Hydrothermal dissolution of deep-buried carbonate rocks and its significance for hydrocarbon exploration in Shunnan area, the Tarim Basin: taking well Peng-1 in Shunnan area as a case
-
摘要: 为揭示深层碳酸盐岩储层的成因机理,对塔里木盆地顺南地区蓬1井进行了研究。顺南蓬1井取心段揭示,在埋深超过7 500 m的碳酸盐岩中发育有大量的裂缝和溶蚀孔洞,基于详细的岩心观察和描述发现这些溶蚀孔洞主要分布在取心段下部上寒武统白云岩中,而在取心段上部下奥陶统碳酸盐岩中很少。溶蚀孔洞的直径随埋藏深度的增加逐渐增大,表明这些孔洞是由来源于深部的热流体而非大气淡水下渗溶蚀形成的。各成岩矿物(白云岩、方解石)与宿主围岩具有相似的碳同位素值和87Sr/86Sr比值,说明成岩流体与原始碳酸盐岩发生了强烈的水—岩反应,主要继承了原始封存的孔隙水的地球化学特征。但是,明显偏负的氧同位素值(平均-13.26‰)表明它们形成于较高温度的成岩流体中,这一推论也得到了流体包裹体显微测温的证实,表明白云岩的重结晶和随后方解石的沉淀都与断裂相关的深部热流体密切相关。此外,全直径CT扫描揭示,裂缝可以明显改善热液白云石化作用形成的白云岩的储集性能,尤其是渗透率,至少提高一个数量级,即从0.02×10-3 μm2提高至0.39×10-3 μm2。鉴于塔深1井及古城地区具有相似的情况,塔里木盆地深层—超深层碳酸盐岩可能广泛发育热液相关的白云岩储层。因此,在塔里木盆地及其他地区未来的油气勘探中,热液改造型相关的白云岩储层值得重点关注。Abstract: In order to reveal the genetic mechanism of deep-buried carbonate reservoirs, a study was made based on well Peng-1 in Shunnan area of the Tarim Basin. The core section of well Peng-1 revealed that a large number of fractures and dissolution pores were developed in the carbonate rocks with buried depth of over 7 500 m. Based on detailed core observation and description, it was found that the dissolution pores were mainly distributed in the Upper Cambrian dolomites in the lower part of the core section and few in the Lower Ordovician carbonates in the upper part of the core section. The diameter of pores increases gradually with the increase of burial depth, which indicated that the pores were formed by infiltration of deep-seated hydrothermal fluids rather than meteoric water. The similar δ13C values and 87Sr/86Sr ratios of different types of minerals (including dolomite and calcite) with host rocks indicated that the diagenetic fluids inherited the geochemical characteristics of original sequestered pore water through intense water-rock action with the original carbonate rocks. However, the significantly negative δ18O values (with an average of -13.26 ‰) suggested that they were precipitated from fluids with high temperatures. This inference was verified by the results of fluid inclusion microthermometry, which confirmed that dolomite recrystallization and subsequent calcite precipitation were closely associated with fault-related deep-seated hydrothermal fluids. In addition, whole diameter CT scanning revealed that fractures can significantly improve the reservoir property and permeability of the dolomite formed by hydrothermal dolomitization. The permeability can be improved by at least one order of magnitude, i.e. from 0.02×10-3 μm2 to 0.39×10-3 μm2. Hydrothermal-related dolomite reservoirs may be extensively developed in the deep/ultra-deep buried carbonates in the Tarim Basin in view of the occurrence of such phenomenon in the well TS1 and Gucheng area. Thus, in the future hydrocarbon exploration in the Tarim Basin and elsewhere, hydrothermal-altered dolomite reservoirs deserve more attention.
