Abnormal pressure genesis and its relationship with continental shale oil accumulation in Paleogene, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
-
摘要: 为了探索渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷地层异常压力对页岩油富集的影响,运用全岩X-衍射分析、常规热解生烃潜力分析和有机地球化学系统分析等方法,研究了4口页岩油专探井古近系的单井地层压力结构、泥页岩岩相、有机质成烃演化、黏土矿物转化、烃类滞留—次生孔隙和微裂缝分布的关系。研究区靠近洼陷中部的古近系沙河街组沙三中、下亚段和沙四上亚段岩相组合以碳酸盐岩为主,而靠近凹陷边缘以碎屑岩/化学岩混合沉积组合为主。利用声波测井、密度测井和钻录井资料,可有效识别单井压力结构和异常高压特征,并揭示生烃洼陷区以碳酸盐—黏土矿物组合为主的富有机质页岩中地层孔隙压力的影响因素。综合应用地球化学证据证实,济阳坳陷古近系地层超压主要来源于成熟泥页岩的生烃增压,泥页岩自源超压段与滞留烃高峰段及次生孔隙发育带相对应。Abstract: In order to explore the effect of abnormal pressure on shale oil accumulation in the Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, the formation pressure distribution, muddy shale lithofacies, hydrocarbon generation evolution of organic matters, clay mineral conversion, hydrocarbon retention, and the distribution of secondary pores and microfractures in each of four exploration wells specially for Paleogene shale oil were studied by total rock X-ray diffraction analysis, conventional pyrolysis analysis on hydrocarbon generation potential, systematic analysis on organic geochemistry, and other methods. In the study area, the lithofacies association in middle and lower submembers of the third member (Es3middle and Eslower)3, and upper submember of the fourth member (Es4upper) of Paleogene Shahejie Formation adjacent to subsag center is mainly carbonate rocks, while near sag margin, there are primarily mixed sediments of clastic rocks/chemical rocks. Based on the data from sonic, density and drilling loggings, pressure distribution and abnormal pressure characteristics in single well could be identified effectively; in addition, the factors that affect formation pore pressure in organic shale containing major association of carbonate and clay minerals could be uncovered. Comprehensive application of geochemical evidences confirmed that Paleogene overpressure in the Jiyang Depression was mainly originated from hydrocarbon generation pressurization in mature muddy shale. Self-source overpressure intervals in muddy shale are in correspondence with the zones of secondary pore development and peak hydrocarbon retention.
-
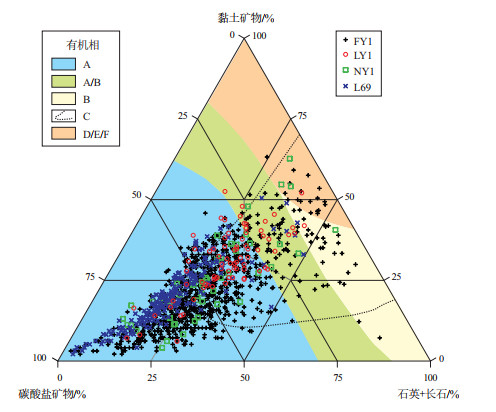
图 1 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷古近系沙河街组烃源岩的全岩矿物组成及其与有机相的关系
有机相A.干酪根类型Ⅰ-S/Ⅱ-S型(适用于海相和陆相富碳酸盐岩—蒸发岩体系);B.干酪根类型Ⅱ型为主;C.干酪根类型Ⅰ型为主(仅适用于陆相淡水沉积体系);D/E.干酪根类型Ⅲ型为主,主要生源为植物角质层、树脂、木质素和细菌;F.干酪根类型Ⅲ型为主,主要生源为木质素,详见参考文献[40]
Figure 1. Relationship between total rock mineral composition and organic facies of source rocks in Paleogene Shahejie Formation, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
表 1 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷页岩油探井各层段岩心样品全岩矿物X-衍射矿物百分含量统计
Table 1. Statistics on total rock mineral percentages by X-ray diffraction in core samples from every interval of shale oil exploration wells in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
% 井名 层位 岩性 样品数/个 黏土矿物 石英 钾长石 斜长石 碳酸盐矿物 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 樊页1 沙三中亚段 泥页岩 43 24 45 34.4 17 28 23.5 2.0 2 5 3.2 24 52 35.3 沙三下亚段 泥页岩 379 6 62 24.2 10 57 23.7 1 5 1.8 1 19 3.2 5 80 46.0 沙四纯上亚段 泥页岩 358 2 57 6.7 2 51 24.7 1 5 3.0 1 35 5.0 3 95 51.1 沙四纯下亚段 泥页岩 19 3 39 12.3 3 60 19.6 1 22 6.0 10 90 60.3 利页1 沙三下亚段 泥页岩 51 16 51 32.4 9 38 24.2 1 3 2.0 2 9 4.4 8 70 35.7 沙四纯上亚段 泥页岩 28 6 39 25.8 13 36 25.2 2 11 4.8 12 78 42.5 牛页1 沙三下亚段 泥页岩 10 11 32 21.2 12 41 24.0 1 25 3.3 18 75 48.0 沙四纯上亚段 泥页岩 33 4 59 23.1 7 45 22.3 2.0 1 22 5.1 5 72 46.4 沙四纯下亚段 泥页岩 6 13 52 34.2 8 28 17.7 3 11 7.5 10 76 37.7 罗69 沙三中亚段 泥页岩 12 11 48 24.8 15 29 23.6 1 4 2.6 19 64 44.8 沙三下亚段 泥页岩 190 5 45 19.1 5 45 18.0 1 2 1.1 1 8 1.4 12 89 57.8 沙四纯上亚段 泥页岩 12 2 24 9.3 3 47 16.3 0.0 33 93 72.3 表 2 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷4口页岩油探井各层段钻井、录井参数统计
Table 2. Statistics on drilling and mud logging parameters in each interval of four shale oil exploration wells in Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin
井名 井段/m 层位 DC指数 地层压力梯度/(MPa·hm-1) 破裂压力梯度/(MPa·hm-1) 岩石密度/(g·cm-3) 压实情况 裂缝发育段深度/m 含油层深度/m 樊页1
(FY1)160.0~2 010.0 平原组—沙一段 0.10~1.44 1.03 1.34~2.04 0.10~.44 正常压实 2 883.0~3 270.5 2 010.0~3 278.0 沙一段—沙四上纯上亚段 0.52~2.60 1.03 1.82~2.12 2.13~2.37 正常压实 3 278.0~622.0 沙四上纯上—沙四下亚段 0.23~1.72 1.15 2.03~2.10 2.38~2.46 欠压实 3 441.0~3 492.0 利页1
(LY1)301.0~1 755.0 明化镇组—东营组 0.42~1.33 1.03 1.10~1.85 正常压实 1 755.0~3 570.0 东营组—沙三下亚段 0.80~1.21 1.03 1.65~2.05 2.00~2.45 正常压实 3 171.8~3 198.1;
3 292.7~3 299.9;
3 322.2~3 325.7;
3 389.1~3 391.1;
3 397.7~3 399.0;3 570.0~3 924.0 沙三下—沙四下亚段 1.52~2.03 1.03 1.95~2.15 2.35~2.70 正常压实 3 872.6~3 879.1;
3 898.6~3 899.9牛页1
(NY1)351.0~1 850.0 明化镇组—东营组 0.42~1.54 1.03 1.01~2.13 正常压实 3 316.0~3 538.0 1 850.0~3 340.0 东营组—沙四上纯上亚段 0.66~2.22 1.03 1.37~2.21 2.00~2.29 正常压实 2 977.0~3 052.0 3 340.0~3 548.0 沙四上纯上—沙四下亚段 1.53~2.34 1.10~1.20 1.90~2.22 2.10~2.40 欠压实 3 389.7~3 486.0 罗69
(L69)157.3~2 200.7 平原组—东营组 0.29~2.24 1.03 1.72~2.11 2.04~2.22 正常压实 2 200.7~2 770.0 东营组—沙二段 0.57~1.54 1.03 2.04~2.10 2.04~2.22 正常压实 2 690.0~2 692.0;
2 762.0~2 763.0;2 770.0~3 390.0 沙二段—沙四下亚段 0.23~1.72 1.11~1.65 1.90~2.19 2.17~2.45 欠压实 3 010.3~3 130.8 3 010.3~3 130.8 -
[1] 刘惠民. 济阳坳陷页岩油认识进展与勘探实践[C]//第九届中国石油地质学会年会. 海口, 2021.LIU Huimin. Research progress and exploration practice of shale oil in Jiyang Depression[C]//9th CAPG. Haikou, 2021. [2] 郑和荣, 黄永玲, 冯有良. 东营凹陷下第三系地层异常高压体系及其石油地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(4): 67-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2000.04.016ZHENG Herong, HUANG Yongling, FENG Youliang. Anomalous overpressure system of early Tertiary in Dongying Depression and its petroleum geology significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(4): 67-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2000.04.016 [3] WANG F P, URSULA H, LI Q H. Overview of Haynesville shale properties and production[M]//HAMMES U, GALE J. Geology of the Haynesville gas shale in east Texas and west Louisiana. AAPG Memoir, 2013, 105: 155-177. [4] FERTL W H, TIMKO D J. Occurrence and significance of abnormal pressure formations[J]. Oil and Gas Journal, 1970, 68(1): 97-108. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/283357877_Occurrence_and_significance_of_abnormal-pressure_formations [5] FERTL W H. Abnormal formation pressures, implications for exploration, drilling, production of oil and gas resources[M]. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Amsterdam-Oxford-New York, 1976, 382. [6] MOUCHET J P, MITCHELL A. Abnormal pressures while drilling; origins-prediction-detection-evaluation[M]. Manuels Techniques 2, Elf Aquitaine Editor, 1989, Boussens, France, 255. [7] 包友书, 张林晔, 李钜源, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系超高压成因探讨[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2012, 33(1): 17-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201201004.htmBAO Youshu, ZHANG Linye, LI Juyuan, et al. Approach to Paleogene overpressure origin in Jiyang Depression[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2012, 33(1): 17-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201201004.htm [8] 王国庆, 宋国奇. 生烃增压在超压形成中的作用: 以东营凹陷西部为例[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(27): 177-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.27.035WANG Guoqing, SONG Guoqi. The effect of hydrocarbon generation pressurization in the development of overpressure: taking the west part of Dongying Depression as an example[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(27): 177-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.27.035 [9] 王国庆. 东营凹陷西部沙四上亚段超压成因及增压模式[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2014, 28(5): 16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2014.05.005WANG Guoqing. Origin of overpressure and booster mode of upper Es4 formation of western Dongying Depression[J]. Petroleum Geo-logy and Engineering, 2014, 28(5): 16-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2014.05.005 [10] 张杰. 