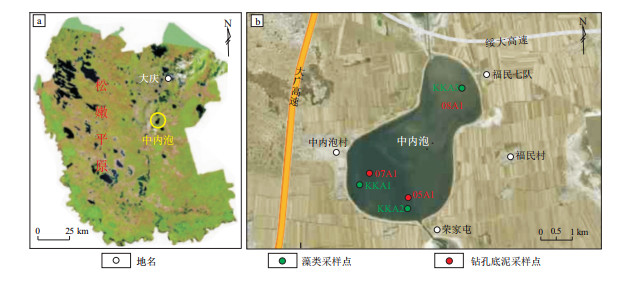
Coupled relationship between algal assemblages and water, surface sediments in modern shallow lakes of the Songnen Plain
-
摘要: 为探究中新生代陆相湖盆页岩有机质富集影响因素,根据藻类在生烃物质中的重要性,从现代湖泊沉积角度出发,采用藻类组合、水体理化性质、底泥粒度、磁化率和色度的皮尔逊相关分析等方法,研究了松嫩平原中内泡中现代藻类组合与水体和底泥之间的耦合关系。研究发现,地形和风场对半封闭混合型弱酸性微咸水湖有机质富集存在一定影响。中内泡不同位置蓝藻、绿藻、硅藻丰度的不同受水温影响,与底泥分选程度存在一定关系,水温和底泥分选程度显著受控于当地风场的干扰。Abstract: In order to study the influencing factors for the enrichment of organic matter in Mesozoic and Cenozoic shale in lacustrine basins, the Pearson analyses of algal assemblages, physical and chemical properties of water body, sedimentary grain size, magnetic susceptibility and chromaticity were carried out from the aspect of modern lacustrine deposition. The coupled relationship between modern algal assemblages and water body, surface sediments in the Zhongnei Lake, which is a semi-enclosed shallow lake in the Songnen Plain, showed that topography and wind field affected the enrichment of organic matter in semi-enclosed brackish lakes with acidic and mixed water bodies. In different sites of the Zhongnei Lake, the abundance of cyanobacteria, green algae and diatoms are affected by water temperature and has a certain relationship with the degree of sediment sorting. Water temperature and sediment sorting are significantly controlled by the interference of local wind field.
-
Key words:
- algae assemblage /
- water body /
- surface sediment /
- magnetic susceptibility /
- chromaticity /
- Songnen Plain
-
图 2 松嫩平原中内泡主要藻类显微图片
硅藻:1,2为针杆藻属;3为直链藻属;4为尖针杆藻;5为桥湾藻属;6为舟形藻属;7,8,9,10为小环藻属;11为小环藻属和脆杆藻属;12,13为针杆藻属;14为羽纹藻属;15为二头脆杆藻;16为针形菱形藻。绿藻:18,19,20,23,24,25为盘星藻属;21,22为微茫藻属;26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,40为栅藻属;35,36,37,38,39为镰形纤维藻属;41为蹄形藻属;42,43为弓形藻属;44为集星藻属。蓝藻:17为席藻属;45,46为色球藻属;47为鱼腥藻属。裸藻:48为扁裸藻属;49为旋纹裸藻。
Figure 2. Micrographs of main algaes in Zhongnei Lake, Songnen Plain
表 1 松嫩平原中内泡湖泊水体主要离子浓度
Table 1. Concentration of main ions in water body of Zhongnei Lake, Songnen Plain
离子类型 浓度/(mg·L-1) 离子类型 浓度/(mg·L-1) 重碳酸根(HCO3-) 5.57×102 镍离子(Ni2+) 1.00×10-2 氯离子(Cl-) 1.86×102 铬离子(Cr3+) 硫酸根(SO42-) 1.39×102 锌离子(Zn2+) 4.00×10-2 钙离子(Ca2+) 3.61×10 锶离子(Sr2+) 4.30×10-1 镁离子(Mg2+) 3.16×10 铜离子(Cu2+) 7.00×10-2 钾离子+钠离子(K++Na+) 2.96×102 钡离子(Ba2+) 8.00×10-2 表 2 松嫩平原中内泡主要藻类植物种类及其组成
Table 2. Main algal species and proportions in Zhongnei Lake, Songnen Plain
门 属 种 占比/% 门 属 种 占比/% 硅藻 布纹藻属 尖布纹藻 1.45 裸藻 扁裸藻属 短刺扁裸藻 0.14 脆杆藻属 钝脆杆藻 0.14 宽扁裸藻 0.72 二头脆杆藻 1.01 卵圆扁裸藻 0.14 中型脆杆藻 0.29 鳞孔藻属 莱韦克鳞孔藻 0.14 菱形藻属 针形菱形藻 2.46 裸藻属 尖尾裸藻 0.29 双菱藻属 布列双菱藻 0.14 梭形裸藻 0.14 桥弯藻属 微细桥弯藻 0.14 旋纹裸藻 0.11 小环藻属 库津小环藻粗点变种 0.14 绿藻 顶棘藻属 顶棘藻 0.14 链形小环藻 4.49 弓形藻属 螺旋弓形藻 0.72 梅尼小环藻 6.95 集星藻属 集星藻c v 0.72 异极藻属 缢缩异极藻 0.14 盘星藻属 短棘盘星藻 0.29 羽纹藻属 绿色羽纹藻 0.58 二角盘星藻 0.29 针杆藻属 尖针杆藻 0.29 盘藻属 盘藻 0.29 头状针杆藻 0.36 十字藻属 四足十字藻 0.29 肘状针杆藻匙形变种 0.36 四角藻属 微小四角藻具角变种 0.14 直链藻属 颗粒直链藻极狭变种 0.42 微芒藻属 微芒藻 0.72 舟形藻属 尖急舟形藻赫里保变种 1.05 韦斯藻属 韦斯藻 0.87 双头舟形藻 2.13 纤维藻属 镰型纤维藻 2.32 黄藻 拟气球藻属 拟气球藻 2.32 针形纤维藻 4.93 蓝藻 棒胶藻属 棒胶藻 0.72 新月藻属 尖新月藻变异变种 0.28 聚球藻属 聚球藻 49.28 微小新月藻狭变种 0.14 平裂藻属 细小平裂藻 0.29 栅藻属 多棘栅藻 0.14 色球藻属 膨胀色球藻 0.87 二形栅藻 0.29 螺旋藻属 螺旋藻 0.87 尖细栅藻 0.14 席藻属 席藻 2.89 四尾栅藻 3.62 鱼腥藻属 类颤藻鱼腥藻小型变种 0.14 爪哇栅藻 0.29 维盖拉鱼腥藻 1.01 隐藻 隐藻属 卵形隐藻 0.88 -
[1] 邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等. 页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(1): 14-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201301003.htmZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, CUI Jingwei, et al. Formation mechanism, geological characteristics and development strategy of nonmarine shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(1): 14-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201301003.htm [2] 赵文智, 朱如凯, 胡素云, 等. 陆相富有机质页岩与泥岩的成藏差异及其在页岩油评价中的意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(6): 1079-1089. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202006003.htmZHAO Wenzhi, ZHU Rukai, HU Suyun, et al. Accumulation contribution differences between lacustrine organic-rich shales and mudstones and their significance in shale oil evaluation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(6): 1079-1089. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202006003.htm [3] 康玉柱. 中国非常规油气勘探重大进展和资源潜力[J]. 