-
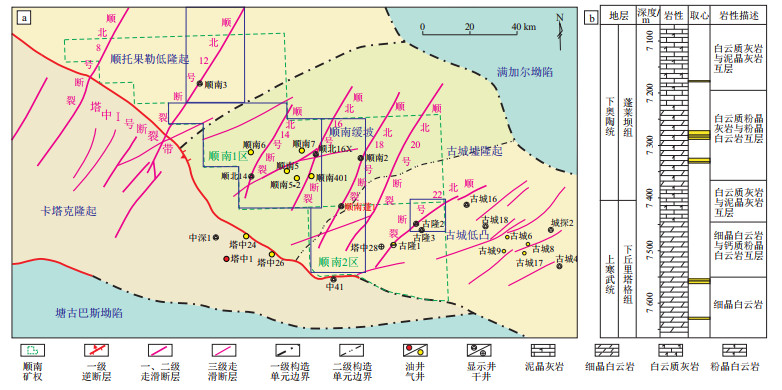
图 1 塔里木盆地顺南地区构造位置(a)及地层综合柱状图(b)
据李宗杰等[16],略有修改。
Figure 1. Simplified geological map (a) and composite stratigraphic column (b) of Shunnan area, the Tarim Basin
图 2 塔里木盆地顺南地区蓬1井上寒武统—下奥陶统岩心宏观特征
a.粉细晶白云岩,发育高角度构造裂缝被方解石完全充填,蓬莱坝组,7 327.17~7 327.37 m;b.纹层状粉细晶白云岩,蓬莱坝组,7 332.94~7 333.14 m;c.浅灰色细晶白云岩,针孔状溶孔发育,下丘里塔格组,7 556.99~7 557.11 m;d.灰白色细—中晶白云岩,溶孔发育,形态不规则,下丘里塔格组,7 561.35~7 561.51m;e.深灰色细—中晶白云岩,蜂窝状溶孔发育,被鞍形白云石和方解石完全充填—半充填,下丘里塔格组,7 626.79~7 626.94 m。
Figure 2. Marcoscopic characteristics of the Upper Cambrian-Lower Ordovician cores from well Peng-1 in Shunnan area, the Tarim Basin
图 3 塔里木盆地顺南地区蓬1井上寒武统—下奥陶统岩心微观特征
a.粉细晶白云岩,蓬莱坝组,7 326.69 m,单偏光;b.残留的原始粪球粒,蓬莱坝组,7 330.92m,单偏光;c.粉细晶白云岩,裂缝被方解石充填,蓬莱坝组,7 326.52~7 326.62 m,阴极发光;d.细—中晶白云岩,镶嵌状接触,下丘里塔格组,7 559.9 m,单偏光;e-f.中粗晶白云岩,鞍形白云石和方解石充填溶蚀孔洞,下丘里塔格组,7 626.79~7 626.94 m,e为单偏光,f为阴极发光。
Figure 3. Microscopic characteristics of the Upper Cambrian-Lower Ordovician cores from well Peng-1 in Shunnan area, the Tarim Basin
表 1 塔里木盆地顺南地区蓬1井各成岩矿物碳、氧、锶同位素测试分析结果
Table 1. Isotopic data (δ13C, δ18O and 87Sr/86Sr ratios) of different types of minerals of well Peng-1 in Shunnan area, the Tarim Basin
样品编号 深度/m 岩性 δ13C/‰ δ18O/‰ 86Sr/87Sr ±2σ SHNP1-01 7 326.52~7 326.62 深灰色泥晶白云岩 -1.24 -8.27 0.709 375 0.000 017 裂缝方解石 -2.35 -13.12 0.709 112 0.000 013 裂缝方解石 -2.19 -13.31 SHNP1-02 7 327.37~7 327.56 浅灰色颗粒泥晶灰岩 -1.44 -12.58 0.709 080 0.000 018 裂缝方解石 -2.25 -13.32 0.709 224 0.000 013 裂缝方解石 -2.42 -13.31 SHNP1-03 7 626.79~7 626.94 灰色细晶白云岩 -1.12 -10.00 0.709 141 0.000 015 孔洞方解石 -2.53 -14.03 0.709 165 0.000 012 SHNP1-04 7 627.42~7 627.51 灰色细晶白云岩 -1.30 -10.55 0.708 956 0.000 016 鞍形白云石 -2.16 -12.40 0.709 516 0.000 009 表 2 塔里木盆地顺南地区蓬1井各成岩矿物流体包裹体显微测温结果
Table 2. Results of fluid inclusion microthermometry of different types of minerals of well Peng-1 in Shunnan area, the Tarim Basin
样号 矿物 个数 均一温度(Th)/℃ 冰点温度(Tm)/℃ 盐度/% 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 最小值 最大值 平均值 SHNP1-1 方解石 3 170.3 173.5 171.7 -28.9 -21.5 -24.9 23.4 28 25.5 2 160.9 160.9 160.9 -23.6 -23.2 -23.4 24.5 24.7 24.6 2 162.3 166.6 164.5 -23.1 -20.4 -21.8 22.6 24.4 23.5 5 173.1 176.3 174.5 -23.8 -21.9 -23.1 23.6 24.8 24.4 1 178.7 178.7 178.7 -22.9 -22.9 -22.9 24.3 24.3 24.3 3 168.5 179.8 175.0 -26.5 -23.4 -25.3 24.6 26.5 25.7 SHNP1-2 方解石 1 192.5 192.5 192.5 -24.6 -24.6 -24.6 25.3 25.3 25.3 2 185.6 193.5 189.6 -25.0 -25.0 -25.0 25.6 25.6 25.6 3 178.1 189.8 182.0 -24.8 -22.0 -23.7 24.0 25.5 24.8 5 172.5 187.3 179.8 -25.6 -18.3 -23.5 21.2 25.9 24.6 3 162.5 173.7 167.9 -24.3 -19.2 -21.8 21.8 25.1 23.5 4 158.8 164.4 162.4 -23.8 -22.5 -23.0 24.2 24.8 24.5 SHNP1-3 鞍形白云石 3 172.5 184.5 179.1 -20.7 -20.7 -20.7 22.8 22.8 22.8 4 186.1 197.8 191.1 -22.8 -19.9 -21.7 22.3 24.2 23.5 方解石 1 215.2 215.2 215.2 -21.2 -21.2 -21.2 23.2 23.2 23.2 2 206.1 210.1 208.1 -21.8 -21.8 -21.8 23.6 23.6 23.6 SHNP1-4 鞍形白云石 3 160.8 172.5 166.1 -20.2 -10.0 -16.4 13.9 22.5 19.4 1 178.5 178.5 178.5 -21.4 -21.4 -21.4 23.3 23.3 23.3 1 184.5 184.5 184.5 -27.9 -27.9 -27.9 27.4 27.4 27.4 石英 3 170.6 188.2 178.7 -14.4 -13.2 -13.8 17.1 18.1 17.6 5 188.2 188.5 188.3 -16.7 -12.9 -14.6 16.8 20.0 18.2 表 3 塔里木盆地顺南地区蓬1井寒武系下丘里塔格组储层特征测井解释
Table 3. Reservoir characteristics of Cambrian Lower Qiulitage Formation of well Peng-1 in Shunnan area of the Tarim Basin revealed by logging interpretation
