Logging identification and distribution characteristics of high-gamma sandstones in the 7th member of Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin
-
摘要: 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段泥页岩层系内发育大量的砂岩夹层,这些砂岩夹层常伴有自然伽马值异常高的现象,部分砂岩的自然伽马值可高达330.5 API,在测井剖面上极易与泥页岩混淆。为识别高伽马砂岩,按照粒度和结构特征将该区延长组长7段碎屑岩划分为细砂岩、粉砂岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥岩和页岩,并应用常规测井数据运算组合成2个新参数——参数A和参数B,参数A和参数B组成的交汇图版以及自然伽马测井曲线,可有效区分识别出长7段中的正常砂岩和高伽马砂岩。长7段高伽马砂岩的累计厚度平面展布图表明,高伽马砂岩主要位于研究区的西南部;高伽马砂岩由湖盆边缘向湖盆中心呈指状发散展布的特征指示,其形成可能与长7段沉积期间的火山喷发有关。Abstract: A large number of sandstone interlayers were developed in the shale strata of the 7th member of the Triassic Yanchang Formation (Chang 7 member) in the Ordos Basin. These sandstone interlayers are frequently accompanied by abnormally high natural gamma values as high as 330.5 API. As a result, they are undistingui shable from shale on well profile. To characterize the high-gamma sandstones, the clastic rocks of the Chang 7 member were classified into fine sandstone, siltstone, argillaceous siltstone, silty mudstone, mudstone and shale according to grain size and structural characteristics. Conventional logging data were recalculated and combined into two new parameters—A and B. The new intersection chart composed of parameters A and B and natural gamma logging data can effectively distinguish and identify normal sandstone and high-gamma sandstone in the Chang 7 member. The plane distribution of cumulative thickness of high-gamma sandstone in the Chang 7 member shows that the high-gamma sandstone is mainly located in the southwest of the study area. The finger-like distribution of high-gamma sandstone from the edge to the center of the lake basin indicates that its formation may be related to the volcanic eruption during sedimentary period.
-
Key words:
- high-gamma sandstone /
- lithologic identification /
- Chang 7 member /
- Yanchang Formation /
- Triassic /
- Ordos Basin
-
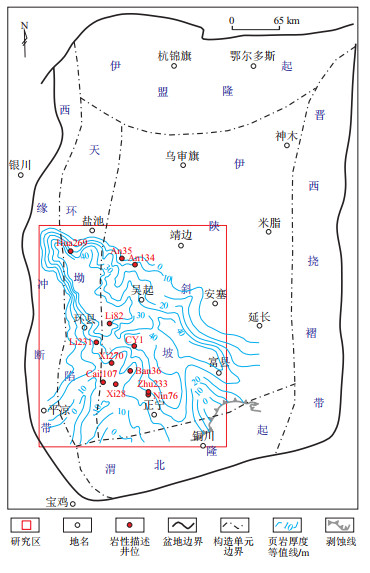
图 1 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段页岩和研究区分布范围
页岩厚度等值线据文献[22]。
Figure 1. Location of study area and distribution of Chang 7 shale, Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin
图 2 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段碎屑岩岩心照片
a.Zhe86井,2 410.4 m,灰色细砂岩,交错层理;b.Zhu174井,1 624.5 m,黑灰色粉砂岩,交错层理;c.Li287井,1 959.6 m,灰黑色泥质粉砂岩,块状层理,断面较粉砂岩更平整;d.Xi233井,1 942.1 m,灰黑色粉砂质泥岩,块状层理;e.Gen138井,2 734.92 m,黑色泥岩,块状层理;f.Hua317井,2 467.5 m,黑色页岩,水平层理,可见水平层理缝
Figure 2. Core photos of clastic rocks in Chang 7 member, Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段泥页岩层系内不同岩性测井数值
Table 1. Logging response of different lithologies in mud shale strata, Chang 7 member, Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin
岩性 AC/(μs·m-1) GR/API CNL/% DEN/(g·cm-3) SP/mV CLL8/(Ω·m)-1 CILD/(Ω·m)-1 细砂岩 $ \frac{191.8 \sim 244.2}{220.8}$ $ \frac{86.8 \sim 189.0}{116.5}$ $\frac{9.2 \sim 20.7}{15.6} $ $\frac{2.5 \sim 2.7}{2.6} $ $\frac{1.4 \sim 87.4}{71.4} $ $ \frac{4.4 \sim 55.7}{24.3}$ $ \frac{5.6 \sim 60.2}{18.9}$ 粉砂岩 $ \frac{209.2 \sim 262.8}{227.4}$ $ \frac{90.2 \sim 217.8}{140.1}$ $\frac{12.3 \sim 26.1}{18.1} $ $ \frac{2.4 \sim 2.7}{2.5}$ $ \frac{-2.5 \sim 87.3}{55.1}$ $\frac{1.1 \sim 46.1}{16.4} $ $ \frac{2.5 \sim 74.9}{18.7}$ 泥质粉砂岩 $\frac{220.3 \sim 269.6}{232.9} $ $ \frac{90.9 \sim 330.5}{149.2}$ $\frac{12.9 \sim 25.5}{19.6} $ $\frac{2.4 \sim 2.7}{2.6} $ $\frac{-0.4 \sim 106.9}{66.7} $ $\frac{0.6 \sim 111.0}{23.8} $ $\frac{2.1 \sim 84.8}{22.1} $ 粉砂质泥岩 $\frac{228.2 \sim 265.5}{244.6} $ $\frac{99.3 \sim 397.4}{174.0} $ $\frac{17.6 \sim 31.4}{23.6} $ $ \frac{2.4 \sim 2.7}{2.6}$ $ \frac{-0.4 \sim 116.0}{60.2}$ $ \frac{13.4 \sim 174.3}{40.3}$ $ \frac{9.4 \sim 149.6}{37.5}$ 泥岩 $\frac{246.2 \sim 288.0}{263.4} $ $ \frac{115.0 \sim 254.0}{156.2}$ $ \frac{19.8 \sim 34.4}{27.9}$ $ \frac{2.4 \sim 2.6}{2.5}$ $ \frac{55.9 \sim 118.1}{94.0}$ $\frac{8.4 \sim 77.3}{29.0} $ $\frac{7.9 \sim 64.0}{33.2} $ 页岩 $ \frac{247.7 \sim 354.1}{286.8}$ $ \frac{111.0 \sim 701.1}{277.0}$ $\frac{20.9 \sim 52.9}{32.9} $ $\frac{2.1 \sim 2.6}{2.4} $ $\frac{46.2 \sim 119.7}{68.6} $ $\frac{0.5 \sim 283.4}{27.5} $ $\frac{0.6 \sim 247.7}{27.6} $ 注:表中分式意义为$ \frac{\text { 最小值} \sim \text {最大值}}{\text { 平均值 }}$。 