Distributional signatures of depositional system of Pinghu Formation, Pinghu slope, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin
-
摘要: 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带始新统平湖组是目前已证实的主力油气富集层系,对其沉积体系已开展过多轮研究,但是仍然存在很大争议。在前人研究的基础上,基于新处理的三维地震、岩心和多种地球化学测试等资料,对平湖斜坡带平湖组沉积环境和沉积体系重新展开了系统分析。平湖斜坡带主要发育三种沉积体系类型:河控三角洲、潮汐改造为主的三角洲和潮坪沉积体系。这三种沉积类型在平面上具有明显的分区性,平北地区以河控三角洲沉积为主,平中地区发育受潮汐改造的三角洲沉积,平南地区处于半封闭海湾湾口,以潮坪体系为主,洋流控制着砂体的空间展布形态和规模。整体而言,平湖斜坡带平湖组沉积格局从北向南表现出受海水影响逐渐加强的变化规律。Abstract: The Eocene Pinghu Formation on the Pinghu slope of Xihu Sag of East China Sea Shelf Basin is a main confirmed strata for hydrocarbon enrichment. At present, many studies have been carried out on its sedimentary system, but certain controversies are still existed. On the basis of previous studies and newly processed 3D seismic, core and geochemical data, it was re-analyzed in this paper for the sedimentary system of Pinghu Formation. Results show that there are three types of sedimentary system on the slope belt: river-controlled delta, tidal-transformed delta and tidal flat depositional system. These three types of sedimentary modes have obvious zoning characteristics in plane. The northern area is dominated by river-controlled delta deposits. The middle area is dominated by tidal-transformed delta deposits. The southern area is in the mouth of a semi-closed bay, dominated by tidal flat system, and ocean currents control the spatial distribution shape and scale of sand bodies. It is concluded that the influence of seawater on the sedimentary pattern of the Pinghu Formation in the slope belt is strengthening from north to south.
-
Key words:
- sedimentary distribution law /
- sedimentary system /
- Pinghu Formation /
- Eocene /
- Xihu Sag /
- East China Sea Shelf Basin
-
图 3 东海西湖凹陷平湖组典型岩心照片
a-e为8井,4 104.86~4 114.21 m:a.灰白色含砾中砂岩,最大粒径0.8 cm;b.板状交错层理,底见冲刷面;c.灰白色砂砾岩,低角度交错层理;d.灰白色中砂岩,冲刷面,正粒序;e.灰白色中砂岩,楔状交错层理。f-h为7井,4 465.89~4 474.79 m:f.灰白色中细砂岩,板状交错层理;g.灰白色中细砂岩,小型交错层理;h.灰色粉砂岩,脉状层理。i.5井,4 015.2 m,灰色细—粉砂岩,羽状交错层理;j.5井,4 341.8 m,粉砂岩,透镜状层理;k.4井,4 203.17 m,灰白色细沙岩,暗色矿物定向,含泥砾;l.4井,4 211.67 m, 灰白色细沙岩,倒粒序。m-o为1井,3 235.5~3 240.7 m:m.浅灰色泥质粉砂岩,岩性截变面;n.底砾岩及碳质泥岩;o.浅灰色泥质粉砂岩,撕裂状泥砾、脉状层理
Figure 3. Typical core pictures of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin
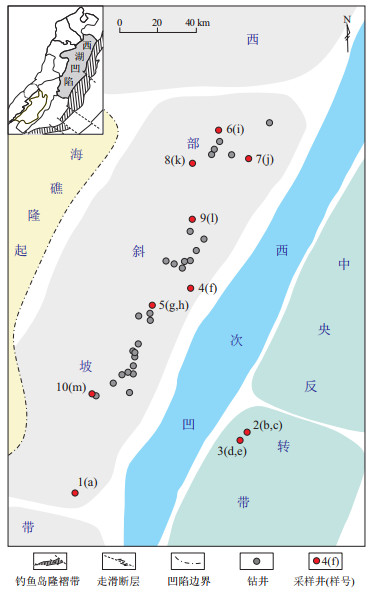
图 6 东海西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带碎屑锆石年龄多维尺度分析
a-l为样品编号,位置见图 1;实线表示亲缘关系最近的样品,虚线表示亲缘关系次之的样品
Figure 6. Multidimensional scale analysis of detrital zircon ages, Pinghu slope belt, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin
表 1 东海西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带平湖组沉积体系类型划分
Table 1. Classification of sedimentary system types of Pinghu Formation in Pinghu slope belt, Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin
沉积相 亚相 微相 河控三角洲 三角洲平原 水上分流河道、分流河道间 三角洲前缘 水下分流河道、分流间湾、河口砂坝 前三角洲 前三角洲泥 潮汐改造为主的三角洲 三角洲平原 水上分流河道、分流河道间、沼泽 三角洲前缘 水下分流河道、河口砂坝、潮汐砂坝、砂脊、席状砂 前三角洲 前三角洲泥 潮坪 潮上带 沼泽、泥坪 潮间带 泥坪、混合坪、砂坪、潮汐砂脊、潮砂丘 潮下带 潮汐水道、潮砂席、水下沙坝 注:表中内容据刘晓晨(2018)[19]修改。 -
[1] 彭伟欣, 刘金水. 东海西湖凹陷保俶斜坡平湖组层序地层分析[J]. 上海地质, 1995(4): 15-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD199504002.htmPENG Weixin, LIU Jinshui. Sequence stratigraphic analysis of Pinghu Formation in Baoshu slope of Xihu Sag in the East China Sea[J]. Shanghai Geology, 1995(4): 15-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHAD199504002.htm [2] 蒋一鸣, 邵龙义, 李帅, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖构造带平湖组沉积体系及层序地层研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(1): 141-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202001013.htmJIANG Yiming, SHAO Longyi, LI Shuai, et al. Deposition system and stratigraphy of Pinghu Formation in Pinghu tectonic belt, Xihu Sag[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(1): 141-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202001013.htm [3] 张志垚, 张昌民, 侯国伟, 等. 东海盆地某凹陷P井区平湖组沉积微相及沉积模式[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(2): 142-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD202002005.htmZHANG Zhiyao, ZHANG Changmin, HOU Guowei, et al. Microfacies distribution and sedimentary model of Pinghu Formation in P well area, East China Sea Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(2): 142-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD202002005.htm [4] 王泽宇, 徐清海, 侯国伟, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷W井区平湖组潮汐沉积模式[J]. 海相油气地质, 2021, 26(2): 159-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ202102008.htmWANG Zeyu, XU Qinghai, HOU Guowei, et al. Tidal depositional model of Pinghu Formation in W well block of Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2021, 26(2): 159-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ202102008.htm [5] 刘成鑫. 