鄂尔多斯盆地城壕地区延长组长7致密油成藏动力研究[J]. 辽宁化工, 2016, 45(2): 214-217. doi: 10.14029/j.cnki.issn1004-0935.2016.02.033ZHANG Jie. Research on tight oil reservoir forming dynamics for Yanchang member Chang7 reservoir in Chenghao area of Ordos Basin[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(2): 214-217. doi: 10.14029/j.cnki.issn1004-0935.2016.02.033 [11] 杨华, 梁晓伟, 牛小兵, 等. 陆相致密油形成地质条件及富集主控因素: 以鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组7段为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(1): 12-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701003.htmYANG Hua, LIANG Xiaowei, NIU Xiaobing, et al. Geological conditions for continental tight oil formation and the main controlling factors for the enrichment: a case of Chang 7 member, Triassic Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 12-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701003.htm [12] 张焕旭, 陈世加, 张亚, 等. 烃源岩生烃增压研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2): 199-207. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0227ZHANG Huanxu, CHEN Shijia, ZHANG Ya, et al. Research progress of the overpressure caused by hydrocarbon generation[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(2): 199-207. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2018.0227 [13] 李伟, 陈竹新, 黄平辉, 等. 中国中西部典型前陆盆地超压体系形成机制与大气田关系[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(3): 536-548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202103010.htmLI Wei, CHEN Zhuxin, HUANG Pinghui, et al. Formation of overpressure system and its relationship with the distribution of large gas fields in typical foreland basins in central and western China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(3): 536-548. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202103010.htm [14] 范彩伟, 刘爱群, 吴云鹏, 等. 莺歌海盆地乐东10区新近系黄流组储层天然气充注与超压演化史[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(6): 1370-1381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202206008.htmFAN Caiwei, LIU Aiqun, WU Yunpeng, et al. Gas charging and overpressure evolution history of the Neogene Huangliu Formation reservoir in Ledong 10 area, Yinggehai Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(6): 1370-1381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202206008.htm [15] 鲁雪松, 张凤奇, 赵孟军, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘高探1井超压成因与盖层封闭能力[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6): 666-675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106004.htmLU Xuesong, ZHANG Fengqi, ZHAO Mengjun, et al. Genesis of overpressure and sealing ability of caprocks in well Gaotan 1 in the southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(6): 666-675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106004.htm [16] 于俊峰, 吴其林, 晁彩霞, 等. 南海常压与超压气水过渡带岩电特征与气藏结构[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(4): 504-508. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104014.htmYU Junfeng, WU Qilin, CHAO Caixia, et al. Petroelectric characte-ristics and gas reservoir structure of the gas-water transition zon e between normal pressure and overpressure in the South China Sea[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(4): 504-508. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104014.htm [17] 宋昊, 蒋有录, 侯帅, 等. 长岭断陷龙凤山地区下白垩统地层压力特征及其对油气成藏的影响[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(2): 42-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202202006.htmSONG Hao, JIANG Youlu, HOU Shuai, et al. Pressure characte-ristics and its influence on hydrocarbon accumulation of Lower Cretaceous Formation in Longfengshan area, Changling Faulted Depression[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(2): 42-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202202006.htm [18] 刘伟新, 卢龙飞, 叶德燎, 等. 川东南地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组页岩气异常压力封存箱剖析与形成机制[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(5): 804-814. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202205804LIU Weixin, LU Longfei, YE Deliao, et al. Significance and formation mechanism of abnormally pressured compartments of shale gas in the Ordovician Wufeng-Silurian Longmaxi formations, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(5): 804-814. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202205804 [19] FERTL W H, TIMKO D J. Application of well logs to geopressure problems in the search, drilling, production of hydrocarbons: Colloque A.R.T.E.P. [M], French Petroleum Institute, 1971, Rueil, June, Paper No. 4. [20] 王志战, 张炜, 杜焕福, 等. 生烃超压随钻预监测方法[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2012, 19(6): 53-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201206020.htmWANG Zhizhan, ZHANG Wei, DU Huanfu, et al. Prediction and detection while drilling of abnormal high pressure origin from hydrocarbon generation[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2012, 19(6): 53-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201206020.htm [21] 曹文渊. 地层超压成因类型及测井识别方法[J]. 国外测井技术, 2018, 39(5): 54-56.CAO Wenyuan. Genetic types of formation overpressure and logging identification methods[J]. World Well Logging Technology, 2018, 39(5): 54-56. [22] 陈沛, 梁豪, 廖高龙. 琼东南盆地深水区综合录井关键技术研究与应用[J]. 录井工程, 2019, 30(2): 16-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGZ201902005.htmCHEN Pei, LIANG Hao, LIAO Gaolong. Research and application of key technology of compound logging in deep-water area of Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 2019, 30(2): 16-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGZ201902005.htm [23] 王江涛, 李育. 沉积盆地异常高压形成机制综述[J]. 石油化工应用, 2014, 33(1): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXSH201401004.htmWANG Jiangtao, LI Yu. Review on the formation mechanism of abnormal high pressure in sedimentary basins[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application, 2014, 33(1): 5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXSH201401004.htm [24] 徐思煌, 梅廉夫, 袁彩萍. 成烃增压数值模拟[J]. 石油实验地质, 1998, 20(3): 85-89. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199803287XU Sihuang, MEI Lianfu, YUAN Caiping. Numerical modeling on pressurizing caused by hydrocarbon generation[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 1998, 20(3): 85-89. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199803287 [25] 郝芳, 姜建群, 邹华耀, 等. 超压对有机质热演化的差异抑制作用及层次[J]. 中国科学(D辑地球科学), 2004, 34(5): 443-451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200405006.htmHAO Fang, JIANG Jianqun, ZOU Huayao, et al. Differential retardation of organic matter maturation by overpressure[J]. Science in China(Series D Earth Sciences), 2004, 47(9): 783-793. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200405006.htm [26] 马中良, 郑伦举, 秦建中, 等. 盆地沉降、抬升过程中源储压差的生排烃效应[J]. 石油实验地质, 2011, 33(4): 402-407. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201104402MA Zhongliang, ZHENG Lunju, QIN Jianzhong, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion caused by pressure difference between source rock and reservoir during basin subsiding and uplifting[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2011, 33(4): 402-407. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201104402 [27] 马卫, 王东良, 李志生, 等. 湖相烃源岩生烃增压模拟实验[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(S1): 65-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2013S1008.htmMA Wei, WANG Dongliang, LI Zhisheng, et al. A simulation experiment of pressurization during hydrocarbon generation from lacustrine source rocks[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(S1): 65-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2013S1008.htm [28] 吴远东, 张中宁, 吉利明, 等. 流体压力对半开放体系有机质模拟生烃产率和镜质体反射率的影响[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(5): 883-891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201605015.htmWU Yuandong, ZHANG Zhongning, JI Liming, et al. The changes of hydrocarbon yields and Ro for source rock in the semi-open simulation with increasing of fluids pressure[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(5): 883-891. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201605015.htm [29] 吴远东, 张中宁, 吉利明, 等. 高压生烃模拟实验及其成油滞后特征[J]. 特种油气藏, 2016, 23(3): 129-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201603031.htmWU Yuandong, ZHANG Zhongning, JI Liming, et al. High-pressure hydrocarbon generation simulation and oil-generation lag[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2016, 23(3): 129-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201603031.htm [30] 吴远东, 张中宁, 孙丽娜, 等. 半开放体系下流体压力对烃源岩HTHP模拟产物产率及镜质体反射率的影响[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(10): 1904-1912. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201610016.htmWU Yuandong, ZHANG Zhongning, SUN Lina, et al. Effect of liquids pressure on hydrocarbon yield and Ro of source rock HTHP simulation experiment in semi-open system[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(10): 1904-1912. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201610016.htm [31] 曹文渊. 异常压力类型及成因机制[J]. 山东化工, 2018, 47(23): 122-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG201823045.htmCAO Wenyuan. Types and mechanism of abnormal pressure[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(23): 122-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG201823045.htm [32] 张磊, 向才富, 董月霞, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷异常压力系统及其形成机理[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(4): 664-675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201804005.htmZHANG Lei, XIANG Caifu, DONG Yuexia, et al. Abnormal pressure system and its origin in the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(4): 664-675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201804005.htm [33] 张守春, 王学军, 王秀红, 等. 陆相断陷盆地成藏流体动力差异性及表征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(6): 941-949. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202206941ZHANG Shouchun, WANG Xuejun, WANG Xiuhong, et al. Dynamic difference and characterization of reservoir fluid in continental rift basins[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(6): 941-949. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202206941 [34] 廉欢, 查明, 高长海, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组异常高压与致密油富集[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2016, 37(2): 163-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201602008.htmLIAN Huan, ZHA Ming, GAO Changhai, et al. Abnormal high pressure and tight oil enrichment of Lucaogou Formation in Jimusaer Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2016, 37(2): 163-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201602008.htm [35] 冯子辉, 柳波, 邵红梅, 等. 松辽盆地古龙地区青山口组泥页岩成岩演化与储集性能[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2020, 39(3): 72-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202003007.htmFENG Zihui, LIU Bo, SHAO Hongmei, et al. The diagenesis evolution and accumulating performance of the mud shale in Qingshankou Formation in Gulong area, Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2020, 39(3): 72-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202003007.htm [36] TISSOT B P, WELTE D H. Petroleum formation and occurrence[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1984. [37] MA Xiaoxiao, LI Maowen, PANG Xiongqi, et al. Paradox in bulk and molecular geochemical data and implications for hydrocarbon migration in the inter-salt lacustrine shale oil reservoir, Qianjiang Formation, Jianghan Basin, central China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2019, 209: 72-88. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166516219302903 [38] 王永诗, 郝雪峰, 胡阳. 