Progress in the study of carbonate clumped isotope in the thermal history of marine basins
-
摘要: 沉积盆地热史研究对于油气成藏分析至关重要,在油气勘探以及油气资源评价领域有着举足轻重的影响,而海相盆地碳酸盐岩层系由于缺乏有效古温标导致很难对其热史进行恢复。碳酸盐团簇同位素是能够指示碳酸盐岩形成温度的指标,它将温度信息记录在13C—18O配对的化学键中,并通过其丰度变化将温度信息反映出来,即碳酸盐团簇同位素的丰度(Δ47)与地层温度演化密切相关。从碳酸盐团簇同位素测温以及热史恢复的基本原理、方法出发,结合近年来其在国内外海相盆地热史恢复的研究实例,综述了碳酸盐团簇同位素古温标的应用情况,并探讨了其存在的问题和未来的发展方向。碳酸盐团簇同位素作为一种新兴的古温标,在碳酸盐岩地层热历史恢复中展现出了巨大的潜力。团簇同位素热史研究实例表明,美国箭峡Bird Spring组经历的最高古温度约为175 ℃,四川盆地二叠系茅口组最高埋藏温度在213~225 ℃,塔里木盆地奥陶系受二叠纪岩浆活动影响存在160 ℃以上的异常高温。团簇同位素由于受热演化模式不成熟,重结晶作用以及沉积埋藏温度变化的影响,使得其在热史恢复方面仍存在不足,并建议精确恢复碳酸盐岩地层热史的下一步发展方向是将碳酸盐团簇同位素和U-Pb定年以及其他古温标相联合。Abstract: The study of thermal history of sedimentary basins is very important for oil-gas accumulation analysis and has decisive influence on oil and gas exploration and oil-gas resource evaluation. However, it is difficult to reconstruct the thermal history of carbonate strata in marine basins due to the lack of effective palaeo-thermometer. The carbonate cluster isotope is an index that can indicate the formation temperature of carbonate rock. It records temperature information in chemical bond through conjugated 13C-18O, and temperature information is revealed through changes in the abundance of conjugated 13C-18O, namely, the abundance of carbonate clumped isotope (Δ47) is closely related to the evolution of strata temperature. This paper reviews the application of carbonate clumped isotope palaeo-thermometer and discusses the existing problems and future development direction based on the basic principle and methods of carbonate clumped isotope thermometry and thermal history reconstruction, and combined with the case studies of thermal history reconstruction in marine basins in recent years. As a new palaeo-thermometer, carbonate clumped isotope shows great potential in the thermal history reconstruction of carbonate strata. Previous studies show that the maximum paleotemperature of the Bird Spring Formation in Arrow Canyon, Nevada, USA is about 175 ℃, and the maximum burial temperature of Permian Maokou Formation in the Sichuan Basin is 213-225 ℃. There is an abnormal high temperature of above 160 ℃ in the Ordovician strata of the Tarim Basin due to the Permian magmatic activity. We believe that the carbonate clumped isotope is still insufficient in the reconstruction of thermal history due to the immaturity of thermal evolution models, the recrystallization, and the change of burial temperature. Thus, we suggest that combining the carbonate clumped isotope, U-Pb dating, and other palaeo-thermometers to accurately reconstruct the thermal history of carbonate strata will be the future development direction.
