Evaluation method for fault safety and its application based on ANSYS: a case study of Baiju aquifer gas storage in Dongtai Depression, Subei Basin
-
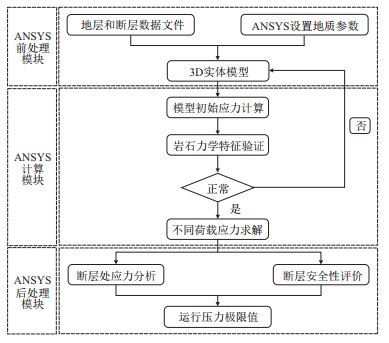
摘要: 含水层储气库利用多孔介质储层储蓄天然气,选址的地理范围较广,不依赖于大型盐矿或者衰竭油气藏,对我国天然气战略具有重大意义。含水层储气库通过天然断层封堵天然气、固井技术实现周期性注采,达到调节季节性峰值的目的,受注采压力变化的影响,运行过程断层容易开启或破裂,导致天然气泄漏。因此,含水层储气库断层安全性评价至关重要,而常见的断层评价和数值模拟方法没有涉及到多孔介质储层,对其膨胀机理研究尚浅,不适合用于含水构造的断层安全性评价。基于含水层储气库的基本特征,借助ANSYS有限元模拟和静态力学分析总结出一套完整的断层安全性评价方法。以苏北盆地东台坳陷大丰—兴化探区白驹储气地质体为例,构建出地层—断层的3D实体模型,根据初始应力平衡分析和断层岩石样本的轴压实验论证模型的有效性,通过位移约束法模拟不同运行压力条件下目标断层的应力状态,预测运行压力的极限值为29.50 MPa,超过该值断层可能发生拉张破坏。Abstract: Aquifer gas storage uses porous media reservoir to store natural gas. The location of aquifer gas storage has a wide geographical range and does not depend on large salt mines or depleted oil and gas reservoirs, which is of great significance to China's natural gas strategy. Aquifer gas storage realizes periodic injection-production through natural fault blocking natural gas and cementing technology, so as to achieve the purpose of adjusting seasonal peak value. Affected by the change of injection-production pressure, faults are easy to be opened or broken during operation, leading to the leakage of natural gas stored. Therefore, it is very important to evaluate the fault safety of aquifer gas storage, but the common fault evaluation and numerical simulation methods do not involve the porous media reservoir, and the study of its expansion mechanism is insufficient, which does not satisfy the fault safety evaluation of water-bearing structure. Based on the basic characteristics of aquifer gas storage, this paper summarizes a set of complete fault safety evaluation methods by ANSYS finite element simulation and static mechanics analysis. A case study was carried out in Baiju aquifer gas storage in the Dongtai Depression of the Subei Basin. A 3D entity model of formation and fault was established. According to the initial stress equilibrium analysis and the axial compression experiments of fault rock samples, the validity of the model can be demonstrated. With displacement constraint method, the stress state of target faults at different operating pressure was simulated. The maximum value of predicted operating pressure is 29.50 MPa, and tensile failure may occur above this value.
-
Key words:
- ANSYS /
- aquifer gas storage /
- fault /
- safety evaluation
-
图 3 苏北盆地东台坳陷大丰—兴化探区层序地层综合划分柱状图
据文献[20]修改。
Figure 3. Comprehensive division of sequence stratigraphy in Dafeng-Xinghua exploration area, Dongtai Depression, Subei Basin
表 1 模型参数
Table 1. Model parameter
目标层 单元属性 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 密度/(kg·m-3) 上覆层(盖层) SOLID185实体单元 47.82 0.32 2 070 地层 T20—T23 46.62 0.30 2 060 T23—T33 T33—T34 T34—T35 储层 T35—T40 44.90 0.28 2 050 下伏层 45.92 0.33 2 090 断层 F008/F022/F023/
F026/F063/F072/
F080/F083/F11547.62 0.33 2 090 -
[1] YIELDING G, FREEMAN B, NEEDHAM D T. Quantitative fault seal prediction[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(6): 897-917. [2] GIBSON R G. Fault-zone seals in siliciclastic strata of the Columbus Basin, offshore Trinidad[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1994, 78(9): 1372-1385. [3] 杨智, 何生, 王锦喜, 等. 断层泥比率(SGR)及其在断层侧向封闭性评价中的应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(3): 347-351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200503019.htmYANG Zhi, HE Sheng, WANG Jinxi, et al. Shale gouge ratio and its application in the fault seal estimation across the faulted zone[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(3): 347-351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200503019.htm [4] KNIPE R J. Juxtaposition and seal diagrams to help analyze fault seals in hydrocarbon reservoirs[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(2): 187-195. [5] 吕延防, 沙子萱, 付晓飞, 等. 断层垂向封闭性定量评价方法及其应用[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(5): 34-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200705007.htmLV Yanfang, SHA Zixuan, FU Xiaofei, et al. Quantitative evaluation method for fault vertical sealing ability and its application[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(5): 34-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200705007.htm [6] 吕延防, 王伟, 胡欣蕾, 等. 断层侧向封闭性定量评价方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(2): 310-316. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201602024.htmLYU Yanfang, WANG Wei, HU Xinlei, et al. Quantitative evaluation method of fault lateral sealing[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(2): 310-316. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201602024.htm [7] 吕延防, 黄劲松, 付广, 等. 砂泥岩薄互层段中断层封闭性的定量研究[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(6): 824-829. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200906006.htmLV Yanfang, HUANG Jinsong, FU Guang, et al. Quantitative study on fault sealing ability in sandstone and mudstone thin interbed[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(6): 824-829. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200906006.htm [8] 赵斌, 李云鹏, 田静, 等. 含水层储气库注采效应的数值模拟[J]. 