Application of "retention coefficiency" method in shale gas resource evaluation: a case study of Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation to Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation, southeastern Sichuan Basin
-
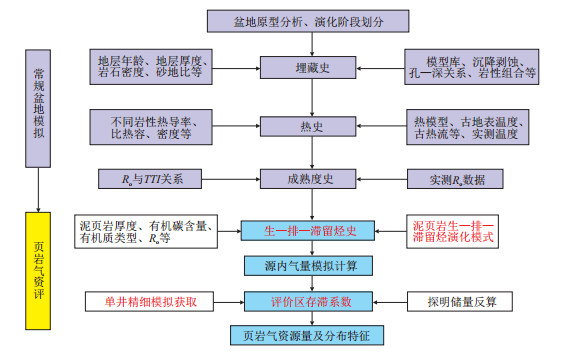
摘要: 资源评价除提供结果数据外,更重要的是要对有利区优选和勘探部署提供依据。针对传统页岩气资评方法存在的不足,结合地层孔隙热压模拟实验和最新盆地模拟技术,提出了采用“存滞系数”法开展页岩气资源评价的流程,并指出泥页岩生—排—滞留烃演化模式和页岩气“存滞系数”是两项最关键的参数。以目前我国页岩气勘探开发程度最高的川东南上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组泥页岩为例,详细阐述了新方法的应用过程,结果显示“存滞系数”法具有较好的适用性和可行性。与传统方法相比,“存滞系数”法既考虑到页岩气的动态演化过程,又考虑到晚期保存条件对页岩气富集的影响,并能刻画页岩气资源的空间展布特征,在页岩气资源评价和有利区优选方面具有广阔的应用前景。Abstract: Besides providing resulting data, the evaluation of resource abundance is more important to provide evidence for the optimization of favorable areas and the deployment of exploration. In view of the drawbacks of traditional methods, combined with the newly developed thermal-pressure simulation method of formation porosity and basin simulation method, this paper puts forward the process of shale gas resource evaluation using the "retention coefficiency" method. It is pointed out that the model of hydrocarbon generation-expulsion-retention and the "retention coefficiency"are the two most critical parameters in this new method. The Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation to Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation, which are the most highly explored shale in China, are taken as targets to illustrate the application process of the new method. Results show that the new method has good applicability and feasibility in shale gas resource evaluation. Compared with traditional methods, the "retention coefficiency" method not only considers the dynamic evolution process of shale gas, but also considers the influence of late preservation conditions on shale gas enrichment. In addition, the new method can describe the spatial distribution characteristics of shale gas resources, with a broad application prospect in shale gas resource evaluation and favorable area optimization.
-
表 1 川东南地区盆地模拟地层格架及剥蚀信息
Table 1. Stratigraphic framework and denudation information of southeastern Sichuan Basin
地层 地层底界年龄/Ma 剥蚀事件 剥蚀开始时间/Ma 剥蚀结束时间/Ma 残留地层底界年龄/Ma Q 2.5 K 144 √ 144 2.5 204 T3-J 232 √ 160 144 198 T2 242 √ 230 227 232 T1 250 P2 268 P1 295 C 355 D 420 S 440 √ 420 416 425 O 480 -C2-3 520 -C1 540 表 2 涪陵探区总生气量、源内生气量及探明储量
Table 2. Total gas production, in-source gas production and proved reserves in Fuling exploration area, Sichuan Basin
矿权区/探明储量区 总生气量/108 m3 源内生气量/108 m3 探明储量/108m3 存滞系数/% 焦石坝主体 29 699.96 12 931.98 4 618.97 35.72 平桥 10 188.15 4 411.47 1 389.17 31.49 -
[1] 宋振响, 邱岐, 赵琳洁, 等. 基于存滞系数的页岩气资源评价方法[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(10): 12-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202010003.htmSONG Zhenxiang, QIU Qi, ZHAO Linjie, et al. A shale gas resource evaluation method based on retention coefficient[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(10): 12-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202010003.htm [2] 郭秋麟, 陈宁生, 柳庄小雪, 等. 盆地模拟关键技术之油气运聚模拟技术进展[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 846-857. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005846GUO Qiulin, CHEN Ningsheng, LIU Zhuangxiaoxue, et al. Advance of basin modeling key techniques: hydrocarbon migration and accumulation simulation[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 846-857. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005846 [3] 刘可禹, 刘建良. 盆地和含油气系统模拟(BPSM)研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 石油科学通报, 2017, 2(2): 161-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201702001.htmLIU Keyu, LIU Jianliang. Current status and future development trends of Basin and Petroleum System Modeling (BPSM)[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2017, 2(2): 161-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201702001.htm [4] 宋振响, 陆建林, 周卓明, 等. 常规油气资源评价方法研究进展与发展方向[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2017, 22(3): 21-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201703003.htmSONG Zhenxiang, LU Jianlin, ZHOU Zhuoming, et al. Research progress and future development of assessment methods for conventional hydrocarbon resources[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(3): 21-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201703003.htm [5] 何川, 郑伦举, 王强, 等. 烃源岩生排烃模拟实验技术现状、应用与发展方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5): 862-870. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105862HE Chuan, ZHENG Lunju, WANG Qiang, et al. Experimental deve-lopment and application of source rock thermal simulation for hydrocarbon generation and expulsion[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2021, 43(5): 862-870. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105862 [6] 徐旭辉, 申宝剑, 李志明, 等. 页岩气实验地质评价技术研究现状及展望[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2020, 10(1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202001002.htmXU Xuhui, SHEN Baojian, LI Zhiming, et al. Status and prospect of experimental technologies of geological evaluation for shale gas[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2020, 10(1): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202001002.htm [7] 徐旭辉, 方成名, 陆建林, 等. 