The essence of gypsum's influence on Tmax of source rocks: a case study of the Lower Ganchaigou Formation of Paleogene in western Qaidam Basin
-
摘要: 沉积盆地中的地质观察和热模拟实验研究均揭示了含膏泥岩生烃高峰提前的现象,而生烃高峰的提前量与膏岩含量之间的关系却尚未明确。选取柴达木盆地西部地区S49-1井中不同膏岩含量的下干柴沟组烃源岩粉末样品,对原样进行抽提,除去可溶有机质(SOM);取部分抽提残余物进行酸洗,除去碳酸盐;对原样和两步前处理后的固体残余物分别进行岩石热解分析。与原样的Tmax相比,不含SOM的残余物的Tmax更高,而去除SOM和碳酸盐矿物的样品Tmax更低,这表明含膏泥页岩中的SOM和硫酸盐矿物(石膏、硬石膏)均可促进有机质热演化。虽然后者的促进效果更为显著,但却与其硫酸盐矿物含量不成正比。这表明硫酸盐矿物与有机质的接触面积对Tmax的影响更为重要。该结论进一步通过不同比例的干酪根与硫酸镁粉末混合物的Tmax值进行了验证。因此,硫酸盐矿物的赋存状态会直接影响有机质与硫酸盐的接触关系,进而对热演化生烃进程产生影响。Abstract: Geological observation and thermal simulation experiments have revealed that the peak period of hydrocarbon generation of gypsum-bearing mudstone is often advanced in sedimentary basins, but the correlation between the amount of advance and the content of gypsum is still not clear. In this study, the source rock powder samples with different gypsum content in the Lower Ganchaigou Formation from well S49-1 in the western Qaidam Basin were selected and extracted to remove soluble organic matter (SOM). Part of the extracted residue was pickled to remove carbonate. Rock pyrolysis analysis was performed on the original samples and the solid residue after two-step pretreatment. Compared to the Tmax of original samples, the Tmax was higher in the SOM-free residue but lower in the SOM-free and carbonate-free residue, showing that SOM and sulfate minerals (gypsum and anhydrite) in gypsum-bearing mudstone can promote the thermal evolution of organic matter. Although the latter has a more significant effect, it is not proportional to its sulfate content, indicating that the contact area of sulfate minerals and organic matter is more important to Tmax. The hypothesis was verified by the Tmax values of different proportions of kerogen and magnesium sulfate powder mixtures. Therefore, the occurrence state of sulfate minerals will directly affect the contact relationship between organic matter and sulfate, which in turn will affect the process of hydrocarbon generation in thermal evolution.
-
表 1 柴达木盆地西部S49-1井古近系下干柴沟组实验样品的有机地化参数、矿物比例和岩石热解参数
Table 1. Organic geochemical parameters, mineral proportion and rock pyrolysis parameters of experimental samples from Lower Ganchaigou Formation of Paleogene in well S49-1, western Qaidam Basin
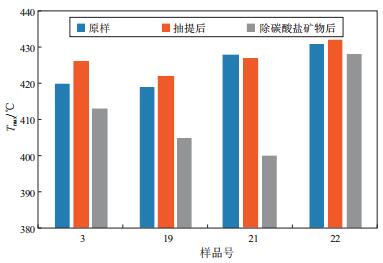
样品号 深度/m 有机质类型 成熟度参数 样品状态 矿物比例XRD/% 可溶有机质/% ω(TOC)/% 岩石热解参数 C29ααα20S/(20S+20R) C29αββ/(αββ+ααα) 升藿烷指数 硬石膏 石膏 S1/(mg·g-1) S2/(mg·g-1) Tmax/℃ 原始样品 3.5 - 0.19 0.49 0.61 1.38 420 3 3 752.37 Ⅱ2 0.317 0 0.213 3 0.613 6 抽提残余物 2.9 0.6 - 0.43 0.07 0.26 426 去除无机碳 - 0.55 0.14 0.60 413 原始样品 43.1 - 0.07 0.23 0.07 0.60 419 19 3 861.15 Ⅱ2 0.377 0 0.205 2 0.339 9 抽提残余物 40.5 0.3 - 0.18 0.07 0.29 422 去除无机碳 - 0.55 0.11 0.64 405 原始样品 1.6 - 0.28 0.64 1.00 2.11 427 21 3 871.17 Ⅱ1 0.349 2 0.202 9 0.602 1 抽提残余物 3.3 0.2 - 0.52 0.03 0.87 427 去除无机碳 - 0.68 0.26 0.96 400 原始样品 9.8 0.3 0.32 1.37 1.06 7.91 431 22 3 872.02 Ⅰ 0.374 7 0.262 6 0.598 8 抽提残余物 9.6 - - 1.15 0.06 6.90 432 去除无机碳 - 1.55 0.23 6.29 428 表 2 柴达木盆地西部S49-1井古近系下干柴沟组实验样品抽提物的族组分组成
Table 2. Group compositions of extracts from experimental samples in Lower Ganchaigou Formation of Paleogene in well S49-1, western Qaidam Basin
样品号 深度/m 族组分/% 饱和烃 芳烃 非烃 沥青质 3 3 752.37 52.64 13.63 30.32 3.41 19 3 861.15 47.34 15.00 32.50 5.16 21 3 871.17 53.81 14.21 30.20 1.78 22 3 872.02 56.46 16.73 23.19 3.61 表 3 不含硫酸盐的有机质与不同比例硫酸镁的Rock-Eval实验结果
Table 3. Rock Eval results of sulfate-free organic matter with different proportions of magnesium sulfate
样品编号 质量比(干酪根∶硫酸镁粉末) 样品量/mg S1/(mg·g-1) S2/(mg·g-1) Tmax/℃ LCG-K 1∶0 9.7 1.11 164.75 447 K1 1∶0.1 10.0 5.98 342.34 446 K2 1∶1 10.3 9.95 208.67 445 K3 1∶10 51.3 0.16 35.58 439 -
