Diagenesis and pore evolution of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation reservoir in western section of southern margin of Junggar Basin
-
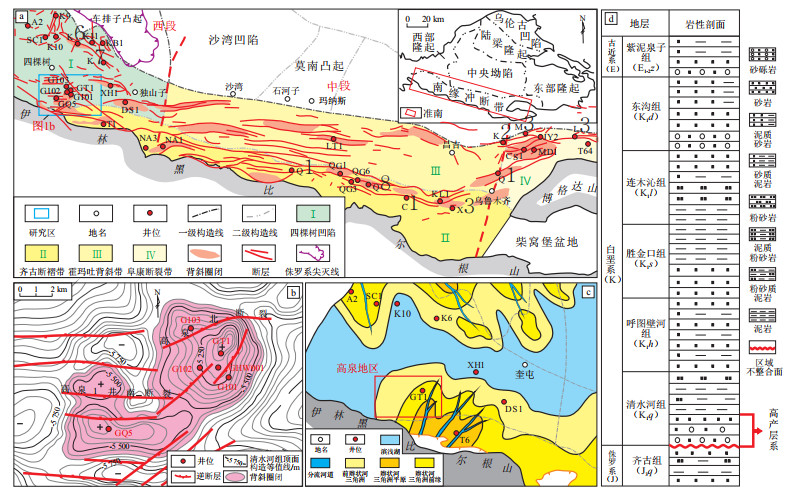
摘要: 准噶尔盆地南缘西段白垩系清水河组具有十分优越的油气勘探前景,系统研究其成岩作用特征及孔隙演化过程,明确有利储层发育区,可以为后期油气精细勘探评价提供指导。基于普通薄片、铸体薄片、全岩X衍射、粒度、扫描电镜、碳酸盐胶结物碳氧同位素与流体包裹体分析,综合研究准南西段清水河组成岩特征及其孔隙演化过程,并进一步探讨了不同成岩相间的储层孔隙演化过程差异。研究表明:(1)研究区清水河组储层以砂砾岩为主,岩屑含量高,平均占比65.97%,并以凝灰岩岩屑为主。胶结物主要为方解石。储层平均孔隙度为6.2%,平均渗透率为7.45×10-3 μm2,整体表现为低孔—低渗型的致密储层,但局部仍有优质储层发育;(2)储层埋藏方式以长期浅埋—晚期快速深埋为特征,并可进一步划分出长期浅埋、构造抬升至近地表、正常深埋和快速深埋4个演化阶段。其中在长期浅埋、构造抬升至近地表、正常深埋阶段储层成岩演化处于早成岩A期,而快速深埋阶段储层处于早成岩B期—中成岩A期;(3)清水河组储层可划分出4种典型成岩相,即强压实相、钙质/铁泥质强胶结相、凝灰质充填—弱溶蚀相和弱压实—孔隙发育相,并以成岩相为约束建立准噶尔盆地南缘清水河组碎屑岩储层孔隙演化模式。弱压实—孔隙发育相为优质储层成岩相类型,其次为凝灰质充填—弱溶蚀相。Abstract: The Qingshuihe Formation in the western section of the southern margin of the Junggar Basin has excellent oil and gas exploration prospects. The systematic study of its diagenesis characteristics and pore evolution process will provide guidance for the later fine exploration and evaluation of oil and gas. Therefore, based on the analysis of ordinary thin sections, cast thin sections, whole rock X-ray diffraction, grain size, scanning electron microscopy, carbon and oxygen isotopes of carbonate cements and fluid inclusions, the diagenesis characteristics and pore evolution process of the Qingshuihe Formation in the western section of the southern margin of the Junggar Basin were systematically studied, and the differences of reservoir pore evolution process between different diagenetic facies were further discussed. The study shows that: (1)The reservoir of the Qingshuihe Formation in the studied area is dominated by glutenite. The content of rock debris is high, with an average of 65.97%, mainly tuff rock debris. The cement is mainly calcite. The average porosity of the reservoir is 6.2%, and the average permeability is 7.45×10-3 μm2. It is generally a tight reservoir of low porosity and low permeability, but high-quality reservoirs are still developed locally; (2)The reservoir burial mode of the Qingshuihe Formation in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin is characterized by long-term shallow burial and late rapid deep burial, and can be further divided into four evolutionary stages: long-term shallow burial, tectonic uplift to near surface, normal deep burial, and rapid deep burial. The diagenetic evolution of the reservoir was in early diagenetic stage A in the long-term shallow burial, tectonic uplift to near surface, and normal deep burial stages, while in the rapid deep burial stage, the reservoir was in early diagenetic stage B to middle diagenetic stage A; (3)The reservoir of the Qingshuihe Formation can be divided into four typical diagenetic facies types, namely, strong compaction facies, calcareous/iron argillaceous strong cementation facies, tuffaceous filling weak dissolution facies, and weak compaction pore development facies. The pore evolution model of the clastic rock reservoir of the Qingshuihe Formation in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin was established based on the constraints of diagenetic facies. The weak compaction pore development facies are high-quality reservoir diagenetic facies, followed by tuffaceous filling weak dissolution facies.
