Origin and exploration prospect of Upper Paleozoic crude oil from Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
-
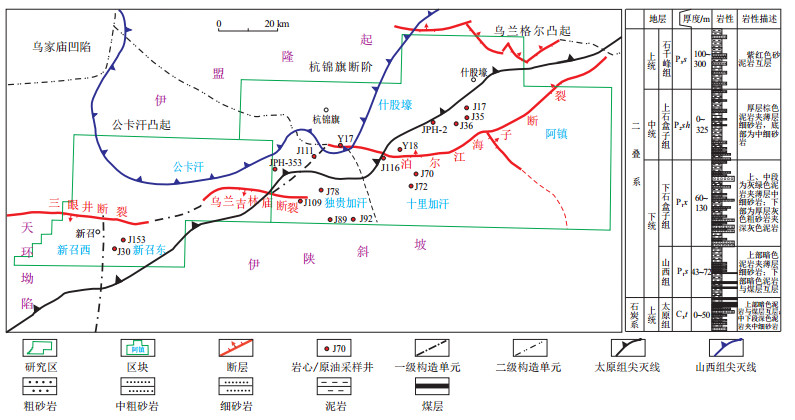
摘要: 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区上古生界海陆过渡相有一套良好的生储盖组合,目前已发现了东胜大气田。该区二叠系下石盒子组产出少量中质原油,但原油的成因及其勘探前景尚不明确。基于对该区原油的物性、饱和烃色谱、生物标志物及碳同位素等地化特征的研究,试图揭示原油的成因和勘探前景。杭锦旗地区上古生界原油具有低硫、高蜡、中等成熟度特征,其甾烷分布显示以陆生植物为主,少量水生生物;Pr/Ph值为2.16~2.26,重排甾烷和重排藿烷含量高,伽马蜡烷含量低,原油碳同位素值为-27.7‰~-26.8‰,正构烷烃单体烃碳同位素前重后轻,这些特征均指示该原油是由沉积环境为弱氧化的陆相煤系地层中的暗色泥岩生成。二叠系山西组烃源岩有机岩石学、生烃热模拟实验及岩石热解等综合分析表明,该区山西组暗色泥岩具有一定生油潜力。结合原油产出井的位置和烃源岩的空间展布,山西组暗色泥岩可能是潜在的烃源岩。杭锦旗地区上古生界良好的生储盖组合条件暗示着该区的原油勘探值得重视,泊尔江海子断裂两侧邻区是原油聚集的潜在有利区。Abstract: A set of favorable source-reservoir-caprock assemblage was found in the Upper Paleozoic transitional facies in the Hangjinqi area of the Ordos Basin, and the large-scale Dongsheng gas field has been discovered. A small amount of crude oil has been produced from the Lower Shihezi Formation reservoir in the area; however, the origin and exploration prospect of the oil are unclear. Based on the studies including physical property, n-alkanes distributions, biomarker compositions, and carbon isotopic ratios, the origin and exploration prospect of the crude oil has been discussed. Results indicate that the Upper Paleozoic crude oil from the Hangjinqi area is mature oil with a low sulfur content and a high wax content, and the steranes are dominated by terrestrial plants and assisted by a small amount of aquatic organism. The Pr/Ph ratio is 2.16-2.26, and the diasteranes and rearranged hopanes are in high contents with a relative low content of gammacerane. The carbon isotopic ratios of the oil range from -27.7‰ to -26.8‰, [JP+1]and the carbon isotopic[JP]compositions of individual n-alkanes are heavy at first and then become light with the increasing of carbon numbers. These characteristics suggest that the oil was generated by the dark mudstone in terrigenous coal measures under weak oxidation environment. The comprehensive analysis combining organic petrography, hydrocarbon generation simulation, and pyrolysis of source rocks in the Shanxi Formation indicates that, the dark mudstone in the Permian Shanxi Formation in the Hangjinqi area displays a certain amount of oil generation potential. In combination with the location of oil producing wells and the spatial distribution of source rocks, the dark mudstone in the Shanxi Formation might be the potential source rocks for the produced oil. The oil exploration of the Upper Paleozoic strata in the Hangjinqi area deserves attention as suggested by the favorable conditions of source-reservoir-caprock assemblage, and the adjacent areas of the Borjianghaizi fault are potential favorable areas for oil accumulation.
