Shale lithofacies types and reservoir characteristics from Ordovician Wufeng Formation to the first sub-member of the first member of Silurian Longmaxi Formation, northeast Zhaotong area
-
摘要: 页岩岩相对页岩储层有着重要的影响,一定程度上控制着页岩的生烃能力、储集和压裂性能。基于岩心、薄片、X射线衍射及各类地化测试数据,对昭通东北地区上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组页岩岩相特征、储层特征和评价进行了研究。研究区主要发育含灰/硅混合质页岩相、混合质页岩相、含黏土/硅混合质页岩相、混合硅质页岩相、含黏土硅质页岩相,南部与北部岩相纵向分布存在差异,南部五峰组—龙一1亚段岩相呈现出从黏土质页岩相组合向硅质页岩相组合再向混合质页岩相组合过渡的特征,北部呈现出从混合质页岩相组合向硅质页岩相组合再向混合质页岩相组合的过渡趋势;横向上岩相展布非均质性强,连续性差。不同岩相储层特征存在差异,硅质页岩储层性能较好,具有有机碳(TOC)含量高、含气量高、脆性矿物含量高的特征;黏土质页岩TOC含量和含气量较高,但脆性矿物含量极低;混合质页岩储层性质复杂,总体上硅质含量高的混合质页岩储层性质较好。基于TOC含量、含气量、脆性矿物含量,利用层次分析法和熵值法相结合的方法,建立了页岩岩相评价标准,确定了优势岩相,研究区混合硅质页岩相、含灰硅质页岩相和含灰/硅混合质页岩相为Ⅰ类优势岩相;含黏土硅质页岩相、混合质页岩相和含黏土/硅混合质页岩相为Ⅱ类优势岩相;混合黏土质页岩相和含硅黏土质页岩相为非优势岩相。Abstract: Shale lithofacies has an important influence on shale reservoirs. It controls the hydrocarbon generation capacity, storage performance and fracturing performance of shale to a certain extent. In order to study the shale lithofacies characteristics, reservoir characteristics and evaluation of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in the northeast Zhaotong area, a detailed research was carried out based on core, thin section, X-ray diffraction and various geochemical test data. Calcareous/siliceous mixed shale lithofacies, mixed shale lithofacies, clayey/siliceous mixed shale lithofacies, mixed siliceous shale lithofacies, clay-rich siliceous shale lithofacies are developed in the study area. There is a difference in the vertical distribution of lithofacies between the south and the north of the study area. The lithofacies from Wufeng Formation to the first sub-member of the first member of Longmaxi Formation (Long1-1 submember) presents the characteristics of transition from clayey shale lithofacies associa- tion to siliceous shale lithofacies association and then to mixed shale lithofacies association in the southern area, while the northern area shows a transition trend from mixed shale lithofacies association to siliceous shale lithofacies association and then to mixed shale lithofacies association. Horizontally, the lithofacies distribution is highly heterogeneous and has poor continuity. The reservoir characteristics of different lithofacies are different. Siliceous shale has good reservoir properties, with the characteristics of "high TOC content, high gas content and high brittle mineral content". The TOC content and gas content of clayey shale are high, but the content of brittle minerals is very low. The properties of mixed shale reservoirs are complex, and generally, the mixed shale reservoirs with high siliceous content have better properties. Based on TOC content, gas content and brittle mineral content, the shale lithofacies evaluation standard is established by combining analytic hierarchy process and entropy method, and the dominant lithofacies are determined. Mixed siliceous shale lithofacies, calcium-rich siliceous shale litho- facies, calcareous/siliceous mixed shale lithofaciesis are class Ⅰ dominant lithofacies; clay-rich siliceous shale lithofacies, mixed shale lithofacies and clayey/siliceous mixed shale lithofacies are class Ⅱ dominant lithofacies; mixed clayey shale lithofacies and silicon-rich clayey shale lithofacies are non-dominant lithofacies.