表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组相对高自然伽马砂岩储层的测井响应特征[3]
Table 2. Logging response characteristics of relatively high natural gamma sandstone reservoirs in Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin
项目 常规砂岩储层 相对高自然伽马砂岩储层 泥质岩石 微电极(微电位、微梯度) 两条曲线呈现明显正幅度差 两条曲线呈现明显正幅度差 两条曲线基本重叠或正负不定幅度差 自然电位(SP) 明显负异常 明显负异常 基线附近,平直 自然伽马(GR) 低值 相对高值 中—高值 自然电位(SP)与自然伽马(GR)曲线幅度差 按照曲线左右幅度基本重合的原则,两条曲线基本重叠 按照曲线左右幅度基本重合原则,两条曲线之间存在明显幅度差 两条曲线基本重叠 声波时差(AC)曲线 相对低—中值 相对高值 中—高值 双感应(ILD)—八侧向(LL8)曲线 相对中—高值,特征明显,不同探测范围电阻率曲线之间一般存在差异 相对低值,特征明显,不同探测范围的电阻率曲线之间一般存在差异 一般为低值,含有机质时为相对高值,曲线之间基本重叠 视电阻率(Ra)曲线 相对高值 相对低值 一般为低值,含有机质时为相对高值 声波时差(AC)—自然电位(SP)曲线重叠图 明显幅度差 明显幅度差 曲线基本重叠 深感应(Rd)—声波时差(英制)曲线重叠图 含油时存在明显幅度差,干层、水层处两条测井曲线基本重叠 对含油性反映不灵敏,含油层、水层、干层处两条测井曲线基本重叠 一般重叠,含有机质时曲线存在幅度差 计算自然电位与实测自然电位(SP)曲线重叠图 含油时存在明显幅度差,干层、水层处两条测井曲线基本重叠 含油时存在明显幅度差,干层、水层处两条测井曲线基本重叠 曲线基本重叠 -
[1] 付金华, 李士祥, 侯雨庭, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组7段Ⅱ类页岩油风险勘探突破及其意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(1): 78-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.008FU Jinhua, LI Shixiang, HOU Yuting, et al. Breakthrough of risk exploration of class Ⅱ shale oil in Chang 7 member of Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin and its significance[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(1): 78-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.008 [2] IMAM B, TREWIN N H. Factors contributing to high gamma-ray levels in Upper Jurassic sandstone reservoirs of the Claymore oilfield, North Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1991, 8(4): 452-460. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(91)90067-B [3] 张小莉, 冯乔, 孙佩, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组高自然伽马砂岩储层特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010, 53(1): 205-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201001024.htmZHANG Xiaoli, FENG Qiao, SUN Pei, et al. Characteristics of high gamma ray reservoir of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(1): 205-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201001024.htm [4] 刘行军, 冯春珍, 柳益群, 等. 陕北长6段高自然伽马砂岩地球化学特征及意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 40(4): 445-456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201304014.htmLIU Xingjun, FENG Chunzhen, LIU Yiqun, et al. Geochemical characteristics and significance of Chang 6 high natural gamma ray sandstones in Yanchang Formation in north of Shaanxi, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 40(4): 445-456. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201304014.htm [5] LIU Huaqing, LI Xiangbo, LIAO Jianbo, et al. Genesis of the high gamma sandstone of the Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Science, 2013, 10(1): 50-54. doi: 10.1007/s12182-013-0248-7 [6] ZHENG Qinghua, LIU Xingjun, YOU Jiyuan, et al. Discovery and prediction of high natural gamma sandstones in Chang 73 submember of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26(7): 1840-1855. doi: 10.1007/s11771-019-4138-z [7] LI Yajun, ZHANG Xiaoli, YAN Yuanzi. Quantitative identification of relatively high-level radioactive sandstone in the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation of the Ordos Basin, China[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2019, 16(3): 314-320. doi: 10.1007/s11770-019-0784-z [8] 李高仁, 郭清娅, 石玉江, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地高自然伽马储层识别研究[J]. 