东海平湖油气田平湖组沉积相研究[J]. 海洋石油, 2010, 30(2): 9-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201002003.htmLIU Chengxin. Study on sedimentary facies for Pinghu Formation in Pinghu oil and gas field in East China Sea Basin[J]. Offshore Oil, 2010, 30(2): 9-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201002003.htm [6] 杨彩虹, 高兆红, 蒋一鸣, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带始新统平湖组碎屑沉积体系再认识[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2013, 35(9): 11-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201309003.htmYANG Caihong, GAO Zhaohong, JIANG Yiming, et al. Reunderstanding of clastic rock sedimentary facies of Eocene Pinghu Formation in Pinghu Slope of Xihu Sag[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2013, 35(9): 11-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201309003.htm [7] XIE Guoliang, SHEN Yulin, LIU Shugen. Trace and rare earth element (REE) characteristics of mudstones from Eocene Pinghu Formation and Oligocene Huagang Formation in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin: implications for provenance, depositional conditions and paleoclimate[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 92: 20-36. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.02.019 [8] SUO Yanhui, LI Sanzhong, ZHAO Shujuan, et al. Continental margin basins in East Asia: tectonic implications of the Meso-Cenozoic East China Sea pull-apart basins[J]. Geological Journal, 2015, 50(2): 139-156. doi: 10.1002/gj.2535 [9] WANG Qian, LI Sanzhong, GUO Lingli, et al. Analogue modelling and mechanism of tectonic inversion of the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 139: 129-141. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.01.026 [10] YANG F L, XU X, ZHAO W F, et al. Petroleum accumulations and inversion structures in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 2011, 34(4): 429-440. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-5457.2011.00513.x [11] 杜学斌, 陆永潮, 曹强, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷深部储层"相—岩—温"三元分级评价原则与效果[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 10-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202003005.htmDU Xuebin, LU Yongchao, CAO Qiang, et al. Grading evaluation of deep reservoir in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 10-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202003005.htm [12] 徐陈杰, 叶加仁, 刘金水, 等. 东海西湖凹陷平湖组Ⅲ型干酪根暗色泥岩生排烃模拟[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(2): 359-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202002013.htmXU Chenjie, YE Jiaren, LIU Jinshui, et al. Simulation of hydrocarbon generation and expulsion for the dark mudstone with type-Ⅲ kerogen in the Pinghu Formation of Xihu Sag in East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(2): 359-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202002013.htm [13] 徐陈杰, 叶加仁, 刘金水, 等. 东海西湖凹陷天然气成藏时期的关键证据: 气烃包裹体[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(11): 64-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202111010.htmXU Chenjie1, YE Jiaren1, LIU Jinshui, et al. Key evidence of gas accumulation period in Xihu Sag of the East China Sea Shelf Basin: gas hydrocarbon inclusion[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(11): 64-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202111010.htm [14] 魏恒飞, 陈践发, 郭旺, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖组层序地层划分和聚煤特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2013, 43(3): 669-679. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201303004.htmWEI Hengfei, CHEN Jianfa, GUO Wang, et al. Concentrating coal characteristics and sequences stratigraphic division of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Depression[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2013, 43(3): 669-679. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201303004.htm [15] 周瑞琦, 傅恒, 徐国盛, 等. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组—花港组沉积层序[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(1): 132-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201801014.htmZHOU Ruiqi, FU Heng, XU Guosheng, et al. Eocene Pinghu Formation-Oligocene Huagang Formation sequence stratigraphy and depositional model of Xihu Sag in East China Sea Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(1): 132-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201801014.htm [16] ZHU Yangming, LI Ying, ZHOU Jie, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Tertiary coal-bearing source rocks in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 35(1): 154-165. [17] ABBAS A, ZHU Hongtao, ZENG Zhiwei, et al. Sedimentary facies analysis using sequence stratigraphy and seismic sedimentology in the Paleogene Pinghu Formation, Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 93: 287-297. [18] HUBERT J F. A zircon-tourmaline-rutile maturity index and the interdependence of the composition of heavy mineral assemblages with the gross composition and texture of sandstone[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1962, 32(3): 440-450. [19] 刘晓晨. 