Fine-grained sedimentary characteristics and evolution model of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area, Junggar Basin
-
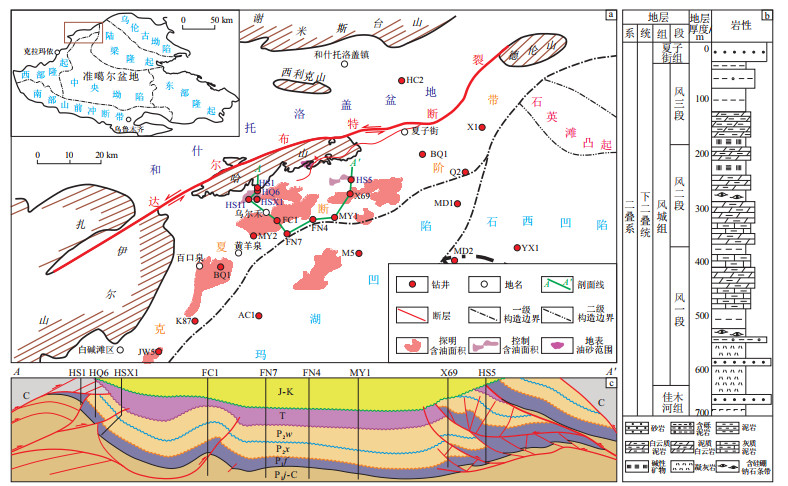
摘要: 准噶尔盆地西北缘哈山地区地质条件复杂,勘探难度大,明确该地区二叠系风城组烃源岩沉积与演化特征对拓展盆缘油气勘探具有重要意义。基于全岩XRD、元素地球化学、有机质丰度、薄片鉴定和岩相组合特征,开展了玛湖凹陷和哈山地区风城组沉积特征与岩性、岩相组合差异分析,恢复了该区古沉积环境演化序列,建立了古沉积演化模式。哈山地区风城组岩相组合特征及古沉积环境演化序列与玛湖凹陷高度相似,整体为火山背景下的碱湖多源混合细粒沉积建造,发育多种岩相组合,沉积古环境具有阶段性演化特征。哈山地区风二段典型碱性矿物的大量出现,揭示该地区发育除玛湖凹陷外的另一湖盆中心。风一段沉积时湖平面相对较高,水体盐度较低,气候半干旱,火山沉积发育,岩相以含有机质块状凝灰岩为主;风二下段沉积时湖盆开始萎缩,气候相对更干旱,水体开始变咸,环境更局限,岩相以富有机质层状云质泥岩为主;风二段顶部和风三段下部沉积时环境相对最封闭,水体盐度大,发育大量碱性矿物,岩相以富有机质纹层状含碱云质泥岩和富有机质纹层状混合质页岩为主;风三段上部沉积时陆源碎屑输入增多,咸化减弱,发育扇三角洲沉积体系,岩相以含有机质块状粉细砂岩为主。风城组沉积环境控制了有机质的富集程度,总体上,碎屑输入少、温暖湿润、盐度相对较小的深水环境更有利于有机质富集。Abstract: The geological conditions of Hashan area on the northwestern margin of the Junggar Basin are complicated and it is difficult to explore. It is of great significance to clarify the sedimentary and evolutionary characte-ristics of source rocks in the Permian Fengcheng Formation in this area for expanding oil and gas exploration on the basin margin. Based on the analysis of whole-rock XRD, elemental geochemistry, organic matter abundance, thin section identification, and lithofacies association characteristics, this paper conducted a comparative analysis of the sedimentary characteristics, lithology, and lithofacies association characteristics of the Fengcheng Formation in the Mahu Sag and Hashan area, restored the ancient sedimentary environment evolution sequence in the study area, and established a model of ancient sedimentary evolution. The research results show that the lithofacies association characteristics and ancient sedimentary environment evolution sequence of the Fengcheng Formation in the Hashan area are highly similar to those in the Mahu Sag, which are generally fine-grained sediments mixed from multiple sources in an alkaline lake with a volcanic background, and various lithofacies associations are developed. The sedimentary paleoenvironment has phased evolution characteristics. The large number of typical alkaline minerals in the second member of Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area reveals the development of another lake basin center in addition to the Mahu Sag. During the deposition of the first member of Fengcheng Formation (P1f1), the lake level was relatively higher, the water salinity was low, the climate was semi-arid, and volcanic sedimentation was developed, with lithofacies mainly composed of organic-rich blocky tuffaceous limestone. In the lower part of the second member of Fengcheng Formation (P1f2), the basin began to shrink, the climate became relatively drier, the water became saltier, the environment became more limited, and the lithofacies were mainly organic-rich layered dolomitic mudstone. In the top of the P1f2 and the lower part of the third member of Fengcheng Formation (P1f3), the environment was relatively closed, the water salinity was higher, a large number of alkaline minerals were developed, and the lithofacies were mainly organic-rich layered alkaline dolomitic mudstone and organic-rich layered mixed shale. In the upper part of P1f3, the input of terrigenous debris increased, salinization weakened, a fan-delta system was developed, and the lithofacies were mainly organic-rich blocky fine sandstone. The sedimentary environment of the Fengcheng Formation has a controlling effect on organic matter enrichment. Overall, a deep-water environment with less input of debris, warm and humid conditions, and relatively lower salinity is more conducive to organic matter enrichment.