-
图 4 准噶尔盆地南缘西段高泉地区清水河组砂砾岩储层成岩作用
a.GHW001井,5 826.96 m,颗粒间以线接触为主;b.GQ5井,6 051.96 m,塑性云母压实变形;c.GHW001井,5 831.6 m,多个颗粒边缘发育石英次生加大边;d.GQ5井,6 051m,与粒间杂基混杂的自生微晶石英;e.GHW001井,5 833.96 m,与粒间火山灰混杂的孤立“斑状”方解石;f.GHW001井,5 825 m,粗晶方解石,形态呈脉状;g.GHW001井,5 825 m,铁方解石交代方解石;h.GHW001井,5 829.77 m,早期“斑状”黄铁矿(反射光);i.GQ5井,6 081.96 m,晚期“草莓状”黄铁矿;j.G101井,6 020.83 m,赤铁矿化杂基(反射光);k.GQ5井,6 051.96 m,叶片状绿泥石(Ch);l.GHW001井,5 833.84 m,与杂基伴生的高岭石(K);m.GHW001井,5 824.19 m,“蜂窝状”伊/蒙混层(I/S);n.GQ5井,6 051.34 m,环颗粒边缘绿泥石与微晶石英;o.GHW001井,5 829.04 m,凝灰岩岩屑斑晶溶蚀;p.GHW001井,5 829.04 m,颗粒间凝灰质杂基呈“片条状”溶蚀。
Figure 4. Diagenesis of the glutenite reservoir of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in Gaoquan area in the western section of the southern margin of the Junggar Basin
图 6 准噶尔盆地南缘西段高泉地区GHW001井清水河组砂砾岩不同期次方解石胶结物特征
a.5 832.84 m,Ⅰ期方解石胶结物产状及能谱元素含量;b.5 833.96 m,Ⅱ期方解石胶结物产状及其能谱元素含量;五角星为能谱打点位置。
Figure 6. Characteristics of calcite cements of different stages in glutenite in Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in well GHW001 in Gaoquan area in the western section of the southern margin of the Junggar Basin
图 7 准噶尔盆地南缘西段高泉地区清水河组碳酸盐胶结物的成因图版
据文献[23]修改。A.有机质热成熟脱羧成因;B.大气淡水淋滤成因;C. 无机碳酸盐岩重溶成因;D.岩浆作用成因;E.浅埋细菌生物气成因。
Figure 7. Genetic mechanism of carbonate cements of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in Gaoquan area in the western section of the southern margin of the Junggar Basin
图 8 准噶尔盆地南缘西段高泉地区GHW001井清水河组流体包裹体特征与均一温度
a.5 820.29 m,石英次生微裂缝中的天然气包裹体及伴生的盐水包裹体; b.5 825.36 m,石英次生微裂缝中的盐水包裹体; c.5 828.19 m,石英加大边微裂隙中的盐水包裹体; d.5 828.19 m,石英加大边中的盐水包裹体; e.石英次生微裂缝中的盐水包裹体均一温度; f.石英加大边中的盐水包裹体均一温度;NGI.天然气包裹体,AI.盐水包裹体。
Figure 8. Fluid inclusion characteristics and homogenization temperature of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation of well GHW001 in Gaoquan area in the western section of the southern margin of the Junggar Basin
图 11 准噶尔盆地南缘西段高泉地区清水河组不同成岩相特征
a.G103井,5 905.9 m,粒间孔隙不发育,颗粒间存在凹凸接触;b.G103井,5 905.9 m,粒间孔隙不发育,仅残留少量粒缘缝;c.G103井,5 905.9 m,粒间凝灰质杂基发生水云母化;d.G101井,6 018.6 m,清水河组,方解石强胶结;e.G101井,6 020.83 m,方解石与赤铁矿化杂基(简称铁泥质)充填粒间孔隙;f.G101井,6 018.6 m,方解石与赤铁矿化杂基(简称铁泥质)充填粒间孔隙;g.GHW001井,5 829.32 m,凝灰质杂基充填孔隙,局部可见溶蚀现象;h.GHW001井,5 830.65 m,粒间凝灰质杂基呈“蜂窝状”溶蚀;i.GHW001井,5 833.96 m,方解石充填凝灰质杂基溶孔;j.GHW001井,5 825.36 m,原生粒间孔隙发育,颗粒以点—线接触为主;k.GHW001井,5 825.64 m,颗粒以点—线接触为主;l.粒间孔隙发育,孔隙内部较为干净。
Figure 11. Characteristics of different diagenetic facies of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in Gaoquan area in the western section of the southern margin of the Junggar Basin
图 13 准噶尔盆地南缘西段高泉地区清水河组不同成岩相孔隙演化模式
a.G103井,5 905.9 m,强压实相;b.G101井,6 018.6 m,钙质、铁泥质强胶结相;c.GHW001井,5 829.32 m,凝灰质充填—弱溶蚀相;d.GHW001井,5 825.36 m,弱压实—孔隙发育相。
Figure 13. Pore evolution model of different diagenetic facies of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in Gaoquan area in the western section of the southern margin of the Junggar Basin
表 1 准噶尔盆地南缘西段高泉地区清水河组不同相带物性特征
Table 1. Physical properties of different facies of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation in Gaoquan area in the western section of the southern margin of the Junggar Basin
岩性 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 沉积微相 样品数 砂砾岩(砾岩) 1.2~26.1(8.2) 0.019~67.7(8.7) 分流河道 21 砂岩 0.6~15.5(5.5) 0.05~12.6(2.4) 河口坝 9 粉砂岩 0.6~10.5(4.3) 0.01~8.1(0.8) 席状砂/远砂坝 5 注:表中数值意义为:最小值~最大值(平均值)。 -
