Development characteristics and quantitative characterization of pore evolution of deep and ultra-deep clastic reservoirs in the hinterland of the Junggar Basin
-
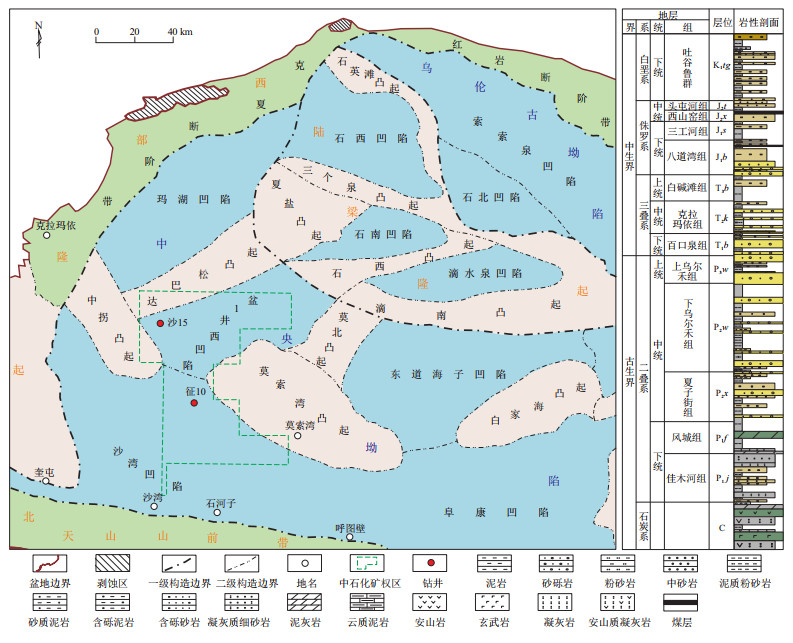
摘要: 腹部下组合(二叠系—三叠系)是准噶尔盆地油气勘探重要的战略接替领域。多井钻揭6 km以下优质碎屑岩储层,大大突破了传统碎屑岩有效储层埋深下限,明确储层发育状况及孔隙演化过程是确定油气能否富集成藏的关键问题。以腹部地区典型钻井为例,综合岩石薄片镜下分析、孔渗测试、图像分析技术、孔隙度演化定量表征及包裹体测温和盆地模拟等方法,从定性和定量的角度全面剖析准噶尔盆地腹部下组合深层—超深层碎屑岩储层的岩石学、物性及孔隙结构特征,并定量恢复孔隙演化过程。结果表明,腹部下组合中三叠系百口泉组砂体最为发育,二叠系上乌尔禾组及三叠系克拉玛依组次之;各层位岩石类型均以岩屑砂岩为主,少量长石岩屑砂岩,岩屑成分主要为中—基性火山岩屑,长石、石英含量偏低,二者之和普遍低于20%;克拉玛依组原生孔隙发育,物性最好,孔隙度最高可达13.18%。上乌尔禾组和百口泉组以次生溶蚀孔为主,溶蚀物质主要为中—基性火山岩屑、浊沸石胶结物及少量长石,二者物性较其上覆克拉玛依组差;克拉玛依组孔隙演化经历较弱压实(压实减孔量21.08%)、弱胶结(胶结减孔量2.88%)和弱溶蚀(溶蚀增孔量1.4%),现今高孔隙度主要得益于弱压实、晚期弱胶结作用下原生孔隙的大量保存;百口泉组和上乌尔禾组经历强压实(压实减孔量分别为26.60%和26.43%)、强胶结(胶结减孔量分别为7.43%和11%)和中等—强溶蚀(溶蚀增孔量分别为6.32%和4.21%),溶蚀作用是二者增孔的最主要途径,但不足以弥补强压实和强胶结的减孔效应,导致二者现今孔隙度较低。Abstract: The lower play (Permian to Triassic) in the hinterland is the most important strategic succession field for oil and gas exploration in the Junggar Basin. Multiple wells have been drilled into high-quality clastic rock reservoirs below 6 000 m, greatly breaking through the deadline of buried depth of traditional clastic rock effective reservoirs. It has been made clear that the development status and pore evolution process are the key issues that determine whether oil and gas can be accumulated. Taking typical drilling wells in the hinterland as an example, this paper comprehensively analyzed the petrology, physical properties and pore structure characteristics of deep and ultra-deep clastic reservoirs in the hinterland of the Junggar Basin from a qualitative and quantitative perspective, and quantitatively restored the pore evolution process by integrating the microscopic analysis of rock thin sections, porosity and permeability tests, image analysis technology, quantitative characterization of porosity evolution, temperature measurement of inclusions, basin modeling and other methods. The results show that the clastic rock in the lower play of the hinterland is mainly developed in the Permian Upper Wuerhe Formation, Triassic Baikouquan Formation and Triassic Kelamayi Formation, of which the sand in the Triassic Baikouquan Formation is the most developed, followed by the Permian Upper Wuerhe Formation and Triassic Kalamayi Formation. There is little difference in rock types among different layers, which mainly composed of lithic sandstone with a small amount of feldspar lithic sandstone. The composition of rock debris is mainly medium-basic volcanic rock debris, with low content of feldspar and quartz, and the sum of them is generally less than 20%. The Kelamayi Formation is dominated by primary pores with the best reservoir property and the highest porosity of 13.18%. The Upper Wuerhe Formation and Baikouquan Formation are dominated by secondary corrosion pores, and the corrosion materials are mainly medium-basic volcanic debris, laumontite cement and a small amount of feldspar. The reservoir properties of them are not as good as those of the Kelamayi Formation. The pore evolution of the Kelamayi Formation has experienced weak compaction (21.08% pore reduction by compaction), weak cementation (2.88% pore reduction by cementation), and weak corrosion (1.4% pore increase by corrosion). Today's high porosity is mainly due to the large amount of preservation of primary pores under weak compaction and late weak cementation. The Baikouquan Formation and Upper Wuerhe Formation have undergone strong compaction (26.60% and 26.43% pore reduction by compaction, respectively), strong cementation (7.43% and 11% pore reduction by cementation, respectively), and strong corrosion (6.32% and 4.21% pore increase by corrosion, respectively). Secondary corrosion is the main way for them to increase porosity, but it is insufficient to compensate for the porosity reduction effect of strong compaction and cementation, resulting in lower porosity in the two formations.
-
图 3 准噶尔盆地腹部下组合岩石类型
部分数据来自文献[8]。
Figure 3. Triangle diagram of rock types of the lower play in the hinterland of the Junggar Basin
图 4 准噶尔盆地腹部下组合岩石成分镜下特征
a.征10井,6 575 m,T2k,绿泥石包壳及方解石胶结,单偏光;b.征10井,6 575 m,T2k,火山岩屑、少量长石、石英及方解石胶结,正交偏光;c.征10井,6 580 m,T2k,火山岩屑、少量石英和方解石胶结,正交偏光;d.征10井,6 801 m,T1b,火山岩屑及大量方解石胶结,少量长石、石英,正交偏光;e.征10井,6 961 m,T1b,浊沸石胶结及石英次生加大,单偏光;f.沙15井,5 793 m,T1b,火山岩屑及少量硅质胶结,单偏光;g.征10井,7 272 m,P3w,火山岩屑及浊沸石强胶结,正交偏光;h.征10井,7 418 m,P3w,方解石及硅质胶结,正交偏光、茜素红染色;i.沙15井,6 147.8 m,P3w,大量火山岩屑及浊沸石胶结,长英质含量较低,正交偏光。
