Quantitative characterization and main controlling factors of shale oil occurrence in Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin
-
摘要: 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油赋存特征及控制因素复杂,赋存状态与定量表征难度大,厘清页岩油赋存特征和主控因素对优选甜点体具有重要意义。为表征玛湖凹陷不同赋存状态页岩油含量,对凹陷中心区和斜坡区的风城组页岩样品进行分步抽提,建立了不同赋存状态页岩油定量表征实验方法,分别得到游离轻烃、游离重烃和吸附烃的含量。在有机地球化学和储层微观特征研究的基础上,得到以下认识:由于研究区有机碳和黏土含量较低,风城组页岩油以游离赋存状态为主,吸附烃含量最少;页岩油多以油膜状赋存于矿物表面和干酪根中,重烃通常赋存于微孔比表面积大的页岩中,宏孔是游离油的主要赋存场所;有机质丰度和孔径增大,不同赋存状态页岩油含量均呈增加趋势,较高有机质丰度和孔径较大的储层有利于页岩油富集;成熟度可以很大程度上影响页岩中流体的吸附能力,有机质成熟度越高的页岩样品游离烃占比越多、吸附烃占比越少;比表面积的增大促进吸附油与游离重烃的富集,制约游离轻烃的富集,中孔比表面积对于页岩油的吸附量具有控制作用,比表面积越大页岩的吸附能力越强。相关研究和认识可为研究区优选甜点段和评价页岩油开采效益提供依据。Abstract: The characteristics and controlling factors of shale oil occurrence in Permian Fengcheng Formation of the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin are complex, making occurrence state identification and quantitative characterization difficult. It is of great significance to clarify the occurrence characteristics and controlling factors of shale oil for selecting sweet spots. In order to characterize the content of shale oil in different occurrence states, some shale samples in the central and slope areas of the sag were extracted step by step, and a quantitative characte-rization experiment method of shale oil in different occurrence states was established, obtaining the contents of free light hydrocarbon, free heavy hydrocarbon and adsorbed hydrocarbon, respectively. Based on the study of organic geochemistry and reservoir micro-characteristics, the following conclusions are obtained. Due to the low TOC and clay contents in the study area, the shale oil in the Fengcheng Formation mainly occurs in dissociative state and has the least adsorbed hydrocarbon content. Shale oil occurs mostly on mineral surface and in kerogen in oil film state, heavy hydrocarbons usually occur in shale with large micropore specific surface area, and macropores are the main occurrence space of free oil. With the increase of organic matter abundance and pore size, the shale oil content in different occurrence states shows an increasing trend, indicating that the higher organic matter abundance and larger pore size are conducive to shale oil enrichment. Maturity can greatly affect the adsorption capacity of fluid in shale, and the higher the maturity of organic matter, the higher the proportion of free hydrocarbons and the lower the proportion of adsorbed hydrocarbons. The increase of specific surface area promotes the enrichment of adsorbed oil and free heavy hydrocarbons, and restricts the enrichment of free light hydrocarbons, indicating that the specific surface area of mesoporous pores has a controlling effect on the adsorption capacity of shale oil, i.e., the larger the specific surface area, the stronger the adsorption capacity of shale oil. The relevant research and recognition can provide a basis for selecting sweet spots and evaluating the benefits of shale oil exploitation in the study area.
-
Key words:
- occurrence characteristics /
- main controlling factor /
- shale oil /
- Fengcheng Formation /
- Permian /
- Mahu Sag /
- Junggar Basin
-
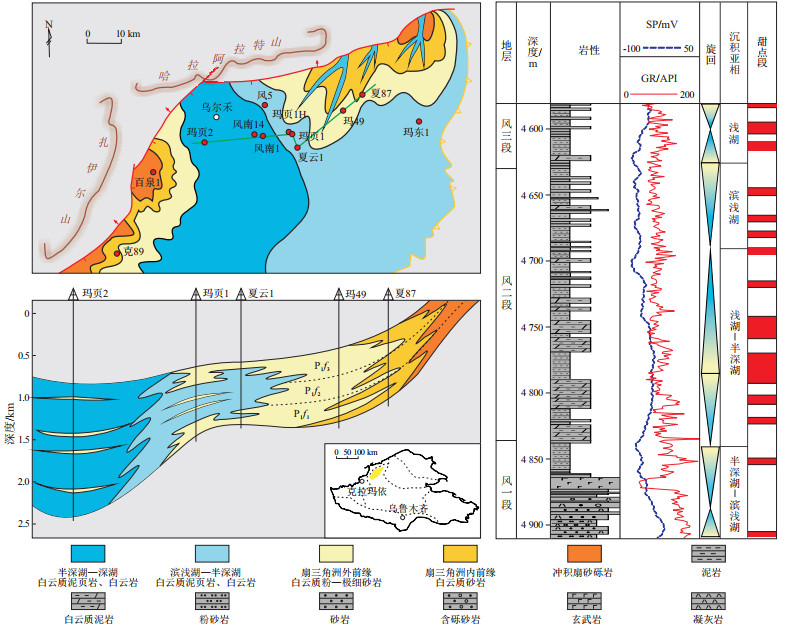
图 1 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组岩相和地层柱状图
据文献[31]修改。
Figure 1. Lithofacies and stratigraphic column of Permian Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin
图 10 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油赋存特征
a.白云质泥岩,灰黑色油斑,晶间孔,玛页1井,4 754.86 m;b.白云质泥岩,灰黑色油斑,粒间孔,玛页1井,4 754.86 m;c.泥岩,黑灰色油斑,溶蚀孔,玛页1井,4 594.65 m;d.泥岩,黑灰色油斑,有机质孔,玛页1井,4 594.65 m;e-f.泥岩,灰色荧光灰质,溶蚀孔,玛页1H井,4 542.85 m。
Figure 10. Occurrence characteristics of shale oil in Permian Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin
表 1 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组样品基本信息
Table 1. Basic information of samples from Permian Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin
样品编号 井号 地层 深度/m 岩性 w(TOC)/% Ro/% 1 玛页2 风三段 3 856.8 云质页岩 2.18 0.73 2 玛页2 风二段 4 431.5 云质页岩 0.97 0.79 3 夏云1 风三段 5 106.8 云质页岩 1.50 1.02 4 玛页1 风二段 4 745.0 含云粉砂岩 0.62 1.16 5 玛页1 风二段 4 442.5 云质页岩 0.93 1.12 6 夏云1 风三段 5 109.4 粉砂质泥岩 1.42 0.95 7 玛页1 风二段 4 545.9 泥质白云岩 0.78 0.84 8 玛页1 风二段 4 637.2 云质页岩 1.72 0.69 表 2 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组游离油与吸附油定量分析实验结果
Table 2. Quantitative analysis results of free oil and adsorbed oil in Permian Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin
序号 ω(TOC)/ % S1/(mg/g) 步骤一:萃取 步骤二:第一次抽提 步骤三:第二次抽提 萃取前质量/g 萃取后质量/g 游离轻烃质量/g 游离轻烃含量/(mg/g) 抽提前质量/g 抽提后质量/g 游离重烃质量/g 游离重烃含量/(mg/g) 抽提前质量/g 抽提后质量/g 吸附烃质量/g 吸附烃含量/(mg/g) 1 2.18 1.37 105.113 103.427 1.579 15.02 103.427 103.085 0.343 3.31 103.085 103.069 0.015 0.15 2 0.97 1.61 45.148 44.873 0.242 5.36 44.873 44.826 0.047 1.05 44.826 44.824 0.002 0.03 3 1.50 1.68 214.362 213.584 0.761 3.55 213.584 213.306 0.279 1.30 213.306 213.287 0.019 0.09 4 0.62 0.61 189.367 188.533 0.716 3.78 188.533 188.235 0.298 1.58 188.235 188.230 0.005 0.02 5 0.93 0.98 139.753 138.666 1.087 7.78 138.666 138.451 0.215 1.55 138.451 138.441 0.010 0.07 6 1.42 1.36 156.782 155.905 0.877 5.59 155.905 155.588 0.317 2.03 155.588 155.576 0.011 0.07 7 0.78 0.82 166.732 166.002 0.399 2.39 166.002 166.137 0.196 1.18 166.137 166.131 0.004 0.02 8 1.72 1.56 49.762 49.073 0.649 13.04 49.073 48.890 0.164 3.34 48.890 48.875 0.012 0.25 -
[1] XU Yi, LUN Zengmin, PAN Zhejun, et al. Occurrence space and state of shale oil: a review[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 211: 110183. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110183 [2] 柳波, 刘俊杰, 付晓飞, 等. 松辽盆地陆相页岩油地质研究方法与勘探评价进展[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(3): 239-248. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2021.03.005LIU Bo, LIU Junjie, FU Xiaofei, et al. Progress in geological research methods and exploration evaluation of continental shale oil in Songliao Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(3): 239-248. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2021.03.005 [3] 杨智, 唐振兴, 李国会, 等. 陆相页岩层系石油富集区带优选、甜点区段评价与关键技术应用[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(8): 2257-2272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.08.001YANG Zhi, TANG Zhenxing, LI Guohui, et al. Optimization of enrichment plays, evaluation of sweet area & section and application of key technologies for the continental shale strata oil in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(8): 2257-2272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.08.001 [4] LI Jiarui, YANG Zhi, WU Songtao, et al. Key issues and deve-lopment direction of petroleum geology research on source rock strata in China[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research, 2021, 5(2): 121-126. doi: 10.46690/ager.2021.02.02 [5] 王伟, 王振林, 刘财广, 等. 页岩油甜点评价关键技术及甜点类型划分: 以玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组为例[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(1): 223-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202301015.htmWANG Wei, WANG Zhenlin, LIU Caiguang, et al. Key technology of shale oil sweet spot evaluation and sweet spot type division in Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(1): 223-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202301015.htm [6] 刘财广, 季瑞雪, 王伟, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油产量影响因素及甜点评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 733-742. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202206011.htmLIU Caiguang, JI Ruixue, WANG Wei, et al. Factors influencing shale oil production and sweet spot evaluation of Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(6): 733-742. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202206011.htm [7] 唐勇, 雷德文, 曹剑, 等. 准噶尔盆地二叠系全油气系统与源内天然气勘探新领域[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 654-662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202206003.htmTANG Yong, LEI Dewen, CAO Jian, et al. Total petroleum system and inner-source natural gas exploration in permian strata of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(6): 654-662. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202206003.htm [8] 龚德瑜, 刘海磊, 杨海波, 等. 准噶尔盆地风城组烃源岩生气潜力与天然气勘探领域[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 674-683. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202206005.htmGONG Deyu, LIU Hailei, YANG Haibo, et al. Gas generation potential of Fengcheng Formation source rocks and exploration fields in Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(6): 674-683. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202206005.htm [9] 金之钧, 梁新平, 王小军, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油富集机制与甜点段优选[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 631-639. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202206001.htmJIN Zhijun, LIANG Xinping, WANG Xiaojun, et al. Shale oil enrichment mechanism and sweet spot selection of Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(6): 631-639. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202206001.htm [10] 马睿, 王民, 李进步, 等. 热释法在页岩吸附油定量评价中的实验探讨[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2019, 33(6): 9-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201906004.htmMA Rui, WANG Min, LI Jinbu, et al. Experimental discussion of heating release method in quantitative evaluation of adsorbed shale oil[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2019, 33(6): 9-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN201906004.htm [11] 赵悦, 蔡进功, 雷天柱, 等. 