-
Key words:
- fine-grained sediment /
- lithofacies /
- sedimentary environment /
- Fengcheng Formation /
- Hasan area /
- Junggar Basin /
-
图 2 准噶尔盆地哈山地区二叠系风城组典型岩石和矿物
a.灰色含砾细砂岩,HSX1井,P1f3,3 305.5 m;b.灰白色层状含碱泥岩,HS5井,P1f2,4 640.8 m;c.白色盐岩(纯碱),HS5井,P1f2,4 797 m;d.灰白色块状泥质白云岩,HSX4井,P1f2,2 175 m;e.灰色纹层状砂/灰混积岩,HS5井,P1f2,4 458 m;f.灰黑色块状杏仁状玄武岩,HS5井,P1f1,5 475 m。
Figure 2. Typical rocks and minerals of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area, Junggar Basin
图 4 准噶尔盆地哈山地区二叠系风城组主要岩相类型、特征及纵向分布
a.HSX1,3 347.5 m,P1f3,富有机质纹层状粉砂质页岩,单偏光;b.为a不同视域下照片,单偏光;c.为a不同视域下照片,正交偏光;d. HS1,2 099 m,P1f2,富有机质纹层状砂/灰混合质页岩;e-f.为d不同视域下照片,正交偏光;g.HS5,4 457 m,P1f2,含有机质层状碱质泥岩,单偏光;h.为g同视域正交偏光照片;i.HS5,P1f2,4 644.8 m,含白云石凝灰质硅硼钠石盐岩;j.HQ6,2 542.1 m,P1f2,含有机质块状泥质白云岩,单偏光;k-l.为j同视域正交偏光照片;m.HQ6,1 563.8 m,P1f3,含有机质块状含凝灰细粉砂岩,正交偏光;n.为m同视域单偏光照片;o.HS5,P1f1,5 137.51 m,沉凝灰岩,单偏光;p.HSX1,P1f1,4 293.5 m,安山岩,正交偏光;q.HSX1,P1f1,4 293.5 m,安山岩,单偏光;r.HSX1,P1f1,4 294.5 m,安山岩,正交偏光;s.HS5,P1f1,5 474 m,杏仁状玄武岩,单偏光;t.为s杏仁状隐晶质—玻璃质斑晶,正交偏光;u.为s长柱状—板条状斜长石微晶基质,正交偏光。
Figure 4. Main lithofacies types, characteristics and vertical distribution of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan area, Junggar Basin
-
[1] 唐勇, 曹剑, 何文军, 等. 从玛湖大油区发现看全油气系统地质理论发展趋势[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202101001.htmTANG Yong, CAO Jian, HE Wenjun, et al. Development tendency of geological theory of total petroleum system: insights from the discovery of Mahu large oil province[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(1): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202101001.htm [2] 何文军, 钱永新, 赵毅, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组全油气系统勘探启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6): 641-655. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106002.htmHE Wenjun, QIAN Yongxin, ZHAO Yi, et al. Exploration implications of total petroleum system in Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(6): 641-655. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202106002.htm [3] 支东明, 唐勇, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组常规—非常规油气有序共生与全油气系统成藏模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(1): 38-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202101006.htmZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, HE Wenjun, et al. Orderly coexistence and accumulation models of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbons in Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Deve-lopment, 2021, 48(1): 38-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202101006.htm [4] 曹剑, 雷德文, 李玉文, 等. 古老碱湖优质烃源岩: 准噶尔盆地下二叠统风城组[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(7): 781-790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201507002.htmCAO Jian, LEI Dewen, LI Yuwen, et al. Ancient high-quality alkaline lacustrine source rocks discovered in the Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(7): 781-790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201507002.htm [5] 唐勇, 郑孟林, 王霞田, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组烃源岩沉积古环境[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(5): 677-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202205001.htmTANG Yong, ZHENG Menglin, WANG Xiatian, et al. Sedimentary paleoenvironment of source rocks of Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(5): 677-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202205001.htm [6] 支东明, 曹剑, 向宝力, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组碱湖烃源岩生烃机理及资源量新认识[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2016, 37(5): 499-506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201605002.htmZHI Dongming, CAO Jian, XIANG Baoli, et al. Fengcheng alkaline lacustrine source rocks of Lower Permian in Mahu Sag in Junggar Basin: hydrocarbon generation mechanism and petroleum resources reestimation[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2016, 37(5): 499-506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201605002.htm [7] 刘得光, 周路, 李世宏, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组烃源岩特征与生烃模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(5): 946-955. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202005005.htmLIU Deguang, ZHOU Lu, LI Shihong, et al. Characteristics of source rocks and hydrocarbon generation models of Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(5): 946-955. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202005005.htm [8] 李学良, 张奎华, 林会喜, 等. 哈山及周缘二叠系风城组沉积环境及沉积相发育特征[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 48(5): 699-708. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201805012.htmLI Xueliang, ZHANG Kuihua, LIN Huixi, et al. Sedimentary environment and facies of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Hashan and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 48(5): 699-708. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201805012.htm [9] 宋永, 杨智峰, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组碱湖型页岩油勘探进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2022, 27(1): 60-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202201006.htmSONG Yong, YANG Zhifeng, HE Wenjun, et al. Exploration progress of alkaline lake type shale oil of the Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2022, 27(1): 60-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202201006.htm [10] 钱永新, 邹阳, 赵辛楣, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷玛页1井二叠系风城组全井段岩心剖析与油气地质意义[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2022, 12(1): 204-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202201018.htmQIAN Yongxin, ZOU Yang, ZHAO Xinmei, et al. Full core analysis and petroleum geological significance of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Well-MY1, Mahu Sag[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2022, 12(1): 204-214. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202201018.htm [11] 李鹏, 熊健, 晏奇, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组岩性对岩石力学特性的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(4): 569-578. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202204569LI Peng, XIONG Jian, YAN Qi, et al. Lithological influences to rock mechanical properties of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(4): 569-578. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202204569 [12] 张志杰, 袁选俊, 汪梦诗, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组碱湖沉积特征与古环境演化[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(6): 972-984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201806006.htmZHANG Zhijie, YUAN Xuanjun, WANG Mengshi, et al. Alkaline-lacustrine deposition and paleoenvironmental evolution in Permian Fengcheng Formation at the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(6): 972-984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201806006.htm [13] 隋风贵. 准噶尔盆地西北缘构造演化及其与油气成藏的关系[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(4): 779-793. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201504010.htmSUI Fenggui. Tectonic evolution and its relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation in the northwest margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(4): 779-793. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201504010.htm [14] 刘政. 准噶尔盆地西北缘哈拉阿拉特山推覆构造形成演化与构造建模[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.LIU Zheng. Formation and evolution and its structural modeling of Hala'alate thrust nappe at the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geoscience (Beijing), 2012. [15] 胡杨, 夏斌. 哈山地区构造演化特征及对油气成藏的影响[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 35(1): 35-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201301004.htmHU Yang, XIA Bin. Tectonic evolution characteristics of Hala'alate mountains and their influence on hydrocarbon accumulation in northern Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 35(1): 35-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201301004.htm [16] MA Delong, HE Dengfa, LI Di, et al. Kinematics of syn-tectonic unconformities and implications for the tectonic evolution of the Hala'alat mountains at the northwestern margin of the Junggar Basin, Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2015, 6(2): 247-264. [17] 匡立春, 唐勇, 雷德文, 等. 准噶尔盆地二叠系咸化湖相云质岩致密油形成条件与勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(6): 657-667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201206004.htmKUANG Lichun, TANG Yong, LEI Dewen, et al. Formation conditions and exploration potential of tight oil in the Permian saline lacustrine dolomitic rock, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(6): 657-667. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201206004.htm [18] 张善文. 准噶尔盆地哈拉阿拉特山地区风城组烃源岩的发现及石油地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(2): 145-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201302003.htmZHANG Shanwen. Identification and its petroleum geologic significance of the Fengcheng Formation source rocks in Hala'alt area, the northern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2013, 34(2): 145-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201302003.htm [19] 王圣柱, 张奎华, 金强. 准噶尔盆地哈拉阿拉特山地区原油成因类型及风城组烃源岩的发现意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(4): 595-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201404016.htmWANG Shengzhu, ZHANG Kuihua, JIN Qiang. The genetic types of crude oils and the petroleum geological significance of the Fengcheng Formation source rock in Hashan area, Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(4): 595-602. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201404016.htm [20] 吕铁良, 王圣柱. 哈山地区构造演化与油气充注耦合关系研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(34): 150-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201534026.htmLV Tieliang, WANG Shengzhu. Coupling relationship between tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon charging in Hashan area[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(34): 150-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201534026.htm [21] 薛雁, 张奎华, 王艺豪, 等. 