Figure 4. Microscopic characteristics of rock composition of the lower play in the hinterland of the Junggar Basin
图 7 准噶尔盆地腹部下组合储层孔隙类型镜下特征
a.征10井,6 711 m,T2k,原生孔发育,少量长石及火山岩屑溶蚀孔,颗粒间点—线接触,压实程度较弱,单偏光;b.征10井,6 721 m,T2k,原生粒间孔及火山岩屑溶蚀孔,局部见火山岩屑内长石强烈溶蚀,原生孔内少量硅质胶结及绿泥石包壳环绕颗粒,单偏光;c.征10井,6 796 m,T2k,原生粒间孔发育,颗粒边缘发育绿泥石包壳,少量方解石及硅质胶结,未见明显溶蚀,单偏光;d.征10井,6 961 m,T1b,浊沸石溶蚀孔发育,溶蚀孔内见沥青质残留,单偏光;e.征10井,7 059.5 m,T1b,溶蚀孔及网状缝发育,溶蚀物质主要为浊沸石及基性火山岩屑,单偏光;f.征10井,7 059.5 m,T1b,浊沸石沿解理缝强烈溶蚀,少量方解石胶结单偏光;g.征10井,7 272 m,P3w,溶蚀孔及微裂缝,溶蚀物质主要为火山岩屑及浊沸石胶结物,单偏光;h.沙15井,6 196 m,P3w,火山岩屑溶蚀孔发育,浊沸石胶结物弱溶蚀,单偏光;i.沙15井,6 294 m,P3w,长石及火山岩屑溶蚀孔,粒间胶结物未见明显溶蚀,单偏光。
Figure 7. Microscopic characteristics of reservoir pore types of the lower play in the hinterland of the Junggar Basin
表 1 准噶尔盆地腹部征10井不同层位孔隙演化参数恢复结果
Table 1. Restoration results of pore evolution parameters in different layers of well Zheng 10 in the hinterland of the Junggar Basin
层位 分选系数 原始孔隙度/% 胶结物面孔率/% 胶结孔隙度/% 溶蚀面孔率/% 溶蚀孔隙度/% 现今孔隙度/% 压实减孔量/% 克拉玛依组 1.48 36.42 0.72 2.88 0.33 1.40 13.18 21.08 百口泉组 1.22 39.68 2.03 7.43 1.70 6.32 7.95 26.60 上乌尔禾组 1.18 40.36 3.12 11.00 1.09 4.21 4.85 26.43 -
[1] 何文军, 王绪龙, 邹阳, 等. 准噶尔盆地石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(2): 75-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2019.02.008HE Wenjun, WANG Xulong, ZOU Yang, et al. The geological conditions, resource potential and exploration direction of oil in Junggar Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(2): 75-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2019.02.008 [2] 李阳, 薛兆杰, 程喆, 等. 中国深层油气勘探开发进展与发展方向[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(1): 45-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.005LI Yang, XUE Zhaojie, CHENG Zhe, et al. Progress and deve-lopment directions of deep oil and gas exploration and development in China[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(1): 45-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.005 [3] 孙龙德, 邹才能, 朱如凯, 等. 中国深层油气形成、分布与潜力分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(6): 641-649. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201306001.htmSUN Longde, ZOU Caineng, ZHU Rukai, et al. Formation, distribution and potential of deep hydrocarbon resources in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(6): 641-649. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201306001.htm [4] 王小军, 宋永, 郑孟林, 等. 准噶尔盆地复合含油气系统与复式聚集成藏[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(4): 29-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.04.003WANG Xiaojun, SONG Yong, ZHENG Menglin, et al. Composite petroleum system and multi-stage hydrocarbon accumulation in Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(4): 29-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.04.003 [5] 贾承造, 庞雄奇. 深层油气地质理论研究进展与主要发展方向[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(12): 1457-1469. doi: 10.7623/syxb201512001JIA Chengzao, PANG Xiongqi. Research processes and main development directions of deep hydrocarbon geological theories[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(12): 1457-1469. doi: 10.7623/syxb201512001 [6] 张仲培, 张宇, 张明利, 等. 准噶尔盆地中部凹陷区二叠系—三叠系油气成藏主控因素与勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(4): 559-568. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202204559ZHANG Zhongpei, ZHANG Yu, ZHANG Mingli, et al. Main contro-lling factors and exploration direction of Permian to Triassic reservoir in the central sag of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(4): 559-568. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202204559 [7] 殷树铮, 张奎华, 于洪洲, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部二叠系地震波组特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 2023, 58(1): 124-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202301008.htmYIN Shuzheng, ZHANG Kuihua, YU Hongzhou, et al. Characte-ristics and its geological significance of seismic wave group of Permian in the central Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2023, 58(1): 124-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202301008.htm [8] 何登发, 张磊, 吴松涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化阶段及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 845-861. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805002.htmHE Dengfa, ZHANG Lei, WU Songtao, et al. Tectonic evolution stages and features of the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 845-861. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805002.htm [9] 孙靖, 郭旭光, 尤新才, 等. 准噶尔盆地深层—超深层致密碎屑岩储层特征及有效储层成因[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(7): 2532-2546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.07.019SUN Jing, GUO Xuguang, YOU Xincai, et al. Characteristics and effective reservoir genesis of deep to ultra-deep tight clastic reservoir of Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(7): 2532-2546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.07.019 [10] 李建忠, 王小军, 杨帆, 等. 准噶尔盆地中央坳陷西部下组合油气成藏模式及勘探前景[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(5): 1059-1072. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202205005.htmLI Jianzhong, WANG Xiaojun, YANG Fan, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation pattern and exploration prospect of the structural traps in lower play of the western Central Depression in the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(5): 1059-1072. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202205005.htm [11] 陈发景, 汪新文, 汪新伟. 准噶尔盆地的原型和构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(3): 77-89. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.03.010CHEN Fajing, WANG Xinwen, WANG Xinwei. Prototype and tectonic evolution of the Junggar Basin, northwestern China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(3): 77-89. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.03.010 [12] 蔡忠贤, 陈发景, 贾振远. 准噶尔盆地的类型和构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(4): 431-440. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.04.010CAI Zhongxian, CHEN Fajing, JIA Zhenyuan. Types and tectonic evolution of Junggar Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2000, 7(4): 431-440. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.04.010 [13] 况军, 齐雪峰. 准噶尔前陆盆地构造特征与油气勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2006, 27(1): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2006.01.002KUANG Jun, QI Xuefeng. The structural characteristics and oil-gas explorative direction in Junggar Foreland Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2006, 27(1): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2006.01.002 [14] 何文军, 费李莹, 阿布力米提·依明, 等. 准噶尔盆地深层油气成藏条件与勘探潜力分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 189-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901019.htmHE Wenjun, FEI Liying, YIMING A, et al. Accumulation conditions of deep hydrocarbon and exploration potential analysis in Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 189-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901019.htm [15] 郑孟林, 樊向东, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地深层地质结构叠加演变与油气赋存[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 22-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901004.htmZHENG Menglin, FAN Xiangdong, HE Wenjun, et al. Superposition of deep geological structural evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Junggar Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 22-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201901004.htm [16] 唐勇, 宋永, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔叠合盆地复式油气成藏规律[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(1): 132-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202201010.htmTANG Yong, SONG Yong, HE Wenjun, et al. Characteristics of composite hydrocarbon accumulation in a superimposed basin, Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(1): 132-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202201010.htm [17] 王芙蓉, 何生, 何治亮, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部地区深层砂岩储层孔隙特征研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(6): 547-552. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.06.006WANG Furong, HE Sheng, HE Zhiliang, et al. The reservoir characteristic of deeply-buried sandstone in the center of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32(6): 547-552. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.06.006 [18] 黄洁, 朱如凯, 侯读杰, 等. 