石油科技论坛, 2018, 37(4): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKT201804001.htmKANG Yuzhu. Significant exploration progress and resource potential of unconventional oil and gas in China[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology Forum, 2018, 37(4): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKT201804001.htm [4] 滕吉文, 司芗, 王玉辰. 我国化石能源勘探、开发潜能与未来[J]. 石油物探, 2021, 60(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT202101002.htmTENG Jiwen, SI Xiang, WANG Yuchen. Potential and future of fossil fuel exploration and development in China[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2021, 60(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT202101002.htm [5] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 赵培荣, 等. 中国陆相页岩油地质特征与勘探实践[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(1): 155-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202201010.htmMA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, ZHAO Peirong, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration practices of continental shale oil in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(1): 155-171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202201010.htm [6] 刘招君, 孙平昌, 柳蓉, 等. 中国陆相盆地油页岩成因类型及矿床特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2016, 18(4): 525-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201604004.htmLIU Zhaojun, SUN Pingchang, LIU Rong, et al. Genetic types and deposit features of oil shale in continental basin in China[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2016, 18(4): 525-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201604004.htm [7] 蒋恕, 唐相路, OSBORNE S, 等. 页岩油气富集的主控因素及误辩: 以美国、阿根廷和中国典型页岩为例[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(7): 1083-1091. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707004.htmJIANG Shu, TANG Xianglu, OSBORNE S, et al. Enrichment factors and current misunderstanding of shale oil and gas: case study of shales in U.S., Argentina and China[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(7): 1083-1091. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707004.htm [8] 金之钧, 王冠平, 刘光祥, 等. 中国陆相页岩油研究进展与关键科学问题[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(7): 821-835. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202107001.htmJIN Zhijun, WANG Guanping, LIU Guangxiang, et al. Research progress and key scientific issues of continental shale oil in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(7): 821-835. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202107001.htm [9] BACHU S. Flow of formation waters, aquifer characteristics, and their relation to hydrocarbon accumulations, northern Alberta Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(5): 712-733. http://aapgbull.geoscienceworld.org/content/81/5/712 [10] 付秀丽, 蒙启安, 郑强, 等. 松辽盆地古龙页岩有机质丰度旋回性与岩相古地理[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2022, 41(3): 38-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202203004.htmFU Xiuli, MENG Qi'an, ZHENG Qiang, et al. Cyclicity of organic matter abundance and lithofacies paleogeography of Gulong shale in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2022, 41(3): 38-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202203004.htm [11] 陈中红, 查明. 陆相断陷咸化湖盆地层水化学场响应及与油气聚集关系: 以渤海湾盆地东营凹陷为例[J]. 地质科学, 2010, 45(2): 476-489. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201002010.htmCHEN Zhonghong, ZHA Ming. Response of formation water chemical fields and its relation to the hydrocarbon accumulation in the saline faulted-basin: a case study of Paleogene system in Dongying Sag[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2010, 45(2): 476-489. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201002010.htm [12] LI Mei, LOU Zhanghua, JIN Aimin, et al. Origin, flow of formation water and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Zhenwu area of the north Jiangsu Basin, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(3): 819-829. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/86253X/201303/46287795.html [13] 刘惠民, 杨怀宇, 张鹏飞, 等. 古湖泊水介质条件对混积岩相组合沉积的控制作用: 以渤海湾盆地东营凹陷古近系沙河街组三段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(2): 297-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202202005.htmLIU Huimin, YANG Huaiyu, ZHANG Pengfei, et al. Control effect of paleolacustrine water conditions on mixed lithofacies assemblages: a case study of the Palaeogene Es3, Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(2): 297-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202202005.htm [14] 柳波, 孙嘉慧, 张永清, 等. 