[1] 张丽媛. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系储层孔隙演化及主控因素研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2013.ZHANG Liyuan. Study on pore evolution and main controlling factors of Jurassic reservoir in southern margin of Junggar Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2013. [2] 刘伟. 准噶尔盆地南缘下组合异常高压形成机制及其演化特征[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2019.LIU Wei. Formation mechanism and evolution characteristics of the lower anomalous high pressure in southern margin of the Junggar Basin[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Shiyou University, 2019. [3] 刘国平. 准噶尔盆地南缘前陆冲断带深部裂缝储层发育模式[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2020.LIU Guoping. Development pattern of deep fractured reservoirs in the foreland thrust belt on the southern margin of Junggar Basin, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2020. [4] 孟颖, 靳军, 高崇龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘西段白垩系深层储层特征及物性保存机制[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(2): 218-232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202202004.htmMENG Ying, JIN Jun, GAO Chonglong, et al. Characteristics and physical property preservation mechanism of Cretaceous deep reservoir in western segment of southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(2): 218-232. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202202004.htm [5] 孙靖, 郭旭光, 尤新才, 等. 准噶尔盆地深层—超深层致密碎屑岩储层特征及有效储层成因[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(7): 2532-2546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.07.019SUN Jing, GUO Xuguang, YOU Xincai, et al. Characteristics and effective reservoir genesis of deep to ultra-deep tight clastic reservoir of Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(7): 2532-2546. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.07.019 [6] 鲁雪松, 张凤奇, 赵孟军, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘高探1井超压成因与盖层封闭能力[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6): 666-675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106004.htmLU Xuesong, ZHANG Fengqi, ZHAO Mengjun, et al. Genesis of overpressure and sealing ability of caprocks in well Gaotan 1 in the southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(6): 666-675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106004.htm [7] 张凤奇, 刘伟, 鲁雪松, 等. 喜马拉雅晚期构造应力场及其与油气分布的关系: 以准噶尔盆地南缘为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(4): 433-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104002.htmZHANG Fengqi, LIU Wei, LU Xuesong, et al. Late Himalayan tectonic stress field and its relationship with hydrocarbon distribution: a case study of southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(4): 433-439. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104002.htm [8] 于景维, 罗刚, 李斌, 等. 沙湾凹陷上乌尔禾组储层成岩作用及成岩相分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(4): 1095-1104. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.206YU Jingwei, LUO Gang, LI Bin, et al. Diagenesis and diagenetic facies of Upper Wuerhe Formation in the Shawan Sag[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(4): 1095-1104. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2022.206 [9] 徐子煜, 王安, 韩长城, 等. 玛湖地区三叠系克拉玛依组优质砂砾岩储层形成机制[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(3): 82-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202003008.htmXU Ziyu, WANG An, HAN Changcheng, et al. Formation mechanism of high-quality sandy-conglomerate reservoir of Triassic Karamay Formation in Mahu area[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(3): 82-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202003008.htm [10] 杨佳颖, 蒋有录, 蔡国钢, 等. 深层砂岩储层特征及成岩差异演化过程: 以辽河坳陷东部凹陷牛居—长滩洼陷沙三上亚段为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(2): 233-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202202005.htmYANG Jiaying, JIANG Youlu, CAI Guogang, et al. Reservoir characteristics and differential diagenetic evolution process of deep buried sandstone reservoirs: case study of the upper Es3 in Niuju-Changtan Subsag of Eastern Sag, Liaohe Depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(2): 233-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202202005.htm [11] 郝绵柱, 姜振学, 聂舟, 等. 