原型控源、迭加控藏: 油气盆地资源分级评价与有利勘探方向优选思维及技术[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 824-836. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005824XU Xuhui, FANG Chengming, LU Jianlin, et al. Hydrocarbon sources controlled by basin prototype and petroleum accumulation controlled by basin superposition: thoughts and technology of resource grading evaluation and exploration optimization in petroliferous basins[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 824-836. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005824 [8] 徐旭辉, 朱建辉, 江兴歌, 等. TSM盆地模拟原理方法与应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(6): 729-737. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201706729XU Xuhui, ZHU Jianhui, JIANG Xingge, et al. Principle of TSM basin simulation system and its application[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2017, 39(6): 729-737. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201706729 [9] 周雨双, 贾存善, 张奎华, 等. 应用TSM盆地模拟技术恢复准噶尔盆地东北缘石炭系烃源岩热演化史[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(2): 297-306. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102297ZHOU Yushuang, JIA Cunshan, ZHANG Kuihua, et al. Thermal evolution history reconstruction of Carboniferous source rocks on the northeastern margin of Junggar Basin using TSM basin simulation technology[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2021, 43(2): 297-306. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102297 [10] 黄振凯, 黎茂稳, 郑伦举, 等. 湖相烃源岩演化全过程中的孔隙演化机理: 基于地质样品与模拟实验的认识[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(4): 639-645. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202004639HUANG Zhenkai, LI Maowen, ZHENG Lunju, et al. Pore deve-lopment in lacustrine source rock evolution: interpretation based on geological samples and simulation experiments[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2020, 42(4): 639-645. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202004639 [11] 李楚雄, 申宝剑, 潘安阳, 等. 波罗的海盆地上奥陶统页岩孔隙演化的热压模拟实验[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(3): 434-442. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003434LI Chuxiong, SHEN Baojian, PAN Anyang, et al. Thermal-pressure simulation experiment of pore evolution of Upper Ordovician shale in Baltic Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2020, 42(3): 434-442. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003434 [12] 邹雨, 王国建, 卢丽, 等. 纳米孔隙中页岩气扩散模拟实验和数学模型分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5): 844-854. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105844ZOU Yu, WANG Guojian, LU Li, et al. Simulation experiment and mathematical model analysis for shale gas diffusion in nano-scale pores[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2021, 43(5): 844-854. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105844 [13] 郭旭升, 李宇平, 腾格尔, 等. 四川盆地五峰组-龙马溪组深水陆棚相页岩生储机理探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(1): 193-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202001021.htmGUO Xusheng, LI Yuping, BORJIGEN Tenger, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and storage mechanisms of deep-water shelf shales of Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(1): 193-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202001021.htm [14] 龙祖烈, 石创, 朱俊章, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷原油半开放条件下裂解成气模拟实验[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(3): 507-512. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103507LONG Zulie, SHI Chuang, ZHU Junzhang, et al. Simulation of crude oil cracking and gas generation with semi-open condition, Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2021, 43(3): 507-512. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103507 [15] 何大祥, 唐友军, 郑彬, 等. 生排烃热模拟中页岩生物标志化合物的变化及其地质意义[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(6): 689-694. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202006004.htmHE Daxiang, TANG Youjun, ZHENG Bin, et al. Changes of shale biomarkers in thermal simulation of hydrocarbon generation and expulsion and its geological significance[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2020, 27(6): 689-694. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202006004.htm [16] 陈璐, 胡志明, 熊伟, 等. 基于动量方程的页岩气体扩散能力表征模型与实验研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2020, 27(5): 132-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202005020.htmCHEN Lu, HU Zhiming, XIONG Wei, et al. Characte-rization model and experimental study of shale gas diffusion capacity based on momentum equation[J]. Special oil&Gas Reservoirs, 2020, 27(5): 132-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202005020.htm [17] 蔡勋育, 赵培荣, 高波, 等. 中国石化页岩气"十三五"发展成果与展望[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(1): 16-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202101003.htmCAI Xunyu, ZHAO Peirong, GAO Bo, et al. SINOPEC's shale gas development achievements during the"Thirteenth Five-Year Plan"period and outlook for the future[J]. Oil&Gas Geology, 2021, 42(1): 16-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202101003.htm [18] 杨跃明, 陈玉龙, 刘燊阳, 等. 