松辽盆地长岭凹陷白垩系青山口组一段页岩油储集空间类型与富集模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(3): 521-535. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202103009.htmLIU Bo, SUN Jiahui, ZHANG Yongqing, et al. Reservoir space and enrichment model of shale oil in the first member of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in the Changling Sag, southern Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Deve-lopment, 2021, 48(3): 521-535. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202103009.htm [15] 高有峰, 王璞珺, 瞿雪姣, 等. 松辽盆地东南隆起区白垩系嫩江组一段沉积相、旋回及其与松科1井的对比[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(1): 99-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201001013.htmGAO Youfeng, WANG Pujun, QU Xuejiao, et al. Sedimentary facies and cyclostratigraphy of the Cretaceous first member of Nenjiang Formation in the southeast uplift zone, Songliao Basin and its correlation with the CCSD-SK-I[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(1): 99-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201001013.htm [16] 裘善文, 王锡魁, 张淑芹, 等. 松辽平原古大湖演变及其平原的形成[J]. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32(5): 1011-1021. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201205020.htmQIU Shanwen, WANG Xikui, ZHANG Shuqin, et al. The evolution of the large paleolake in Songliao Plain and its formation[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32(5): 1011-1021. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201205020.htm [17] 隋丰阳. 松嫩平原部分地区湖泊、泡沼藻类植物的初步研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨师范大学, 2010: 168.SUI Fengyang. Preliminary studies on algae from some lakes in Songnen Plain, China[D]. Harbin: Harbin Normal University, 2010: 168. [18] 胡鸿钧, 魏印心. 中国淡水藻类系统、分类及生态[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.HU Hongjun, WEI Yinxin. The freshwater algae of China freshwater algae of China systematics, taxonomy and ecology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006. [19] 翁建中, 徐恒省. 中国常见淡水浮游藻类图谱[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2010.WENG Jianzhong, XU Hengsheng. Atlas of common freshwater phytoplankton in China[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2010. [20] 高瑞祺, 乔秀云, 何承全. 松辽盆地白垩纪微体浮游植物群及其环境讨论[J]. 微体古生物学报, 1992, 9(2): 111-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT199202000.htmGAO Ruiqi, QIAO Xiuyun, HE Chengquan. Cretaceous microphytoplankton from the Songliao Basin and its depositional environment[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 1992, 9(2): 111-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT199202000.htm [21] 万传彪, 乔秀云, 赵传本, 等. 中国各时代油气形成母源体探讨[J]. 世界地质, 2004, 23(1): 35-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ200401005.htmWAN Chuanbiao, QIAO Xiuyun, ZHAO Chuanben, et al. Discussion on original bodies of gas-oil formation in different stages in China[J]. Global Geology, 2004, 23(1): 35-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ200401005.htm [22] 白海锋, 王怡睿, 宋进喜, 等. 渭河陕西段浮游植物群落结构时空变化与影响因子分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(8): 3290-3301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202108034.htmBAI Haifeng, WANG Yirui, SONG Jinxi, et al. Spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of phytoplankton community structure in the Shaanxi section of Weihe River, China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(8): 3290-3301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202108034.htm [23] EFREMOVA T V, PAL'SHIN N I, BELASHEV B Z. Water temperature in different types of lakes in Karelia under changing climate based on data of instrumental measurements in 1953-2011[J]. Water Resources, 2016, 43(2): 402-411. doi: 10.1134%2FS0097807816020020.pdf [24] HEISKANEN J J, MAMMARELLA I, OJALA A, et al. Effects of water clarity on lake stratification and lake-atmosphere heat exchange[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2015, 120(15): 7412-7428. http://istina.msu.ru/media/publications/article/143/5a9/10362455/9._Effects_of_water_clarity_on_lake_stratification_and_lake-atmosphere_heat_exchange.pdf [25] BOEHRER B, SCHULTZE M. Stratification of lakes[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2008, 46(2): RG2005. [26] SOMMER U, GLIWICZ Z M, LAMPERT W I, et al. The PEG-model of seasonal succession of planktonic events in fresh waters[J]. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie, 1986, 106(4): 433-471. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313700672_The_plankton_ecology_group_model_of_seasonal_succession_of_planktonic_events_in_fresh_waters [27] FONG P, BOYER K E, DESMOND J S, et al. Salinity stress, nitrogen competition, and facilitation: what controls seasonal succession of two opportunistic green macroalgae?[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 1996, 206(1/2): 203-221. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035100777410_f0ad.html [28] FINE P, SINGER M J, VEROSUB K L. Use of magnetic-susceptibility measurements in assessing soil uniformity in chronosequence studies[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1992, 56(4): 1195-1199. http://soilslab.cfr.washington.edu/SSSAJ/SSAJ_Abstracts/data/contents/a056-04-1195.pdf [29] 吴艳宏, 李世杰. 湖泊沉积物色度在短尺度古气候研究中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(5): 789-792. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200405016.htmWU Yanhong, LI Shijie. Significance of lake sediment color for short time scale climate variation[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2004, 19(5): 789-792. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200405016.htm [30] 郑国栋, 孟庆涛, 刘招君. 松辽盆地北部青一段油页岩地球化学特征及其记录的古湖泊学信息[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(2): 392-404. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202002008.htmZHENG Guodong, MENG Qingtao, LIU Zhaojun. Geochemical characteristics and paleolimnological information of oil shale in 1st member of Qingshankou Formation in northern Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2020, 50(2): 392-404. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202002008.htm [31] 贾建亮, 刘招君, BECHTEL A, 等. 松辽盆地嫩江组油页岩发育控制因素[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2014, 39(2): 174-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201402006.htmJIA Jianliang, LIU Zhaojun, BECHTEL A, et al. Major factors controlling formation of oil shale in Nenjiang Formation of Songliao Basin[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2014, 39(2): 174-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201402006.htm [32] 拜文华, 吴彦斌, 高智梁, 等. 浅湖—半深湖相湖湾环境油页岩成矿富集机理研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2010, 33(3): 207-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ201003010.htmBAI Wenhua, WU Yanbin, GAO Zhiliang, et al. Study on the mechanism of oil shale minerogenetic enrichment in the arm of shallow to half-deep lake depositional environment[J]. Geolo-gical Survey and Research, 2010, 33(3): 207-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ201003010.htm [33] 刘全有, 李鹏, 金之钧, 等. 湖相泥页岩层系富有机质形成与烃类富集: 以长7为例[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2022, 52(2): 270-290. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202202006.htmLIU Quanyou, LI Peng, JIN Zhijun, et al. Organic-rich formation and hydrocarbon enrichment of lacustrine shale strata: a case study of Chang 7 Member[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2022, 65(1): 118-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202202006.htm [34] 支东明, 唐勇, 杨智峰, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷陆相页岩油地质特征与聚集机理[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(3): 524-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201903009.htmZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, YANG Zhifeng, et al. Geological characteristics and accumulation mechanism of continental shale oil in Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3): 524-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201903009.htm [35] 刘伟新, 朱晓军, 马安林, 等. 不同泥岩相有机质赋存特征及对比表面积的影响: 以渤海湾盆地沾化凹陷古近系为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(2): 204-210. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201602204LIU Weixin, ZHU Xiaojun, MA Anlin, et al. Occurrence of organic matter in different mudstone lithofacies and its influence on specific surface area: a case study of the Paleogene in the Zhanhua Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(2): 204-210. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201602204 -





 下载:
下载:





 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号