-
Key words:
- clumped isotope /
- carbonate strata /
- marine basin /
- thermal history /
- Tarim Basin /
- Sichuan Basin
-
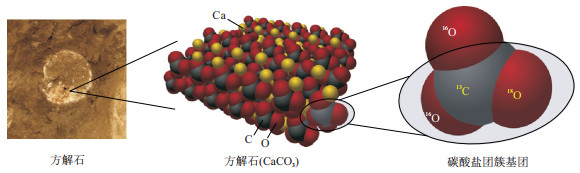
图 1 碳酸盐团簇同位素示意[12]
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of carbonate clumped isotope
图 2 一阶近似模型预测的T(Δ47)—埋藏温度图[31]
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of T(Δ47)-burial T trajectories predicted by first-order approximation model
图 3 热史路径和最高古温度对碳酸盐中13C—18O键重排和T(Δ47)值的影响示意[41]
Figure 3. Impact of thermal history path and maximum paleotemperature on 13C-18O bond reordering and T(Δ47) in carbonate
图 5 美国特拉华盆地不同地温梯度最佳拟合路径模拟[25]
a图为埋藏史; b图为不同地温梯度下T(Δ47)演化曲线,黑带表示95%可信度。
Figure 5. Best fitting path of different geothermal gradients in Delaware Basin, USA
图 6 塔中北部斜坡构造带TZ35井碳酸盐团簇同位素温度模拟[52]
Figure 6. Modeling results of carbonate clumped isotope temperature in well TZ35 on the northern slope of Tazhong Uplift
图 7 利用交换/扩散模型模拟的塔里木盆地顺托果勒地区团簇同位素温度热模拟结果[27]
Figure 7. Thermal modeling results of clumped isotope temperature in Shuntuoguole area, Tarim Basin using exchange-diffusion model
图 9 四川盆地普光气田白云岩团簇同位素温度演化过程[55]
D83、D89和D99分别代表白云石样品的T(Δ47)及其误差。
Figure 9. Evolution of clumped isotope temperature of dolostone from Puguang Gas Field, Sichuan Basin
图 10 基于包裹体宿主矿物年龄、团簇同位素温度约束的川中古隆起震旦系灯影组温度演化[57]
Figure 10. Temperature evolution of Sinian Dengying Formation in paleo-uplift in central Sichuan Basin based on the constraints of the age of the host mineral of the inclusion and the clumped isotope temperature
-
[1] EILER J M. "Clumped-isotope" geochemistry—The study of naturally-occurring, multiply-substituted isotopologues[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 262(3/4): 309-327. [2] CAME R E, EILER J M, VEIZER J, et al. Coupling of surface temperatures and atmospheric CO2 concentrations during the Palaeozoic era[J]. Nature, 2007, 449(7159): 198-201. doi: 10.1038/nature06085 [3] FINNEGAN S, BERGMANN K, EILER J M, et al. The magnitude and duration of Late Ordovician-Early Silurian glaciation[J]. Science, 2011, 331(6019): 903-906. doi: 10.1126/science.1200803 [4] GARZIONE C N, HOKE G D, LIBARKIN J C, et al. Rise of the Andes[J]. Science, 2008, 320(5881): 1304-1307. doi: 10.1126/science.1148615 [5] VANDEVELDE J H, BOWEN G J, PASSEY B H, et al. Climatic and diagenetic signals in the stable isotope geochemistry of dolomitic paleosols spanning the Paleocene-Eocene boundary[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 109: 254-267. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.02.005 [6] WANG Yang, PASSEY B, ROY R, et al. Clumped isotope thermo-metry of modern and fossil snail shells from the Himalayan-Tibetan Plateau: implications for paleoclimate and paleoelevation reconstructions[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2021, 133(7/8): 1370-1380. [7] LOPEZ-MALDONADO R, BATEMAN J B, ELLIS A, et al. Paleoclimate changes in the Pacific northwest over the past 36, 000 years from clumped isotope measurements and model analysis[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2023, 38(2): e2021PA004266. doi: 10.1029/2021PA004266 [8] HUNTINGTON K W, BUDD D A, WERNICKE B P, et al. Use of clumped-isotope thermometry to constrain the crystallization temperature of diagenetic calcite[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2011, 81(9): 656-669. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2011.51 [9] BRENNER D C, PASSEY B H, HOLDER R M, et al. Clumped-isotope geothermometry and carbonate U-Pb geochronology of the Alta stock metamorphic aureole, Utah, USA: insights on the kinetics of metamorphism in carbonates[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2021, 22(4): e2020GC009238. doi: 10.1029/2020GC009238 [10] TEMOVSKI M, RINYU L, FUTÓ I, et al. Combined use of conventional and clumped carbonate stable isotopes to identify hydrothermal isotopic alteration in cave walls[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 9202. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12929-4 [11] GHOSH P, ADKINS J, AFFEK H, et al. 13C-18O bonds in carbonate minerals: a new kind of paleothermometer[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(6): 1439-1456. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.11.014 [12] HUNTINGTON K W, SAYLOR J, QUADE J, et al. High late Miocene-Pliocene elevation of the Zhadabasin, southwestern Tibetan plateau, from carbonate clumped isotope thermometry[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2015, 127(1/2): 181-199. [13] QUADE J, EILER J, DAËRON M, et al. The clumped isotope geothermometer in soil and paleosol carbonate[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 105: 92-107. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.11.031 [14] NING Zijie, ZHANG Laiming, HUNTINGTON K W, et al. The burial and exhumation history of the Liuqu Conglomerate in the Yarlung Zangbo suture zone, southern Tibet: insights from clumped isotope thermometry[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 174: 205-217. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.12.009 [15] XIONG Zhongyu, DING Lin, SPICER R A, et al. The early Eocene rise of the Gonjo Basin, SE Tibet: from low desert to high forest[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 543: 116312. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2020.116312 [16] CUMMINS R C, FINNEGAN S, FIKE D A, et al. Carbonate clumped isotope constraints on Silurian ocean temperature and seawater δ18O[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 140: 241-258. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.05.024 [17] THIAGARAJAN N, ADKINS J, EILER J. Carbonate clumped isotope thermometry of deep-sea corals and implications for vital effects[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75(16): 4416-4425. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2011.05.004 [18] PRICE G D, BAJNAI D, FIEBIG J. Carbonate clumped isotope evidence for latitudinal seawater temperature gradients and the oxygen isotope composition of Early Cretaceous seas[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 552: 109777. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109777 [19] MECKLER A N, SEXTON P F, PIASECKI A M, et al. Cenozoic evolution of deep ocean temperature from clumped isotope thermometry[J]. Science, 2022, 377(6601): 86-90. doi: 10.1126/science.abk0604 [20] SUAREZ M B, PASSEY B H. Assessment of the clumped isotope composition of fossil bone carbonate as a recorder of subsurface temperatures[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 140: 142-159. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.05.026 [21] EAGLE R A, SCHAUBLE E A, TRIPATI A K, et al. Body temperatures of modern and extinct vertebrates from 13C-18O bond abundances in bioapatite[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(23): 10377-10382. [22] EAGLE R A, TÜTKEN T, MARTIN T S, et al. Dinosaur body temperatures determined from isotopic (13C-18O) ordering in fossil biominerals[J]. Science, 2011, 333(6041): 443-445. doi: 10.1126/science.1206196 [23] HENKES G A, PASSEY B H, WANAMAKER JR A D, et al. Carbonate clumped isotope compositions of modern marine mollusk and brachiopod shells[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 106: 307-325. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.12.020 [24] SHENTON B J, GROSSMAN E L, PASSEY B H, et al. Clumped isotope thermometry in deeply buried sedimentary carbonates: the effects of bond reordering and recrystallization[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2015, 127(7/8): 1036-1051. [25] NAYLOR H N, DEFLIESE W F, GROSSMAN E L, et al. Investigation of the thermal history of the Delaware Basin (West Texas, USA) using carbonate clumped isotope thermometry[J]. Basin Research, 2020, 32(5): 1140-1155. doi: 10.1111/bre.12419 [26] 徐秋晨, 邱楠生, 刘雯, 等. 利用团簇同位素恢复沉积盆地热历史的探索[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(5/6): 566-578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2019Z1007.htmXU Qiuchen, QIU Nansheng, LIU Wen, et al. Reconstructing the basin thermal history with clumped isotope[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(5/6): 566-578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB2019Z1007.htm [27] 刘雨晨, 邱楠生, 常健, 等. 碳酸盐团簇同位素在沉积盆地热演化中的应用: 以塔里木盆地顺托果勒地区为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(2): 597-611. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX202002021.htmLIU Yuchen, QIU Nansheng, CHANG Jian, et al. Application of clumped isotope thermometry to thermal evolution of sedimentary basins: a case study of Shuntuoguole area in Tarim Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(2): 597-611. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX202002021.htm [28] EILER J M. 'Clumped' isotope geochemistry[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(18): A156. [29] SCHAUBLE E A, GHOSH P, EILER J M. Preferential formation of 13C-18O bonds in carbonate minerals, estimated using first-principles lattice dynamics[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(10): 2510-2529. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.02.011 [30] PASSEY B H, HENKES G A. Carbonate clumped isotope bond reordering and geospeedometry[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 351-352: 223-236. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2012.07.021 [31] HENKES G A, PASSEY B H, GROSSMAN E L, et al. Temperature limits for preservation of primary calcite clumped isotope paleotemperatures[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 139: 362-382. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.04.040 [32] AFFEK H P, EILER J M. Abundance of mass 47 CO2 in urban air, car exhaust, and human breath[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(1): 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.08.021 [33] KLUGE T, JOHN C M, JOURDAN A L, et al. Laboratory calibration of the calcium carbonate clumped isotope thermometer in the 25-250 ℃ temperature range[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 157: 213-227. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.02.028 [34] STOLPER D A, EILER J M. The kinetics of solid-state isotope-exchange reactions for clumped isotopes: a study of inorganic calcites and apatites from natural and experimental samples[J]. American Journal of Science, 2015, 315(5): 363-411. doi: 10.2475/05.2015.01 [35] ZHANG Youxue. Diffusion in minerals and melts: theoretical background[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2010, 72(1): 5-59. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2010.72.2 [36] MANGENOT X, GASPARRINI M, GERDES A, et al. An emerging thermochronometer for carbonate-bearing rocks: Δ47/(U-Pb)[J]. Geology, 2018, 46(12): 1067-1070. doi: 10.1130/G45196.1 [37] PAGEL M, BONIFACIE M, SCHNEIDER D A, et al. Improving-paleohydrological and diagenetic reconstructions in calcite veins and breccia of a sedimentary basin by combining Δ47 temperature, δ18Owater and U-Pb age[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 481: 1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.12.026 [38] LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao, HAO Fang, et al. Using clumped isotopes to determine the origin of the Middle Permian Qixia Formation dolostone, NW Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 122: 104660. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104660 [39] LU Chaojin, ZOU Huayao, WANG Guangwei, et al. Clumped isotopes of paired dolomite and calcite constraining alteration histories of ancient carbonate successions[J]. Chemical Geology, 2023, 617: 121264. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2022.121264 [40] 柏雪. 湖泊中萝卜螺属壳体团簇同位素特征与温度重建[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2021.BAI Xue. Clumped isotopic characteristics in the modern aquatic gastropod Radix and temperature reconstruction[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Normal University, 2021. [41] HUNTINGTON K W, LECHLER A R. Carbonate clumped isotope thermometry in continental tectonics[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 647-648: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.02.019 [42] MACDONALD J M, FAITHFULL J W, ROBERTS N M W, et al. Clumped-isotope palaeothermometry and LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of lava-pile hydrothermal calcite veins[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2019, 174(7): 63. doi: 10.1007/s00410-019-1599-x [43] BRIGAUD B, BONIFACIE M, PAGEL M, et al. Past hot fluid flows in limestones detected by Δ47-(U-Pb) and not recorded by other geothermometers[J]. Geology, 2020, 48(9): 851-856. doi: 10.1130/G47358.1 [44] QIU Nansheng, CHANG Jian, ZHU Chuanqing, et al. Thermal regime of sedimentary basins in the Tarim, Upper Yangtze and North China Cratons, China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2022, 224: 103884. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103884 [45] LI Dan, CHANG Jian, QIU Nansheng, et al. The thermal history in sedimentary basins: a case study of the central Tarim Basin, Western China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 229: 105149. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105149 [46] CHANG Jian, YANG Xin, QIU Nansheng, et al. Zircon (U-Th)/He thermochronology and thermal evolution of the Tarim Basin, Western China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 230: 105210. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105210 [47] CHANG Jian, LI Dan, QIU Nansheng, et al. Differential thermal regimes of the Tarim and Sichuan Basins in China: implications for hydrocarbon generation and conservation[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 2022, 96(4): 1308-1322. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14980 [48] LI Meijun, WANG Tieguan, CHEN Jianfa, et al. Paleo-heat flow evolution of the Tabei uplift in Tarim Basin, northwest China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2010, 37(1): 52-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.07.007 [49] QIU Nansheng, CHANG Jian, ZUO Yinhui, et al. Thermal evolution and maturation of Lower Paleozoic source rocks in the Tarim Basin, Northwest China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(5): 789-821. doi: 10.1306/09071111029 [50] CHANG Jian, QIU Nansheng, XU Wei. Thermal regime of the Tarim Basin, Northwest China: a review[J]. International Geology Review, 2017, 59(1): 45-61. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2016.1210546 [51] 李慧莉, 邱楠生, 金之钧, 等. 塔里木盆地的热史[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(5): 613-617. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.05.009LI Huili, QIU Nansheng, JIN Zhijun, et al. Geothermal history of Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2005, 26(5): 613-617. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2005.05.009 [52] 熊昱杰, 邱楠生, 李丹, 等. 碳酸盐团簇同位素约束下塔中隆起奥陶系热历史[J]. 地球物理学报, 2023. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0498.XIONG Yujie, QIU Nansheng, LI Dan, et al, Thermal history of the Ordovician in the Tazhong uplift under the constraint of carbonate clumped isotope[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2023. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022Q0498. [53] CONG Fuyun, TIAN Jinqiang, HAO Fang, et al. A thermal pulse induced by a Permian mantle plume in the Tarim Basin, northwest China: constraints from clumped isotope thermometry and in situ calcite U-Pb dating[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2021, 126(4): e2020JB020636. doi: 10.1029/2020JB020636 [54] 沈安江, 胡安平, 郑剑锋, 等. 基于U-Pb同位素年龄和团簇同位素(Δ47)温度约束的构造—埋藏史重建: 以塔里木盆地阿克苏地区震旦系奇格布拉克组为例[J]. 