Distribution and significance of maleimides in organic matter-enriched shales and derived crude oils
-
摘要: 马来酰亚胺或1H-吡咯-2, 5-二酮来源于叶绿素或细菌叶绿素的降解,是沉积有机质和石油中一类新型生物标志化合物。通过对国内外几个含油气盆地富有机质页岩的可溶有机质(EOM)和原油进行精细分离,在目标馏分F2中发现了丰富的马来酰亚胺类化合物,尤其是主要由光合绿硫细菌生成的2-甲基-3-异丁基(Me, i-Bu)和2-甲基-3-正丙基(Me, n-Pr)马来酰亚胺。研究表明,2-甲基-3-异丁基和2-甲基-3-正丙基马来酰亚胺在海相和咸化湖盆中十分发育,表明透光滞水带(PZE)发生在松辽盆地嫩江组微咸水环境、渤海湾盆地沙河街组咸水—半咸水环境和奥连特盆地Napo组海相环境,指示强还原的保存条件。北部湾盆地2-甲基-3-异丁基和2-甲基-3-正丙基马来酰亚胺的出现反映流沙港组二段油页岩形成过程中存在PZE,同样反映还原环境以及微咸水水体。可见,PZE是有机质富集和优质烃源层发育的有利因素。进一步分析发现,(Me, i-Bu)/(Me, Et)(甲基, 乙基)和(Me, n-Pr)/(Me, Et)参数可以区分海相、半咸水—咸水湖相和微咸水湖相环境。Abstract: The maleimides, or 1H-pyrrole-2, 5-diones, are one of the novel types of biological markers existed in both sedimentary organic matter and petroleum, which could be products derived from the degradation of chlorophylls and bacteriochlorophylls. In this study, the maleimides composition was investigated in detail for several crude oils and petroleum source rocks with varying depositional settings, and abundant 2-methyl-3-n-propyl (Me, n-Pr) and 2-methyl-3-isobutyl (Me, i-Bu) maleimide, together with aryl isoprenoids were detected. These pigments-derived products were prominently generated by Chlorobiaceae and are especially abundant in the saline and marine black shales and related oils, indicating that PZE (photic zone euxinia) occurred in the brackish water environment of the Nenjiang Formation in the Songliao Basin, the saline to semi-saline water environment of the Shahejie Formation in the Bohai Bay Basin, and the marine environment of the Napo Formation in the Oriente Basin, showing strong reduction preservation conditions. It can be concluded that PZE is a favorable factor for the enrichment of organic matter and the development of high-quality source layers. In addition, the ratios of Me, i-Bu/Me, Et and Me, n-Pr/Me, when coupled together, could be used to diagnose the depositional conditions such as marine, saline, semi-saline or brackish water column.
-
Key words:
- aryl isoprenoid /
- maleimide /
- Chlorobiaceae /
- PZE (photic zone euxinia) /
- OM-rich shales /
- source rock /
- deposition environment
-
表 1 原油和页岩样品基本地球化学信息
Table 1. Basic information of oil and shale samples
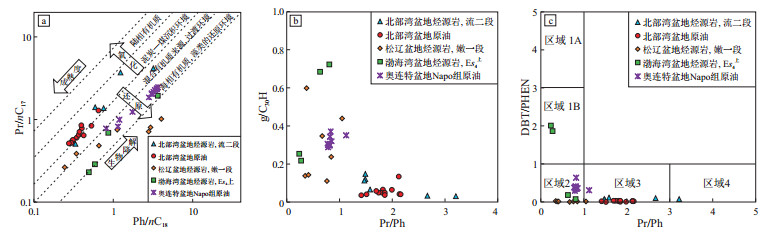
编号 井号 盆地 类型 层位 ω(TOC)/% S1/(mg·g-1) S2/(mg·g-1) Tmax/℃ Pr/Ph Pr/ nC17 Ph/ nC18 DBT GI AIR i-Bu n-Pr 1 3380 北部湾 油页岩 流二段 4.85 2.77 12.91 442 1.59 1.38 0.75 0.11 0.07 - 0.07 0.07 2 3490 北部湾 油页岩 流二段 7.52 6.86 23.40 432 1.49 0.53 0.32 0.05 0.15 - 0.18 0.04 3 2-1 北部湾 油页岩 流二段 6.34 0.43 7.03 429 1.49 0.51 0.33 0.06 0.12 - 0.03 0.03 4 2-2 北部湾 油页岩 流二段 2.08 0.90 6.04 442 1.48 4.15 3.20 0.08 0.11 - 0.00 0.01 5 2326 北部湾 油页岩 流二段 5.31 1.62 38.53 435 3.21 3.73 1.23 0.08 0.03 - 0.00 0.03 6 2644 北部湾 油页岩 流二段 6.47 3.21 33.55 435 2.67 1.42 0.58 0.10 0.03 - 0.01 0.05 7 3-4 北部湾 原油 流三段 1.82 0.54 0.30 0.01 0.07 - 0.21 0.01 8 1N-2 北部湾 原油 流一段 1.52 0.65 0.42 0.00 0.04 - 0.05 0.04 9 1N-3 北部湾 原油 流一段 1.42 0.84 0.52 0.01 0.04 - 0.09 0.06 10 1-5 北部湾 原油 涠三段 1.81 0.61 0.34 0.02 0.05 - 1.17 0.19 11 1-6 北部湾 原油 涠二段 1.74 0.66 0.36 0.02 0.05 - 0.39 0.19 12 2-5 北部湾 原油 流二段 2.14 0.79 0.40 0.03 0.04 - 1.72 0.56 13 2-1 北部湾 原油 流三段 1.86 0.70 0.37 0.00 0.05 - 1.72 0.50 14 11-3 北部湾 原油 流二段 1.86 0.56 0.31 0.02 0.04 - 4.54 0.49 15 2SA 北部湾 原油 流一段 2.17 0.85 0.40 0.01 0.04 - 2.73 0.53 16 10-1 北部湾 原油 涠三段 1.70 0.53 0.30 0.02 0.06 - 1.61 0.39 17 8-1 北部湾 原油 流一段 2.13 1.29 0.64 0.01 0.13 - 3.76 0.53 18 1S-2 北部湾 原油 流一段 1.99 0.52 0.27 0.00 0.06 - 1.88 0.39 19 C2 松辽 油页岩 嫩一段 7.76 2.25 58.91 439 0.35 0.81 2.92 0.03 0.14 1.05 0.000 0.006 20 L65 松辽 油页岩 嫩一段 2.11 1.17 11.82 437 0.38 0.72 2.76 0.01 0.60 0.89 0.000 0.003 21 D610 松辽 油页岩 嫩一段 2.29 0.68 13.12 435 0.42 1.02 4.02 0.01 0.15 0.78 0.000 0.003 22 Y15 松辽 油页岩 嫩一段 1.94 3.17 9.76 438 0.85 0.26 0.24 0.02 0.24 1.09 0.009 0.076 23 G12 松辽 油页岩 嫩一段 5.72 5.03 35.38 445 0.76 0.48 0.65 0.01 0.11 0.88 0.011 0.059 24 J1 松辽 页岩 嫩一段 1.80 2.50 9.91 442 0.68 0.75 1.11 0.00 0.35 0.57 0.006 0.035 25 J3 松辽 