-
Key words:
- shale lithofacies /
- reservoir characteristics /
- reservoir evaluation /
- Wufeng Formation /
- Ordovician /
- Longmaxi Formation /
- Silurian /
- Zhaotong area
-
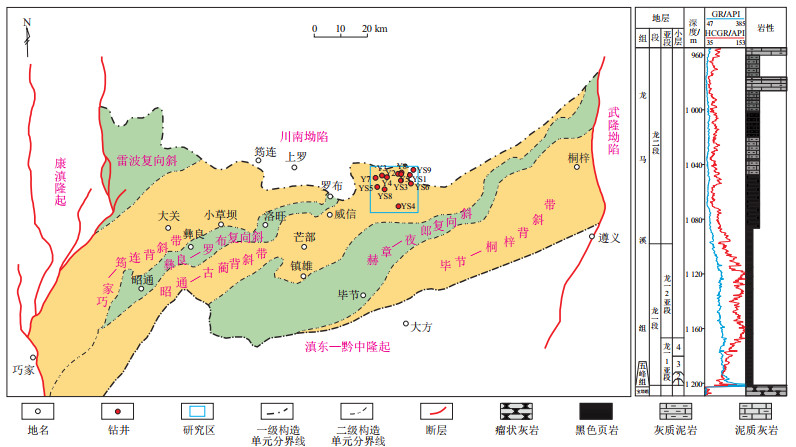
图 1 昭通东北地区区域构造地质图与岩性柱状图
据文献[20]修改。
Figure 1. Regional tectonic geological map and lithologic histogram of northeast Zhaotong area
图 2 昭通东北地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙一1亚段页岩岩相划分三端元图
底图据文献[16],有修改。
C-1.灰质页岩相;C-2.混合灰质页岩相;C-3.含硅灰质页岩相;C-4.含黏土灰质页岩;M-1.含灰/硅混合质页岩相;M-2.混合质页岩相;M-3.含黏土/灰混合质页岩相;M-4.含黏土/硅混合质页岩相;S-1.硅质页岩相;S-2.混合硅质页岩相;S-3.含灰硅质页岩相;S-4.含黏土硅质页岩相;CM-1.黏土质页岩相;CM-2.混合黏土质页岩相;CM-3.含灰黏土质页岩相;CM-4.含硅黏土质页岩相Figure 2. Three terminal diagram of shale lithofacies division from Ordovician Wufeng Formation to the first section of the first member of Silurian Longmaxi Formation in northeast Zhaotong area
图 3 昭通东北地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙一1亚段页岩主要岩相岩心特征
a.M-1,发育水平层理,YS4井,1 638.86~1 639.19 m,2小层;b.M-1,发育笔石,YS6井,1 998.34~1 998.49 m,3小层;c.M-2,发育直管笔石,YS4井,1 647.47~1 647.48 m,五峰组;d.M-2,发育大量被方解石充填的高角度缝,YS4井,1 648.66~1 648.71 m,五峰组;e.M-4,可见水平层理和被方解石充填的高角度裂缝,YS4井,1 622.04~1 622.16 m,4小层;f.S-2,可见厚约1 cm的黄铁矿条带,YS6井,2 004.73~2 004.77 m,3小层;g.S-2,发育笔石,YS6井,2 004.73~2 004.77 m,3小层;h.S-4,层理发育程度差,YS4井,1 635.84~1 636.20 m,3小层;i.S-4,发育笔石,YS4井,1 635.84~1 636.20 m,3小层
Figure 3. Core characteristics of main shale lithofacies from Ordovician Wufeng Formation to the first section of the first member of Silurian Longmaxi Formation in northeast Zhaotong area
图 4 昭通东北地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙一1亚段页岩主要岩相镜下特征
a.M-1,可见棘皮碎屑,YS4井,1 644.29 m,1小层,单偏光;b.M-1,可见未充填的微裂缝,YS8井,1 984.62 m,2小层,单偏光;c.M-2,微裂缝发育,Y3井,1 068.1 m,3小层,单偏光;d.M-2,硅质纹层与黏土纹层互层,Y5井,1 659.96 m,4小层,单偏光;e.M-4,碳质条带呈定向排列,部分碳质条带半充填于微裂缝中,YS4井,1 619.71 m,4小层,单偏光;f.S-2,发育近圆形碳质颗粒,石英颗粒磨圆度较高,YS4井,1 640.98 m,2小层,单偏光;g.S-2,可见近圆形黄铁矿和碳质条带,YS4井,1 624.84 m,4小层,正交光;h.S-4,较发育黄铁矿,可见黄铁矿呈条带状分布,YS4井,1 636.39 m,2小层,单偏光;i.S-4,可见未被充填的微裂缝,YS5井,1 081.23 m,3小层,单偏光
Figure 4. Microscopic characteristics of main shale lithofacies from Ordovician Wufeng Formation to the first section of the first member of Silurian Longmaxi Formation in northeast Zhaotong area
图 8 昭通东北地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙一1亚段不同岩相TOC含量、含气量和脆性矿物含量柱状图
CM-2.混合黏土质页岩相;CM-4.含硅黏土质页岩相;M-1.含灰/硅混合质页岩相;M-2.混合质页岩相;M-4.含黏土/硅混合质页岩相;S-2.混合硅质页岩相;S-3.含灰硅质页岩相;S-4.含黏土硅质页岩相
Figure 8. TOC content, gas content and brittle mineral content histogram of different lithofacies from Ordovician Wufeng Formation to the first section of the first member of Silurian Longmaxi Formation, northeast Zhaotong area
表 1 判断矩阵标度
Table 1. Judgement matrix scale
Aij 含义 1 Ai与Aj相比,同等重要 3 Ai比Aj稍微重要 5 Ai比Aj较强重要 7 Ai比Aj强烈重要 9 Ai比Aj绝对重要 2,4,6,8 两相邻判断的中间值 表 2 随机一致性RI表格
Table 2. Random consistency (RI) table
n阶 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 RI值 0.52 0.89 1.12 1.26 1.36 1.41 1.46 1.49 1.52 1.54 表 3 昭通东北地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙一1亚段不同岩相评价指标(AECS)及评价结果
Table 3. AECS and evaluation results of different shale lithofacies from Ordovician Wufeng Formation to the first section of the first member of Silurian Longmaxi Formation, northeast Zhaotong area
岩相类型 TOC平均含量/% 平均含气量/(m3·t-1) 脆性矿物平均含量/% AECS 评价结果 含灰硅质页岩相(S-3) 3.77 2.68 75.5 12.45 Ⅰ 混合硅质页岩相(S-2) 3.67 2.80 75.7 12.47 含灰/硅混合质页岩相(M-1) 3.66 2.58 73.4 12.09 含黏土硅质页岩相(S-4) 3.17 2.20 68.9 11.14 Ⅱ 混合质页岩相(M-2) 3.34 2.45 63.3 10.61 含黏土/硅混合质页岩相(M-4) 2.86 2.46 62.0 10.21 含硅黏土质页岩相(CM-4) 3.06 2.94 30.3 6.47 非优势 混合黏土质页岩相(CM-2) 2.60 2.70 22.8 5.20 -
