Shale dominant lithofacies and shale oil enrichment model of Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area, Junggar Basin
-
摘要: 相较于准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷,与之紧邻的哈山地区经历了多期推覆改造,油气形成演化过程复杂,页岩油勘探面临优势岩相不明、富集规律不清等诸多挑战。为落实哈山地区下二叠统风城组页岩优势岩相,总结页岩油富集模式,以该区的哈山5井、哈深斜1井等8口探井200余块样品为基础,基于岩心、普通薄片观察等手段,在沉积环境及沉积相研究的基础上系统开展页岩岩相类型划分;结合XRD、扫描电镜、低温氮气吸附、热解等实验方法分岩相综合开展了储层物性及含油性评价;基于页岩矿物组成及有机质丰度和含油性的相关性分析,初步建立了哈山地区风城组页岩油富集模式。哈山地区风城组页岩可分为陆源碎屑岩相、白云质混积岩相、含碱性矿物混积岩相和含火山碎屑混积岩相4种岩相类型。陆源碎屑岩相中的(泥质)粉砂岩、白云质混积岩相中的白云质砂岩及含火山碎屑混积岩相储层物性及含油性较好,为有利的页岩油储集岩。页岩油富集模式可分为3类:在三角洲外前缘的陆源碎屑岩相中,主要为邻层运移的页岩油富集模式;在滨浅湖—半深湖发育段,白云质混积岩相发育段主要为同层裂缝运移以及邻层运移的页岩油富集模式;在含火山碎屑混积岩相发育的层段,为自生自储的基质型页岩油富集模式。Abstract: Compared with the Mahu Sag in the Junggar Basin, the adjacent Hashan area has undergone multi-stage napping and complicated oil-gas formation and evolution process, making its shale oil exploration facing many challenges, such as unclear dominant lithofacies and enrichment law. In order to optimize the dominant lithofacies of the Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation shale in Hashan area and summarize the enrichment model of shale oil, by taking more than 200 samples from 8 exploration wells in the area, including Hashan 5 and Hashen X1 wells, and using methods such as core and ordinary thin section observation, a systematic classification of shale lithofacies types was carried out based on the study of sedimentary environment and facies. A comprehensive evaluation of reservoir physical properties and oil content was conducted based on lithofacies by combining experimental methods such as XRD, scanning electron microscopy, low-temperature nitrogen adsorption, and pyrolysis. The enrichment law of the Fengcheng Formation shale oil in Hashan area was preliminarily revealed based on the correlation analysis of shale mineral composition, organic matter abundance and oil content. The results show that the Fengcheng Formation shale in Hashan area can be divided into four lithofacies types: terrigenous clastic, dolomitic diamict, alkaline mineral diamict and volcanic clastic diamict. The (argillaceous) siltstone in terrigenous clastic lithofacies, the dolomitic sandstone in dolomitic diamict lithofacies, and the volcanic clastic diamict lithofacies have good physical properties and oil content, which are good shale oil reservoirs. The shale oil enrichment patterns can be divided into three types: in the terrigenous clastic lithofacies of the outer delta front, the shale oil enrichment patterns are mainly migrated from adjacent strata. In the shallow- semi-deep lake section, the dolomitic mixed-deposit lithofacies are mainly the shale oil enrichment model of the same layer fracture migration and adjacent layer migration, while the volcaniclastic mixed-deposit lithofacies are mainly the self-generated and self-stored matrix shale oil enrichment model.