地层 深度/m GR/API RT/(Ω·m) AC/(μs/ft) SH/% 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 解释结论储层级别 
7 579~7 606 29.2~19 920~562 49.2~46.1 1.6 2.8 0.02 Ⅲ类 7 606~7 611.5 14.7~21.9 199~168 56.3~52.4 3.5 6.6 0.12~0.26 Ⅱ类 7 611.5~7 618 18.9~11.8 319~1 066 49.9~46.2 2.4 2.6~3.7 0.04~0.12 Ⅲ类 7 618~7 621 21.9~16.5 44.3~52.7 56.1~53.7 5.7 8.6 0.39 Ⅱ类 7 625~7 629.5 11.5~16.1 1 217~623 43.7~47.2 2.8 3.6 0.02 Ⅲ类 -
[1] 陈代钊. 构造—热液白云岩化作用与白云岩储层[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(5): 614-622. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200805014.htmCHEN Daizhao. Structure-controlled hydrothermal dolomitization and hydrothermal dolomite reservoirs[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(5): 614-622. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200805014.htm [2] ZHU Dongya, JIN Zhijun, HU Wenxuan. Hydrothermal recrystallization of the Lower Ordovician dolomite and its significance to reservoir in northern Tarim Basin[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2010, 53(3): 368-381. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-0028-9 [3] 焦存礼, 何治亮, 邢秀娟, 等. 塔里木盆地构造热液白云岩及其储层意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(1): 277-284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201101020.htmJIAO Cunli, HE Zhiliang, XING Xiujuan, et al. Tectonic hydrothermal dolomite and its significance of reservoirs in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(1): 277-284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201101020.htm [4] JIANG Lei, CAI Chunfang, WORDEN R H, et al. Multiphase dolomitization of deeply buried Cambrian petroleum reservoirs, Tarim Basin, north-west China[J]. Sedimentology, 2016, 63(7): 2130-2157. doi: 10.1111/sed.12300 [5] JIANG Lei, PAN Wenqin, CAI Chunfang, et al. Fluid mixing induced by hydrothermal activity in the Ordovician carbonates in Tarim Basin, China[J]. Geofluids, 2015, 15(3): 483-498. doi: 10.1111/gfl.12125 [6] GUO Chuan, CHEN Daizhao, QING Hairuo, et al. Multiple dolomitization and later hydrothermal alteration on the Upper Cambrian-Lower Ordovician carbonates in the northern Tarim Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 72: 295-316. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.01.023 [7] EHRENBERG S N, WALDERHAUG O, BJØRLYKKE K. Carbonate porosity creation by mesogenetic dissolution: reality or illusion?[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(2): 217-233. doi: 10.1306/05031110187 [8] 漆立新, 云露, 曹自成, 等. 顺北油气田地质储量评估与油气勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(2): 127-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202102001.htmQI Lixin, YUN Lu, CAO Zicheng, et al. Geological reserves assessment and petroleum exploration targets in Shunbei oil & gas field[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(2): 127-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202102001.htm [9] 李映涛, 漆立新, 张哨楠, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北地区中—下奥陶统断溶体储层特征及发育模式[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(12): 1470-1484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201912005.htmLI Yingtao, QI Lixin, ZHANG Shaonan, et al. Characteristics and development mode of the Middle and Lower