Correlation between formation pressure and hydrocarbon enrichment in Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Western Sichuan Depression
-
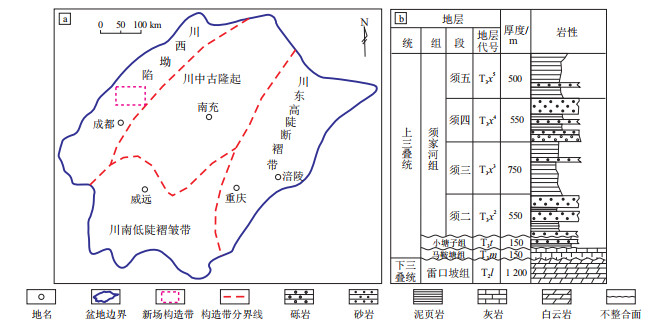
摘要: 川西坳陷新场构造带的上三叠统须家河组是四川盆地重要的致密砂岩油气勘探开发目的层。为提升勘探开发成效,提出以流体动力学为切入点,从动态角度研究油气运动特征,并结合静态研究成果确定油气分布特征的方法,开展油气富集与地层压力关系研究。该区域发育超压,须三段超压发育程度最高,主要产气层须二段地层压力普遍在60~80MPa之间;剩余压力最高可达40MPa,大部分区域的剩余压力梯度在0~3MPa/km之间,最高可达10MPa/km。通过动态法油气富集理论和对剩余压力、剩余压力梯度等的相关研究,认为其与断层、流体、油气分布具有重要的关系:剩余压力梯度较高(1~2MPa/km)的区域能兼顾断层改善流体运移能力和较好储层的优势,有利于长期高产稳产。Abstract: The Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Xinchang structural belt of the Western Sichuan Depression is an important exploration target for tight sandstone hydrocarbon in the Sichuan Basin. Several studies are carried out in this paper to improve the effectiveness of exploration and development including the characteristics of oil and gas movement with a view of dynamic point combining with fluid dynamics, determine the distribution characteristics of oil and gas in combination with static research results, and study the relationship between hydrocarbon enrichment and formation pressure. Overpressure is developed in the study area, and the degree of overpressure in the third member of Xujiahe Formation is the highest. Whilst the formation pressure of the main gas producing layer, the second member of Xujiahe Formation, is generally between 60-80 MPa with the maximum residual pressure reaches 40 MPa. The residual pressure gradients in most areas distribute between 0-3 MPa/km and up to 10 MPa/km as the highest. According to dynamic hydrocarbon enrichment theory and the relevant research on residual pressure and residual pressure gradient, it is considered that it has an important relationship with faults, fluids, hydrocarbon distribution and production performance. The area with higher residual pressure gradient (1-2 MPa/km) both improves fluid migration capacity and provides favorable reservoir, which is conducive to long-term high-yield and stable production.
-
图 5 川西坳陷上三叠统须家河组二段联井剖面剩余压力梯度
剖面位置见图 3。
Figure 5. Residual pressure gradients of well connection sections of second member of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, West Sichuan Depression
-
[1] 贾承造, 郑民, 张永峰. 中国非常规油气资源与勘探开发前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(2): 129-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201202002.htmJIA Chengzao, ZHENG Min, ZHANG Yongfeng. Unconventional hydrocarbon resources in China and the prospect of exploration and development[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(2): 129-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201202002.htm [2] 段文燊. 四川盆地中侏罗统下沙溪庙组致密气勘探潜力及有利方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(3): 424-431. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103424DUAN Wenshen. Exploration potential and favorable direction of tight gas in Middle Jurassic Xiashaximiao Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(3): 424-431. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103424 [3] 郑和荣, 刘忠群, 徐士林, 等. 四川盆地中国石化探区须家河组致密砂岩气勘探开发进展与攻关方向[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(4): 765-783. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202104002.htmZHENG Herong, LIU Zhongqun, XU Shilin, et al. Progress and key research directions of tight gas exploration and development in Xujiahe Formation, SINOPEC exploration areas, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(4): 765-783. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202104002.htm [4] 刘忠群, 徐士林, 刘君龙, 等. 四川盆地川西坳陷深层致密砂岩气藏富集规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(2): 31-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202002005.htmLIU Zhongqun, XU Shilin, LIU Junlong, et al. Enrichment laws of deep tight sandstone gas reservoirs in the Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(2): 31-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202002005.htm [5] 刘君龙, 刘忠群, 肖开华, 等. 四川盆地新场地区三叠系须家河组二段致密砂岩有利岩石相表征及油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(6): 1111-1121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202006007.htmLIU Junlong, LIU Zhongqun, XIAO Kaihua, et al. Characterization of favorable lithofacies in tight sandstone reservoirs and its significance for gas exploration and exploitation: a case study of the 2nd member of Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Xinchang area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6): 1111-1121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202006007.htm [6] 李智武, 刘树根, 林杰, 等. 川西坳陷构造格局及其成因机制[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(6): 645-653. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200906011.htmLI Zhiwu, LIU Shugen, LIN Jie, et al. Structural configuration and its genetic mechanism of the West Sichuan Depression in China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2009, 36(6): 645-653. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200906011.htm [7] LIU Shugen, YANG Yu, DENG Bin, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2021, 213: 103470. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103470 [8] 刘殊, 任兴国, 姚声贤, 等. 