Characteristics of the deep and ultra-deep shale reservoirs of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in the southeastern Sichuan Basin and the significance of shale gas exploration
-
摘要: 四川盆地东南地区上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组中深层领域页岩气勘探及页岩储层特征与主控因素的研究已经取得了丰硕成果,而作为当前页岩气勘探重点的深层、超深层领域,由于受钻井等因素的制约,对于其储层发育特征及与中深层页岩储层的差异等研究还不够深入。为了明确五峰组—龙马溪组深层、超深层页岩储层特征,为勘探部署提供依据,选取川东南地区4口埋深在2 000~6 000 m的典型页岩气钻井,系统开展了深层、超深层页岩储层发育特征及差异对比研究,探讨了储层孔隙发育的成因。研究表明:(1)埋深在6 000 m以内,五峰组—龙马溪组页岩储层依然能够发育高孔有效储层,且随埋深的增大孔隙度无明显变化,但是有机质孔的形态、孔隙结构及连通性存在一定差异,即随着埋深的增大,有机质孔孔径相对变小,孔隙连通性变差;(2)明确了生物成因的硅质是孔隙发育的基础,流体超压是储层孔隙保持的关键,在两者联合作用下,深层、超深层页岩高孔隙优质储层得以发育和保持;(3)基于储层发育的研究,将页岩气勘探拓深至6 000 m,明确了下一步页岩气勘探方向。初步评价四川盆地及周缘五峰组—龙马溪组深层、超深层页岩气(埋深为4 000~5 000 m)资源量超2×1012 m3。Abstract: Fruitful achievements have been made in shale gas exploration in the middle and deep areas from the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation to the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the southeastern Sichuan Basin, and in the research on shale reservoir characteristics and main controlling factors. As the key direction of current shale exploration, the deep and ultra-deep areas are limited by drilling and other factors, and the research on reservoir development characteristics and differences with the middle and deep shale reservoirs is insufficient. In order to clarify the characteristics of the deep and ultra-deep shale reservoirs of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formatiosns, four typical shale gas wells at the depth of 2 000-6 000 m in the southeastern Sichuan exploration area were selected to systematically carry out a comparative study of deep and ultra-deep shale reservoir development characteristics and differences, and the causes of pore development were discussed. The results show that: (1) With a burial depth of less than 6 000 m, the shale reservoirs of the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations are effective reservoirs with high porosity, and the porosity has no obvious change with the change of burial depth. However, there are certain differences in the morphology, structure and connectivity of organic matter pores, that is, with the increase of burial depth, the size of organic matter pores relatively decreases, and the pore connectivity deteriorates; (2) It has been clarified that biogenic silica is the foundation of pore development, and fluid overpressure is the key to maintaining reservoir pores. Under the combined action of biogenic silica and biogenic silica, the deep and ultra-deep shale reservoirs with high porosity and high quality can be developed and maintained; (3) Based on the research of reservoir development, shale gas exploration will be extended to 6 000 m, which provides a clear direction for shale gas exploration in the next step. It is preliminarily assessed that the deep and ultra-deep shale gas (buried depth of 4 000-5 000 m) resources in the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in the Sichuan Basin and its surrounding areas exceed 2×1012 m3.