测井技术, 2006, 30(6): 511-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200606007.htmLI Gaoren, GUO Qingya, SHI Yujiang, et al. Identification of high gamma ray reservoir in Ordos Basin[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2006, 30(6): 511-515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJJS200606007.htm [9] LYU Qiqi, LUO Shunshe, GUAN Yulong, et al. A new method of lithologic identification and distribution characteristics of fine-grained sediments: a case study in southwest of Ordos Basin, China[J]. Open Geosciences, 2019, 11(1): 17-28. doi: 10.1515/geo-2019-0002 [10] 成大伟, 袁选俊, 周川闽, 等. 测井岩性识别方法及应用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地中西部长7油层组为例[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(5): 117-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201605016.htmCHENG Dawei, YUAN Xuanjun, ZHOU Chuanmin, et al. Logging-lithology identification methods and their application: a case study on Chang 7 Member in central-western Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(5): 117-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201605016.htm [11] FENG Congjun, YANG Hua, PU Renhai, et al. Lithology and oil-bearing properties of tight sandstone reservoirs: Chang 7 member of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, southwestern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Geosciences Journal, 2017, 21(2): 201-211. doi: 10.1007/s12303-016-0048-3 [12] 杨华, 席胜利. 长庆天然气勘探取得的突破[J]. 天然气工业, 2002, 22(6): 10-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200206003.htmYANG Hua, XI Shengli. Having made a breakthrough in natural gas exploration at Changqing[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2002, 22(6): 10-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG200206003.htm [13] 杨俊杰. 鄂尔多斯盆地构造演化与油气分布规律[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2002: 36-37.YANG Junjie. Tectonic evolution and oil-gas reservoirs distribution in Ordos Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2002: 36-37. [14] LIU Shaofeng. The coupling mechanism of basin and orogen in the western Ordos Basin and adjacent regions of China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1998, 16(4): 369-383. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Shaofeng_Liu3/publication/222313882_The_coupling_mechanism_of_basin_and_orogen_in_the_western_Ordos_Basin_and_adjacent_regions_of_China/links/00b4952e73f8423514000000 [15] LIU Shaofeng, YANG S G. Upper Triassic-Jurassic sequence stratigraphy and its structural controls in the western Ordos Basin, China[J]. Basin Research, 2000, 12(1): 1-18. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Shaofeng_Liu3/publication/230383635_Upper_Triassic__Jurassic_sequence_stratigraphy_and_its_structural_controls_in_the_western_Ordos_Basin_China/links/0a85e52e737a3c468e000000.pdf [16] QIU Xinwei, LIU Chiyang, MAO Guangzhou, et al. Late Triassic tuff intervals in the Ordos Basin, Central China: their depositional, petrographic, geochemical characteristics and regional implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 80: 148-160. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912013005774 [17] ZHANG Wenzheng, YANG Weiwei, XIE Liqin. Controls on organic matter accumulation in the Triassic Chang 7 lacustrine shale of the Ordos Basin, Central China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2017, 183: 38-51. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=27df24081b246e2d1c52cee0cb6f4e7b [18] 杨华, 张文正. 