Review on molecular structures of asphaltene macromolecules and instrumental analytical approaches
-
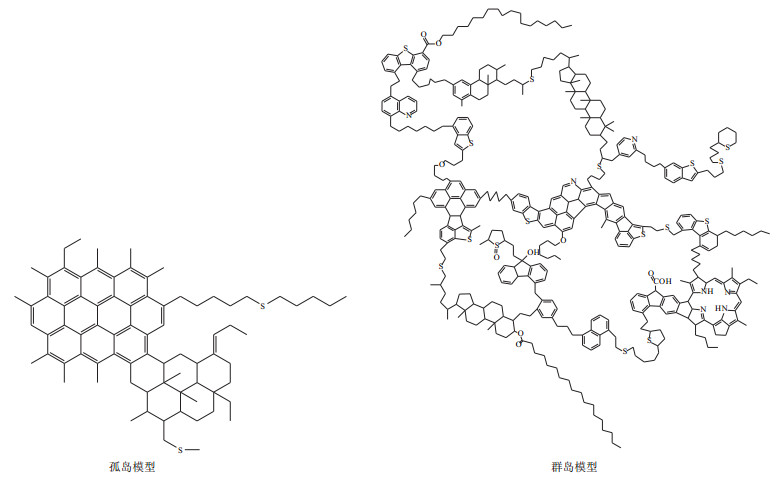
摘要: 沥青质是石油或岩石可溶有机质的重要组分之一,通常具有复杂的大分子结构和较高的分子量。沥青质中包裹(或键合)的生物标志物被认为具有重要的油气地球化学研究价值,而对沥青质大分子的实际分子量和分子结构的研究在油藏勘探开发、地球化学实验以及油品存储、运输和炼化生产等方面也具有潜在价值。对文献中报道的沥青质结构、分子量及相关的实验测定方法等开展综述,试图为沥青质的分子结构、分子量以及物理化学性质提供更加全面的认识,从而为沥青质地球化学研究在常规、非常规油藏勘探、开发研究中的应用提供基础资料。针对沥青质分子的结构及分子量方面存在的不同观点开展成果综述并结合实验测定技术的现状探讨了存在争议的主要原因,指出相关研究的下一步发展方向。目前对沥青质大分子结构的认识主要是基于两种完全不同的模型,即“孤岛”模型和“群岛”模型。前者认为沥青质具有单个芳核,表征的分子量相对较低;而后者则认为沥青质具有多个芳核,表征的分子量高。上述两种沥青质分子结构的模型均有各自的实验测定结果得以支持,其中“孤岛”模型的证据主要来自荧光光谱及激光气化/离子化质谱(L2MS)分析以及基于不同离子化方式的高分辨质谱(FT-ICR-MS)分析技术;“群岛”模型的证据主要来自气相渗透测量法、体积排阻色谱法和化学降解法等。Abstract: As one of the major fractions of petroleum and/or source rock extracts, asphaltene is commonly characte-rized by complicate molecular structures as well as relatively higher molecular weight (MW). The asphaltene occluded biomarkers have been well introduced to be valuable for geochemical research whilst the actual molecular weight and molecular structures of asphaltene macromolecules studies show value in petroleum exploration and production, laboratory treatments as well as petroleum chemical storage and transportation etc. The structure, molecular weight and related experimental measurement methods of asphaltenes reported in this paper are reviewed, in an attempt to provide a more comprehensive understanding on the molecular structure, molecular weight and physicochemical properties of asphaltenes, so as to provide basic data for applying asphaltene geochemical research in the exploration and development study of conventional and unconventional reservoirs. In view of the different views on the structure and molecular weight of asphaltene molecules, the results are reviewed, the main reasons for the controversy are discussed based on the current status of experimental measurement technology, and the future development trend of related researches is pointed out. The current understanding of the structure of asphaltene macromolecules is mainly based on two completely different models, i.e., the island model and archipelago model. The former suggests that asphaltenes have a single aromatic nucleus and the molecular weight characterized is relatively lower. The latter believes that asphaltenes have multiple aromatic nuclei and the molecular weight characterized is relatively higher. The above two models of asphaltene molecular structure are supported by their own experimental measurement results, among which the evidences of the "island" model mainly come from fluorescence spectroscopy, laser vaporization/laser ionization mass spectrometry (L2MS) analysis and stem from various ionization high-resolution (Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, FT-ICR-MS) analysis technologies. The evidences for the archipelago model mainly come from gas phase permeation measurement, size exclusion chromatography and chemical degradation.