西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带平湖组砂体精细刻画及时空演化研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.LIU Xiaochen. Fine characterization and evolution of sand body of Pinghu Formation in Pinghu Slope, Xihu Sag[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2018. [20] VERMEESCH P. Multi-sample comparison of detrital age distributions[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 341: 140-146. [21] 赵珂, 杜学斌, 贾冀新, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带的物源分析: 来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学及重矿物的证据[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 68-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202003011.htmZHAO Ke, DU Xuebin, JIA Jixin, et al. Provenance analysis of the Pinghu slope belt in Xihu Depression: evidence from detrital zircon U-Pb chronology and heavy minerals[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 68-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202003011.htm [22] 王行信, 韩守华. 中国含油气盆地砂泥岩黏土矿物的组合类型[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2002, 29(4): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200204000.htmWANG Xingxin, HAN Shouhua. The combination pattern of clay minerals of sandstone and mud rock in China's petroliferous basins[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2002, 29(4): 1-3. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK200204000.htm [23] 张哨楠, 丁晓琪, 万友利, 等. 致密碎屑岩中粘土矿物的形成机理与分布规律[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 34(3): 174-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201203028.htmZHANG Shaonan, DING Xiaoqi, WAN Youli, et al. Formation mecha-nism and distribution of clay minerals of deeply tight siliciclastic reservoirs[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2012, 34(3): 174-182. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201203028.htm [24] 黄苏卫, 张传运, 刘峰. 西湖凹陷Y构造花港组黏土矿物特征及对储层物性的影响[J]. 海洋石油, 2018, 38(2): 13-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201802003.htmHUANG Suwei, ZHANG Chuanyun, LIU Feng. Clay mineral characteristics of Huagang Formation and impact on the physical property of sandstone reservoir in structure Y of Xihu Sag[J]. Offshore Oil, 2018, 38(2): 13-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYSY201802003.htm [25] 吴嘉鹏, 万丽芬, 张兰, 等. 西湖凹陷平湖组岩相类型及沉积相分析[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(1): 27-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201701004.htmWU Jiapeng, WAN Lifen, ZHANG Lan, et al. Lithofacies types and sedimentary facies of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Depression[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2017, 29(1): 27-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201701004.htm [26] 赵雷昭, 刘腾腾, 庞江, 等. 砂岩储层中自生高岭石的成因与演化[J]. 辽宁化工, 2018.47(2): 116-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNHG201802015.htmZHAO Leizhao, LIU Tengteng, PANG Jiang, et al. Formation causes and evolution of authigenic kaolinite in sandstone reservoir[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(2): 116-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNHG201802015.htm [27] 杨飞, 邹妞妞, 史基安, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘马仙地区古近系碎屑岩沉积环境粒度概率累积曲线特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(4): 690-700. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201304007.htmYANG Fei, ZOU Niuniu, SHI Ji'an, et al. Probability cumulative grain size curves in the Paleogene clastic sediments and environmental significance in Maxian region of northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(4): 690-700. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201304007.htm [28] 张婕茹, 杨宏飞, 韩建斌, 等. 粒度概率曲线特征及岩相组合分析在沉积环境研究中的应用[J]. 天然气技术与经济, 2018, 12(4): 20-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRJJ201804007.htmZHANG Jieru, YANG Hongfei, HAN Jianbin, et al. Application of probability cumulative grain size curves and lithofacies association to sedimentology[J]. Natural Gas Technology and Economy, 2018, 12(4): 20-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRJJ201804007.htm -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号