论鄂尔多斯盆地长7段优质油源岩在低渗透油气成藏富集中的主导作用: 地质地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2005, 34(2): 147-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200502006.htmYANG Hua, ZHANG Wenzheng. Leading effect of the seventh member high-quality source rock of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin during the enrichment of low-penetrating oil-gas accumulation: geology and geochemistry[J]. Geochimica, 2005, 34(2): 147-154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200502006.htm [19] 张文正, 杨华, 彭平安, 等. 晚三叠世火山活动对鄂尔多斯盆地长7优质烃源岩发育的影响[J]. 地球化学, 2009, 38(6): 573-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200906010.htmZHANG Wenzheng, YANG Hua, PENG Ping'an, et al. The influence of Late Triassic volcanism on the development of Chang 7 high grade hydrocarbon source rock in Ordos Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2009, 38(6): 573-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200906010.htm [20] YUAN Wei, LIU Guangdi, BULSECO A, et al. Controls on U enrichment in organic-rich shales from the Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, Northern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2021, 212: 104735. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912021000730 [21] 邱欣卫, 刘池洋, 毛光周, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组火山灰沉积物岩石地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2011, 36(1): 139-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201101016.htmQIU Xinwei, LIU Chiyang, MAO Guangzhou, et al. Petrological-geochemical characteristics of volcanic ash sediments in Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2011, 36(1): 139-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201101016.htm [22] 杨华, 李士祥, 刘显阳. 鄂尔多斯盆地致密油、页岩油特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301000.htmYANG Hua, LI Shixiang, LIU Xianyang. Characteristics and resource prospects of tight oil and shale oil in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301000.htm [23] 付锁堂, 姚泾利, 李士祥, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中生界延长组陆相页岩油富集特征与资源潜力[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(5): 698-710. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005698FU Suotang, YAO Jingli, LI Shixiang, et al. Enrichment characteristics and resource potential of continental shale oil in Mesozoic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(5): 698-710. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202005698 [24] 宋延杰, 陈科贵, 王向公. 地球物理测井[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011: 109-110.SONG Yanjie, CHEN Kegui, WANG Xianggong. Geophysical logging[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011: 109-110. [25] 李雪英, 赵玉秋, 范长海, 等. 超浅疏松地层泥质粉砂岩与粉砂质泥岩识别方法: 以大庆某地区黑帝庙层为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(1): 159-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201501024.htmLI Xueying, ZHAO Yuqiu, FAN Changhai, et al. An identification method of argillaceous siltstone and silty mudstone in extra shallow unconsolidated formation: taking an example of Heidimiao reservoir in an area of Daqing[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2015, 30(1): 159-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201501024.htm [26] 杨华, 牛小兵, 徐黎明, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长7段页岩油勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(4): 511-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201604003.htmYANG Hua, NIU Xiaobing, XU Liming, et al. Exploration potential of shale oil in Chang7 Member, Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(4): 511-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201604003.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号