-
Key words:
- asphaltene /
- macro-molecular structure /
- archipelago model /
- island model /
- molecular weight /
- polarity
-
图 2 沥青质单体聚合Yen-Mullins模型[2]
Figure 2. Yen-Mullins model of asphaltene monomer polymerization
-
[1] SEMPLE K M, CYR N, FEDORAK P M, et al. Characterization of asphaltenes from cold lake heavy oil: variations in chemical structure and composition with molecular size[J]. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 1990, 68(7): 1092-1099. doi: 10.1139/v90-169 [2] MULLINS O C. The asphaltenes[J]. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 4: 393-418. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-061010-113849 [3] 陶国亮, 刘鹏, 黎茂稳, 等. 塔河油田原油沥青质包裹烃地球化学特征及油源判识[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(2): 151-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201802005.htmTAO Guoliang, LIU Peng, LI Maowen, et al. Geochemical characteristics of hydrocarbons occluded in asphaltene and oil source identification in Tahe Oilfield[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(2): 151-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201802005.htm [4] WILSON R E, KEITH P C JR, HAYLETT R E. Liquid propane use in dewaxing, deasphalting, and refining heavy oils[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1936, 28(9): 1065-1078. [5] THANH N X, HSIEH M, PHILP R P. Waxes and asphaltenes in crude oils[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1999, 30(2/3): 119-132. [6] XIONG Ruiying, GUO Jixiang, KIYINGI W, et al. Asphaltene deposition under different injection gases and reservoir conditions[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2023, 194: 87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2023.03.036 [7] TANANYKHIN D S, STRUCHKOV I A, KHORMALI A, 等. 基于数值模拟研究沥青质沉积对油田开发的影响[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(5): 987-995. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202205014.htmTANANYKHIN D S, STRUCHKOV I A, KHORMALI A, et al. Investigation of the influences of asphaltene deposition on oilfield development using reservoir simulation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(5): 987-995. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202205014.htm [8] 黄梁帅, 犹佳雨, 李丹丹. 塔河油田X区块奥陶系沥青质油井防堵技术研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(S1): 52-55. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2016S1052HUANG Liangshuai, YOU Jiayu, LI Dandan. Prevention of asphaltene chokes in Ordovician oil production wells, district X, Tahe Oil Field[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(S1): 52-55. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2016S1052 [9] 高达, 张乔良, 米洪刚. 沥青质沉积对油井产能影响的模拟分析: 以南海北部湾盆地W-1油田为例[J]. 中国海上油气, 2016, 28(6): 53-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201606009.htmGAO Da, ZHANG Qiaoliang, MI Honggang. Simulation analysis of the influence of asphaltene deposition on oil well productivity: a case study of W-1 Oilfield in Beibuwan Basin of South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2016, 28(6): 53-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201606009.htm [10] 杨祖国, 王雷, 程仲富, 等. 塔河油田稠油沥青质解堵技术研究与应用[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(S1): 99-103. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2014S1099YANG Zuguo, WANG Lei, CHENG Zhongfu, et al. Dispersion and removal of asphaltene in heavy oil, Tahe Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(S1): 99-103. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2014S1099 [11] 杨小腾, 于建, 张坤, 等. 巴什托油田胶质沥青质堵塞机理及预测[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(S1): 92-94. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2014S1092YANG Xiaoteng, YU Jian, ZHANG Kun, et al. Plugging mechanism and prediction of asphaltene in Bashituo Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(S1): 92-94. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2014S1092 [12] 李二庭, 靳军, 陈亮, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘井筒堵塞物中沥青质分子组成研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(2): 306-313. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202202306LI Erting, JIN Jun, CHEN Liang, et al. Molecular composition of asphaltene in wellbore blockage on the southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(2): 306-313. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202202306 [13] FAKHER S, IMQAM A. Asphaltene precipitation and deposition during CO2 injection in nano shale pore structure and its impact on oil recovery[J]. Fuel, 2019, 237: 1029-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.10.039 [14] ELTURKI M, IMQAM A. Asphaltene precipitation and deposition during nitrogen gas cyclic miscible and immiscible injection in Eagle Ford shale and its impact on oil recovery[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2022, 36(20): 12677-12694. [15] CARBOGNANI L, ESPIDEL J. Preparative subfractionation of petroleum resins and asphaltenes. Ⅱ. Characterization of size exclusion chromatography isolated fractions[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2003, 21(11/12): 1705-1720. [16] ADAMS J J. Asphaltene adsorption, a literature review[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(5): 2831-2856. [17] 蔡新恒, 龙军, 任强, 等. 沥青质分子聚集体的聚集内因[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2019, 35(5): 920-928. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2019.05.013CAI Xinheng, LONG Jun, REN Qiang, et al. Aggregation mechanism of asphaltene molecular aggregates[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2019, 35(5): 920-928. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2019.05.013 [18] LI Jiguang, GUO Xin, SHEN Haiping, et al. The solubility of asphal-tene in organic solvents and its relation to the molecular structure[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 327: 114826. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114826 [19] STRAUSZ O P, MOJELSKY T W, FARAJI F, et al. Additional structural details on Athabasca asphaltene and their ramifications[J]. Energy & Fuels, 1999, 13(2): 207-227. [20] STRAUSZ O P, MOJELSKY T W, LOWN E M, et al. Structural features of Boscan and Duri asphaltenes[J]. Energy & Fuels, 1999, 13(2): 228-247. [21] ŠANOVI A, et al. Pyrolysis and Pt(Ⅳ)- and Ru(Ⅲ)-ion catalyzed pyrolysis of asphaltenes in organic geochemical investigation of a biodegraded crude oil (Gaj, Serbia)[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(2): 287-296. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2008.09.014 [22] SPEIGHT J G, MOSCHOPEDIS S E. On the molecular nature of petroleum asphaltenes[J]. Advances in Chemistry, 1982, 195: 1-15. [23] 张伟森, 尹洪超, 付云, 等. 渤海油田井筒沥青质沉积评价及防治研究[J]. 天然气与石油, 2023, 41(2): 106-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5539.2023.02.015ZHANG Weisen, YIN Hongchao, FU Yun, et al. Evaluation and prevention of asphaltene deposition in Bohai Oilfield wellbore[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2023, 41(2): 106-111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5539.2023.02.015 [24] 赵琳, 秦冰, 江建林. 原油沥青质沉积评价方法研究进展[J]. 油田化学, 2021, 38(4): 754-760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJHX202104030.htmZHAO Li, QIN Bing, JIANG Jianlin. Research progress on evaluation methods of asphaltene deposition in crude oil[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2021, 38(4): 754-760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJHX202104030.htm [25] 程斌, 廖泽文, 田彦宽, 等. 川西北侏罗系沙溪庙组固体沥青包裹烃的释放及其地球化学意义[J]. 地球化学, 2012, 41(5): 425-432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2012.05.006CHENG Bin, LIAO Zewen, TIAN Yankuan, et al. Release of the hydrocarbons occluded inside solid bitumen in Jurassic Shaximiao Formation of northwestern Sichuan Basin and its geochemical significance[J]. Geochimica, 2012, 41(5): 425-432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2012.05.006 [26] 吴应琴, 夏燕青, 王永莉, 等. 严重生物降解稠油沥青质包裹体中生标的研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(5): 480-483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.05.013WU Yingqin, XIA Yanqing, WANG Yongli, et al. Study on the biomarkers of asphaltene inclusions in severely biodegraded thick oil[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32(5): 480-483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.05.013 [27] LIAO Zewen, GENG Ansong. Characterization of nC7-soluble fractions of the products from mild oxidation of asphaltenes[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33(12): 1477-1486. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(02)00179-1 [28] LIAO Zewen, ZHOU Honggang, GRACIAA A, et al. Adsorption/occlusion characteristics of asphaltenes: some implication for asphaltene structural features[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2005, 19(1): 180-186. [29] LIAO Zewen, GENG Ansong, GRACIAA A, et al. Different adsorption/occlusion properties of asphaltenes associated with their secon-dary evolution processes in oil reservoirs[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2006, 20(3): 1131-1136. [30] LIAO Zewen, GENG Ansong, GRACIAA A, et al. Saturated hydrocarbons occluded inside asphaltene structures and their geochemical significance, as exemplified by two Venezuelan oils[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2006, 37(3): 291-303. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2005.10.010 [31] LIAO Zewen, GRACIAA A, GENG Ansong, et al. A new low-interference characterization method for hydrocarbons occluded inside asphaltene structures[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2006, 21(5): 833-838. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.02.005 [32] SILVA T F, AZEVEDO D A, RANGEL M D, et al. Effect of biodegradation on biomarkers released from asphaltenes[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2008, 39(8): 1249-1257. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2008.03.015 [33] TIAN Yankuan, YANG Chupeng, LIAO Zewen, et al. Geochemical quantification of mixed marine oils from Tazhong area of Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Enginee-ring, 2012, 90-91: 96-106. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2012.04.028 [34] TIAN Yankuan, ZHAO Jing, YANG Chupeng, et al. Multiple-sourced features of marine oils in the Tarim Basin, NW China: geochemical evidence from occluded hydrocarbons inside asphaltenes[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 54-55: 174-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.04.010 [35] ZHANG Zhirong, VOLKMAN J K, XIE Xiaomin, et al. Stepwise pyrolysis of the kerogen from the Huadian oil shale, NE China: algaenan-derived hydrocarbons and mid-chain ketones[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2016, 91: 89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2015.10.011 [36] 熊永强, 耿安松, 王春江, 等. 实验温度对沥青质热解的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2000, 22(1): 85-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2000.01.017XIONG Yongqiang, GENG Ansong, WANG Chunjiang, et al. The effect of temperature on pyrolysis of asphaltenes[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2000, 22(1): 85-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2000.01.017 [37] BURDELNAYA N S, BORISOVA L S, BUSHNEV D A, et al. Geochemical significance of the molecular and supramolecular structures of asphaltenes (a review)[J]. Petroleum Chemistry, 2023, 63(1): 31-51. doi: 10.1134/S0965544123020172 [38] SNOWDON L R, VOLKMAN J K, ZHANG Zhirong, et al. The organic geochemistry of asphaltenes and occluded biomarkers[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2016, 91: 3-15. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2015.11.005 [39] YEN T F, ERDMAN J G, POLLACK S S. Investigation of the structure of petroleum asphaltenes by x-ray diffraction[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1961, 33(11): 1587-1594. doi: 10.1021/ac60179a039 [40] DICKIE J P, YEN T F. Macrostructures of the asphaltic fractions by various instrumental methods[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 1967, 39(14): 1847-1852. doi: 10.1021/ac50157a057 [41] WU Qinghao, POMERANTZ A E, MULLINS O C, et al. Laser-based mass spectrometric determination of aggregation numbers for petroleum- and coal-derived asphaltenes[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(1): 475-482. [42] ZHANG Liyan, XU Zhenghe, MASLIYAH J H. Langmuir and Langmuir-Blodgett films of mixed asphaltene and a demulsifier[J]. Langmuir, 2003, 19(23): 9730-9741. doi: 10.1021/la034894n [43] ANDREATTA G, GONCALVES C C, BUFFIN G, et al. Nanoaggregates and structure-function relations in asphaltenes[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2005, 