海相油气地质, 2021, 26(3): 200-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2021.03.002SHEN Anjiang, HU Anping, ZHENG Jianfeng, et al. Reconstruction of tectonic-burial evolution based on the constraints of laser in situ U-Pb date and clumped isotopic temperature: a case study from Sinian Qigebulak Formation in Akesuarea, Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2021, 26(3): 200-210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2021.03.002 [55] LI Pingping, DUAN Jinbao, CHENG Zhongzhen, et al. Using clumped isotopes to reconstruct the maximum burial temperature: a case study in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9: 759372. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.759372 [56] 胡安平, 沈安江, 陈亚娜, 等. 基于U-Pb同位素年龄和团簇同位素(Δ47)温度约束的四川盆地震旦系灯影组构造—埋藏史重建[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5): 896-905. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105896HU Anping, SHEN Anjiang, CHEN Yana, et al. Reconstruction of tectonic-burial evolution history of Sinian Dengying Formation in Sichuan Basin based on the constraints of in-situ laser ablation U-Pb date and clumped isotopic thermometer (Δ47)[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(5): 896-905. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202105896 [57] 沈安江, 赵文智, 胡安平, 等. 碳酸盐矿物定年和定温技术及其在川中古隆起油气成藏研究中的应用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(3): 476-487. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202103005.htmSHEN Anjiang, ZHAO Wenzhi, HU Anping, et al. The dating and temperature measurement technologies for carbonate minerals and their application in hydrocarbon accumulation research in the paleo-uplift in central Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(3): 476-487. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202103005.htm [58] 程开虎, 肖晖. 基于U—Pb定年和团簇同位素测定的古老碳酸盐岩地层热演化史恢复及成藏过程重建[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(1): 111-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202301010.htmCHENG Kaihu, XIAO Hui. Recovery of thermal evolution history and reconstruction of accumulation process of ancient carbonate strata based on U-Pb dating and cluster isotope measurement[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(1): 111-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202301010.htm [59] PAN Liyin, SHEN Anjiang, ZHAO Jianxin, et al. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology and clumped isotope constraints on the formation and evolution of an ancient dolomite reservoir: the Middle Permian of northwest Sichuan Basin (SW China)[J]. Sedimentary Geo-logy, 2020, 407: 105728. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2020.105728 [60] EILER J M. Paleoclimate reconstruction using carbonate clumped isotope thermometry[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(25/26): 3575-3588. [61] FERNANDEZ A, TANG Jianwu, ROSENHEIM B E. Siderite 'clumped' isotope thermometry: a new paleoclimate proxy for humid continental environments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochi-mica Acta, 2014, 126: 411-421. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.11.006 [62] KELE S, BREITENBACH S F M, CAPEZZUOLI E, et al. Temperature dependence of oxygen- and clumped isotope fractionation in carbonates: a study of travertines and tufas in the 6-95 ℃ temperature range[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 168: 172-192. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.06.032 [63] TRIPATI A K, HILL P S, EAGLE R A, et al. Beyondtemperature: clumped isotope signatures in dissolved inorganic carbon species and the influence of solution chemistry on carbonate mineral composition[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 166: 344-371. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.06.021 [64] TRIPATI A K, EAGLE R A, THIAGARAJAN N, et al. 13C-18O isotope signatures and 'clumped isotope' thermometry in foraminifera and coccoliths[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(20): 5697-5717. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.07.006 [65] GALLAGHER T M, SHELDON N D, MAUK J L, et al. Constraining the thermal history of the North American Midcontinent Rift System using carbonate clumped isotopes and organic thermal maturity indices[J]. Precambrian Research, 2017, 294: 53-66. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2017.03.022 [66] MANGENOT X, DEÇONINCK J F, BONIFACIE M, et al. Thermal and exhumation histories of the northern subalpine chains (Bauges and Bornes—France): evidence from forward thermal modeling coupling clay mineral diagenesis, organic maturity and carbonate clumped isotope (Δ47) data[J]. Basin Research, 2019, 31(2): 361-379. doi: 10.1111/bre.12324 [67] WATKINS J M, HUNT J D. A process-based model for non-equilibrium clumped isotope effects in carbonates[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 432: 152-165. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.09.042 [68] HERLAMBANG A, JOHN C M. Combining clumped isotope and trace element analysis to constrain potential kinetic effects in calcite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2021, 296: 117-130. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2020.12.024 [69] LLOYD M K, RYB U, EILER J M. Experimental calibration of clumped isotope reordering in dolomite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 242: 1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.08.036 -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号