Differential deformation characteristics and genetic mechanism of boundary normal faults in Wangfu Fault Depression, Songliao Basin
-
摘要: 为揭示松辽盆地王府断陷断层的差异变形特征,深化对边界正断层变形机理的规律性认识,在构造解析及断层差异性分析的基础上,结合构造物理模拟在“连续正演”和“控制变量”方面的优势,探讨边界正断层差异变形的控制因素和成因机制。研究表明:(1)根据断层活动强度划分为4个区域构造演化阶段,王府西边界正断层活动性最强,但由北至南断层倾角逐渐增大,并且在局部呈现“上凸”形态。(2)综合构造物理模拟和实际地质背景表明,边界正断层形态受控于岩性横向变化、同构造沉积作用和基底先存凸起等3个主要因素。边界正断层若同时发育在不同岩性的地层中,或者伴随强烈的同构造沉积作用,都会导致倾角发生改变;此外,断层延伸到坚硬的基底凸起附近会改变延伸趋势,绕过其顶端继续传播,导致在局部出现“上凸”形态。Abstract: In order to reveal the differential deformation characteristics of the Wangfu Fault Depression in Songliao Basin and study the regularity of the deformation mechanism of boundary normal faults, this paper, based on the structural analysis and fault differential analysis, discusses the controlling factors and genetic mechanism of differential deformation of boundary normal faults in combination with the advantages of tectonophysical simulation in "continuous forward modeling" and "control variables". The results show that: (1) According to the intensity of fault activity, four regional tectonic evolution stages can be divided. The boundary normal faults in the west of Wangfu Fault Depression is the most active, but the dip angle of the faults gradually increases from north to south, showing a "convex" shape locally. (2) Combining tectonophysical simulation with actual geological background, it is showed that the shape of boundary normal fault was controlled by three main factors, including lateral lithologic change, syntectonic sedimentation and pre-existing uplift of basement. If boundary normal faults are developed in strata with different lithology at the same time, or accompanied by strong syntectonic sedimentation, the dip angle will change. In addition, the extension of the fault near the hard basement bulge will change its trend and continue to spread around the bulge top, resulting in the local appearance of "uplift".
-
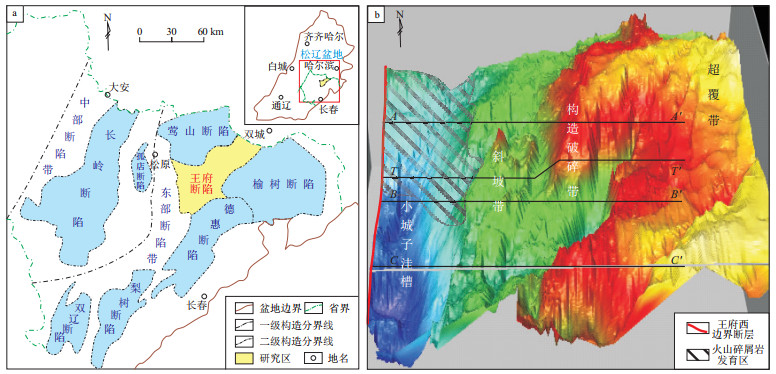
图 2 松辽盆地王府断陷典型剖面构造演化和油藏剖面
测线位置见图 1。
Figure 2. Structural evolution and reservoir profile of typical profile in Wangfu Fault Depression, Songliao Basin
图 3 松辽盆地王府断陷由北至南连续地质剖面
测线位置见图 1。
Figure 3. Continuous geological profile from north to south of Wangfu Fault Depression, Songliao Basin
表 1 构造物理模拟实验模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of tectonophysical simulation experiment models
模型序号 基底材料 基底厚度/cm 盖层材料 盖层厚度/cm 其他因素 ① 高岭土 4 石英砂 2 无 ② 高岭土 4 石英砂 2 同构造沉积 ③ 高岭土 3 石英砂 3 基底先存凸起 -
[1] 单俊峰, 陈昌, 周晓龙, 等. 辽河坳陷台安—大洼断裂带新生代构造演化及油气成藏[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(6): 11-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2021.06.002SHAN Junfeng, CHEN Chang, ZHOU Xiaolong, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation of Taian-Dawa Fault Zone, Liaohe Sag[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(6): 11-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2021.06.002 [2] 刘欢, 许长海, 申雯龙, 等. 东海丽水凹陷构造转移带特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28(4): 12-22. doi: 10.13673/j.cnki.cn37-1359/te.2021.04.002LIU Huan, XU Changhai, SHEN Wenlong, et al. Characteristics of transfer zones in Lishui Sag, East China Sea and its significance for petroleum geology[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2021, 28(4): 12-22. doi: 10.13673/j.cnki.cn37-1359/te.2021.04.002 [3] 王东晔. 临南地区扭张构造形成机制及其控藏作用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28(2): 60-67. doi: 10.13673/j.cnki.cn37-1359/te.2021.02.008WANG Dongye. Formation and evolution of transtensional structure and its hydrocarbon accumulation control in Linnan area[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2021, 28(2): 60-67. doi: 10.13673/j.cnki.cn37-1359/te.2021.02.008 [4] BRAUN J, BATT G E, SCOTT D L, et al. A simple kinematic model for crustal deformation along two- and three-dimensional listric normal faults derived from scaled laboratory experiments[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1994, 16(10): 1477-1490. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(94)90010-8 [5] 单帅强, 何登发, 方成名, 等. 渤海湾盆地冀中坳陷高阳低凸起构造特征及成因机制[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(6): 989-996. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202206989SHAN Shuaiqiang, HE Dengfa, FANG Chengming, et al. Structural characteristics and genetic mechanism of Gaoyang Low Uplift in Jizhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(6): 989-996. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202206989 [6] BYERLEE J. Friction of rocks[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1978, 116(4/5): 615-626. http://www.depts.ttu.edu/gesc/Fac_pages/Yoshinobu/4361_5361_Folder/2013-readings/Byerlee,%201978.pdf [7] TONG Hengmao, YIN An. Reactivation tendency analysis: a theory for predicting the temporal evolution of preexisting weakness under uniform stress state[J]. Tectonophysics, 2011, 503(3/4): 195-200. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195111000825 [8] TONG Hengmao, KOYI H, ZHAO H, et al. The effect of multiple pre-existing weaknesses on formation and evolution of faults in extended sandbox models[J]. Tectonophysics, 2014, 626: 197-212. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2014.04.046 [9] 漆家福, 杨桥. 伸展盆地的结构形态及其主控动力学因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28(5): 634-640. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.05.015QI Jiafu, YANG Qiao. Structural styles of extensional basins and their main controlling factors of dynamics[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2007, 28(5): 634-640. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2007.05.015 [10] 漆家福, 杨桥. 陆内裂陷盆地构造动力学分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(5): 19-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205005.htmQI Jiafu, YANG Qiao. Dynamic analysis of continental rifting basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(5): 19-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205005.htm [11] 桂宝玲. 伸展盆地构造几何学、运动学: 以渤海湾盆地廊固凹陷为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011.GUI Baoling. The structural geometry and kinematics of extensional basin: an example from Langfang-Gu'an Depression, Bohai Gulf Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2011. [12] SCHÖPFER M P J, CHILDS C, WALSH J J. Localisation of normal faults in multilayer sequences[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2006, 28(5): 816-833. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2006.02.003 [13] 冯阵东, 戴俊生, 张继标, 等. 伸展构造物理模拟中存在的问题及解决办法[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(3): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2011.03.002FENG Zhendong, DAI Junsheng, ZHANG Jibiao, et al. Problems and solutions in physical simulation of extensional structures[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2011, 35(3): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2011.03.002 [14] 侯贵廷, 钱祥麟, 蔡东升. 渤海湾盆地中、新生代构造演化研究[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 37(6): 845-851. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2001.06.016HOU Guiting, QIAN Xianglin, CAI Dongsheng. The tectonic evolution of Bohai Basin in Mesozoic and Cenozoic time[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2001, 37(6): 845-851. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0479-8023.2001.06.016 [15] 周建波, 张兴洲, 马志红, 等. 中国东北地区的构造格局与盆地演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2009, 30(5): 530-538. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.05.002ZHOU Jianbo, ZHANG Xingzhou, MA Zhihong, et al. Tectonic framework and basin evolution in Northeast China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2009, 30(5): 530-538. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2009.05.002 [16] 刘伟, 唐大卿, 陈明月, 等. 松辽盆地南部孤店断陷断裂构造特征及演化[J]. 断块油气田, 2022, 29(6): 816-823. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202206015.htmLIU Wei, TANG Daqing, CHEN Mingyue, et al. Fault structure characteristics and evolution in the Gudian Fault Depression, southern Songliao Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2022, 29(6): 816-823. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202206015.htm [17] 邓铭哲, 左宗鑫, 邱岐, 等. 松辽盆地南部梨树断陷正断层演化特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(2): 288-296. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102288DENG Mingzhe, ZUO Zongxin, QIU Qi, et al. Normal fault evolution in Lishu Fault Depression, southern Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(2): 288-296. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202102288 [18] 李建忠, 郑民, 张国生, 等. 