油页岩 嫩一段 2.46 2.58 15.84 441 1.05 0.39 0.34 0.01 0.44 0.87 0.004 0.028 26 L2 渤海湾 页岩 沙四段上部 1.05 1.04 4.01 437 0.24 0.23 0.49 2.00 0.25 0.06 0.08 0.12 27 L53 渤海湾 页岩 沙四段上部 1.46 1.27 7.88 421 0.28 0.29 0.59 1.85 0.22 0.13 0.058 0.13 28 G2 渤海湾 油页岩 沙四段上部 4.55 2.71 29.02 430 0.64 1.93 3.64 0.18 0.68 0.66 0.001 0.005 29 L89 渤海湾 页岩 沙四段上部 1.84 0.64 6.66 441 0.81 0.69 0.86 0.07 0.72 1.05 0.05 0.17 30 M38 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.79 2.34 3.52 0.29 0.30 0.65 0.87 0.40 31 M27 奥连特 原油 Napo组 1.13 0.79 0.81 0.30 0.35 0.85 1.03 0.21 32 M14 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.81 2.34 3.48 0.38 0.30 0.74 0.30 0.24 33 M16 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.81 2.43 3.62 0.37 0.30 0.61 0.44 0.33 34 M21 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.84 1.24 1.75 0.34 0.37 0.51 0.62 0.32 35 M22 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.81 2.24 3.37 0.37 0.30 0.43 0.56 0.42 36 M35 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.82 2.33 3.48 0.40 0.30 0.80 0.71 0.42 37 M42 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.83 0.83 1.14 0.63 0.34 0.53 0.24 0.32 38 M45 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.82 2.04 3.07 0.37 0.30 0.53 0.25 0.31 39 M50 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.82 2.14 3.16 0.34 0.30 0.63 0.61 0.52 40 M51 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.82 2.06 3.05 0.35 0.30 0.59 0.51 0.36 41 M52 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.86 0.99 1.20 0.37 0.32 0.66 0.59 0.36 42 M53 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.78 1.86 2.82 0.38 0.31 0.52 0.54 0.37 43 M54 奥连特 原油 Napo组 0.79 2.39 3.56 0.39 0.29 0.67 0.61 0.41 注:DBT为DBT/PHEN(二苯并噻吩/菲);GI为伽马蜡烷/C30藿烷;AIR为C13-17/C18-22芳基类异戊二烯;i-Bu为(Me, i-Bu)/(Me, Et);n-Pr为(Me, n-Pr)/(Me, Et)。 -
[1] PANCOST R D, CRAWFORD N, MAXWELL J R. Molecular evidence for basin-scale photic zone euxinia in the Permian Zechstein Sea[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 188(3/4): 217-227. [2] GALLEGO-TORRES D, MARTÍNEZ-RUIZ F, PAYTAN A, et al. Pliocene-Holocene evolution of depositional conditions in the eastern Mediterranean: role of anoxia vs. productivity at time of sapropel deposition[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 246(2/4): 424-439. [3] 冯子辉, 霍秋立, 王雪, 等. 松辽盆地松科1井晚白垩世沉积地层有机地球化学研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(5): 181-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200905022.htmFENG Zihui, HUO Qiuli, WANG Xue, et al. Geochemical research on the Late Cretaceous strata of well SK1 in Songliao Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(5): 181-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200905022.htm [4] 冯子辉, 方伟, 李振广, 等. 松辽盆地陆相大规模优质烃源岩沉积环境的地球化学标志[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2011, 41(9): 1253-1267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201109005.htmFENG Zihui, FANG Wei, LI Zhenguang, et al. Depositional environment of terrestrial petroleum source rocks and geochemical indicators in the Songliao Basin[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2011, 54(9): 1304-1317. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201109005.htm [5] 张林晔, 刘庆, 张春荣. 东营凹陷成烃与成藏关系研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005.ZHANG Linye, LIU Qing, ZHANG Chunrong. Study on the genetic relationships between hydrocarbon occurrence and pools formation in Dongying Depression[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2005. [6] ZHANG Linye, LIU Qing, ZHU Rifang, et al. Source rocks in Mesozoic-Cenozoic continental rift basins, east China: a case from Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2009, 40(2): 229-242. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2008.10.013 [7] 黄保家, 黄合庭, 吴国瑄, 等. 