哈拉阿拉特山地区构造演化及其石油地质意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2015, 36(6): 687-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201506010.htmXUE Yan, ZHANG Kuihua, WANG Yihao, et al. Techtonic evolution of Hala'alate Mountain area and implications in petroleum geo-logy[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2015, 36(6): 687-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201506010.htm [22] LIANG Y Y, ZHANG Y Y, CHEN S, et al. Controls of a strike-slip fault system on the tectonic inversion of the Mahu Depression at the northwestern margin of the Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 198: 104229. [23] TANG W B, ZHANG Y Y, PE-PIPER G, et al. Permian to Early Triassic tectono-sedimentary evolution of the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, western China: sedimentological implications of the transition from rifting to tectonic inversion[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 123: 104730. [24] 郑荣才, 柳梅青. 鄂尔多斯盆地长6油层组古盐度研究[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1999, 20(1): 22-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT901.019.htmZHENG Rongcai, LIU Meiqing. Study on palaeosalinity of Chang 6 oil reservoir set in Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 1999, 20(1): 22-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT901.019.htm [25] 张才利, 高阿龙, 刘哲, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7油层组沉积水体及古气候特征研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(4): 582-587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201104004.htmZHANG Caili, GAO Along, LIU Zhe, et al. Study of character on sedimentary water and palaeoclimate for Chang7 oil layer in Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(4): 582-587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201104004.htm [26] 张文正, 杨华, 杨奕华, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7优质烃源岩的岩石学、元素地球化学特征及发育环境[J]. 地球化学, 2008, 37(1): 59-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200801008.htmZHANG Wenzheng, YANG Hua, YANG Yihua, et al. Petrology and element geochemistry and development environment of Yanchang Formation Chang-7 high quality source rocks in Ordos Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2008, 37(1): 59-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200801008.htm [27] 王益友, 郭文莹, 张国栋. 几种地球化学标志在金湖凹陷阜宁群沉积环境中的应用[J]. 同济大学学报, 1979(2): 51-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ197902005.htmWANG Yiyou, GUO Wenying, ZHANG Guodong. Application of some geochemical indicators in determining of sedimentary environment of the Funing Group (Paleogene), Jin-Hu Depression, Kiangsu Province[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 1979(2): 51-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ197902005.htm [28] 陈洪德, 李洁, 张成弓, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地山西组沉积环境讨论及其地质启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(8): 2213-2229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201108001.htmCHEN Hongde, LI Jie, ZHANG Chenggong, et al. Discussion of sedimentary environment and its geological enlightenment of Shanxi Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(8): 2213-2229. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201108001.htm [29] 付金华, 李士祥, 徐黎明, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组长7段古沉积环境恢复及意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(6): 936-946. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201806003.htmFU Jinhua, LI Shixiang, XU Liming, et al. Paleo-sedimentary environmental restoration and its significance of Chang 7 Member of Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(6): 936-946. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201806003.htm [30] 田洋, 赵小明, 王令占, 等. 重庆石柱二叠纪栖霞组地球化学特征及其环境意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(6): 1035-1045. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201406005.htmTIAN Yang, ZHAO Xiaoming, WANG Lingzhan, et al. Geoche-mical characteristics and its paleoenvironmental implication of Permian Qixia Formation in Shizhu, Chongqing[J]. Acta Sedi-mentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(6): 1035-1045. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201406005.htm [31] 孟昊, 任影, 钟大康, 等. 四川盆地东部寒武系龙王庙组地球化学特征及其古环境意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(7): 1299-1311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201607014.htmMENG Hao, REN Ying, ZHONG Dakang, et al. Geochemical characteristic and its paleoenvironmental implication of Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation in eastern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(7): 1299-1311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201607014.htm [32] 陈骏, 汪永进, 陈旸, 等. 中国黄土地层Rb和Sr地球化学特征及其古季风气候意义[J]. 