中国常规与非常规天然气资源潜力及发展前景[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(S1): 89-98. doi: 10.7623/syxb2012S1011LI Jianzhong, ZHENG Min, ZHANG Guosheng, et al. Potential and prospects of conventional and unconventional natural gas resource in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(S1): 89-98. doi: 10.7623/syxb2012S1011 [19] 蒋飞, 李忠诚, 程日辉, 等. 王府断陷小城子气田火石岭组气藏天然气成藏模式及富集规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(10): 46-55. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.10.006JIANG Fei, LI Zhongcheng, CHENG Rihui, et al. Natural gas accumulation models and enrichment patterns of the Huoshiling Fm reservoirs in the Xiaochengzi Gas Field, Wangfu Fault Depression, Songliao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(10): 46-55. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2016.10.006 [20] 潘红卫, 石存英, 王晶淼, 等. 王府断陷天然气藏的识别[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2012, 47(S1): 97-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ2012S1019.htmPAN Hongwei, SHI Cunying, WANG Jingmiao, et al. Gas reservoir identification in Wangfu Fault Depression[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2012, 47(S1): 97-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ2012S1019.htm [21] 王玉学, 张为民, 丛玉梅, 等. 王府断陷断裂特征及其对深层火山岩气藏的控制作用研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(7): 2189-2199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201807023.htmWANG Yuxue, ZHANG Weimin, CONG Yumei, et al. The fault characteristics of the Wangfu Fault Depression and its controlling effects on deep-seated volcanic gas reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolo-gica Sinica, 2018, 34(7): 2189-2199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201807023.htm [22] 张君峰, 徐兴友, 白静, 等. 松辽盆地南部白垩系青一段深湖相页岩油富集模式及勘探实践[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(4): 637-652. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202004002.htmZHANG Junfeng, XU Xingyou, BAI Jing, et al. Enrichment and exploration of deep lacustrine shale oil in the first member of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation, southern Songliao Basin, NE China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(4): 637-652. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202004002.htm [23] WANG Pujun, CHEN Shumin. Cretaceous volcanic reservoirs and their exploration in the Songliao Basin, Northeast China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2015, 99(3): 499-523. doi: 10.1306/09041413095 [24] 王璞珺, 赵然磊, 蒙启安, 等. 白垩纪松辽盆地: 从火山裂谷到陆内拗陷的动力学环境[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(3): 99-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201503011.htmWANG Pujun, ZHAO Ranlei, MENG Qi'an, et al. The Cretaceous Songliao Basin: dynamic background from volcanic rift to interior sag basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(3): 99-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201503011.htm [25] 黄翠叶, 申维. 松辽盆地东南隆起区深层断陷的构造特征及其对油气勘探的意义[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(7): 841-848. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200707006.htmHUANG Cuiye, SHEN Wei. Structural characteristics of deep fault depressions in the southeastern uplift area of the Songliao Basin, China and their significance for petroleum exploration[J]. Geolo-gical Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(7): 841-848. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200707006.htm [26] GUO Zhanqian, WANG Xianbin, LIU Wenlong. Reservoir-forming features of abiotic origin gas in Songliao Basin[J]. Science in China (Series D: Earth Sciences), 1997, 40(6): 621-626. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=3001014062 [27] 赵志魁, 张金亮, 赵占银, 等. 松辽盆地南部坳陷湖盆沉积相和储层研究[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2009.ZHAO Zhikui, ZHANG Jinliang, ZHAO Zhanyin, et al. Reservoir sedimentology in southern Songliao Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2009. [28] 葛荣峰, 张庆龙, 王良书, 等. 松辽盆地构造演化与中国东部构造体制转换[J]. 地质论评, 2010, 56(2): 180-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201002005.htmGE Rongfeng, ZHANG Qinglong, WANG Liangshu, et al. Tectonic evolution of Songliao Basin and the prominent tectonic regime transition in eastern China[J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56(2): 180-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201002005.htm [29] KRANTZ R W. Measurements of friction coefficients and cohesion for faulting and fault reactivation in laboratory models using sand and sand mixtures[J]. Tectonophysics, 1991, 188(1/2): 203-207. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035691050410_81bb.html [30] SCHELLART W P. Shear test results for cohesion and friction coefficients for different granular materials: scaling implications for their usage in analogue modelling[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 324(1/2): 1-16. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100001116 [31] 李强, 柳广弟, 宋泽章, 等. 川中古隆起北斜坡构造演化及其对震旦系—寒武系油气成藏的控制[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(6): 997-1007. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202206997LI Qiang, LIU Guangdi, SONG Zezhang, et al. Influence of tectonic evolution of the northern slope in the central Sichuan paleo-uplift on the Sinian-Cambrian hydrocarbon accumulations[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(6): 997-1007. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202206997 [32] 罗群, 王仕琛, 贾春, 等. 断控气藏的动态成藏物理模拟与启示: 以柴达木盆地西北地区典型气藏为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(5): 790-803. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202205790LUO Qun, WANG Shichen, JIA Chun, et al. Physical simulation of dynamic accumulation of fault-controlled gas reservoirs and its implications: a case study of typical gas reservoirs in northwestern part of Qaidam Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(5): 790-803. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202205790 [33] 吴宇翔, 柳保军, 张春生, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷古近纪挠曲缓坡带三角洲沉积过程响应水槽模拟[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(3): 476-486. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202203476WU Yuxiang, LIU Baojun, ZHANG Chunsheng, et al. Flume simulation of response of deltaic sedimentary process to Paleogene flexural gentle slope belt in Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(3): 476-486. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202203476 [34] 徐宏远, 孙玮, 邵红君, 等. 西昌地区米市盆地构造特征及构造演化模拟[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28(5): 64-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202105007.htmXU Hongyuan, SUN Wei, SHAO Hongjun, et al. Tectonic characteristics and tectonic evolution simulation in Mishi Basin, Xichang area[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2021, 28(5): 64-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202105007.htm [35] 王瑾, 冯建伟, 蒋榕韬, 等. 东营凹陷东辛断裂带联合应力机制构造物理模拟[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(1): 78-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202101016.htmWANG Jin, FENG Jianwei, JIANG Rongtao, et al. Structural physical simulation of combined stress mechanism of Dongxin fault zone in Dongying Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(1): 78-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202101016.htm [36] LOHRMANN J, KUKOWSKI N, ADAM J, et al. The impact of analogue material properties on the geometry, kinematics, and dynamics of convergent sand wedges[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2003, 25(10): 1691-1711. [37] LONG Wei, LI Zhongquan, LI Ying, et al. Experimental insights on the structural patterns and their formation mechanisms of the Xujiaweizi Fault Depression in the Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2018, 29(2): 369-375. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=ZDDY201802011 [38] 周建勋, 漆家福, 董亨茂, 等. 盆地构造研究中的砂箱模拟实验方法[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 1999.ZHOU Jianxun, QI Jiafu, DONG Hengmao, et al. Sandbox simulation method in basin structure research[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1999. [39] 蔺鹏, 吴胜和, 胡光义. 被动陆缘盆地逆冲、底辟构造对深水层序结构的控制: 以尼日尔三角洲盆地某深水区为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(9): 21-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202209003.htmLIN Peng, WU Shenghe, HU Guangyi. Control of thrust and diapir structures on deep-water sequence architectures in passive continental margin basins: a case study on a deep-water zone in the Niger Delta Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(9): 21-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202209003.htm [40] 王心雨. 