Ordovician fault-karst reservoir in Shunbei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(12): 1470-1484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201912005.htm [10] 马永生, 蔡勋育, 云露, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北超深层碳酸盐岩油气田勘探开发实践与理论技术进展[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(1): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202201001.htmMA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, YUN Lu, et al. Practice and theoretical and technical progress in exploration and development of Shunbei ultra-deep carbonate oil and gas field, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(1): 1-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202201001.htm [11] 贾承造. 中国塔里木盆地构造特征与油气[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997.JIA Chengzao. Tectonic characteristics and petroleum, Tarim Basin, China[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1977. [12] 何登发, 周新源, 张朝军, 等. 塔里木地区奥陶纪原型盆地类型及其演化[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(S1): 126-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2007S1015.htmHE Dengfa, ZHOU Xinyuan, ZHANG Chaojun, et al. Tectonic types and evolution of Ordovician proto-type basins in the Tarim region[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(S1): 164-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2007S1015.htm [13] LIN Changsong, YANG Haijun, LIU Jingyan, et al. Sequence architecture and depositional evolution of the Ordovician carbonate platform margins in the Tarim Basin and its response to tectonism and sea-level change[J]. Basin Research, 2012, 24(5): 559-582. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.2011.00536.x [14] LIN Changsong, YANG Haijun, LIU Jingyan, et al. Distribution and erosion of the Paleozoic tectonic unconformities in the Tarim Basin, Northwest China: significance for the evolution of paleo-uplifts and tectonic geography during deformation[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 46: 1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.10.004 [15] 漆立新. 塔里木盆地顺托果勒隆起奥陶系碳酸盐岩超深层油气突破及其意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(3): 38-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201603004.htmQI Lixin. Oil and gas breakthrough in ultra-deep Ordovician carbonate formations in Shuntuoguole Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(3): 38-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201603004.htm [16] 李宗杰, 王鹏, 陈绪云, 等. 塔里木盆地顺南地区超深白云岩储层地震、地质综合预测[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(1): 59-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202001007.htmLI Zongjie, WANG Peng, CHEN Xuyun, et al. Integrated seismic and geological prediction of ultra-deep dolomite reservoir in Shunnan area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(1): 59-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202001007.htm [17] 云露, 曹自成. 塔里木盆地顺南地区奥陶系油气富集与勘探潜力[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(6): 788-797. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201406008.htmYUN Lu, CAO Zicheng. Hydrocarbon enrichment pattern and exploration potential of the Ordovician in Shunnan area, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(6): 788-797. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201406008.htm [18] 任建业, 张俊霞, 阳怀忠, 等. 塔里木盆地中央隆起带断裂系统分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(1): 219-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201101015.htmREN Jianye, ZHANG Junxia, YANG Huaizhong, et al. Analysis of fault systems in the Central Uplift, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(1): 219-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201101015.htm [19] DONG Shaofeng, CHEN Daizhao, QING Hairuo, et al. Hydrothermal alteration of dolostones in the Lower Ordovician, Tarim Basin, NW China: multiple constraints from petrology, isotope geochemistry and fluid inclusion microthermometry[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 46: 270-286. [20] DONG Shaofeng, CHEN Daizhao, ZHOU Xiqiang, et al. Tectonically driven dolomitization of Cambrian to Lower Ordovician carbonates of the Quruqtagh area, north-eastern flank of Tarim Basin, north-west China[J]. Sedimentology, 2017, 64(4): 1079-1106. [21] BODNAR R J. Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1993, 57(3): 683-684. [22] QING Hairuo, VEIZER J. Oxygen and carbon isotopic composition of Ordovician brachiopods: implications for coeval seawater[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(20): 4429-4442. [23] VEIZER J, ALA D, AZMY K, et al. 87Sr/86Sr, δ13C and δ18O evolution of Phanerozoic seawater[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 161(1/3): 59-88. [24] BURKE W H, DENISON R E, HETHERINGTON E A, et al. Variation of seawater 87Sr/86Sr throughout Phanerozoic time[J]. Geology, 1982, 10(10): 516-519. [25] DAVIES G R, SMITH L B. Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies: An overview[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2006, 90(11): 1641-1690. [26] HITZMAN M W, ALLAN J R, BEATY D W. Regional dolomitization of the Waulsortian limestone in southeastern Ireland: evidence of large-scale fluid flow driven by the Hercynian orogeny[J]. Geology, 1998, 26(6): 547-550. [27] MACHEL H G, ANDERSON J H. Pervasive subsurface dolomitization of the Nisku Formation in central Alberta[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1989, 59(6): 891-911. [28] 邓尚, 李慧莉, 张仲培, 等. 塔里木盆地顺北及邻区主干走滑断裂带差异活动特征及其与油气富集的关系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 878-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htmDENG Shang, LI Huili, ZHANG Zhongpei, et al. Characteristics of differential activities in major strike-slip fault zones and their control on hydrocarbon enrichment in Shunbei area and its surroundings, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 878-888. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201805004.htm [29] WOODY R E, GREGG J M, KOEDERITZ L F. Effect of texture on the petrophysical properties of dolomite-evidence from the Cambrian-Ordovician of southeastern Missouri[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1996, 80(1): 119-132. [30] QING Hairuo, MOUNTJOY E. Large-scale fluid flow in the Middle Devonian Presqu'ile Barrier, Western Canada sedimentary basin[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(10): 903-906. [31] YAO Qingjun, DEMICCO R V. Paleoflow patterns of dolomitizing fluids and paleohydrogeology of the southern Canadian Rocky Mountains: evidence from