地质学报, 2001, 75(2): 259-266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200102019.htmCHEN Jun, WANG Yongjin, CHEN Yang, et al. Rb and Sr geochemical characterization of the Chinese Loess and its implications for palaeomonsoon climate[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2001, 75(2): 259-266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200102019.htm [33] 尹锦涛, 俞雨溪, 姜呈馥, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地张家滩页岩元素地球化学特征及与有机质富集的关系[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(6): 1544-1556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201706023.htmYIN Jintao, YU Yuxi, JIANG Chengfu, et al. Relationship between element geochemical characteristic and organic matter enrichment in Zhangjiatan shale of Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(6): 1544-1556. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201706023.htm [34] 张天福, 孙立新, 张云, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘侏罗纪延安组、直罗组泥岩微量、稀土元素地球化学特征及其古沉积环境意义[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(12): 3454-3472. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201612013.htmZHANG Tianfu, SUN Lixin, ZHANG Yun, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the Jurassic Yan'an and Zhiluo formations in the northern margin of Ordos Basin and their paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(12): 3454-3472. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201612013.htm [35] 刘刚, 周东升. 微量元素分析在判别沉积环境中的应用: 以江汉盆地潜江组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(3): 307-310. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200703307LIU Gang, ZHOU Dongsheng. Application of microelements analysis in identifying sedimentary environment: taking Qianjiang Formation in the Jianghan Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2007, 29(3): 307-310. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200703307 [36] 钱门辉, 王绪龙, 黎茂稳, 等. 玛页1井风城组页岩含油性与烃类赋存状态[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 693-703. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202206007.htmQIAN Menhui, WANG Xulong, LI Maowen, et al. Oil-bearing pro-perties and hydrocarbon occurrence states of Fengcheng Formation shale in well Maye-1, Mahu Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(6): 693-703. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202206007.htm [37] 姜福杰, 黄任达, 胡涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油地质特征与分级评价[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(7): 899-911. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202207002.htmJIANG Fujie, HUANG Renda, HU Tao, et al. Geological characteristics and classification evaluation of shale oil in Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(7): 899-911. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202207002.htm [38] 杨智峰, 唐勇, 郭旭光, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油赋存特征与影响因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5): 784-796. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105784YANG Zhifeng, TANG Yong, GUO Xuguang, et al. Occurrence states and potential influencing factors of shale oil in the Permian Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(5): 784-796. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105784 [39] SAGEMAN B B, MURPHY A E, WERNE J P, et al. A tale of shales: the relative roles of production, decomposition, and dilution in the accumulation of organic-rich strata, Middle-Upper Devonian, Appalachian Basin[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 195(1/4): 229-273. [40] CALVERT S E, FONTUGNE M R. On the late Pleistocene-Holocene sapropel record of climatic and oceanographic variability in the eastern Mediterranean[J]. Paleoceanography, 2001, 16(1): 78-94. [41] MORT H, JACQUAT O, ADATTE T, et al. The Cenomanian/Turonian anoxic event at the Bonarelli Level in Italy and Spain: enhanced productivity and/or better preservation?[J]. Cretaceous Research, 2007, 28(4): 597-612. [42] WU Z Y, ZHAO X Z, WANG E Z, et al. Sedimentary environment and organic enrichment mechanisms of lacustrine shale: a case study of the Paleogene Shahejie Formation, Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 573: 110404. [43] 赵研, 郭佩, 鲁子野, 等. 准噶尔盆地下二叠统风城组硅硼钠石发育特征及其富集成因探讨[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(5): 966-979. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202005007.htmZHAO Yan, GUO Pei, LU Ziye, et al. Genesis of reedmergnerite in the Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation of the Junggar Basin, NE China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(5): 966-979. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202005007.htm [44] 张元元, 曾宇轲, 唐文斌. 准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠纪原型盆地分析[J]. 石油科学通报, 2021, 6(3): 333-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE202103001.htmZHANG Yuanyuan, ZENG Yuke, TANG Wenbin. Permian attributes and tectonic evolution of the west Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2021, 6(3): 333-343. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE202103001.htm -





 下载:
下载:







 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号