油气储运, 2012, 31(3): 211-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY201203018.htmZHAO Bin, LI Yunpeng, TIAN Jing, et al. Numerical simulation on gas injection-production effects of underground gas storage in aquifer[J]. Oil & GAS Storage and Transportation, 2012, 31(3): 211-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY201203018.htm [9] 危齐, 王晓强, 王迪晋, 等. 呼图壁地下储气库三维有限元数值模拟分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2018, 38(5): 477-481. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201805009.htmWEI Qi, WANG Xiaoqiang, WANG Dijin, et al. Finite element nume-rical simulation analysis of Hutubi underground gas storage[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2018, 38(5): 477-481. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB201805009.htm [10] ZHANG Yanhua, UNDERSCHULTZ J, LANGHI L, et al. Numerical modelling of coal seam depressurization during coal seam gas production and its effect on the geomechanical stability of faults and coal beds[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 195: 1-13. [11] HUANG Na, LIU Richeng, JIANG Yujing, et al. Shear-flow coupling characteristics of a three-dimensional discrete fracture network-fault model considering stress-induced aperture variations[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 571: 416-424. [12] 王则, 商琳, 龚丽荣, 等. 基于地质力学方法对不同结构断层破碎带封闭性评价: 以渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷车镇凹陷M区为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(6): 893-900. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906893WANG Ze, SHANG Lin, GONG Lirong, et al. Sealing performance evaluation of fault fracture zone of different structures based on geomechanical methods: a case study in M area, Chezhen Sag, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(6): 893-900. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201906893 [13] 谭丽娟, 解宏泽, 张辉, 等. 一种生长断层封闭性定量研究方法: 以辽河坳陷辽中凹陷JX1-1油田为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(2): 268-273. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201802268TAN Lijuan, XIE Hongze, ZHANG Hui, et al. A quantitative research method on the sealing of growth faults: a case study of JX1-1 oil field in Liaozhong Sag, Liaohe Depression[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(2): 268-273. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201802268 [14] 赵乐强, 贾凡建, 曹剑, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北地区断层内流体活动过程及对断层启闭性的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(4): 461-466. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201704461ZHAO Leqiang, JIA Fanjian, CAO Jian. Fluid activity in faults in the northwestern Junggar Basin and its influence on fault opening and sealing[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(4): 461-466. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201704461 [15] 景紫岩, 李国斌, 付晓飞, 等. 基于砂箱物理模拟的断层封闭有效性评价新方法[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(1): 348-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202201026.htmJING Ziyan, LI Guobin, FU Xiaofei, et al. New methods for evaluation fault sealing effectiveness based on sand box physical simulation[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(1): 348-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202201026.htm [16] 于本福. 含水层地下储气库注采模拟及安全可靠性研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2015.YU Benfu. Research on injection-production and reliability of aquifer underground gas storage[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2015. [17] 王珂, 戴俊生. 地应力与断层封闭性之间的定量关系[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(1): 74-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201201008.htmWANG Ke, DAI Junsheng. A Quantitative relationship between the crustal stress and fault sealing ability[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(1): 74-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201201008.htm [18] CUSS R J, HARRINGTON J F. An experimental study of the potential for fault reactivation during changes in gas and pore-water pressure[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2016, 53: 41-55. [19] YIN Shuai, XIE Runcheng, WU Zhonghu, et al. In situ stress heterogeneity in a highly developed strike-slip fault zone and its effect on the distribution of tight gases: a 3D finite element simulation study[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 99: 75-91. [20] 魏祥峰, 张廷山, 黄静, 等. 苏北盆地白驹凹陷古近系层序地层特征及充填演化模式[J]. 地球学报, 2011, 32(4): 427-437. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201104012.htmWEI Xiangfeng, ZHANG Tingshan, HUANG Jing, et al. Sequence stratigraphy characteristics and filling evolution models of Paleogene in Baiju Sag, Subei Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2011, 32(4): 427-437. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201104012.htm [21] 尹雪英, 杨春和, 陈剑文. 金坛盐矿老腔储气库长期稳定性分析数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2006, 27(6): 869-874. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200606003.htmYIN Xueying, YANG Chunhe, CHEN Jianwen. Numerical simulation research on long-term stability of gas storage in Jintan Salt Mine[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(6): 869-874. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200606003.htm -





 下载:
下载:













 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号