北部湾盆地始新统湖相富有机质页岩特征及成因机制[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(1): 25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201201002.htmHUANG Baojia, HUANG Heting, WU Guoxuan, et al. Geochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of Eocene lacustrine organic-rich shales in the Beibuwan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(1): 25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201201002.htm [8] 李友川, 兰蕾, 王柯, 等. 北部湾盆地流沙港组湖相烃源岩的差异[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(12): 1451-1459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201912003.htmLI Youchuan, LAN Lei, WANG Ke, et al. Differences in lacustrine source rocks of Liushagang Formation in the Beibuwan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(12): 1451-1459. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201912003.htm [9] 常睿, 王广利, 张枝焕, 等. 北部湾盆地沟鞭藻类分子化石的分布及成因[J]. 沉积学报, 2021. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2021.075.CHANG Rui, ANG Guangli, ZHANG Zhihuan, et al. Distribution and genesis of dinoflagellate-derived molecular fossils in Beibuwan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2021.075. [10] 张文正, 杨华, 彭平安, 等. 晚三叠世火山活动对鄂尔多斯盆地长7优质烃源岩发育的影响[J]. 地球化学, 2009, 38(6): 573-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200906010.htmZHANG Wenzheng, YANG Hua, PENG Ping'an, et al. The influence of Late Triassic volcanism on the development of Chang 7 high grade hydrocarbon source rock in Ordos Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2009, 38(6): 573-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200906010.htm [11] 张文正, 杨华, 解丽琴, 等. 湖底热水活动及其对优质烃源岩发育的影响: 以鄂尔多斯盆地长7烃源岩为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(4): 424-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201004006.htmZHANG Wenzheng, YANG Hua, XIE Liqin, et al. Lake-bottom hydrothermal activities and their influences on the high-quality source rock development: a case from Chang 7 source rocks in Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(4): 424-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201004006.htm [12] 张文正, 杨华, 解丽琴, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7优质烃源岩中超微化石的发现及意义[J]. 古生物学报, 2011, 50(1): 109-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201101012.htmZHANG Wenzheng, YANG Hua, XIE Liqin, et al. Discovery of micro-and nannofossils in high grade hydrocarbon source rocks of the Triassic Yanchang Formation Chang 7 member in Ordos Basin and its scientific significance[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 50(1): 109-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX201101012.htm [13] 韩载华, 赵靖舟, 孟选刚, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠纪湖盆东部"边缘"长7段烃源岩的发现及其地球化学特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(6): 991-1000. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202006991HAN Zaihua, ZHAO Jingzhou, MENG Xuangang, et al. Discovery and geochemical characteristics of Chang 7 source rocks from the eastern margin of a Triassic lacustrine basin in the Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(6): 991-1000. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202006991 [14] PANCOST R D, CRAWFORD N, MAGNESS S, et al. Further evidence for the development of photic-zone euxinic conditions during Mesozoic oceanic anoxic events[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2004, 161(3): 353-364. doi: 10.1144/0016764903-059 [15] GRICE K, GIBBISON R, ATKINSON J E, et al. Maleimides (1H-pyrrole-2, 5-diones) as molecular indicators of anoxygenic photosynthesis in ancient water columns[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(20): 3913-3924. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00199-8 [16] 王广利, NAEHER S, 李婧仪, 等. 1H-吡咯-2, 5-二酮(马来酰亚胺): 油气地球化学中的新生物标志物[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(2): 176-181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201902005.htmWANG Guangli, NAEHER S, LI Jingyi, et al. 1H-Pyrrole-2, 5-diones (maleimides): the novel biomarkers in petroleum geochemistry[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(2): 176-181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201902005.htm [17] GRICE K, SCHAEFFER P, SCHWARK L, et al. Changes in palaeoenvironmental conditions during deposition of the Permian Kupferschiefer (Lower Rhine Basin, northwest Germany) inferred from molecular and isotopic compositions of biomarker components[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1997, 26(11/12): 677-690. [18] NAEHER S, GRICE K. Novel 1H-Pyrrole-2, 5-dione (maleimide) proxies for the assessment of photic zone euxinia[J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 404: 100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.03.020 [19] 丁聪, 孙平昌, 热西提·亚力坤, 等. 松辽盆地青山口乡青山口组细粒沉积岩分类及其成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(4): 418-427. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202104005.htmDING Cong, SUN Pingchang, Rexiti·YALIKUN, et al. Classification and genesis of fine-grained sedimentary rocks of Qingshankou Formation in Songliao Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroloeum Geology, 2021, 42(4): 418-427. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202104005.htm [20] 赵琳洁, 陆建林, 王保华, 等. 基于不同岩性的总有机碳分段预测方法: 以东营凹陷始新统沙河街组三段下亚段为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(4): 721-727. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202104721ZHAO Linjie, LU Jianlin, WANG Baohua, et al. Segmented prediction of TOC based on lithology: a case study of the lower sub-member of the third member of the Eocene Shahejie Formation, Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(4): 721-727. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202104721 [21] 高岗, 徐新德, 刘诗局, 等. 涠西南凹陷流沙港组二段优质烃源岩判别及其控油作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(2): 339-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202002011.htmGAO Gang, XU Xinde, LIU Shiju, et al. Organic geochemistry identification of high-quality source rocks in the 2nd member of Liushagang Fm and its controls on petroleum occurrence in the Weixi'nan Sag, Beibuwan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(2): 339-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202002011.htm [22] 谢寅符, 季汉成, 苏永地, 等. Oriente-Maranon盆地石油地质特征及勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(1): 51-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201001008.htmXIE Yinfu, JI Hancheng, SU Yongdi. Petroleum geology and exploration potential of Oriente-Maranon Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(1): 51-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201001008.htm [23] MA Zhongzhen, TIAN Zuoji, ZHOU Yubing, et al. Geochemical characterization and origin of crude oils in the Oriente basin, Ecuador, South America[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2020, 104: 102790. [24] MA Zhongzhen, CHEN Heping, YANG Xiaofa, et al. Geochemical characteristics and charge history of oil in the Upper Cretaceous M1 sandstones (Napo Formation) in Block T, Oriente Basin, Ecuador[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 2021, 44(2): 167-186. [25] 王广利, 王铁冠, 张林晔. 济阳坳陷渤南洼陷湖相碳酸盐岩成烃特征[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(2): 62-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200702010.htmWANG Guangli, WANG Tieguan, ZHANG Linye. Hydrocarbon-generation characteristics for lacustrine carbonate source rocks in Bonan Sag of Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(2): 62-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200702010.htm [26] WANG Guangli, SIMONEIT B R T, SHI Shengbao, et al. A GC×GC-ToFMS investigation of the unresolved complex mixture and associated biomarkers in biodegraded petroleum[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2018, 92(5): 1959-1972. [27] NAEHER S, LENGGER S K, GRICE K. A new method for the rapid analysis of 1H-Pyrrole-2, 5-diones (maleimides) in environmental samples by two-dimensional gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2016, 1435: 125-135. [28] PETERS K E, FRASER T H, AMRIS W, et