19(4): 1282-1289. [44] BETANCOURT S S, VENTURA G T, POMERANTZ A E, et al. Nanoaggregates of asphaltenes in a reservoir crude oil and reservoir connectivity[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2009, 23(3): 1178-1188. [45] AGUILERA-MERCADO B, HERDES C, MURGICH J, et al. Mesoscopic simulation of aggregation of asphaltene and resin molecules in crude oils[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2006, 20(1): 327-338. [46] ACEVEDO S, CASTRO A, NEGRIN J G, et al. Relations between asphaltene structures and their physical and chemical properties: the rosary-type structure[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2007, 21(4): 2165-2175. [47] MURGICH J, ABANERO J A, STRAUSZ O P. Molecular recognition in aggregates formed by asphaltene and resin molecules from the Athabasca oil sand[J]. Energy & Fuels, 1999, 13(2): 278-286. [48] GRAY M R, CHACÓN-PATIÑO M L, RODGERS R P. Structure-reactivity relationships for petroleum asphaltenes[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2022, 36(8): 4370-4380. [49] HOSSEINI-DASTGERDI Z, TABATABAEI-NEJAD S A R, KHO-DAPANAH E, et al. A comprehensive study on mechanism of formation and techniques to diagnose asphaltene structure; molecular and aggregates: a review[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2015, 10(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1002/apj.1836 [50] 刘必心, 龙军. 沥青质对塔河稠油黏度的影响机理研究[J]. 中国科学(化学), 2018, 48(4): 434-441. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK201804011.htmLIU Bixin, LONG Jun. The mechanism of how asphaltene affects the viscosity of Tahe heavy oil[J]. Scientia Sinica (Chimica), 2018, 48(4): 434-441. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK201804011.htm [51] GROENZIN H, MULLINS O C. Asphaltene molecular size and structure[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 1999, 103(50): 11237-11245. doi: 10.1021/jp992609w [52] SPEIGHT J G. Petroleum asphaltenes-part 1: asphaltenes, resins and the structure of petroleum[J]. Oil & Gas Science and Technology, 2004, 59(5): 467-477. [53] BERGMANN U, MULLINS O C, CRAMER S P. X-ray raman spectroscopy of carbon in asphaltene: light element characte-rization with bulk sensitivity[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2000, 72(11): 2609-2612. doi: 10.1021/ac990730t [54] STRAUSZ O P, PENG Ping'an, MURGICH J. About the colloidal nature of asphaltenes and the mw of covalent monomeric units[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2002, 16(4): 809-822. [55] GRAY M R, TYKWINSKI R R, STRYKER J M, et al. Supramolecular assembly model for aggregation of petroleum asphaltenes[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2011, 25(7): 3125-3134. [56] 张文, 龙军, 任强, 等. 沥青质分子聚集行为研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(5): 2158-2163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJZ201905011.htmZHANG Wen, LONG Jun, REN Qiang, et al. Research progress on aggregation behavior of asphaltene[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(5): 2158-2163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJZ201905011.htm [57] DERAKHSHESH M, GRAY M R, DECHAINE G P. Dispersion of asphaltene nanoaggregates and the role of Rayleigh scattering in the absorption of visible electromagnetic radiation by these nanoaggregates[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(2): 680-693. [58] HURT M R, BORTON D J, CHOI H J, et al. Comparison of the structures of molecules in coal and petroleum asphaltenes by using mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(7): 3653-3658. [59] LV Jinghui, WEI Xianyong, QING Yu, et al. Insight into the structural features of macromolecular aromatic species in Huolinguole lignite through ruthenium ion-catalyzed oxidation[J]. Fuel, 2014, 128: 231-239. [60] ZHU Yonghong, DU Chongpeng, ZHENG Huaan, et al. Molecular representation of coal-derived asphaltene based on high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 2022, 15(1): 103531. [61] 张庆, 邓文安, 李传, 等. 