硝酸镉对高岭土力学及电化学特性影响的试验研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2014.WANG Xinyu. Experimental study on mechanical properties and electrochemical properties of cadmium nitrate contaminated kaolin[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2014. [41] 漆家福, 陈书平. 构造地质学(富媒体)[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2017.QI Jiafu, CHEN Shuping. Structural geology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2017. [42] CORVER M P, DOUST H, VAN WEES J D, et al. Source-rock maturation characteristics of symmetric and asymmetric grabens inferred from integrated analogue and numerical modeling: the southern Viking Graben (North Sea)[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(4): 921-935. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817210000334 [43] 何登发, 马永生, 刘波, 等. 中国含油气盆地深层勘探的主要进展与科学问题[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901002.htmHE Dengfa, MA Yongsheng, LIU Bo, et al. Main advances and key issues for deep-seated exploration in petroliferous basins in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901002.htm [44] 王绪诚, 陈维涛, 何叶, 等. 珠江口盆地惠西南地区古新世火山机构对有利储层的控制作用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(3): 466-475. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202203466WANG Xucheng, CHEN Weitao, HE Ye, et al. Control of Paleocene volcanic edifice on favorable reservoirs: a case study of the southwestern Huizhou Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(3): 466-475. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202203466 [45] 黄芸, 梁舒艺, 杨迪生, 等. 原生韵律型火山岩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(6): 54-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202106007.htmHUANG Yun, LIANG Shuyi, YANG Disheng, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of primary rhyolite volcanic reservoir[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(6): 54-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202106007.htm [46] 宁超众, 李勇, 邓晓娟, 等. 哈拉哈塘地区热液岩溶形成演化与油气分布[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(4): 399-409. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202104003.htmNING Chaozhong, LI Yong, DENG Xiaojuan, et al. Formation and evolution of hydrothermal karst and hydrocarbon distribution in Halahatang area[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(4): 399-409. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202104003.htm [47] 许廷生. 渤海湾盆地岩浆侵入活动与油气成藏特征[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(1): 81-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202101011.htmXU Tingsheng. Research on the magmatic intrusion and oil and gas reservoir forming characteristics in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(1): 81-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202101011.htm [48] 董树文, 张岳桥, 龙长兴, 等. 中国侏罗纪构造变革与燕山运动新诠释[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(11): 1449-1461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200711002.htmDONG Shuwen, ZHANG Yueqiao, LONG Changxing, et al. Jurassic tectonic revolution in China and new interpretation of the Yanshan Movement[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(11): 1449-1461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200711002.htm [49] WANG Yanjun, JIA Dong, PAN Jianguo, et al. Multiple-phase tectonic superposition and reworking in the Junggar Basin of northwestern China: implications for deep-seated petroleum exploration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2018, 102(8): 1489-1521. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=2245e7fdef9b51e016a10868e13b817a [50] 张希晨, 马德龙, 魏凌云, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘呼图壁背斜变形机理物理模拟实验[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(1): 120-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202001020.htmZHANG Xichen, MA Delong, WEI Lingyun, et al. Deformation mechanism of Hutubi Anticline in the southern margin of Junggar Basin: insights from physical simulation experiment[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2020, 41(1): 120-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202001020.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号