-
图 5 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区上古生界原油正构烷烃单体碳同位素分布曲线
川科1井和雷北1井数据引自文献[27]。
Figure 5. Distribution curves of carbon isotopic compositions of individual n-alkanes in Upper Paleozoic crude oil from Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区上古生界原油物理性质和族组成
Table 1. Physical properties and group compositions of Upper Paleozoic crude oil from Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
样品号 层位 密度(20 ℃)/(g·cm-3) 黏度(50 ℃)/(mPa·s) 硫/% 蜡/% 饱和烃/% 芳香烃/% 非烃+沥青质/% 饱芳比 (饱+芳)/(非+沥) JPH-353 P1x 0.86 6.96 0.08 15.60 78.36 17.28 4.36 4.53 21.94 JPH-2 P1x 0.89 10.42 0.27 12.15 67.53 26.26 6.21 2.57 15.10 表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区上古生界原油地球化学参数
Table 2. Geochemical parameters of Upper Paleozoic crude oil from Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
样品号 地球化学参数 Ⅰ1 Ⅰ2 Ⅰ3 Ⅰ4 Ⅰ5 Ⅰ6 Ⅰ7 Ⅰ8 Ⅰ9 Ⅰ10 Ⅰ11 Ⅰ12 JPH-353 2.26 0.45 0.69 0.71 0.34 1.62 0.69 1.87 0.64 0.34 0.09 -27.7 JPH-2 2.16 0.48 0.48 1.35 0.28 2.44 0.66 1.27 0.46 0.38 0.09 -26.8 注:Ⅰ1.姥鲛烷/植烷;Ⅰ2.C29规则甾烷/C27-C29规则甾烷;Ⅰ3.C29重排甾烷/C27-C29重排甾烷;Ⅰ4.C27-C29重排甾烷/C27-C29规则甾烷;Ⅰ5.规则甾烷/17α藿烷;Ⅰ6.C24四环萜烷/C26三环萜烷;Ⅰ7.C35藿烷(22 S)/ C34藿烷(22 S);Ⅰ8.18 α(H)-22, 29, 30-三降藿烷(Ts)/17α(H)-22, 29, 30-三降藿烷(Tm);Ⅰ9.18 α(H)-30-降新藿烷(C29Ts)/17 α(H), 21 β(H)-30-降藿烷(C29H);Ⅰ10.C30重排藿烷/17 α(H), 21 β(H)-C30藿烷;Ⅰ11.伽马蜡烷/21 β(H)-C30藿烷;Ⅰ12. δ13C/‰。 表 3 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区上古生界原油成熟度参数
Table 3. Maturity parameters of Upper Paleozoic crude oil from Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin
成熟度参数 JPH-353 JPH-2 OEP 1.02 0.95 CPI 1.08 0.97 C21-/C22+ 1.36 2.26 庚烷值 30.57 异庚烷值 2.83 C29甾烷20 S/(20 S+20 R) 0.53 0.50 C29甾烷ββ/(αα+ ββ) 0.48 0.50 Ts/(Ts+Tm) 0.65 0.56 C31藿烷22 S/(22 S+22 R) 0.54 0.58 MPI1 0.70 0.59 MPI2 0.74 0.64 MPR 0.52 0.92 单金刚烷指数/% 63 64 双金刚烷指数/% 47.1 33.3 注:MPI1=1.5(2-MP+3-MP)/(P+1-MP+9-MP);MPI2=3×2-MP/(P+9-MP+1-MP);MPR=(3-MP+2-MP)/(9-MP+1-MP)。样品JPH-2的OEP、CPI、C21-/C22+数据是根据色质m/z 85的峰积分得来的。 -
[1] 戴金星, 倪云燕, 董大忠, 等. "十四五"是中国天然气工业大发展期: 对中国"十四五"天然气勘探开发的一些建议[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(1): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202101001.htmDAI Jinxing, NI Yunyan, DONG Dazhong, et al. 2021-2025 is a period of great development of China's natural gas industry: suggestions on the exploration and development of natural gas during the 14th Five-Year Plan in China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(1): 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202101001.htm [2] 齐荣, 何发岐, 王付斌, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部长探1井上古生界勘探突破及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(3): 68-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202103006.htmQI Rong, HE Faqi, WANG Fubin, et al. Exploration breakthrough of Upper Paleozoic of well Changtan 1 in southern Ordos Basin and its significance[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(3): 68-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202103006.htm [3] 倪春华, 朱建辉, 刘光祥, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区上古生界煤系烃源岩生烃潜力再评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5): 826-834. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105826NI Chunhua, ZHU Jianhui, LIU Guangxiang, et al. Re-evaluation of hydrocarbon generation potential of the Upper Paleozoic coal-measure source rocks in the Hangjinqi area of Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2021, 43(5): 826-834. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105826 [4] 刘友民. 陕甘宁盆地北缘乌兰格尔地区白垩系油苗成因及意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1982, 9(3): 39-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK198203004.htmLIU Youmin. Genesis and significance of Cretaceous oil seeps in Wulanger area, northern margin of Shaanxi-Gansu-Ningxia Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1982, 9(3): 39-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK198203004.htm [5] 李剑锋, 马军, 昝川莉, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界凝析油成因研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2012, 23(2): 313-318. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201202017.htmLI Jianfeng, MA Jun, ZAN Chuanli, et al. Genesis of Upper Paleozoic condensates in Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2012, 23(2): 313-318. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201202017.htm [6] 纪文明, 李潍莲, 刘震, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部杭锦旗地区上古生界气源岩分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(5): 905-914. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201305005.htmJI Wenming, LI Weilian, LIU Zhen, et al. Research on the Upper Paleozoic gas source of the Hangjinqi block in the northern Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(5): 905-914. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201305005.htm [7] 李浩. 鄂尔多斯盆地中部上古生界烃源岩研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2015.LI Hao. Research of source rocks in Upper Paleozoic, central Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2015. [8] 郝蜀民, 李良, 张威, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘石炭系-二叠系大型气田形成条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(2): 149-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201602002.htmHAO Shumin, LI Liang, ZHANG Wei, et al. Forming conditions of large-scale gas fields in Permo-Carboniferous in the northern Ordos Basin[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 2016, 37(2): 149-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201602002.htm [9] 赵桂萍. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区上古生界烃源岩热演化特征模拟研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(5): 641-646. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201605641ZHAO Guiping. Thermal evolution modeling of Neopaleozoic source rocks in Hangjinqi region, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2016, 38(5): 641-646. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201605641 [10] 陈建平, 黄第藩, 李晋超, 等. 吐哈盆地侏罗纪煤系油气主力源岩探讨[J]. 地质学报, 1999, 73(2): 140-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199902004.htmCHEN Jianping, HUANG Difan, LI Jinchao, et al. Main source rocks of petroleum from Jurassic coal-bearing strata in the Turpan-Hami Basin, northwest China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1999, 73(2): 140-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE199902004.htm [11] 包建平, 马安来, 黄光辉, 等. 三塘湖盆地原油地球化学特征及其成因类型[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1999, 26(4): 25-29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1999.04.007BAO Jianping, MA Anlai, HUANG Guanghui, et al. The origin and geochemical characteristics of crude oils from Santanghu Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1999, 26(4): 25-29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1999.04.007 [12] 苏爱国, 朱扬明, 梁狄刚, 等. 青海柴达木盆地南八仙油气田油源与成藏机理[J]. 地球化学, 2003, 32(4): 393-399. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.04.014SU Aiguo, ZHU Yangming, LIANG Digang, et al. Source of oils and mechanism of reservoir-formation of the Nanbaxian oil and gas field, Qaidam Basin, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Geochimica, 2003, 32(4): 393-399. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.04.014 [13] PETERS K E, WALTERS C C, MOLDOWAN J M. The biomarker guide, biomarkers and isotopes in petroleum exploration and earth history, volume 2[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005. [14] 程克明, 张朝富. 吐鲁番-哈密盆地煤成油研究[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1994, 24(11): 1216-1222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199411013.htmCHENG Keming, ZHANG Chaofu. Study on coal-derived oils in Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Science in China (Series B), 1994, 24(11): 1216-1222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK199411013.htm [15] 朱扬明, 周洁, 顾圣啸, 等. 