Controlling factors for effective reservoir development of Ordovician Kelimoli Formation in western Ordos Basin
-
摘要: 近年来,鄂尔多斯盆地西部奥陶系的天然气勘探取得了一定进展,其中以奥陶系克里摩里组天然气聚集程度最高,但其有效储层发育控制因素复杂,导致勘探效果不理想。基于岩心观察、薄片鉴定、钻录井等资料,系统研究了克里摩里组有效储层发育类型及控制因素,建立了有效储层发育模式。鄂尔多斯盆地西部克里摩里组有效储层类型主要有白云岩晶间(溶)孔、灰岩岩溶缝洞和构造微裂缝,局部发育台缘滩颗粒孔型储层;有效储层发育主要受控于沉积相带、成岩作用、古岩溶风化作用及构造运动,其中潮坪相及台缘滩相为克里摩里组提供了原始储层的物质基础,并在此基础上形成了成岩早期的白云岩晶间(溶)孔和台缘滩颗粒孔型储层;埋藏成岩作用阶段,重结晶作用对原始白云岩储层改造明显,晶体骨架更加稳固,新的晶间(溶)孔形成或经历二次重结晶改造,同时台缘滩颗粒孔的原始结构部分被破坏、充填或改善,形成现今的台缘滩残余颗粒孔;古岩溶风化作用控制克里摩里组中上部岩溶缝洞型储层的发育,高产井主要发育在岩溶斜坡沟槽地带的上槽方向及岩溶高地;多期构造运动不断改造、控制微裂缝系统的发育,形成断裂带周边分布的多孔介质储集体。因此,寻找克里摩里组潮坪相和台缘滩相有利相带、岩溶古地貌上倾部位或断裂带高部位,是下一步勘探的有利方向。Abstract: In recent years, some progress has been made in the exploration of Ordovician natural gas in the western Ordos Basin, among which, the Ordovician Kelimoli Formation has the highest degree of natural gas accumulation. However, the controlling factors for effective reservoir development are complicated, leading to unsatisfactory exploration effect. Based on the data of core observation, thin section identification, drilling and logging, the development types and controlling factors of effective reservoir in the Kelimoli Formation were systematically studied, and a development model of effective reservoir was established. The results show that the effective reservoir types of Kelimoli Formation in the western Ordos Basin mainly include dolomite intercrystal (dissolved) pore, limestone karst fracture and structural micro-fracture, and marginal platform granular pore type reservoir is locally developed. The development of effective reservoir was mainly controlled by sedimentary facies, diagenesis, paleokarst weathering and tectonic movement. The tidal flat facies and marginal platform facies provided the material basis for the original reservoir of the Kelimoli Formation, and on this basis, the dolomite intercrystal (dissolved) pore and marginal platform granular pore reservoirs were formed in the early diagenesis. In the stage of burial diagenesis, recrystallization obviously reformed the original dolomite reservoir, and the crystal framework became more stable. New intercrystal (dissolved) pores were formed or underwent secondary recrystallization. At the same time, the original structure of marginal platform granular pores was damaged, filled or improved, and the present marginal platform residual granular pores were formed. Paleo-karst weathering controlled the development of fracture-vuggy reservoirs in the middle and upper parts of the Kelimoli Formation, and high-yield wells were mainly drilled in the upper groove direction of the karst slope groove zone and karst highlands. The multi-stage tectonic movement continuously transformed and controlled the development of micro-fracture system, forming porous media reservoirs distributed around the fault zone. Therefore, it is a favorable direction for further exploration to find favorable facies belts of tidal flat facies and marginal platform facies, updip positions of karst paleo-geomorphology or high positions of fault zone.