-
Key words:
- shale oil /
- lithofacies /
- enrichment model /
- Fengcheng Formation /
- Hashan area /
- Junggar Basin
-
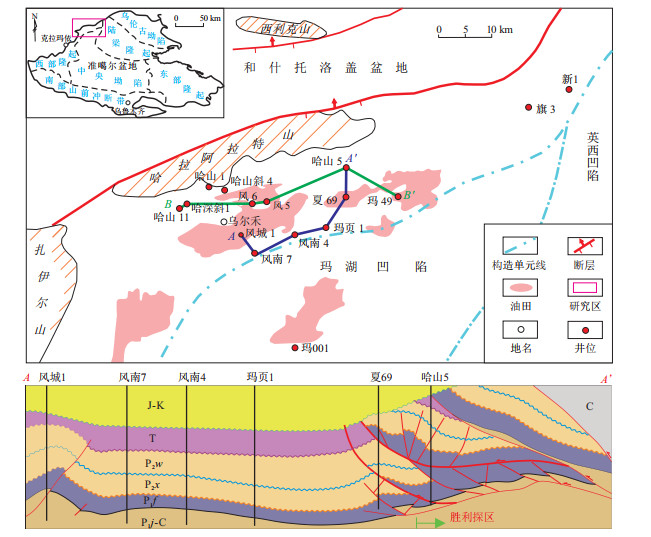
图 1 准噶尔盆地哈山地区区域构造与位置P2w, P2x, P1f, P1j分别为二叠系乌尔禾组、下子街组、风城组和佳木河组;图据文献[12]修改。
Figure 1. Regional structure and location of Hashan area, Junggar Basin
图 8 准噶尔盆地哈山地区哈山5井二叠系风城组页岩不同岩相样品的含油性特征
a. 3 928.5 m,陆源碎屑岩相,泥质粉砂岩,粉砂岩基质孔隙内含油; b.3 928.5 m,陆源碎屑岩相,泥质粉砂岩,粉砂岩基质孔隙内含油孔隙内含油;c.3 928.5 m,陆源碎屑岩相,长英质孔隙内含油,扫描电镜;d.4 462.2~4 464.7 m,白云质混积岩相,白云质泥岩裂缝含油;e.4 455.6 m,白云质混积岩相,高角度裂缝被石英脉充填(石英脉体内含大量油包裹体)荧光薄片;f.4 798.7 m,含碱性矿物混积岩相,溶蚀孔缝内含油,后期被碱性矿物充填;g.4 885.7 m,含碱性矿物混积岩相,溶蚀孔缝内含油,后期被碱性矿物充填;h.4 802.8 m,含碱性矿物混积岩相,长石溶孔内含油,扫描电镜;i.5 130.7 m,含火山碎屑混积岩相,凝灰岩溶蚀孔洞含油;j.5 133.3 m,含火山碎屑混积岩相,纹层状凝灰质泥岩,层理缝内含油;k.5 133.3 m,含火山碎屑混积岩相,顺层缝充填方解石(方解石脉体中含大量油包裹体)荧光薄片。
Figure 8. Oil content characteristics of different lithofacies samples of Permian Fengcheng Formation shale from well Hashan 5 in Hashan area, Junggar Basin
表 1 准噶尔盆地哈山地区二叠系风城组页岩岩相分类及沉积特征
Table 1. Lithofacies classification and sedimentary characteristics of Permian Fengcheng Formation shale in Hashan area, Junggar Basin
岩相组合类型 陆源碎屑岩相 白云质混积岩相 含碱性矿物混积岩相 含火山碎屑混积岩相 (粉砂质)泥岩 (泥质)粉砂岩 白云质砂岩 白云质泥岩 发育层位 风三段,风二段上部 风二段 风一段上部、风二段 风一段、风二段 沉积相带 三角洲外前缘 滨浅湖 半深湖 滨浅湖—半深湖/火山岩相 主要岩性及岩相组合 泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、 白云质泥岩、泥质白云岩、白云质砂岩 含碱白云质泥岩、含碱灰云质泥岩 凝灰岩、凝灰质细砂岩、凝灰质泥岩 表 2 准噶尔盆地哈山地区二叠系风城组不同岩相泥页岩氮气吸附孔隙体积分布
Table 2. Nitrogen adsorption pore volume distribution of different lithofacies of Permian Fengcheng Formation shale in Hashan area, Junggar Basin
岩相 微孔孔容/(cm3/g) 介孔孔容/(cm3/g) 宏孔孔容/(cm3/g) 累计孔容/(cm3/g) 陆源碎屑岩相 (粉砂质)泥岩 $\frac{0.00009 \sim 0.00073}{0.00041}\quad $ $\frac{0.00108 \sim 0.00662}{0.00385} $ $ \frac{0.00196 \sim 0.00536}{0.00366} $ $\frac{0.00653 \sim 0.00932}{0.00792} $ (泥质)粉砂岩 $\frac{0.00127 \sim 0.00240}{0.00184} $ $ \frac{0.00686 \sim 0.01219}{0.00953} $ $\frac{0.00194 \sim 0.00254}{0.00224} $ $\frac{0.01067 \sim 0.01653}{0.01360} $ 白云质混积岩相 白云质砂岩 0.000 16 0.000 86 0.003 46 0.004 49 白云质泥岩 $ \frac{0.00009 \sim 0.00018}{0.00014}$ $\frac{0.00047 \sim 0.00096}{0.00071} $ $\frac{0.00268 \sim 0.00373}{0.00321} $ $ \frac{0.00382 \sim 0.00429}{0.00406}$ 含碱性矿物混积岩相 $\frac{0.00002 \sim 0.00097}{0.00048} $ $\frac{0.00121 \sim 0.00333}{0.00204} $ $\frac{0.002042 \sim 0.03012}{0.01687} $ $\frac{0.00348 \sim 0.03202}{0.01939} $ 含火山碎屑混积岩相 $\frac{0.00984 \sim 0.01345}{0.01030}$ $\frac{0.00924 \sim 0.01773}{0.01193} $ $ \frac{0.00266 \sim 0.00433}{0.00406}$ $\frac{0.02174 \sim 0.03552}{0.02630} $ 注:表中分式意义为:最小值~最大值平均值。 -
[1] 张善文. 准噶尔盆地哈拉阿拉特山地区风城组烃源岩的发现及石油地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(2): 145-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201302003.htmZHANG Shanwen. Identification and its petroleum geologic significance of the Fengcheng Formation source rocks in Hala'alt area, the northern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2013, 3(2): 145-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201302003.htm [2] 支东明, 宋永, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地中—下二叠统页岩油地质特征、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(4): 389-401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201904002.htmZHI Dongming, SONG Yong, HE Wenjun, et al. Geological characteristics, resource potential and exploration direction of shale oil in Middle-Lower Permian, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(4): 389-401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201904002.htm [3] 胡涛, 庞雄奇, 于飒, 等. 