西湖凹陷始新统平湖组煤系烃源岩分子地球化学特征[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(1): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201201003.htmZHU Yangming, ZHOU Jie, GU Shengxiao, et al. Molecular geochemistry of Eocene Pinghu Formation coal-bearing source rocks in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(1): 32-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201201003.htm [16] 赵孟军, 肖中尧, 彭燕, 等. 煤系泥岩和煤岩生成原油的地球化学特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1998, 25(5): 8-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK805.002.htmZHAO Mengjun, XIAO Zhongyao, PENG Yan, et al. Geochemistry of oils from coal and from the shale in coal measure strata[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1998, 25(5): 8-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK805.002.htm [17] 包建平, 吴浩, 朱翠山, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘牛东地区煤成油及其地球化学特征[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(5): 1056-1069. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201805011.htmBAO Jianping, WU Hao, ZHU Cuishan, et al. Geochemical characteristics of coal-derived oils in the Niudong area in the northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(5): 1056-1069. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201805011.htm [18] 程克明, 赵长毅, 苏爱国, 等. 吐哈盆地煤成油气的地质地球化学研究[J]. 勘探家, 1997, 2(2): 5-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY199702001.htmCHENG Keming, ZHAO Changyi, SU Aiguo, et al. Geological and geochemical studies on coal-formed oil and gas in Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Petroleum Explorationist, 1997, 2(2): 5-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY199702001.htm [19] MELLO M R, TELNAES N, GAGLIANONE P C, et al. Organic geochemical characterization of depositional palaeoenvironments of source rocks and oils in Brazilian marginal basins[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1988, 13(1/3): 31-45. [20] MOLDOWAN J M, SEIFERT W K, GALLEGOS E J. Relationship between petroleum composition and depositional environment of petroleum source rocks[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1985, 69(8): 1255-1268. [21] 王春江, 王有孝, 罗斌杰, 等. 民和盆地中侏罗统煤-油页岩层系生油特征[J]. 沉积学报, 1997, 15(1): 60-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB701.010.htmWANG Chunjiang, WANG Youxiao, LUO Binjie, et al. Characteristics of the oil formation in the Middle Jurassic coal shale strata in the Minhe Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1997, 15(1): 60-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB701.010.htm [22] HOFFMANN C F, MACKENZIE A S, LEWIS C A, et al. A biological marker study of coals, shales and oils from the Mahakam Delta, Kalimantan, Indonesia[J]. Chemical Geology, 1984, 42(1/4): 1-23. [23] PHILP R P, BRASSELL S. Arguments against abiogenic origin for hydrocarbons[J]. Chemical&Engineering News, 1986, 64(50): 2. [24] 张立平, 黄第藩, 廖志勤. 伽马蜡烷: 水体分层的地球化学标志[J]. 沉积学报, 1999, 17(1): 136-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB901.021.htmZHANG Liping, HUANG Difan, LIAO Zhiqin. Gammacerane: Geochemical indicator of water column stratification[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1999, 17(1): 136-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB901.021.htm [25] 黄第藩, 李晋超, 张大江. 干酪根的类型及其分类参数的有效性、局限性和相关性[J]. 沉积学报, 1984, 2(3): 18-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198403001.htmHUANG Difan, LI Jinchao, ZHANG Dajiang. Kerogen types and study on effectiveness, limitation and interrelation of their identification parameters[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1984, 2(3): 18-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198403001.htm [26] SUN Yongge, SHENG Guoying, PENG Ping'an, et al. Compound-specific stable carbon isotope analysis as a tool for correlating coal-sourced oils and interbedded shale-sourced oils in coal measures: an example from Turpan Basin, north-western China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(12): 1349-1362. [27] 朱扬明, 李颖, 郝芳, 等. 