[1] SEEWALD J S. Organic-inorganic interactions in petroleum-producing sedimentary basins[J]. Nature, 2003, 426(6964): 327-333. doi: 10.1038/nature02132 [2] SUN Yuzhuang. Influences of secondary oxidation and sulfide formation on several maturity parameters in Kupferschiefer[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1998, 29(5/7): 1419-1429. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S0146638098001284&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1400974139&md5=4b93fe1da0e91b4c2fba8d81d0a66312 [3] SUN Yuzhuang, PVTTMANN W. Oxidation of organic matter in the transition zone of the Zechstein Kupferschiefer from the Sangerhausen Basin, Germany[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2001, 15(4): 817-829. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036565742810_2aed.html [4] SUN Yuzhuang, PVTTMANN W. The role of organic matter during copper enrichment in Kupferschiefer from the Sangerhausen Basin, Germany[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(11): 1143-1161. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00117-0 [5] CAO Jian, XIA Liuwen, WANG Tingting, et al. An alkaline lake in the Late Paleozoic Ice Age (LPIA): a review and new insights into paleoenvironment and petroleum geology[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 202: 103091. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103091 [6] WU Linmei, ZHOU Chunhui, KEELING J, et al. Towards an understanding of the role of clay minerals in crude oil formation, migration and accumulation[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2012, 115(4): 373-386. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.10.001 [7] 王娟. 咸化环境盐类物质与有机质相互作用研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2009.WANG Juan. A study on interaction of source rock and oil with evaporates in saline-lake facies[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2009. [8] 马中良, 郑伦举, 李志明, 等. 盐类物质对泥质烃源岩生排烃过程的影响[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 35(1): 43-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201301005.htmMA Zhongliang, ZHENG Lunju, LI Zhiming, et al. The effect of salts on hydrocarbon generation and expulsion of argillaceous source rock[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 35(1): 43-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201301005.htm [9] DING Kangle, WANG Shasha, LI Shuyuan, et al. Thermochemical reduction of magnesium sulfate by natural gas: insights from an experimental study[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2011, 45(2): 97-108. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.1.0103 [10] 李术元, 郭绍辉, 郑红霞. 褐煤催化降解生烃过程的动力学研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1997, 24(3): 21-23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1997.03.005LI Shuyuan, GUO Shaohui, ZHENG Hongxia. A study of catalytic degradation kinetics of fanshi lignite[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1997, 24(3): 21-23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1997.03.005 [11] 罗厚勇, 刘文汇, 王万春, 等. TSR对碳酸盐岩中沥青生烃影响的模拟实验[J]. 海相油气地质, 2016, 21(3): 29-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2016.03.004LUO Houyong, LIU Wenhui, WANG Wanchun, et al. Simulation experiment of TSR effects on hydrocarbon generation of bitumen in carbonate rocks[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2016, 21(3): 29-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2016.03.004 [12] 吴德云, 张国防. 盐湖相有机质成烃模拟实验研究[J]. 地球化学, 1994, 23(S1): 173-181. doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.1994.s1.020WU Deyun, ZHANG Guofang. Simulation experiment study on hydrocarbon generation from organic matter in saline lake facies rocks[J]. Geochimica, 1994, 23(Sl): 173-181. doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.1994.s1.020 [13] 慕小水. 东濮凹陷文留地区含盐层系油气成藏机理与模式[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011.MU Xiaoshui. Hydrocabon reservoir formation mechanism and pattern for saline series in Wenliu area, Dongpu Depression[D]. Beijing: China University of Geoscience (Beijing), 2011. [14] 孟庆强, 李京洲, 刘文汇, 等. 