-
Key words:
- effective reservoir type /
- paleokarst /
- weathering /
- diagenesis /
- Kelimoli Formation /
- Ordovician /
- western Ordos Basin
-
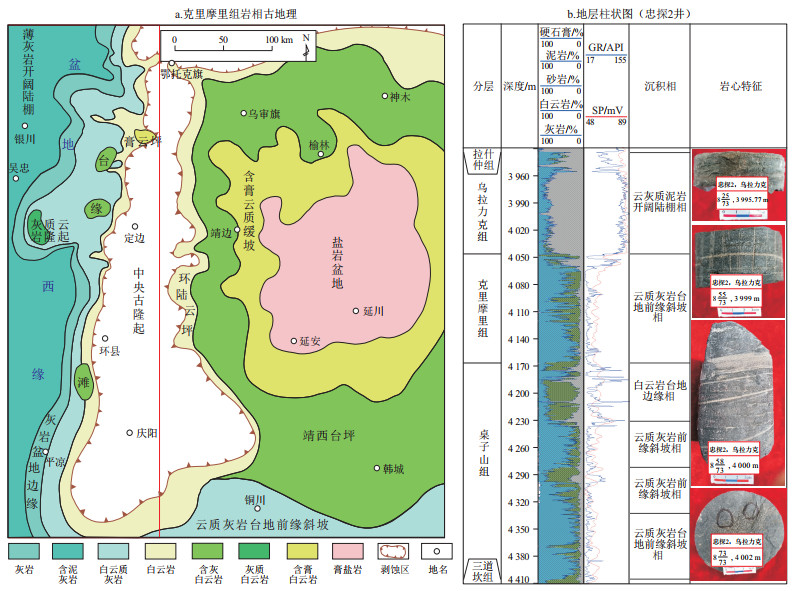
图 2 鄂尔多斯盆地西部奥陶系克里摩里组典型岩石及其孔隙特征显微图片
a.忠探1井,4 264.1 m,角砾状灰岩, 含黄铁矿, 为深水滑塌成因;b.忠探1井,4 265.0 m, 角砾状灰岩;c.忠探1井,4 366.8 m,滑塌角砾岩,砾石具有一定磨圆;d.余3井,4 144.8 m,岩溶作用形成的孔洞;e.余探1井,4 051.1 m,灰岩,发育灰岩缝洞;f.余3井,4 137.5 m,杂基支撑的滑塌构造,发育微裂缝;g.惠探1井,4 660.0 m,发育白云岩晶间(溶)孔;h.梁探1井,5 062.9 m,细晶白云岩,发育晶间孔;i.鄂65井,3 980.8 m,粉—细晶云岩,晶间溶孔;j.天1井,3 936.0 m,藻屑灰岩溶孔;k.余3井,4 140.4 m,灰岩岩溶缝洞发育;l.李1井,3 909.0 m,颗粒灰岩[7];m.余探2井,3 978.2 m,电子探针下的裂缝及局部方解石充填;n.惠探1井,4 660.0 m,发育微裂缝;o.忠探1井,4 520.2 m,发育构造微裂缝
Figure 2. Microscopic images of typical rocks and pore characteristics of Ordovician Kelimoli Formation in western Ordos Basin
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地西部奥陶系克里摩里组有效储层物性特征
Table 1. Physical characteristics of effective reservoir of Ordovician Kelimoli Formation in western Ordos Basin
有效储层类型 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 物性解释 范围 平均 范围 平均 白云岩晶间(溶)孔 3.1~10.7 7.2 1.2~4.7 3.1 孔隙度高,渗透性中等 台缘滩颗粒孔 3.2~15.8 10.2 2.3~10.2 4.3 孔渗性最好,但储层规模极小 灰岩岩溶缝洞 4.2~14.8 9.8 1.7~7.9 3.7 孔渗性良好,但储层非均质性差 构造微裂缝 0.2~3.5 1.6 3.1~10.8 5.2 孔隙度较小,局部渗透性较好 表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地西部奥陶系克里摩里组部分探井钻井液漏失情况统计
Table 2. Statistics of drilling fluid loss in some exploration wells in Ordovician Kelimoli Formation, western Ordos Basin
井号 深度/m 底深/m 厚度/m 识别标志 布1 4 125.4 4 132.5 7.1 钻时加快 棋探1 4 444.0 4 527.0 83.0 4 444 m开始钻井液漏失(累积漏失1 014 m3),4 450 m处钻具放空20 cm 天1 3 934.0 3 940.0 6.0 发生井喷,其中3 934.7~3 935.8 m井段钻具放空1.1 m,钻井液漏失共99.5 m3 天深1 4 069.0 4 175.0 106.0 钻井液漏失323 m3 -
[1] 李蒙. 鄂尔多斯西缘奥陶纪沉积与构造演化研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2019.LI Meng. Analysis of sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the western margin of Ordos area in Ordovician[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2019. [2] 高春云. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘南段构造特征及演化研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2020.GAO Chunyun. Research on the characteristics of structure and tectonic evolution of southern section of western margin of Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern University, 2020. [3] 王振涛. 鄂尔多斯盆地基底特征及西、南缘奥陶纪构造演化及沉积响应[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.WANG Zhentao. Basement features of the Ordos Basin and the Ordovician tectonic-sedimentary respond in the western and southern margin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014. [4] 于洲, 周进高, 李程善, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘奥陶纪克里摩里期—乌拉力克期构造—岩相古地理特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(6): 816-825. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202106004.htmYU Zhou, ZHOU Jingao, LI Chengshan, et al. Tectonic-lithofacies paleogeographic characteristics of Ordovician Kelimoli and Wulalike stages in the western edge of Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(6): 816-825. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202106004.htm [5] 吴东旭, 孙六一, 周进高, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘克里摩里组白云岩储层特征及成因[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(6): 51-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201906009.htmWU Dongxu, SUN Liuyi, ZHOU Jingao, et al. Characteristics and genesis of the Ordovician Kelimoli dolomite reservoirs in the western edge of the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(6): 51-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201906009.htm [6] 吴伟涛, 赵靖舟, 孙六一, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部奥陶系克里摩里组天然气成藏特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(10): 1862-1872. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2015.10.1862WU Weitao, ZHAO Jingzhou, SUN Liuyi, et al. Accumulation characteristics of natural gas from the Ordovician Kelimoli Formation, western Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(10): 1862-1872. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2015.10.1862 [7] 苏中堂, 呼尚才, 刘宝宪, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘克里摩里组古喀斯特洞穴特征及发育控制因素[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 43(2): 233-240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2016.02.10SU Zhongtang, HU Shangcai, LIU Baoxian, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of paleokarst caves in Kelimoli Formation, west Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2016, 43(2): 233-240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2016.02.10 [8] 舒鹏程, 冯强汉, 许淑梅, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部奥陶系风化壳岩溶作用模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(6): 1565-1579. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202106018.htmSHU Pengcheng, FENG Qianghan, XU Shumei, et al. Model of weathering crust karstification in the Ordovician, western Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(6): 1565-1579. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202106018.htm [9] 王淑敏. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘克里摩里组白云岩储层成因及分布预测[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019.WANG Shumin. Origin and distribution prediction of dolomite reservoirs in the Kelimoli Formation in western Ordos Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2019. [10] 杜金虎, 李相博, 包洪平, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中新元古界—下古生界天然气成藏地质条件及勘探新领域[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(5): 820-835.DU Jinhu, LI Xiangbo, BAO Hongping, et al. Geological conditions of natural gas accumulation and new exploration areas in the Mesoproterozoic to Lower Paleozoic of Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(5): 820-835. [11] 李斌. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部冲断带构造与控油气因素研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2019.LI Bin. Thrust structure and its effect on hydrocarbon in the western margin of Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern University, 2019. [12] 罗星, 叶超, 雷迅, 等. 鄂尔多斯西缘奥陶系储层特征及主控因素研究[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版), 2013, 10(10): 52-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201310020.htmLUO Xing, YE Chao, LEI Xun, et al. The west margin of Ordos Ordovician reservoir characteristics and main control factors study[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 10(10): 52-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201310020.htm [13] 万延周. 鄂尔多斯西缘奥陶系烃源岩及储盖层特征研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2009.WAN Yanzhou. A study on the characteristics of Ordovician source rocks and reservoirs cap rocks on the west margin of the Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2009. [14] 吴东旭, 吴兴宁, 王少依, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系颗粒滩白云岩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 海相油气地质, 2017, 22(2): 40-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ201702006.htmWU Dongxu, WU Xingning, WANG Shaoyi, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of Ordovician grain beach dolomite reservoir in Ordos Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2017, 22(2): 40-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ201702006.htm [15] 束宁凯, 汪新文, 郭建平. 鄂尔多斯盆地西北部奥陶系"三元"主控成藏规律[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 44(1): 43-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201701020.htmSHU Ningkai, WANG Xinwen, GUO Jianping. Analysis of three controlling regularities on the Ordovician gas accumulation in the northwest Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2017, 44(1): 43-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG201701020.htm [16] 张道锋, 刘新社, 高星, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部奥陶系海相碳酸盐岩地质特征与成藏模式研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(1): 92-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201601011.htmZHANG Daofeng, LIU Xinshe, GAO Xing, et al. Geological characteristics and accumulation model of Ordovician marine carbonate in western Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(1): 92-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201601011.htm [17] 张春林, 朱秋影, 张福东, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部奥陶系古岩溶类型及主控因素[J]. 非常规油气, 2016, 3(2): 11-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FCYQ201602002.htmZHANG Chunlin, ZHU Qiuying, ZHANG Fudong, et al. Paleokarst types and main controlling factors of Ordovician in western Ordos Basin[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2016, 3(2): 11-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FCYQ201602002.htm [18] 刘燕, 付金华, 李建明. 鄂尔多斯盆地东部奥陶系马家沟组白云岩成因机理分析[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2011, 33(11): 46-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201111010.htmLIU Yan, FU Jinhua, LI Jianming. Dolomite genetic analysis on Ordovician Majiagou Formation in eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2011, 33(11): 46-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201111010.htm [19] 吴兴宁, 吴东旭, 丁振纯, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘奥陶系白云岩地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 海相油气地质, 2020, 25(4): 312-318. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ202004003.htmWU Xingning, WU Dongxu, DING Zhenchun, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genetic analysis of Ordovician dolomites in the western margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2020, 25(4): 312-318. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ202004003.htm [20] 张春林. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部奥陶系古岩溶储层形成机理及勘探目标评价[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.ZHANG Chunlin. Formation mechanics and exploration targets evaluation of Ordvician paleokarst reservoir in western Ordos Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013. [21] 阳雨杉, 李建明, 梅小元, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地天环北地区克里摩里组古岩溶储层发育控制因素分析[C]//2015年全国沉积学大会沉积学与非常规资源论文摘要集. 武汉, 2015: 382-383.YANG Yushan, LI Jianming, MEI Xiaoyuan, et al. Controlling factors of paleokarst reservoir development in Kelimoli Formation in north Tianhuan area, Ordos Basin[C]//Abstract collection of papers on sedimentology and unconventional resources in 2015 National Sedimentology Congress. Wuhan, 2015: 382-383. [22] 付锁堂, 付金华, 席胜利, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系海相页岩气地质特征及勘探前景[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(2): 33-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202102004.htmFU Suotang, FU Jinhua, XI Shengli, et al. Geological characteristics of Ordovician marine shale gas in the Ordos Basin and its prospects[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(2): 33-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202102004.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号