江口盆地西江凹陷南部文昌组层序地层及沉积体系研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(1): 146-158.WU Yuxiang, LIU Baojun, DING Lin, et al. Study on sequence stratigraphy and sedimentary systems of the Wenchang Formation in the southern Xijiang Depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Marine Geology&Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(1): 146-158. [17] 陈长民. 珠江口盆地东部石油地质及油气藏形成条件初探[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2000, 14(2): 73-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200002000.htmCHEN Changmin. Petroleum geology and conditions for hydrocarbon accumulation in the Eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 2000, 14(2): 73-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200002000.htm [18] 米立军, 张向涛, 庞雄, 等. 珠江口盆地形成机制与油气地质[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(S1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2019S1001.htmMI Lijun, ZHANG Xiangtao, PANG Xiong, et al. Formation mechanism and petroleum geology of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(S1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2019S1001.htm [19] 孙珍, 钟志洪, 周蒂, 等. 南海的发育机制研究: 相似模拟证据[J]. 中国科学(D辑): 地球科学, 2006, 36(9): 797-810. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200609001.htmSUN Zhen, ZHONG Zhihong, ZHOU Di, et al. Research on the dynamics of the South China Sea opening: evidence from analogue modeling[J]. Science in China (Series D): Earth Sciences, 2006, 49(10): 1053. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200609001.htm [20] 张丽丽, 舒誉, 蔡国富, 等. 珠江口盆地东部始新世-渐新世沉积环境演变及对烃源条件的影响[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(S1): 153-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2019S1013.htmZHANG Lili, SHU Yu, CAI Guofu, et al. Eocene-Oligocene sedimentary environment evolution and its impact on hydrocarbon source conditions in eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(S1): 153-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2019S1013.htm [21] 孙珍, 庞雄, 钟志洪, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷新生代构造演化动力学[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(4): 489-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200504024.htmSUN Zhen, PANG Xiong, ZHONG Zhihong, et al. Dynamics of tertiary tectonic evolution of the Baiyun Sag in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(4): 489-498. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200504024.htm [22] 张功成. 南海北部陆坡深水区构造演化及其特征[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(4): 529-533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201004001.htmZHANG Gongcheng. Tectonic evolution of deepwater area of northern continental margin in South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(4): 528-533. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201004001.htm [23] 施和生, 杜家元, 梅廉夫, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州运动及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(3): 447-461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202003003.htmSHI Hesheng, DU Jiayuan, MEI Lianfu, et al. Huizhou Movement and its significance in Pearl River Mouth Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(3): 447-461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202003003.htm -





 下载:
下载:












 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号