准噶尔盆地风城地区风城组烃源岩生排烃特征及致密油资源潜力[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 48(2): 427-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201702022.htmHU Tao, PANG Xiongqi, YU Sa, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion characteristics of P1f source rocks and tight oil accumulation potential of Fengcheng area on northwest margin of Junggar Basin, northwest China[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2017, 48(2): 427-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201702022.htm [4] 郑国伟, 高之业, 黄立良, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩储层润湿性及其主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(5): 1206-1220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202205016.htmZHENG Guowei, GAO Zhiye, HUANG Liliang, et al. Wettability of the Permian Fengcheng Formation shale in the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, and its main control factors[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(5): 1206-1220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202205016.htm [5] 贾承造. 论非常规油气对经典石油天然气地质学理论的突破及意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701002.htmJIA Chengzao. Breakthrough and significance of unconventional oil and gas to classical petroleum geological theory[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201701002.htm [6] 宋永, 杨智峰, 何文军. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组碱湖型页岩油勘探进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2022, 27(1): 60-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202201006.htmSONG Yong, YANG Zhifeng, HE Wenjun. Exploration progress of alkaline lake type shale oil of the Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2022, 27(1): 60-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202201006.htm [7] 支东明, 唐勇, 郑孟林, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油藏地质特征与成藏控制因素[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5): 615-623. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.008ZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, ZHENG Menglin, et al. Geological characteristics and accumulation controlling factors of shale reservoirs in Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5): 615-623. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.008 [8] 支东明, 曹剑, 向宝力, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组碱湖烃源岩生烃机理及资源量新认识[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2016, 37(5): 499-506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201605002.htmZHI Dongming, CAO Jian, XIANG Baoli, et al. Fengcheng alkaline lacustrine source rocks of Lower Permian in Mahu Sag in Junggar Basin: hydrocarbon generation mechanism and petroleum resources reestimation[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2016, 37(5): 499-506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201605002.htm [9] 张关龙, 张奎华, 王圣柱, 等. 哈拉阿拉特山石炭系裂缝发育特征及成藏意义[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 36(3): 9-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201403002.htmZHANG Guanlong, ZHANG Kuihua, WANG Shengzhu, et al. Characteristics of the Carboniferous volcanic fractures and its hydrocarbon accumulation significance in Hala'alate Mountains[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2014, 36(3): 9-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201403002.htm [10] 刘勇, 袁海锋, 高耀, 等. 准噶尔盆地哈山地区石炭系—二叠系裂缝充填方解石的成因机制及石油地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(11): 2573-2583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.11.012LIU Yong, YUAN Haifeng, GAO Yao, et al. Genetic mechanism of calcite veins in Carboniferous-Permian volcanic reservoirs in the Hashan area, Junggar Basin and its petroleum geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(11): 2573-2583. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.11.012 [11] 钱永新, 邹阳, 赵辛楣, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷玛页1井二叠系风城组全井段岩心剖析与油气地质意义[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2022, 12(1): 204-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202201018.htmQIAN Yongxin, ZOU Yang, ZHAO Xinmei, et al. Full core analysis and petroleum geological significance of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Well-MY1, Mahu Sag[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2022, 12(1): 204-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202201018.htm [12] 于洪洲, 王越, 周健, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘哈山地区二叠系风城组沉积体系[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(4): 396-403. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202204003.htmYU Hongzhou, WANG Yue, ZHOU Jian, et al. Sedimentary system of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(4): 396-403. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202204003.htm [13] 肖雄飞. 哈山地区二叠系风城组云质岩储层发育特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学, 2014.XIAO Xiongfei. Study on dolomitic rock reservoir characteristics of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2014. [14] 马遵敬. 哈山地区二叠系油源对比及成烃演化研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学, 2014.MA Zunjing. Source rock-oil correlation and hydrocarbon genera-tion research of Hashan region[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2014. [15] 于春勇, 贾雨萌, 李晓祥, 等. 准噶尔盆地哈山地区石炭—二叠系油气成藏期次及时间厘定[J]. 录井工程, 2022, 33(3): 110-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGZ202203019.htmYU Chunyong, JIA Yumeng, LI Xiaoxiang, et al. Determination of Carboniferous-Permian hydrocarbon accumulation period and time in Hala'alate Mountain area, Junggar Basin[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 2022, 33(3): 110-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJGZ202203019.htm [16] 曾治平, 柳忠泉, 赵乐强, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘哈山地区二叠系风城组页岩油储层特征及其控制因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(1): 25-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202301003.htmZENG Zhiping, LIU Zhongquan, ZHAO Leqiang, et al. Shale oil reservoir characteristics and controlling factors of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area, northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(1): 25-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202301003.htm [17] 杨智峰, 唐勇, 郭旭光, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油赋存特征与影响因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5): 784-796. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105784YANG Zhifeng, TANG Yong, GUO Xuguang, et al. Occurrence states and potential influencing factors of shale oil in the Permian Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(5): 784-796. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105784 [18] 何文军, 钱永新, 赵毅, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组全油气系统勘探启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6): 641-655. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106002.htmHE Wenjun, QIAN Yongxin, ZHAO Yi, et al. Exploration implications of total petroleum system in Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(6): 641-655. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106002.htm [19] 张凤奇, 刘伟, 鲁雪松, 等. 喜马拉雅晚期构造应力场及其与油气分布的关系: 以准噶尔盆地南缘为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(4): 433-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104002.htmZHANG Fengqi, LIU Wei, LU Xuesong, et al. Late Himalayan tectonic stress field and its relationship with hydrocarbon distribution: a case study of southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(4): 433-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104002.htm [20] 匡立春, 唐勇, 雷德文, 等. 准噶尔盆地二叠系咸化湖相云质岩致密油形成条件与勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(6): 657-667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201206004.htmKUANG Lichun, TANG Yong, LEI Deiwen, et al. Formation conditions and exploration potential of tight oil in the Permian saline lacustrine dolomitic rock, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(6): 657-667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201206004.htm [21] 唐勇, 曹剑, 何文军, 等. 从玛湖大油区发现看全油气系统地质理论发展趋势[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202101001.htmTANG Yong, CAO Jian, HE Wenjun, et al. Development tendency of geological theory of total petroleum system: insights from the discovery of Mahu large oil province[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202101001.htm [22] 牛海青, 陈世悦, 张鹏, 等. 准噶尔盆地乌夏地区二叠系碎屑岩储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 41(2): 749-758. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201002061.htmNIU Haiqing, CHEN Shiyue, ZHANG Peng, et al. Diagenesis and porosity evolution of Permian reservoir in Wu-Xia area, Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2010, 41(2): 749-758. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201002061.htm [23] 李佳思, 付磊, 张金龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地乌夏地区中上二叠统碎屑岩成岩作用及次生孔隙演化[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(6): 54-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201906006.htmLI Jiasi, FU Lei, ZHANG Jinlong, et al. Diagenesis and secondary pore evolution of Middle and Upper Permian clastic rocks in Wu-Xia area, Junggar Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(6): 54-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX201906006.htm [24] 于洪洲. 准西北缘哈山地区石炭系火山岩储层特征及影响因素[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(2): 206-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201902061.htmYU Hongzhou. Characteristics and influencing factors of Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs in Hashan area, northwestern margin of the Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(2): 206-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201902061.htm [25] 李鹏, 熊健, 晏奇, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组岩性对岩石力学特性的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(4): 569-578. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202204569LI Peng, XIONG Jian, YAN Qi, et al. Lithological influences to rock mechanical properties of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(4): 569-578. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202204569 [26] 支东明, 唐勇, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组常规—非常规油气有序共生与全油气系统成藏模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(1): 38-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202101006.htmZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, HE Wenjun, et al. Orderly coexistence and accumulation models of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbons in Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Deve-lopment, 2021, 48(1): 38-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202101006.htm [27] 李萧, 劳海港, 胡秋媛, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘乌夏断裂带构造特征及物理模拟实验[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(4): 567-572. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201704567LI Xiao, LAO Haigang, HU Qiuyuan, et al. Tectonic evolution and its physical simulation of Wuxia fault belt in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(4): 567-572. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201704567 [28] 李宗浩, 刘海磊, 卞保力, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘掩伏带构造特征及勘探潜力分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2018, 25(5): 56-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201805011.htmLI Zonghao, LIU Hailei, BIAN Baoli, et al. Structure characte-rization and exploration potential analysis of the shielding belt in the northwestern rim of Junggar Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2018, 25(5): 56-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201805011.htm [29] BRUNAUER S, EMMETT P H, TELLER E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1938, 60(2): 309-319. [30] 孙中良, 王芙蓉, 韩元佳, 等. 江汉盆地潜江凹陷古近系潜江组盐间可动页岩油赋存空间多尺度表征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(4): 586-595. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202004586SUN Zhongliang, WANG Furong, HAN Yuanjia, et al. Multi-scale characterization of the spatial distribution of movable hydrocarbon in intersalt shale of Qianjiang Formation, Qianjiang Sag, Jianghan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(4): 586-595. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202004586 [31] BRUNAUER S, DEMING L S, EDWARDS DEMING W, et al. On a theory of the van der Waals adsorption of gases[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1940, 62(7): 1723-1732. -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号