-
表 1 川东南上奥陶统五峰组—下志留统龙马溪组优质页岩段储层孔隙度、含气量及压力系数
Table 1. Reservoir porosity, gas content and pressure coefficient of the high-quality shale section of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation to Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the southeastern Sichuan Basin
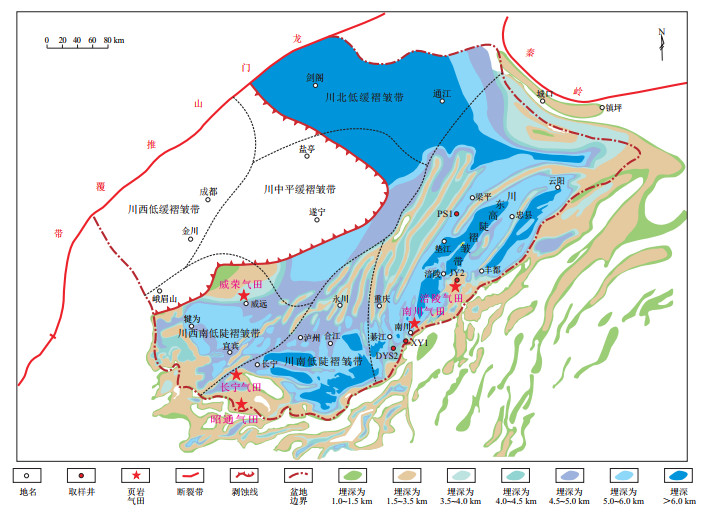
钻井名称 页岩埋深/m 孔隙度/% 含气量/(m3/t) 压力系数 JY2井 2 575 6.20 6.46 1.55 XY1井 3 650 6.05 5.95 1.90 DYS2井 4 278 7.40 6.69 2.06 PS1井 5 969 5.22 7.44 1.95 -
[1] 郭旭升, 胡东风, 魏志红, 等. 涪陵页岩气田的发现与勘探认识[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(3): 24-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201603003.htmGUO Xusheng, HU Dongfeng, WEI Zhihong, et al. Discovery and exploration of Fuling shale gas field[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(3): 24-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201603003.htm [2] 马新华, 谢军. 川南地区页岩气勘探开发进展及发展前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(1): 161-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201801020.htmMA Xinhua, XIE Jun. The progress and prospects of shale gas exploration and exploitation in southern Sichuan Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(1): 161-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201801020.htm [3] 梁兴, 王高成, 张介辉, 等. 昭通国家级示范区页岩气一体化高效开发模式及实践启示[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2017, 22(1): 29-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201701005.htmLIANG Xing, WANG Gaocheng, ZHANG Jiehui, et al. High-efficiency integrated shale gas development model of Zhaotong National Demonstration Zone and its practical enlightenment[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(1): 29-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201701005.htm [4] 熊亮. 川南威荣页岩气田五峰组—龙马溪组页岩沉积相特征及其意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(3): 326-332. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903326XIONG Liang. Characteristics and significance of sedimentary facies of Wufeng-Longmaxi formation shale in Weirong Shale Gas Field, southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(3): 326-332. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903326 [5] 郭旭升. 南方海相页岩气"二元富集"规律: 四川盆地及周缘龙马溪组页岩气勘探实践认识[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(7): 1209-1218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201407001.htmGUO Xusheng. Rules of two-factor enrichiment for marine shale gas in southern China: understanding from the Longmaxi Formation shale gas in Sichuan Basin and its surrounding area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(7): 1209-1218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201407001.htm [6] 郭旭升, 腾格尔, 魏祥峰, 等. 四川盆地深层海相页岩气赋存机理与勘探潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(4): 453-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202204001.htmGUO Xusheng, BORJIGEN Tenger, WEI Xiangfeng, et al. Occurrence mechanism and exploration potential of deep marine shale gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(4): 453-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202204001.htm [7] 蔡勋育, 刘金连, 张宇, 等. 中国石化"十三五"油气勘探进展与"十四五"前景展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(1): 31-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202101003.htmCAI Xunyu, LIU Jinlian, ZHANG Yu, et al. Oil and gas exploration progress of Sinopec during the 13th Five-Year Plan period and prospect forecast for 14th Five-Year Plan[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(1): 31-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202101003.htm [8] 龙胜祥, 冯动军, 李凤霞, 等. 四川盆地南部深层海相页岩气勘探开发前景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(4): 443-451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201804001.htmLONG Shengxiang, FENG Dongjun, LI Fengxia, et al. Prospect of the deep marine shale gas exploration and development in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(4): 443-451. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201804001.htm [9] 何治亮, 聂海宽, 胡东风, 等. 深层页岩气有效开发中的地质问题: 以四川盆地及其周缘五峰组—龙马溪组为例[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(4): 379-391. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202004003.htmHE Zhiliang, NIE Haikuan, HU Dongfeng, et al. Geological problems in the effective development of deep shale gas: a case study of Upper Ordovician Wufeng-Lower Silurian Longmaxi formations in Sichuan Basin and its periphery[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(4): 379-391. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202004003.htm [10] 张成林, 张鉴, 李武广, 等. 渝西大足区块五峰组—龙马溪组深层页岩储层特征与勘探前景[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(12): 1794-1804. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201912013.htmZHANG Chenglin, ZHANG Jian, LI Wuguang, et al. Deep shale reservoir characteristics and exploration potential of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations in Dazu area, western Chongqing[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(12): 1794-1804. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201912013.htm [11] 郝绵柱, 姜振学, 聂舟, 等. 深层页岩储层孔隙连通性发育特征及其控制因素: 以川南地区龙马溪组为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2022, 29(6): 761-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202206007.htmHAO Mianzhu, JIANG Zhenxue, NIE Zhou, et al. Development characteristics of pore connectivity in deep shale reservoirs and its controlling factors: a case study of Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2022, 29(6): 761-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202206007.htm [12] 姜振学, 李鑫, 王幸蒙, 等. 