富油凹陷油气分布有序性与富集差异性: 以渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷东营凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(5): 785-794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201805005.htmWANG Yongshi, HAO Xuefeng, HU Yang. Orderly distribution and differential enrichment of hydrocarbon in oil-rich sags: a case study of Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(5): 785-794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201805005.htm [39] LI Sumei, PANG Xiongqi, LI Maowen, et al. Geochemistry of petroleum systems in the Niuzhuang south slope of Bohai Bay Basin Part 1: source rock characterization[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2003, 34(3): 389-412. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S0146638002002103&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1494247674&md5=8fab5db72d6929a350d1f162910054bc [40] 黎茂稳, 马晓潇, 金之钧, 等. 中国海、陆相页岩层系岩相组合多样性与非常规油气勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(1): 1-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202201020.htmLI Maowen, MA Xiaoxiao, JIN Zhijun, et al. Diversity in the litho-facies assemblages of marine and lacustrine shale strata and significance for unconventional petroleum exploration in China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(1): 1-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202201020.htm [41] HERMANRUD C, WENSAAS L, TEIGE G M, et al. Shale porosity from well logs on Haltenbanken (offshore mid-Norway) show no influence of overpressuring[M]. Law B E, Ulmishek G F, Slavin V I. Abnormal pressures in hydrocarbon environments, AAPG memoir 70. Tulsa: AAPG, 1998: 65-85. [42] HARWOOD R J. Oil and gas generation by laboratory pyrolysis of kerogen[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1977, 61(12): 2082-2102. http://aapgbull.geoscienceworld.org/content/61/12/2082 [43] 李鑫羽, 欧阳传湘, 杨博文, 等. 基于BP神经网络的黏土矿物预测模型[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(5): 624-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202105018.htmLI Xinyu, OUYANG Chuanxiang, YANG Bowen, et al. BP neural network-based models to predict clay minerals[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(5): 624-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202105018.htm [44] 张启明, 董伟良. 中国含油气盆地中的超压体系[J]. 石油学报, 2000, 21(6): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200006000.htmZHANG Qiming, DONG Weiliang. Overpressure system of hydrocarbon-bearing basins in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2000, 21(6): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200006000.htm [45] 张善文. 东营凹陷古近系砂岩储层成岩耗水评价[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(4): 719-723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200904017.htmZHANG Shanwen. Water consumption appraisal of sandstone reservoir of Paleogene in the Dongying Sag[J]. Geoscience, 2009, 23(4): 719-723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ200904017.htm [46] 李迎辉. 东营凹陷粘土矿物成岩演化与异常高压带成因关系研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2003.LI Yinghui. Relationship between diagenetic evolution of clay minerals and genesis of abnormal high pressure zone in Dongying Depression[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2003. [47] 包友书. 济阳坳陷超压和应力场对页岩油富集的影响[J]. 断块油气田, 2018, 25(5): 585-588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201805009.htmBAO Youshu. Influence of overpressure and stress on shale oil enrichment in Jiyang Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2018, 25(5): 585-588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201805009.htm [48] 蒋启贵, 黎茂稳, 钱门辉, 等. 不同赋存状态页岩油定量表征技术与应用研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(6): 842-849. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201606842JIANG Qigui, LI Maowen, QIAN Menhui, et al. Quantitative characterization of shale oil in different occurrence states and its application[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(6): 842-849. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201606842 -





 下载:
下载:






 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号