[1] 李剑, 王晓波, 侯连华, 等. 四川盆地页岩气地球化学特征及资源潜力[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(8): 1093-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202108001.htmLI Jian, WANG Xiaobo, HOU Lianhua, et al. Geochemical characteristics and resource potential of shale gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(8): 1093-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202108001.htm [2] ZOU Caineng, XUE Huaqing, XIONG Bo, et al. Connotation, innovation and vision of "carbon neutrality"[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2021, 8(5): 523-537. doi: 10.1016/j.ngib.2021.08.009 [3] 陆扬博. 上扬子五峰组和龙马溪组富有机质页岩岩相定量表征及沉积过程恢复[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2020.LU Yangbo. Quantitative characterization of lithofacies and reconstruction of the sedimentary process for upper Yangtze Wufeng and Longmaxi organic-rich shales[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2020. [4] TIAN Jijun, XU Chuanzheng, LI Xin, et al. Depositional environment and pore structure of mixed lithofacies shale of the Longmaxi Formation in the DM block, the southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2020, 38(3): 629-653. http://www.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=18b4556ab9e58d3e13686af1d0ecddfe [5] 徐传正, 李鑫, 田继军, 等. 四川盆地南缘龙马溪组混合岩相页岩及其沉积环境[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(5): 208-217. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.05.027XU Chuanzheng, LI Xin, TIAN Jijun, et al. Mixed lithofacies shale and depositional environment of Longmaxi Formation in southern margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(5): 208-217. doi: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.05.027 [6] 李明隆, 谭秀成, 李延钧, 等. 页岩岩相划分及含气性评价: 以滇黔北地区五峰组—龙马溪组为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(6): 727-732. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202106003.htmLI Minglong, TAN Xiucheng, LI Yanjun, et al. Shale lithofacies classification and evaluation of gas-bearing property: a case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in northern Yunnan and Guizhou[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(6): 727-732. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202106003.htm [7] XU Shang, GUO Qiyang, HAO Fang, et al. Shale pore structure characteristics of the high and low productivity wells, Jiaoshiba shale gas field, Sichuan Basin, China: dominated by lithofacies or preservation condition?[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 114: 104211. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.104211 [8] 欧成华, 梁成钢, 罗利, 等. 页岩岩相分类表征及对建产区产能的影响[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(2): 269-280. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2020.132OU Chenghua, LIANG Chenggang, LUO Li, et al. The lithofacies classification and its influence on the gas production capacity in the shale gas production area[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(2): 269-280. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2020.132 [9] GOU Qiyang, XU Shang, HAO Fang, et al. Quantitative calculated shale gas contents with different lithofacies: a case study of Fuling gas shale, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 76: 103222. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103222 [10] 沈骋, 任岚, 赵金洲, 等. 页岩岩相组合划分标准及其对缝网形成的影响: 以四川盆地志留系龙马溪组页岩为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(1): 98-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202101010.htmSHEN Cheng, REN Lan, ZHAO Jinzhou, et al. Division of shale lithofacies associations and their impact on fracture network formation in the Silurian Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(1): 98-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202101010.htm [11] WANG Guochang, CARR T R. Methodology of organic-rich shale lithofacies identification and prediction: a case study from Marcellus shale in the Appalachian Basin[J]. Computers and Geosciences, 2012, 49: 151-163. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2012.07.011 [12] 彭君, 周勇水, 李红磊, 等. 渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷盐间细粒沉积岩岩相与含油性特征[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(2): 212-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202102013.htmPENG Jun, ZHOU Yongshui, LI Honglei, et al. Lithofacies and oil-bearing characteristics of fine-grained sedimentary rocks of salt-layers in Dongpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(2): 212-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202102013.htm [13] 廖崇杰, 陈雷, 郑健, 等. 四川盆地长宁西部地区上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组龙一1亚段页岩岩相划分及意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(6): 1037-1047. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2022061037LIAO Chongjie, CHEN Lei, ZHENG Jian, et al. Classification of shale lithofacies from Ordovician Wufeng Formation to first section of first member of Silurian Longmaxi Formation, western Changning area, Sichuan Basin, and its significance[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(6): 1037-1047. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2022061037 [14] WANG Ziyi, CHEN Lei, CHEN Dongxia, et al. Characterization and evaluation of shale lithofacies within the lowermost Longmaxi-Wufeng Formation in the southeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 193: 107353. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107353 [15] KRUMBEIN W C. Lithofacies maps and regional sedimentary-stratigraphic analysis[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1948, 32(10): 1909-1923. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/302213916_Lithofacies_maps_and_regional_sedimentary-stratigraphic_analysis [16] 吴蓝宇, 胡东风, 陆永潮, 等. 四川盆地涪陵气田五峰组—龙马溪组页岩优势岩相[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(2): 189-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201602005.htmWU Lanyu, HU Dongfeng, LU Yongchao, et al. Advantageous shale lithofacies of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in Fuling gas field of Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(2): 189-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201602005.htm [17] ZHANG Luchuan, XIAO Dianshi, LU Shuangfang, et al. Pore deve-lopment of the Lower Longmaxi shale in the southeastern Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas: insights from lithofacies identification and organic matter[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 122: 104662. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104662 [18] LIU Bo, WANG Haoli, FU Xiaofei, et al. Lithofacies and depositional setting of a highly prospective lacustrine shale oil succession from the Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in the Gulong Sag, northern Songliao Basin, northeast China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2019, 103(2): 405-432. doi: 10.1306/08031817416 [19] 梁兴, 张廷山, 舒红林, 等. 滇黔北昭通示范区龙马溪组页岩气资源潜力评价[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(1): 72-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202001007.htmLIANG Xing, ZHANG Tingshan, SHU Honglin, et al. Evaluation of shale gas resource potential of Longmaxi Formation in Zhaotong national shale gas demonstration area in the northern Yunnan-Guizhou[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(1): 72-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202001007.htm [20] 徐政语, 梁兴, 鲁慧丽, 等. 