四川盆地海、陆相烃源岩有机质稳定碳同位素组成变化及其地球化学意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(6): 1254-1264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201706016.htmZHU Yangming, LI Ying, HAO Fang, et al. Compositional variations and geochemical significances of stable carbon isotope for organic matters from marine and terrestrial source rocks in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(6): 1254-1264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201706016.htm [28] 马安来, 林会喜, 云露, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区奥陶系超深层原油金刚烷化合物分布及意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(3): 334-346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202103002.htmMA Anlai, LIN Huixi, YUN Lu, et al. Characteristics of diamondoids in oils from the ultra-deep Ordovician in the North Shuntuoguole area in Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(3): 334-346. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202103002.htm [29] 程克明, 熊英, 马立元, 等. 华北地台早二叠世太原组和山西组煤沉积模式与生烃关系研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(4): 142-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200504027.htmCHENG Keming, XIONG Ying, MA Liyuan, et al. Relationship between coal depositional modes and hydrocarbon generation of the Early Permian Taiyuan and Shanxi Formation in Huabei Platform[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(4): 142-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200504027.htm [30] 苏传国, 朱建国, 孟旺才, 等. 吐哈盆地"煤成油"问题再认识[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2005, 26(4): 453-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200504034.htmSU Chuanguo, ZHU Jianguo, MENG Wangcai, et al. Re-discussion of coal-formed oil mechanism in Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2005, 26(4): 453-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200504034.htm [31] 帅燕华, 张水昌, 陈建平. 煤和煤系泥岩生油能力再评价[J]. 地球化学, 2009, 38(6): 583-590. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200906011.htmSHUAI Yanhua, ZHANG Shuichang, CHEN Jianping. Comparison of the oil potential of coal and coaly mudstone[J]. Geochimica, 2009, 38(6): 583-590. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200906011.htm [32] 张斌, 毛治国, 张忠义, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长7段黑色页岩形成环境及其对页岩油富集段的控制作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(6): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202106006.htmZHANG Bin, MAO Zhiguo, ZHANG Zhongyi, et al. Black shale formation environment and its control on shale oil enrichment in Triassic Chang 7 Member, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(6): 1127-1136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202106006.htm [33] 李延钧, 陈义才, 杨远聪, 等. 鄂尔多斯下古生界碳酸盐烃源岩评价与成烃特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999, 20(4): 349-353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199904017.htmLI Yanjun, CHEN Yicai, YANG Yuancong, et al. Source rock evaluation and characteristics of hydrocarbon generation from Lower Paleozoic carbonate in Ordos Basin[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 1999, 20(4): 349-353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT199904017.htm [34] 王大锐. 油气稳定同位素地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2000.WANG Darui. Stable isotope geochemistry of oil and gas[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2000. [35] 何发岐, 王付斌, 张威, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘勘探思路转变与天然气领域重大突破[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(6): 39-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202006004.htmHE Faqi, WANG Fubin, ZHANG Wei, et al. Transformation of exploration ideas and major breakthrough in natural gas discovery in the northern margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(6): 39-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202006004.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号