稠油沥青质的基本化学组成结构与缔合性研究[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2014, 45(6): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYLH201406007.htmZHANG Qing, DENG Wenan, LI Chuan, et al. Study on basic chemical structure and association of asphaltene in heavy oil[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2014, 45(6): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYLH201406007.htm [62] GROENZIN H, MULLINS O C. Molecular size and structure of asphaltenes from various sources[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2000, 14(3): 677-684. [63] ANDREATTA G, BOSTROM N, MULLINS O C. High-Q ultrasonic determination of the critical nanoaggregate concentration of asphaltenes and the critical micelle concentration of standard surfactants[J]. Langmuir, 2005, 21(7): 2728-2736. [64] 廖泽文, 耿安松. 沥青质傅里叶变换红外光谱(FT IR)分析及其在有机地球化学研究中的应用[J]. 地球化学, 2001, 30(5): 433-438. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200105003.htmLIAO Zewen, GENG Ansong. Characterization of FT IR analysis of asphaltenes and its geochemical implications[J]. Geochimica, 2001, 30(5): 433-438. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200105003.htm [65] 刘鹏, 黎茂稳, 孙永革, 等. 加拿大油砂沥青中极性化合物的电喷雾—高分辨质谱研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(1): 89-94, 101. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201401089LIU Peng, LI Maowen, SUN Yongge et al. Molecular characte-rization of polar species in Canadian oil sand bitumens by electrospray ionization and high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(1): 89-94, 101. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201401089 [66] PAN Yinhua, LIAO Yuhong, SHI Quan, et al. Acidic and neutral polar NSO compounds in heavily biodegraded oils characterized by negative-ion ESI FT-ICR MS[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(6): 2960-2973. [67] GASPAR A, ZELLERMANN E, LABABIDI S, et al. Characte-rization of saturates, aromatics, resins, and asphaltenes heavy crude oil fractions by atmospheric pressure laser ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2012, 26(6): 3481-3487. [68] PEREIRA T M C, VANINI G, OLIVEIRA E C S, et al. An eva-luation of the aromaticity of asphaltenes using atmospheric pressure photoionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry - APPI(±)FT-ICR MS[J]. Fuel, 2014, 118: 348-357. [69] ZHANG Yahe, ZHANG Linzhou, XU Zhiming, et al. Molecular characterization of vacuum resid and its fractions by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry with various ionization techniques[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(12): 7448-7456. [70] ROGEL E, MOIR M, WITT M. Atmospheric pressure photoionization and laser desorption ionization coupled to Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry to characterize asphaltene solubility fractions: studying the link between mole-cular composition and physical behavior[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2015, 29(7): 4201-4209. [71] PEREIRA T M C, VANINI G, TOSE L V, et al. FT-ICR MS analysis of asphaltenes: asphaltenes go in, fullerenes come out[J]. Fuel, 2014, 131: 49-58. [72] SABBAH H, POMERANTZ A E, WAGNER M, et al. Laser desorption single-photon ionization of asphaltenes: mass range, compound sensitivity, and matrix effects[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2012, 26(6): 3521-3526. [73] FONSECA V R, FOLLI G S, SOUZA L M, et al. Optimisation of LDI(+)-FT-ICR MS analysis of asphaltenes to prevent the formation of fullerenes[J]. Fuel, 2023, 347: 128451. [74] POMERANTZ A E, HAMMOND M R, MORROW A L, et al. Two-step laser mass spectrometry of asphaltenes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008, 130(23): 7216-7217. [75] POMERANTZ A E, HAMMOND M R, MORROW A L, et al. Aspha-ltene molecular-mass distribution determined by two-step laser mass spectrometry[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2009, 23(3): 1162-1168. [76] SABBAH H, MORROW A L, POMERANTZ A E, et al. Evidence for island structures as the dominant architecture of asphaltenes[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2011, 25(4): 1597-1604. [77] ELKHATIB O, ZHANG Bingjun, GOUAL L. New insights into asphaltene structure and aggregation by high-resolution microscopy[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2022, 36(16): 8692-8700. -





 下载:
下载:


 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号