泥质烃源岩中不同赋存状态有机质定量表征: 以东营凹陷沙河街组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(4): 416-423. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201804006.htmZHAO Yue, CAI Jingong, LEI Tianzhu, et al. Quantitative characte-rization of organic matters with different occurrences in argillaceous source rocks: a case of Shahejie Formation, Dongying Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(4): 416-423. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201804006.htm [12] 蒋启贵, 黎茂稳, 钱门辉, 等. 不同赋存状态页岩油定量表征技术与应用研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(6): 842-849. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201606842JIANG Qigui, LI Maowen, QIAN Menghui, et al. Quantitative characterization of shale oil in different occurrence states and its application[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(6): 842-849. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201606842 [13] SANEI H, WOOD J M, ARDAKANI O H, et al. Characterization of organic matter fractions in an unconventional tight gas siltstone reservoir[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2015, 150-151: 296-305. [14] 蔡进功, 包于进, 杨守业, 等. 泥质沉积物和泥岩中有机质的赋存形式与富集机制[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2007, 37(2): 234-243. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200702010.htmCAI Jingong, BAO Yujin, YANG Shouye, et al. The occurrence and enrichment mechanism of organic matter in argillaceous sediments and mudstones[J]. Science in China (Series D: Earth Sciences), 2007, 37(2): 234-243. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200702010.htm [15] 潘银华, 黎茂稳, 孙永革, 等. 低熟湖相泥质烃源岩中不同赋存状态可溶有机质的地球化学特征[J]. 地球化学, 2018, 47(4): 335-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201804002.htmPAN Yinhua, LI Maowen, SUN Yongge, et al. Geochemical characterization of soluble organic matter with different existing states in low-maturity argillaceous source rocks of lacustrine facies[J]. Geochimica, 2018, 47(4): 335-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201804002.htm [16] 关平, 徐永昌, 刘文汇. 烃源岩有机质的不同赋存状态及定量估算[J]. 科学通报, 1998, 43(14): 1556-1559. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199814025.htmGUAN Ping, XU Yongchang, LIU Wenhui. Different occurrence states and quantitative estimation of organic matter in source rocks[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43(14): 1556-1559. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199814025.htm [17] 钱门辉, 蒋启贵, 黎茂稳, 等. 湖相页岩不同赋存状态的可溶有机质定量表征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2): 278-286. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702278QIAN Menghui, JIANG Qigui, LI Maowen, et al. Quantitative characterization of extractable organic matter in lacustrine shale with different occurrences[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(2): 278-286. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201702278 [18] 李俊乾, 卢双舫, 张婕, 等. 页岩油吸附与游离定量评价模型及微观赋存机制[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(3): 583-592. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201903014.htmLI Junqian, LU Shuangfang, ZHANG Jie, et al. Quantitative evaluation models of adsorbed and free shale oil and its microscopic occurrence mechanism[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3): 583-592. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201903014.htm [19] 宋国奇, 徐兴友, 李政, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系陆相页岩油产量的影响因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(3): 463-471. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201503017.htmSONG Guoqi, XU Xingyou, LI Zheng, et al. Factors controlling oil production from Paleogene shale in Jiyang Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(3): 463-471. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201503017.htm [20] 宋永, 杨智峰, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组碱湖型页岩油勘探进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2022, 27(1): 60-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202201006.htmSONG Yong, YANG Zhifeng, HE Wenjun, et al. Exploration progress of alkaline lake type shale oil of the Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2022, 27(1): 60-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202201006.htm [21] 何登发, 张磊, 吴松涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化阶段及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 845-861. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805002.htmHE Dengfa, ZHANG Lei, WU Songtao, et al. Tectonic evolution stages and features of the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 845-861. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805002.htm [22] CAO Jian, YAO Suping, JIN Zhijun, et al. Petroleum migration and mixing in the northwestern Junggar Basin (NW China): constraints from oil-bearing fluid inclusion analyses[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37(7): 827-846. [23] JIN Zhijun, CAO Jian, HU Wenxuan, et al. Episodic petroleum fluid migration in fault zones of the northwestern Junggar Basin (northwest China): evidence from hydrocarbon-bearing zoned calcite cement[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2008, 92(9): 1225-1243. [24] YU Shuang, WANG Xulong, XIANG Baoli, et al. Molecular and carbon isotopic geochemistry of crude oils and extracts from Permian source rocks in the northwestern and central Junggar Basin, China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2017, 113: 27-42. [25] 陈新, 卢华复, 舒良树, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化分析新进展[J]. 高校地质学报, 2002, 8(3): 257-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200203002.htmCHEN Xin, LU Huafu, SHU Liangshu, et al. Study on tectonic evolution of Junggar Basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2002, 8(3): 257-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200203002.htm [26] 张元元, 李威, 唐文斌. 玛湖凹陷风城组碱湖烃源岩发育的构造背景和形成环境[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(1): 48-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201801012.htmZHANG Yuanyuan, LI Wei, TANG Wenbin. Tectonic setting and environment of alkaline lacustrine source rocks in the lower Permian Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(1): 48-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201801012.htm [27] 张元元, 曾宇轲, 唐文斌. 准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠纪原型盆地分析[J]. 石油科学通报, 2021, 6(3): 333-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE202103001.htmZHANG Yuanyuan, ZENG Yuke, TANG Wenbin. Permian attributes and tectonic evolution of the west Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2021, 6(3): 333-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE202103001.htm [28] 雷德文, 陈刚强, 刘海磊, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷大油(气)区形成条件与勘探方向研究[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(7): 1604-1619. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201707013.htmLEI Dewen, CHEN Gangqiang, LIU Hailei, et al. Study on the forming conditions and exploration fields of the Mahu giant oil (gas) province, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(7): 1604-1619. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201707013.htm [29] 曹剑, 雷德文, 李玉文, 等. 古老碱湖优质烃源岩: 准噶尔盆地下二叠统风城组[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(7): 781-790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201507002.htmCAO Jian, LEI Dewen, LI Yuwen, et al. Ancient high-quality alkaline lacustrine source rocks discovered in the Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(7): 781-790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201507002.htm [30] TANG Wenbin, ZHANG Yuanyuan, PE-PIPER G, et al. Soft-sediment deformation structures in alkaline lake deposits of Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Junggar Basin, NW China: implications for syn-sedimentary tectonic activity[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2020, 406: 105719. [31] 何文军, 钱永新, 赵毅, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组全油气系统勘探启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6): 641-655. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106002.htmHE Wenjun, QIAN Yongxin, ZHAO Yi, et al. Exploration implications of total petroleum system in Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(6): 641-655. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106002.htm [32] 李进步. 页岩油赋存机理及可动性研究: 以济阳坳陷沙河街组为例[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2020.LI Jinbu. Study on occurrence mechanism and mobility of shale oil: a case study of Shahejie Formation in Jiyang Depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2020. [33] 张安达, 王继平, 王永超, 等. 松辽盆地古龙页岩储集空间类型及油赋存状态[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2021, 40(5): 68-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202105006.htmZHANG Anda, WANG Jiping, WANG Yongchao, et al. Reservoir space types and oil occurrence of Gulong shale in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2021, 40(5): 68-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202105006.htm [34] TISSOT B P, WELTE D H. Petroleum formation and occurrence[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1984: 643. -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号