深层页岩储层孔隙连通性发育特征及其控制因素: 以川南地区龙马溪组为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2022, 29(6): 761-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202206007.htmHAO Mianzhu, JIANG Zhenxue, NIE Zhou, et al. Development characteristics of pore connectivity in deep shale reservoirs and its controlling factors: a case study of Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2022, 29(6): 761-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202206007.htm [12] 郑荣才, 耿威, 周刚, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地白豹地区长6砂岩成岩作用与成岩相研究[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(2): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX200702000.htmZHENG Rongcai, GENG Wei, ZHOU Gang, et al. Diagenesis and diagenetic facies of Chang 6 sandstone of Yanchang Formation in Baibao area, Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 19(2): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX200702000.htm [13] 胡凡君. 库车坳陷克深地区超深层有效储层形成机理和分布规律[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2019.HU Fanjun. Formation mechanism and distribution regularities of ultra-deep buried sandstone effective reservoirs in Keshen area, Kuqa Depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2019. [14] 曾庆鲁, 莫涛, 赵继龙, 等. 7000m以深优质砂岩储层的特征、成因机制及油气勘探意义: 以库车坳陷下白垩统巴什基奇克组为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1): 38-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001009.htmZENG Qinglu, MO Tao, ZHAO Jilong, et al. Characteristics, genetic mechanism and oil & gas exploration significance of high-quality sandstone reservoirs deeper than 7 000 m: a case study of the Bashijiqike Formation of Lower Cretaceous in the Kuqa Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1): 38-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202001009.htm [15] 杨海军, 张荣虎, 杨宪彰, 等. 超深层致密砂岩构造裂缝特征及其对储层的改造作用: 以塔里木盆地库车坳陷克深气田白垩系为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(7): 942-950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201807003.htmYANG Haijun, ZHANG Ronghu, YANG Xianzhang, et al. Characteristics and reservoir improvement effect of structural fracture in ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoir: a case study of Keshen gasfield, Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(7): 942-950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201807003.htm [16] 杜飞, 姚宗全, 刘勇, 等. 疏松砂岩储层成岩相划分与定量表征: 以准噶尔盆地东部三台油田北10井区为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(4): 481-486, 503. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104010.htmDU Fei, YAO Zongquan, LIU Yong, et al. Division and quantitative characterization of diagenetic facies of unconsolidated sandstone reservoir: a case study of Bei 10 well area, Santai Oilfield, eastern Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2021, 28(4): 481-486, 503. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202104010.htm [17] 陈建平, 王绪龙, 倪云燕, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘天然气成藏及勘探方向[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(5): 1002-1019. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201905002.htmCHEN Jianping, WANG Xulong, NI Yunyan, et al. The accumulation of natural gas and potential exploration regions in the southern margin of the Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(5): 1002-1019. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201905002.htm [18] 杜金虎, 支东明, 李建忠, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘高探1井重大发现及下组合勘探前景展望[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(2): 205-215. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201902003.htmDU Jinhu, ZHI Dongming, LI Jianzhong, et al. Major breakthrough of well Gaotan 1 and exploration prospects of lower assemblage in southern margin of Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(2): 205-215. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201902003.htm [19] 林潼, 李文厚, 孙平, 等. 新疆准噶尔盆地南缘深层有利储层发育的影响因素[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(9): 1461-1470. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201309016.htmLIN Tong, LI Wenhou, SUN Ping, et al. Factors influencing deep favorable reservoirs on the southern margin of Junggar Basin, Xinjiang province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(9): 1461-1470. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201309016.htm [20] 靳军, 刘明, 刘雨晨, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘下组合现今温压场特征及其控制因素[J]. 地质科学, 2021, 56(1): 28-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202101003.htmJIN Jun, LIU Ming, LIU Yuchen, et al. Present-day temperature-pressure field and its controlling factors of the lower composite reservoir in the southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2021, 56(1): 28-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX202101003.htm [21] 吕焕泽, 邹妞妞, 蔡宁宁, 等. 玛湖凹陷北斜坡百口泉组碳酸盐胶结物形成机理及其地质意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(5): 554-562. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202205007.htmLV Huanze, ZOU Niuniu, CAI Ningning, et al. Formation mechanism and geological significance of carbonate cements in Baikouquan formation on northern slope of Mahu sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(5): 554-562. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202205007.htm [22] TERANES J L, MCKENZIE J A, LOTTER A F, et al. Stable isotope response to lake eutrophication: calibration of a high-resolution lacustrine sequence from Baldeggersee, Switzerland[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1999, 44(2): 320-333. [23] IRWIN H, CURTIS C D, COLEMAN M. Isotopic evidence for source of diagenetic carbonates formed during burial of organic-rich sediments[J]. Nature, 1977, 269(5625): 209-213. [24] 刘可禹, BOURDET J, 张宝收, 等. 应用流体包裹体研究油气成藏: 以塔中奥陶系储集层为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 40(2): 171-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201302004.htmLIU Keyu, BOURDET J, ZHANG Baoshou, et al. Hydrocarbon charge history of the Tazhong Ordovician reservoirs, Tarim Basin as revealed from an integrated fluid inclusion study[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 40(2): 171-180. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201302004.htm [25] 刘华, 蒋有录, 卢浩, 等. 渤南洼陷流体包裹体特征与成藏期流体压力恢复[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(8): 1384-1394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201608010.htmLIU Hua, JIANG Youlu, LU Hao, et al. Restoration of fluid pressure during hydrocarbon accumulation period and fluid inclusion feature in the Bonan Sag[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(8): 1384- 1394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201608010.htm [26] 胡宗全, 朱筱敏. 准噶尔盆地西北缘侏罗系储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 26(3): 16-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200203004.htmHU Zongquan, ZHU Xiaomin. Diageneses and pore evolution of Jurassic reservoir in northwestern edge of Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 2002, 26(3): 16-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX200203004.htm [27] 王艳忠, 操应长, 葸克来, 等. 碎屑岩储层地质历史时期孔隙度演化恢复方法: 以济阳坳陷东营凹陷沙河街组四段上亚段为例[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(6): 1100-1111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201306008.htmWANG Yanzhong, CAO Yingchang, XI Kelai, et al. A recovery method for porosity evolution of clastic reservoirs with geological time: a case study from the upper submember of Es4 in the Dongying Depression, Jiyang Subbasin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(6): 1100-1111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201306008.htm [28] BEARD D C, WEYL P K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1973, 57(2): 349-369. -





 下载:
下载:












 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号