dolomite geometry and numerical modeling[J]. Geology, 1995, 23(9): 791-794. [32] BRAITHWAITE C J R, RIZZI G. The geometry and petrogenesis of hydrothermal dolomites at Navan, Ireland[J]. Sedimentology, 1997, 44(3): 421-440. [33] DUGGAN J P, MOUNTJOY E W, STASIUK L D. Fault-controlled dolomitization at Swan Hills Simonette oil field (Devonian), deep basin west-central Alberta, Canada[J]. Sedimentology, 2001, 48(2): 301-323. [34] GREGG J M, SHELTON K L, JOHNSON A W, et al. Dolomitization of the waulsortian limestone (lower Carboniferous) in the Irish midlands[J]. Sedimentology, 2001, 48(4): 745-766. [35] CARMICHAEL S K, FERRY J M, MCDONOUGH W F. Formation of replacement dolomite in the Latemar carbonate buildup, dolomites, Northern Italy: part 1. field relations, mineralogy, and geochemistry[J]. American Journal of Science, 2008, 308(7): 851-884. [36] ZHANG Juntao, HU Wenxuan, QIAN Yixiong, et al. Formation of saddle dolomites in Upper Cambrian carbonates, western Tarim Basin (northwest China): implications for fault-related fluid flow[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(8): 1428-1440. [37] WEI Wenwen, CHEN Daizhao, QING Hairuo, et al. Hydrothermal dissolution of deeply buried Cambrian dolomite rocks and porosity generation: integrated with geological studies and reactive transport modeling in the Tarim Basin, China[J]. Geofluids, 2017, 2017: 9562507. [38] 王珊, 曹颖辉, 杜德道, 等. 塔里木盆地古城地区奥陶系鹰山组白云岩特征及孔隙成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(11): 3477-3492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202011014.htmWANG Shan, CAO Yinghui, DU Dedao, et al. Characteristics and pore genesis of dolomite in Ordovician Yingshan Formation in Gucheng area, Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(11): 3477-3492. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202011014.htm [39] 刘红, 冯子辉, 邵红梅, 等. U-Pb同位素定年分析在热液对白云岩储层改造研究中的应用——以塔里木盆地古城地区下奥陶统鹰三段为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(3): 765-776. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202203010.htmLIU Hong, FENG Zihui, SHAO Hongmei, et al. Application of U-Pb dating technique in the study of hydrothermal activities of dolomite reservoir: a case study on 3rd member of Yingshan Formation in Gucheng area, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(3): 765-776. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202203010.htm [40] LU Ziye, CHEN Honghan, QING Hairuo, et al. Petrography, fluid inclusion and isotope studies in Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in the Shunnan area, Tarim Basin, NW China: implications for the nature and timing of silicification[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2017, 359: 29-43. [41] YOU Donghua, HAN Jun, HU Wenxuan, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanisms of silicified carbonate reservoirs in well SN4 of the Tarim Basin[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2018, 36(4): 820-849. [42] DONG Shaofeng, YOU Donghua, GUO Zenghui, et al. Intense silicification of Ordovician carbonates in the Tarim Basin: constraints from fluid inclusion Rb-Sr isotope dating and geochemistry of quartz[J]. Terra Nova, 2018, 30(6): 406-413. -





 下载:
下载:





 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号