膏盐岩含量对成熟阶段页岩生烃影响的模拟实验[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(5): 113-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202205016.htmMENG Qingqiang, LI Jingzhou, LIU Wenhui, et al. Simulation study on the effect of gypsum-salt content on hydrocarbon generation in mature stage shale[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(5): 113-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202205016.htm [15] 宋金鹏, 田盼盼, 代俊杰, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷膏盐岩分布特征及油气地质意义[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(6): 800-804. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202106016.htmSONG Jinpeng, TIAN Panpan, DAI Junjie, et al. Distribution characteristics of gypsum-salt rock and petroleum geological significance in Kuqa Depression of Tarim Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(6): 800-804. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202106016.htm [16] WU Jia, QI Wen, JIANG Fujie, et al. Influence of sulfate on the generation of bitumen components from kerogen decomposition during catagenesis[J]. Petroleum Science, 2021, 18(6): 1611-1618. doi: 10.1016/j.petsci.2021.09.029 [17] CHEN Xueze, LIU Quanyou, MENG Qingqiang, et al. Assessing effects of sulfate minerals on petroleum generation in sedimentary basins using hydrous pyrolysis: Ⅰ. Light alkanes[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 110: 737-746. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.07.004 [18] 王力, 金强, 林腊梅, 等. 柴达木盆地西部古近系—新近系优质烃源岩特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2009, 29(2): 23-26. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.02.005WANG Li, JIN Qiang, LIN Lamei, et al. Characteristics of quality Tertiary source rocks in west Qaidam Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2009, 29(2): 23-26. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2009.02.005 [19] 舒豫川, 胡广, 庞谦, 等. 柴达木盆地咸湖相烃源岩特征: 以英西地区下干柴沟组上段为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(2): 179-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202102008.htmSHU Yuchuan, HU Guang, PANG Qian, et al. Characteristics of source rocks of salt lake facies in Qaidam Basin: taking upper member of Xiaganchaigou Formation in Yingxi region as an example[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(2): 179-186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202102008.htm [20] 金强, 查明, 赵磊. 柴达木盆地西部第三系盐湖相有效生油岩的识别[J]. 沉积学报, 2001, 19(1): 125-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.01.021JIN Qiang, CHA Ming, ZHAO Lei. Identification of effective source rocks in the Tertiary evaporate facies in the western Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2001, 19(1): 125-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2001.01.021 [21] 张敏, 张枝焕, 欧光习, 等. 柴达木盆地西部古近系干柴沟组页岩储层特征[J]. 地质通报, 2016, 35(2/3): 329-338. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2016Z1015.htmZHANG Min, ZHANG Zhihuan, OU Guangtxi, et al. Characteristics of shale gas reservoir rocks in Paleogene Ganchagou Formation, western Qaidam Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2016, 35(2/3): 329-338. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2016Z1015.htm [22] 伍劲, 刘占国, 朱超, 等. 柴达木盆地西部下干柴沟组下段碎屑岩储层物性差异主控因素分析[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2021, 28(4): 46-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202104006.htmWU Jin, LIU Zhanguo, ZHU Chao, et al. Main controlling factors of clastic reservoir property difference of Lower Ganchaigou Formation in western Qaidam Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2021, 28(4): 46-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202104006.htm [23] LI Meijun, SIMONEIT B R T, ZHONG Ningning, et al. The distribution and origin of dimethyldibenzothiophenes in sediment extracts from the Liaohe Basin, East China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2013, 65: 63-73. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2013.10.007 [24] ZHU Xiaojun, CAI Jingong, LIU Weixin, et al. Occurrence of stable and mobile organic matter in the clay-sized fraction of shale: signi-ficance for petroleum geology and carbon cycle[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 160-161: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.03.011 [25] LEWAN M D. Sulphur-radical control on petroleum formation rates[J]. Nature, 1998, 391(6663): 164-166. http://www.nature.com/articles/34391.pdf [26] HUNT J M, LEWAN M D, HENNET R J C. Modeling oil generation with time-temperature index graphs based on the Arrhenius equation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1991, 75(4): 795-807. http://aapgbull.geoscienceworld.org/content/75/4/795 [27] DU Pengyan, CAI Jingong, LIU Qing, et al. A comparative study of source rocks and soluble organic matter of four sags in the Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, NE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2021, 216: 104822. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912021001607 [28] WANG Min, SHERWOOD N, LI Zhongsheng, et al. Shale oil occurring between salt intervals in the Dongpu Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2015, 152: 100-112. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0166516215300239 [29] 张斌, 何媛媛, 陈琰, 等. 柴达木盆地西部咸化湖相优质烃源岩形成机理[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(6): 674-685. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201806006.htmZHANG Bin, HE Yuanyuan, CHEN Yan, et al. Formation mechanism of excellent saline lacustrine source rocks in western Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(6): 674-685. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201806006.htm [30] 江继纲, 彭平安, 傅家谟, 等. 盐湖油气的形成、演化和运移聚集[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 2004: 224-242.JIANG Jigang, PENG Pingan, FU Jiamo, et al. Generation, migration and accumlation of oils and gases in hypersaline lacustrine basin, China[M]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Science & Technology Press, 2004: 224-242. [31] HE Jinyi, CAI Jingong, ZHU Xiaojun, et al. The role of soluble organic matter in shale oil "sweet spots" prediction: an investigation of shale with different lithofacies in the Dongying Sag[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9: 718596. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/353393639_The_Role_of_Soluble_Organic_Matter_in_Shale_Oil_Sweet_Spots_Prediction_An_Investigation_of_Shale_With_Different_Lithofacies_in_the_Dongying_Sag [32] 李术元, 林世静, 郭绍辉, 等. 无机盐类对干酪根生烃过程的影响[J]. 地球化学, 2002, 31(1): 15-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200201002.htmLI Shuyuan, LIN Shijing, GUO Shaohui, et al. Effects of inorganic salts on the hydrocarbon generation from kerogens[J]. Geochi-mica, 2002, 31(1): 15-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200201002.htm [33] TANNENBAUM E, HUIZINGA B J, KAPLAN I R. Role of minerals in thermal alteration of organic matter—Ⅱ: a material balance[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1986, 70(9): 1156-1165. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/11542070 [34] TANNENBAUM E, KAPLAN I R. Role of minerals in the thermal alteration of organic matter—Ⅰ: generation of gases and condensates under dry condition[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1985, 49(12): 2589-2604. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-0016703785901280&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1430956975&md5=3d782cf75410e88f4983cf1ad1c61590 [35] 高先志, 张万选, 张厚福. 矿物质对热解影响的研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 1990, 12(2): 201-205. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199002201GAO Xianzhi, ZHANG Wanxuan, ZHANG Houfu. Study of the influence of minerals on pyrolysis[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 1990, 12(2): 201-205. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199002201 [36] 曹慧缇, 张义纲, 徐翔, 等. 碳酸盐岩生烃机制的新认识[J]. 石油实验地质, 1991, 13(3): 222-237. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199103222CAO Huiti, ZHANG Yigang, XU Xiang, et al. A new understanding of hydrocarbon generation mechanism of carbonate rocks[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 1991, 13(3): 222-237. doi: 10.11781/sysydz199103222 [37] 彭平安, 盛国英, 傅家谟, 等. 盐湖沉积环境未成熟油的成因与碳酸盐沉积阶段沉积的有机质有关[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45(S1): 2689-2694. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2000S1000.htmPENG Ping'an, SHENG Guoying, FU Jiamo, et al. The genesis of immature oil in the sedimentary environment of salt lakes is related to the organic matter deposited during the carbonate sedimentary stage[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(S1): 2689-2694. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2000S1000.htm [38] FAURE P, JEANNEAU L, LANNUZEL F. Analysis of organic matter by flash pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in the presence of Na-smectite: when clay minerals lead to identical molecular signature[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37(12): 1900-1912. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0146638006002415 [39] DEMBICKI H. The effects of the mineral matrix on the determination of kinetic parameters using modified Rock Eval pyrolysis[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1992, 18(4): 531-539. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/014663809290116F [40] EGLINTON T I, ROWLAND S J, CURTIS C D, et al. Kerogen-mineral reactions at raised temperatures in the presence of water[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1986, 10(4/6): 1041-1052. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0146638086800432 [41] QI Wen, WU Jia, XIA Yanqing, et al. Influence of ionic composition on minerals and source rocks: an investigation between carbonate-type and sulfate-type lacustrine sediments based on hydrochemical classification[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 130: 105099. [42] 张津宁, 张金功, 杨乾政, 等. 膏盐岩对异常高压形成与分布的控制: 以柴达木盆地狮子沟地区为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(3): 563-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201603014.htmZHANG Jinning, ZHANG Jingong, YANG Qianzheng, et al. The control effect of gypsum-salt rocks on formation and distribution of overpressure: a case of Shizigou area, Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(3): 563-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201603014.htm [43] 金强, 朱光有, 王娟. 咸化湖盆优质烃源岩的形成与分布[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 32(4): 19-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200804005.htmJIN Qiang, ZHU Guangyou, WANG Juan. Deposition and distribution of high-potential source rocks in saline lacustrine environments[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2008, 32(4): 19-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200804005.htm [44] 陈湘飞, 李素梅, 张洪安, 等. 东濮凹陷膏盐岩对烃源岩成烃演化的控制作用及其石油地质意义[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6): 1125-1136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806002.htmCHEN Xiangfei, LI Sumei, ZHANG Hongan, et al. Controlling effects of gypsum-salt on hydrocarbon generation of source rocks in Dongpu Sag and its significance on petroleum geology[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(6): 1125-1136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201806002.htm -





 下载:
下载:
 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号