中国南方典型页岩孔隙特征差异及其控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(1): 41-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202101005.htmJIANG Zhenxue, LI Xin, WANG Xingmeng, et al. Characteristic differences and controlling factors of pores in typical South China shale[J]. OIL & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(1): 41-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202101005.htm [13] 郭旭升, 李宇平, 刘若冰, 等. 四川盆地焦石坝地区龙马溪组页岩微观孔隙结构特征及其控制因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(6): 9-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201406002.htmGUO Xusheng, LI Yuping, LIU Ruobing, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of micro-pore structures of Longmaxi shale play in the Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2014, 34(6): 9-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201406002.htm [14] 杨峰, 宁正福, 胡昌蓬, 等. 页岩储层微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(2): 301-311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201302013.htmYANG Feng, NING Zhengfu, HU Changpeng, et al. Characterization of microscopic pore structures in shale reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(2): 301-311. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201302013.htm [15] 刘树根, 叶玥豪, 冉波, 等. 差异保存条件下页岩孔隙结构特征演化及其意义[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2020, 10(5): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202005003.htmLIU Shugen, YE Yuehao, RAN Bo, et al. Evolution and implications of shale pore structure characteristics under different pre-servation conditions[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2020, 10(5): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202005003.htm [16] 李廷微, 姜振学, 宋国奇, 等. 陆相和海相页岩储层孔隙结构差异性分析[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(1): 65-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201901007.htmLI Tingwei, JIANG Zhengxue, SONG Guoqi, et al. Analysis of differences in pore structure between continental and marine shale reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(1): 65-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201901007.htm [17] 刘伟新, 卢龙飞, 魏志红, 等. 川东南地区不同埋深五峰组—龙马溪组页岩储层微观结构特征与对比[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(3): 378-386. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003378LIU Weixin, LU Longfei, WEI Zhihong, et al. Microstructure characteristics of Wufeng-Longmaxi shale gas reservoirs with different depth, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(3): 378-386. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003378 [18] 于炳松. 页岩气储层孔隙分类与表征[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(4): 211-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304020.htmYU Bingsong. Classification and characterization of gas shale pore system[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4): 211-220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304020.htm [19] 陈洋, 唐洪明, 廖纪佳, 等. 基于埋深变化的川南龙马溪组页岩孔隙特征及控制因素分析[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(2): 472-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202202009.htmCHEN Yang, TANG Hongming, LIAO Jijia, et al. Analysis of shale pore characteristics and controlling factors based on variation of buried depth in the Longmaxi Formation, southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(2): 472-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202202009.htm [20] 丁江辉, 张金川, 杨超, 等. 页岩有机孔成因演化及影响因素探讨[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 41(2): 33-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201902004.htmDING Jianghui, ZHANG Jinchuan, YANG Chao, et al. Formation evolution and influencing factors of organic pores in shale[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Techno-logy Edition), 2019, 41(2): 33-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201902004.htm [21] 卢龙飞, 刘伟新, 俞凌杰, 等. 生物蛋白石早期成岩相变特征及对硅质页岩孔隙发育与孔径分布的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(3): 363-370. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003363LU Longfei, LIU Weixin, YU Lingjie, et al. Early diagenesis characteristics of biogenic opal and its influence on porosity and pore network evolution of siliceous shale[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(3): 363-370. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202003363 [22] 郭旭升, 李宇平, 腾格尔, 等. 四川盆地五峰组—龙马溪组深水陆棚相页岩生储机理探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(1): 193-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202001021.htmGUO Xusheng, LI Yuping, BORJIGEN Tenger, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and storage mechanisms of deep-water shelf shales of Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(1): 193-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202001021.htm [23] 刘若冰. 超压对川东南地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩储层影响分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(4): 817-827. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201504022.htmLIU Ruobing. Analyses of influences on shale reservoirs of Wufeng-Longmaxi formation by overpressure in the south-eastern part of Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(4): 817-827. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201504022.htm [24] 王强, 魏祥峰, 魏富彬, 等. 川东南涪陵地区五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气藏中的超压作用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(3): 333-340. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903333WANG Qiang, WEI Xiangfeng, WEI Fubin, et al. Overpressure in shale gas reservoirs of Wufeng-Longmaxi formations, Fuling area, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(3): 333-340. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201903333 -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号