深部碎屑岩储层次生孔隙发育机理研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2007, 26(6): 76-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200706014.htmHUANG Jie, ZHU Rukai, HOU Dujie, et al. The new advances of secondary porosity genesis mechanism in deep clastic reservoir[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2007, 26(6): 76-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200706014.htm [19] 张振宇, 张立宽, 罗晓容, 等. 准噶尔盆地中部地区深层西山窑组砂岩成岩作用及其对储层质量评价的启示[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(5): 686-700. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201905009.htmZHANG Zhenyu, ZHANG Likuan, LUO Xiaorong, et al. Diagenesis of sandstone and its implications for reservoir quality evaluation in the deep Xishanyao Formation in the central Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(5): 686-700. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201905009.htm [20] 操应长, 远光辉, 王艳忠, 等. 准噶尔盆地北三台地区清水河组低渗透储层成因机制[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(5): 758-771. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201205005.htmCAO Yingchang, YUAN Guanghui, WANG Yanzhong, et al. Genetic mechanisms of low permeability reservoirs of Qingshuihe Formation in Beisantai area, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(5): 758-771. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201205005.htm [21] 操应长, 远光辉, 杨海军, 等. 含油气盆地深层—超深层碎屑岩油气勘探现状与优质储层成因研究进展[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(1): 112-140.CAO Yingchang, YUAN Guanghui, YANG Haijun, et al. Current situation of oil and gas exploration and research progress of the origin of high-quality reservoirs in deep-ultra-deep clastic reservoirs of petroliferous basins[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(1): 112-140. [22] 曹江骏, 陈朝兵, 程皇辉, 等. 成岩作用对深水致密砂岩储层微观非均质性的影响: 以鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区长7油层组为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(4): 1031-1046. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202104020.htmCAO Jiangjun, CHEN Chaobin, CHENG Huanghui, et al. Effect of diagenesis on microheterogeneity of deepwater tight sandstone reservoirs: a case study from the Triassic Chang 7 oilbearing formation in Heshui area, Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(4): 1031-1046. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202104020.htm [23] 鲁新川, 张顺存, 蔡冬梅, 等. 准噶尔盆地车拐地区三叠系成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(6): 1123-1129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201206014.htmLU Xinchuan, ZHANG Shuncun, CAI Dongmei, et al. Diagenesis and pore evolution of the Triassic reservoirs in Cheguai area, northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(6): 1123-1129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201206014.htm [24] 何涛, 王芳, 宋汉华. 苏里格气田南部盒8段储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2013, 35(2): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201302006.htmHE Tao, WANG Fang, SONG Hanhua. Diagenesis and pore evolution of reservoir of 8th member of Lower Shihezi Formation in the south of Sulige Gas-Field[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2013, 35(2): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JHSX201302006.htm [25] 钟大康, 祝海华, 孙海涛, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组砂岩成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(2): 61-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201302010.htmZHONG Dakang, ZHU Haihua, SUN Haitao, et al. Diagenesis and porosity evolution of sandstones in Longdong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(2): 61-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201302010.htm [26] 王芙蓉, 何生, 何治亮, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部永进地区砂岩储层中碳酸盐胶结物特征及其成因意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28(2): 169-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200902009.htmWANG Furong, HE Sheng, HE Zhiliang, et al. Characteristics and genetic mechanism of carbonate cement in sandstone reservoirs of Yongjin area in central Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolo-gica et Mineralogica, 2009, 28(2): 169-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200902009.htm [27] 孙全力, 孙晗森, 贾趵, 等. 川西须家河组致密砂岩储层绿泥石成因及其与优质储层关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(5): 751-757. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201205013.htmSUN Quanli, SUN Hansen, JIA Bao, et al. Genesis of chlorites and its relationship with high-quality reservoirs in the Xujiahe Formation tight sandstones, Western Sichuan Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(5): 751-757. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201205013.htm [28] 赵承锦, 蒋有录, 刘景东, 等. 基于正演与反演结合的孔隙度演化恢复方法: 以川东北地区须家河组为例[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(6): 708-723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202106002.htmZHAO Chengjin, JIANG Youlu, LIU Jingdong, et al. A recovery method of porosity evolution based on forward and inverse analyses: a case study of the tight sandstone of Xujiahe Formation, northeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(6): 708-723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202106002.htm [29] 王彤, 朱筱敏, 张自力, 等. 莱州湾凹陷北洼沙河街组三段砂岩储层孔隙定量演化模式[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(6): 671-690. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202006005.htmWANG Tong, ZHU Xiaomin, ZHANG Zili, et al. Quantitative pore evolution model of sandstone reservoirs for member 3 of Shahejie Formation in the northern subsag of Laizhouwan Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(6): 671-690. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202006005.htm [30] 赖锦, 王贵文, 柴毓, 等. 致密砂岩储层孔隙结构成因机理分析及定量评价—以鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区长8油层组为例[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(11): 2119-2130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201411009.htmLAI Jin, WANG Guiwen, CHAI Yu, et al. Mechanism analysis and quantitative assessment of pore structure for tight sandstone reservoirs: an example from Chang 8 oil layer in the Jiyuan area of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(11): 2119- 2130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201411009.htm [31] 潘高峰, 刘震, 赵舒, 等. 砂岩孔隙度演化定量模拟方法—以鄂尔多斯盆地镇泾地区延长组为例[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(2): 249-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201102010.htmPAN Gaofeng, LIU Zhen, ZHAO Shu, et al. Quantitative simulation of sandstone porosity evolution: a case from Yanchang Formation of the Zhenjing area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(2): 249-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201102010.htm [32] 刘贵满, 孟元林, 魏巍. 松辽盆地北部泉三、四段低渗透储层孔隙度演化史[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2012, 31(3): 266-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201203009.htmLIU Guiman, MENG Yuanlin, WEI Wei. Porosity evolving history of low permeability reservoirs in the third and the fourth members of the Quantou Formation in the northern Songliao Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2012, 31(3): 266-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201203009.htm [33] 张兴良, 田景春, 王峰, 等. 致密砂岩储层成岩作用特征与孔隙演化定量评价: 以鄂尔多斯盆地高桥地区二叠系下石盒子组盒8段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(2): 212-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201402008.htmZHANG Xingliang, TIAN Jingchun, WANG Feng, et al. Diagenetic characteristics and quantitative porosity estimation of tight sandstone reservoirs: a case from the 8th member of Permian Xiashihezi Formation in the Gaoqiao region, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(2): 212-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201402008.htm [34] 李杪, 罗静兰, 赵会涛, 等. 不同岩性的成岩演化对致密砂岩储层储集性能的影响—以鄂尔多斯盆地东部上古生界盒8段天然气储层为例[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 45(1): 97-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201501023.htmLI Miao, LUO Jinglan, ZHAO Huitao, et al. Impact of the diagenetic evolution of different lithology on tight sandstone reservoir performance: a case study from He 8 natural gas reservoir of the Upper Paleozoic in eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 45(1): 97-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201501023.htm [35] 曾庆鲁, 莫涛, 赵继龙, 等. 7000m以深优质砂岩储层的特征、成因机制及油气勘探意义—以库车坳陷下白垩统巴什基奇克组为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1): 38-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001009.htmZENG Qinglu, MO Tao, ZHAO Jilong, et al. Characteristics, genetic mechanism and oil & gas exploration significance of high-quality sandstone reservoirs deeper than 7000 m: a case study of the Bashijiqike Formation of Lower Cretaceous in the Kuqa Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1): 38-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001009.htm -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号