四川盆地南缘昭通页岩气示范区构造变形特征及页岩气保存条件[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(10): 22-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201910003.htmXU Zhengyu, LIANG Xing, LU Huili, et al. Structural deformation characteristics and shale gas preservation conditions in the Zhaotong national shale gas demonstration area along the southern margin of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(10): 22-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201910003.htm [21] FENG Ziqi, DONG Dazhong, TIAN Jinqiang, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Lower Silurian shale gas in the Changning-Zhaotong exploration blocks, southern periphery of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 174: 281-290. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.11.022 [22] 梁兴, 管彬, 李军龙, 等. 山地浅层页岩气地质工程一体化高效压裂试气技术: 以昭通国家级页岩气示范区太阳气田为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(S1): 124-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG2021S1019.htmLIANG Xing, GUAN Bin, LI Junlong, et al. Key technologies of shallow shale gas reservoir in mountainous area: taking Taiyang gas field in Zhaotong national shale gas demonstration area as an example[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(S1): 124-132. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG2021S1019.htm [23] 芮昀, 王长江, 张凤生, 等. 昭通国家级页岩气示范区页岩气储层微观孔喉表征[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(S1): 78-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG2021S1012.htmRUI Yun, WANG Changjiang, ZHANG Fengsheng, et al. Characterization of micro-pore throats in the shale gas reservoirs of Zhaotong national shale gas demonstration area[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(S1): 78-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG2021S1012.htm [24] 王鹏万, 李昌, 张磊, 等. 五峰组—龙马溪组储层特征及甜点层段评价: 以昭通页岩气示范区A井为例[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(11): 2925-2935. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201711018.htmWANG Pengwan, LI Chang, ZHANG Lei, et al. Characteristic of the shale gas reservoirs and evaluation of sweet spot in Wufeng-Longmaxi formation: a case from the A well in Zhaotong shale gas demonsration zone[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(11): 2925-2935. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201711018.htm [25] 汤良杰, 郭彤楼, 田海芹, 等. 黔中地区多期构造演化、差异变形与油气保存条件[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 82(3): 298-307. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200803001.htmTANG Liangjie, GUO Tonglou, TIAN Haiqin, et al. Poly-cycle tectonic evolution, differential deformation and hydrocarbon reservation of central Guizhou and adjacent region[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 82(3): 298-307. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200803001.htm [26] 周楚凌. 滇黔北昭通示范区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气保存条件分析[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2018.ZHOU Chuling. Analysis of shale gas preservation conditions of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formation in Zhaotong demonstration area, northern Yunnan and Guizhou[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2018. [27] 赵圣贤, 杨跃明, 张鉴, 等. 四川盆地下志留统龙马溪组页岩小层划分与储层精细对比[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(3): 470-487. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201603011.htmZHAO Shengxian, YANG Yueming, ZHANG Jian, et al. Micro-layers division and fine reservoirs contrast of Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(3): 470-487. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201603011.htm [28] ABOUELRESH M, BABALOLA L, BOKHARI A, et al. Sedi-mentology, geochemistry and reservoir potential of the organic-rich Qusaiba Shale, Tabuk Basin, NW Saudi Arabia[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 111: 240-260. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817219301928 [29] LIU Bo, WANG Sheng, KE Xuan, et al. Mechanical characteristics and factors controlling brittleness of organic-rich continental shales[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 194: 107464. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817220300982 [30] 杨万芹. 东营凹陷沙三下—沙四上亚段页岩岩相特征及发育规律[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2018.YANG Wanqin. Shale lithofacies characteristics and development rule of the lower Es3 and upper Es4, Dongying Sag[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (North China), 2018. [31] DE S, KUMAR VIKRAM V, SENGUPTA D. Application of support vector regression analysis to estimate total organic carbon content of Cambay shale in Cambay Basin, India: a case study[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2019, 37(10): 1155-1164. [32] MAHMOUD A A, GAMAL H, ELKATATNY S, et al. Estimating the total organic carbon for unconventional shale resources during the drilling process: a machine learning approach[J]. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 2022, 144(4): 043004. [33] ZHANG Weiwei, HUANG Zhilong, GUO Xiaobo, et al. A study on pore systems of Silurian highly mature marine shale in southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 76: 103094. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1875510019303464 [34] LI Junqian, LU Shuangfang, ZHANG Pengfei, et al. Estimation of gas-in-place content in coal and shale reservoirs: a process analysis method and its preliminary application[J]. Fuel, 2020, 259: 116266. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236119316205 [35] MEWS K S, ALHUBAIL M M, BARATI R G. A review of brittleness index correlations for unconventional tight and ultra-tight reservoirs[J]. Geosciences, 2019, 9(7): 319. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/334576595_A_Review_of_Brittleness_Index_Correlations_for_Unconventional_Tight_and_Ultra-Tight_Reservoirs [36] IBAD S M, PADMANABHAN E. Lithofacies, mineralogy, and pore types in Paleozoic gas shales from Western Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 212: 110239. [37] 张冲, 夏富国, 夏玉琴, 等. 基于层次分析法的致密砂岩储层可压性综合评价[J]. 钻采工艺, 2021, 44(1): 61-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCGY202101014.htmZHANG Chong, XIA Fuguo, XIA Yuqing, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of fracability of tight sandstone reservoirs based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2021, 44(1): 61-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCGY202101014.htm [38] 陆亚秋, 王进, 曹梦茜. 基于改进的层次分析法的页岩气开发选区评价方法[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2021, 11(2): 204-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202102009.htmLU Yaqiu, WANG Jin, CAO Mengxi. Evaluation method of shale gas development area selection based on improved analytic hierarchy process[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2021, 11(2): 204-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202102009.htm [39] 张军华, 黄广谭, 李军, 等. 基于层次分析法的地震有利储层预测[J]. 特种油气藏, 2015, 22(5): 23-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201505004.htmZHANG Junhua, HUANG Guangtan, LI Jun, et al. Seismic favorable reservoir prediction based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2015, 22(5): 23-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201505004.htm -





 下载:
下载:








 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号