al. Geochemistry of crude oils from eastern Indonesia[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1999, 83(12): 1927-1942. [29] MOLDOWAN J M, SEIFERT W K, GALLEGOS E J. Relationship between petroleum composition and depositional environment of petroleum source rocks[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1985, 69(8): 1255-1268. [30] SINNINGHE DAMSTÉ J S, KENIG F, KOOPMANS M P, et al. Evidence for gammacerane as an indicator of water column strati-fication[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(9): 1895-1900. [31] HUGHES W B, HOLBA A G, DZOU L I P. The ratios of dibenzothiophene to phenanthrene and pristane to phytane as indicators of depositional environment and lithology of petroleum source rocks[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(17): 3581-3598. [32] WANG Guangli, WANG Tieguan, SIMONEIT B R T, et al. Sulfur rich petroleum derived from lacustrine carbonate source rocks in Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2010, 41(4): 340-354. [33] SCHWARK L, FRIMMEL A. Chemostratigraphy of the Posidonia black shale, SW-Germany: Ⅱ. Assessment of extent and persistence of photic-zone anoxia using aryl isoprenoid distributions[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 206(3/4): 231-248. [34] REPETA D J, SIMPSON D J. The distribution and recycling of chlorophyll, bacteriochlorophyll and carotenoids in the Black Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 1991, 38, Suppl 2: S969-S984. [35] KOOPMANS M P, KÖSTER J, VAN KAAM-PETERS H M E, et al. Diagenetic and catagenetic products of isorenieratene: molecular indicators for photic zone anoxia[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(22): 4467-4496. [36] 孙永革, 肖中尧, 徐世平, 等. 塔里木盆地原油中芳基类异戊二烯烃的检出及其地质意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2004, 25(2): 215-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200402032.htmSUN Yongge, XIAO Zhongyao, XU Shiping, et al. Aryl-isoprenoids in crude oil and its implication in geological exploration[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2004, 25(2): 215-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200402032.htm [37] 段宏亮, 刘世丽, 付茜. 苏北盆地古近系阜宁组二段富有机质页岩特征与沉积环境[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(4): 612-617. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202004612DUAN Hongliang, LIU Shili, FU Qian. Characteristics and sedimentary environment of organic-rich shale in the second member of Paleogene Funing Formation, Subei Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(4): 612-617. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202004612 [38] 张玉玺, 陈建文, 周江羽. 苏北地区早寒武世黑色页岩地球化学特征与有机质富集模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(4): 838-851. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004017.htmZHANG Yuxi, CHEN Jianwen, ZHOU Jiangyu. Geochemical features and organic matter enrichment in the Early Cambrian black shale, northern Jiangsu area[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(4): 838-851. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202004017.htm [39] 侯读杰, 黄清华, 黄福堂, 等. 松辽盆地海侵地层的分子地球化学特征[J]. 石油学报, 1999, 20(2): 30-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB902.005.htmHOU Dujie, HUANG Qinghua, HUANG Futang, et al. The characteristics of molecular geochemistry of marine transgression strata in Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1999, 20(2): 30-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB902.005.htm [40] 侯读杰, 王铁冠, 张一伟, 等. 中国东部第三系陆相沉积中的甲藻甾烷: 海侵指相的标志物?[J]. 地质论评, 1997, 43(5): 524-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199705012.htmHOU Dujie, WANG Tieguan, ZHANG Yiwei, et al. Dinosteranes in the tertiary terrestrial deposits, eastern China the marker of marine transgression facies?[J]. Geological Review, 1997, 43(5): 524-528. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP199705012.htm -





 下载:
下载:




 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号