四川盆地上三叠统须家河组气藏分布与构造体系的关系[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(11): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201811001.htmLIU Shu, REN Xingguo, YAO Shengxian, et al. Relationship between gas reservoir distribution and structural system of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Fm in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(11): 1-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201811001.htm [9] LI Mengyao, ZHU Rong, LOU Zhanghua, et al. Diagenesis and its impact on the reservoir quality of the fourth member of Xujiahe Formation, Western Sichuan Depression, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 103: 485-498. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.03.011 [10] YANG Peng, ZHANG Likuan, LIU Keyu, et al. Diagenetic history and reservoir evolution of tight sandstones in the second member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation, western Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 201: 108451. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108451 [11] 郝芳, 邹华耀, 方勇, 等. 断—压双控流体流动与油气幕式快速成藏[J]. 石油学报, 2004, 25(6): 38-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200406009.htmHAO Fang, ZOU Huayao, FANG Yang, et al. Overpressure-fault controlled fluid flow and episodic hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2004, 25(6): 38-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200406009.htm [12] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望: 以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2): 173-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201202002.htmZOU Caineng, ZHU Rukai, WU Songtao, et al. Types, characteristics, genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations: taking tight oil and tight gas in China as an instance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 173-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201202002.htm [13] 李明诚, 李剑. "动力圈闭": 低渗透致密储层中油气充注成藏的主要作用[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(5): 718-722. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201005005.htmLI Mingcheng, LI Jian. "Dynamic trap": a main action of hydrocarbon charging to form accumulations in low permeability-tight reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(5): 718-722. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201005005.htm [14] 吴小奇, 周小进, 陈迎宾, 等. 四川盆地川西坳陷上三叠统须家河组烃源岩分子地球化学特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(5): 854-865. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202205854WU Xiaoqi, ZHOU Xiaojin, CHEN Yingbin, et al. Molecular characteristics of source rocks in Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(5): 854-865. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202205854 [15] 王志宏, 郝翠果, 李建明, 等. 川西前陆盆地超压分布及成因机制[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(6): 36-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201906004.htmWANG Zhihong, HAO Cuiguo, LI Jianming, et al. Distribution and genetic mechanism of overpressure in western Sichuan foreland basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(6): 36-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201906004.htm [16] 郭迎春, 庞雄奇, 陈冬霞, 等. 川西坳陷中段陆相地层压力演化及其成藏意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(4): 426-433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201204006.htmGUO Yingchun, PANG Xiongqi, CHEN Dongxia, et al. Evolution of continental formation pressure in the middle part of the Western Sichuan Depression and its significance for hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(4): 426-433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201204006.htm [17] 王震亮, 李耀华, 张健. 川西地区上三叠统异常流体压力的主要形成机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28(1): 43-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200701005.htmWANG Zhengliang, LI Yaohua, ZHANG Jian. Analysis on main formation mechanisms of abnormal fluid pressure in the Upper Triassic, west Sichuan area[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2007, 28(1): 43-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200701005.htm [18] 裴森奇, 李跃纲, 张本健, 等. 川西地区上三叠统天然气成藏主控因素及勘探方向[J]. 天然气工业, 2012, 32(10): 6-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201210003.htmPEI Senqi, LI Yuegang, ZHANG Benjian, et al. Major controlling factors of gas pooling and exploration directions in the Upper Triassic in the western Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2012, 32(10): 6-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201210003.htm [19] 刘华, 李君, 冯月琳, 等. 渤海湾盆地渤南洼陷沙河街组三段剩余压力梯度与油气分布关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(5): 1083-1091. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202005019.htmLIU Hua, LI Jun, FENG Yuelin, et al. Relationship between excess pressure gradient and hydrocarbon distribution in the 3rd member of Shahejie Formation in Bonan Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(5): 1083-1091. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202005019.htm [20] 冯月琳, 刘华, 宋国奇, 等. 平面压降梯度计算原则及其应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(4): 598-605. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904598FENG Yuelin, LIU Hua, SONG Guoqi, et al. Calculation and application of plane pressure decrease gradient[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(4): 598-605. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201904598 [21] 孙明亮, 柳广弟, 李剑. 超压盆地内剩余压力梯度与天然气成藏的关系[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 32(3): 19-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200803006.htmSUN Mingliang, LIU Guangdi, LI Jian. Relationship between excess-pressure gradient and gas accumulation in overpressured basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2008, 32(3): 19-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200803006.htm [22] WANG Qiaochu, CHEN Dongxia, WANG Fuwei, et al. Attenuating gradient of residual stratigraphic pressure and its controls on hydrocarbon migration and accumulation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 196: 108062. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0920410520311177 [23] HAO Fang, ZHU Weilin, ZOU Huayao, et al. Factors controlling petroleum accumulation and leakage in overpressured reservoirs[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2015, 99(5): 831-858. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288873069_Reservoir_Feature_of_the_Middle-Deep_Strata_in_Suning-Dawangzhuang_District_of_Jizhong_and_Its_Influencing_Factors [24] XU Shang, HAO Fang, XU Changgui, et al. Hydrocarbon migration and accumulation in the northwestern Bozhong subbasin, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 172: 477-488. [25] XIE Runcheng, ZHOU Wen, XIANG Mingliang, et al. Development mode of reverse fault-associated fractures in deep tight sandstones: a case study in Xinchang Gas Field, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2021, 56(6): 2997-3011. doi: 10.1002/gj.4084 [26] 杨威, 谢武仁, 俞凌杰, 等. 四川盆地上三叠统须家河组致密砂岩溶蚀实验及地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(4): 655-663. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202104655YANG Wei, XIE Wuren, YU Lingjie, et al. Dissolution experiments and geological implications of tight sandstones in the Xujiahe Formation of Upper Triassic, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(4): 655-663. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202104655 [27] 祝海华, 钟大康, 张亚雄, 等. 川南地区三叠系须家河组致密砂岩孔隙类型及物性控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(1): 65-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201401010.htmZHU Haihua, ZHONG Dakang, ZHANG Yaxiong, et al. Pore types and controlling factors on porosity and permeability of Upper Triassic Xujiahe tight sandstone reservoir in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(1): 65-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201401010.htm [28] 康保平, 黄小燕, 郭淑萍, 等. 川西坳陷须二气藏气田水成因、运移及其成藏演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(2): 309-317. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201802011.htmKANG Baoping, HUANG Xiaoyan, GUO Shuping, et al. Origin, migration, and accumulation evolution of reservoir water in the gas field with Xu 2 gas reservoir, Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(2): 309-317. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201802011.htm [29] 叶素娟, 朱宏权, 李嵘, 等. 天然气运移有机—无机地球化学示踪指标: 以四川盆地川西坳陷侏罗系气藏为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(4): 549-560. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201704010.htmYE Sujuan, ZHU Hongquan, LI Rong, et al. Tracing natural gas migration by integrating organic and inorganic geochemical data: a case study of the Jurassic gas fields in western Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(4): 549-560. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201704010.htm [30] 楼章华, 朱蓉, 金爱民, 等. 沉积盆地地下水与油气成藏—保存关系[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(8): 1188-1194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200908019.htmLOU Zhanghua, ZHU Rong, JIN Aimin, et al. Relationship between groundwater and hydrocarbon accumulation-preservation in sedimentary basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(8): 1188-1194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200908019.htm [31] 楼章华, 苏一哲, 朱蓉, 等. 四川盆地新场构造带上三叠统须家河组二段地层水化学动态特征及其成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(4): 841-851. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202104007.htmLOU Zhanghua, SU Yizhe, ZHU Rong, et al. Dynamic chemical characteristics and origin of formation water in the second member of Xujiahe Formation, Xinchang structural belt, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(4): 841-851. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202104007.htm [32] 张世华, 田军, 叶素娟, 等. 断层输导型天然气成藏模式的动态成藏过程: 以川西坳陷新场构造带上三叠统须二段气藏为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(7): 49-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201907010.htmZHANG Shihua, TIAN Jun, YE Sujuan, et al. Dynamic accumulation process of fault-translocation natural gas accumulation model: a case study on the gas reservoir of the second member of Upper Triassic Xujiahe Fm in the Xinchang structural zone of the Western Sichuan Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(7): 49-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201907010.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号