四川盆地及其周缘页岩气勘探开发现状、潜力与展望[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(1): 42-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202101006.htmYANG Yueming, CHEN Yulong, LIU Shenyang, et al. Status, potential and prospect of shale gas exploration and development in the Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(1): 42-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202101006.htm [19] 龙胜祥, 冯动军, 李凤霞, 等. 四川盆地南部深层海相页岩气勘探开发前景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(4): 443-451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201804001.htmLONG Shengxiang, FENG Dongjun J, LI Fengxia, et al. Prospect of the deep marine shale gas exploration and development in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(4): 443-451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201804001.htm [20] 饶松, 胡迪, 胡圣标, 等. 叠合盆地深层构造-热演化研究方法: 以四川盆地为例[J]. 地质科学, 2019, 54(1): 159-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHS202206011.htmRAO Song, HU Di, HU Shengbiao, et al. Tectono-thermal reconstruction methods for deep zone in superimposed basins: a case study from Sichuan Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2019, 54(1): 159-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHS202206011.htm [21] 李春荣, 饶松, 胡圣标, 等. 川东南焦石坝页岩气区现今地温场特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(2): 617-627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201702016.htmLI Chunrong, RAO Song, HU Shengbiao, et al. Present-day geothermal field of the Jiaoshiba shale gas area in southeast of the Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(2): 617-627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201702016.htm [22] 石广仁. 计算烃类成熟度史的实地TTI-Ro法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2001, 28(4): 50-52.SHI Guangren. A practical TTI-Ro method for hydrocarbon maturity history reconstruction[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2001, 28(4): 50-52. [23] 王晔, 邱楠生, 仰云峰, 等. 四川盆地五峰-龙马溪组页岩成熟度研究[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(3): 953-971. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903022.htmWANG Ye, QIU Nansheng, YANG Yunfeng, et al. Thermal maturity of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale in Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(3): 953-971. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201903022.htm [24] 冯动军, 胡宗全, 高波, 等. 川东南地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气成藏条件分析[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(6): 1521-1532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201606014.htmFENG Dongjun, HU Zongquan, GAO Bo, et al. Analysis of shale gas reservoir-forming condition of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in southeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(6): 1521-1532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201606014.htm [25] 秦建中, 申宝剑, 腾格尔, 等. 不同类型优质烃源岩生排油气模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(2): 179-186. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201302179QIN Jianzhong, SHEN Baojian, BORJIGEN Tenger, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion pattern of different types of excellent source rocks[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2013, 35(2): 179-186. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201302179 [26] 吴蓝宇, 胡东风, 陆永潮, 等. 四川盆地涪陵气田五峰组-龙马溪组页岩优势岩相[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(2): 189-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201602005.htmWU Lanyu, HU Dongfeng, LU Yongchao, et al. Advantageous shale lithofacies of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in Fuling gas field of Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(2): 189-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201602005.htm [27] 陈斐然, 段金宝, 张汉荣, 等. 页岩气"压力系数"分级资源评价方法: 以川东南上奥陶统五峰组-下志留统龙马溪组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(3): 405-414. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003405CHEN Feiran, DUAN Jinbao, ZHANG Hanrong, et al. Shale gas resource evaluation based on "pressure coefficient": a case study of Upper Ordovician Wufeng-Lower Silurian Longmaxi formations in southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology&Experiment, 2020, 42(3): 405-414. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003405 [28] 李建忠, 吴晓智, 郑民, 等. 常规与非常规油气资源评价的总体思路、方法体系与关键技术[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(9): 1557-1565.LI Jianzhong, WU Xiaozhi, ZHENG Min, et al. General philosophy, method system and key technology of conventional and unconventional oil&gas resource assessment[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(9): 1557-1565. [29] 张金川, 林腊梅, 李玉喜, 等. 页岩气资源评价方法与技术: 概率体积法[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(2): 184-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201202028.htmZHANG Jinchuan, LIN Lamei, LI Yuxi, et al. The method of shale gas assessment: probability volume method[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(2): 184-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201202028.htm -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号