Micro characteristics and formation mechanism of low-quality gas reservoirs in Taiyuan Formation of Shenmu Gas Field, Ordos Basin
-
摘要: 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田与周边气田开发效果差异较大,表现出低品质气藏特征,给气田勘探部署及持续稳产带来一定困扰。为了揭示低品质气藏成因,基于不同尺度微观实验手段,对神木气田太原组储层开展了微观特征及形成机理研究。结果表明,神木气田太原组储层具有“富石英、贫长石、岩屑含量较高”的特征,发育小孔—细喉型孔喉组合,孔喉连通性较差,储渗能力较弱,为低孔—超低渗致密砂岩储层;太原组低品质储层的形成受杂基、喷发岩岩屑含量及成岩作用的共同影响。储层在形成过程中,受晚石炭世—早二叠世鄂尔多斯盆地北部内蒙古古隆起火山活动的影响明显,砂岩内喷发岩岩屑和杂基含量普遍较高,喷发岩岩屑为次生孔隙的发育提供了主要物质基础,杂基在堵塞孔隙的同时也产生了一定数量杂基溶孔,对储层的影响具有双重性。成岩过程中的溶蚀作用对于太原组储层的形成至关重要,增孔效应占现今孔隙度的64.3%。晚白垩世末期,燕山运动末幕导致鄂尔多斯盆地构造反转,气水重新调整,盆地东部天然气沿断裂部分逸散,最终形成了现今神木气田太原组的低品质气藏。神木气田下一步勘探重点应在摸清成岩作用宏观展布规律及有利岩性圈闭的基础上,寻找高含量喷发岩岩屑和低含量杂基的发育区。Abstract: Shenmu Gas Field in Ordos Basin shows the characteristics of low quality gas reservoir, and its deve-lopment effect is quite different from that of surrounding gas fields, which brings some problems to the exploration deployment and sustainable production of the gas field. In order to reveal the origin of low-quality gas reservoirs, the microscopic characteristics and formation mechanism of Taiyuan Formation reservoirs in Shenmu Gas Field were studied based on microscopic experiments at different scales. The results show that the reservoir of Taiyuan Formation in Shenmu Gas Field is characterized by "rich in quartz, poor in feldspar, and high content of rock detritus". The reservoir of Taiyuan Formation is a low porosity and ultra-low permeability tight sandstone reservoir with small pore-fine throat combination, poor pore throat connectivity, and weak reservoir permeability. The formation of low-quality reservoirs in Taiyuan Formation is affected by the matrix, the content of rock detritus in eruptive rocks and diagenesis. During the late Carboniferous to early Permian, the formation of the reservoir was significantly affected by the volcanic activity of the Inner Mongolia ancient uplift in the north of the Ordos Basin. The content of matrix and rock detritus of the eruptive rock in the sandstone was generally high. The rock detritus of the eruptive rock provided the main material basis for the development of secondary pores. While the matrix blocked the pores, it also produced a certain number of matrix dissolved pores, which had a dual impact on the reservoir. The dissolution during diagenesis is critical to the formation of Taiyuan Formation reservoir, and the increased porosity accounts for 64.3% of the current porosity. At the end of the Late Cretaceous, the late Yanshan movement led to the structural inversion of the Ordos Basin, the readjustment of gas and water, and the escape of natural gas along the fault in the eastern part of the basin. Finally, the low quality gas reservoir of Taiyuan Formation in Shenmu Gas Field is formed. The next exploration focus of Shenmu Gas Field should be based on the clear macro distribution law of diagenesis and favorable lithologic traps, and further search for the development area with high content of eruptive rock detritus and low content of matrix.
-
Key words:
- diagenesis /
- pore throat structure /
- tuffaceous matrix /
- structural inversion /
- Taiyuan Formation /
- Shenmu Gas Field /
- Ordos Basin
-
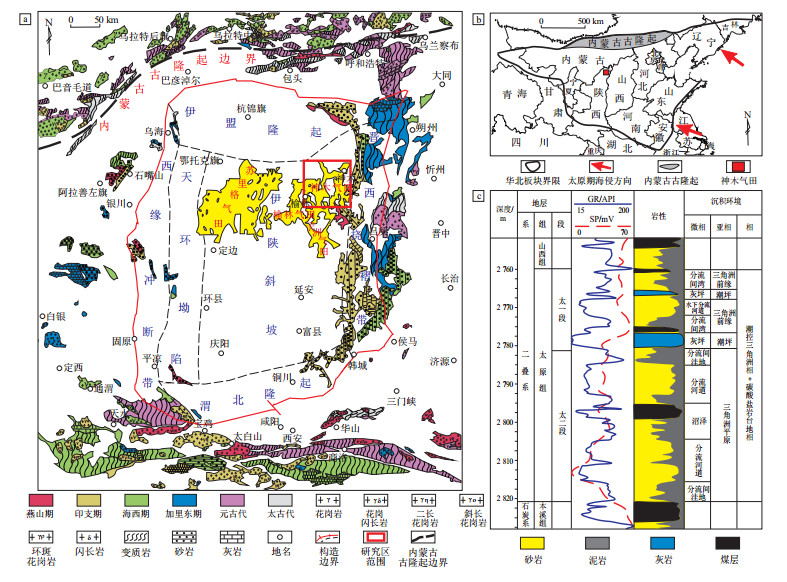
图 1 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田构造位置及地层柱状图
a.构造位置及周边物源岩性分布;b.太原期古构造背景[26];c.太原组地层综合柱状图
Figure 1. Structural location and stratigraphic column of Shenmu Gas Field in Ordos Basin
图 3 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田太原组储层微观特征
a.毛发状伊利石及晶间孔,S108,2 192.5 m,扫描电镜;b.书页状高岭石及晶间孔,S108,2 192.5m,扫描电镜;c.铁白云石与伊利石胶结物,S175,2 412.0 m,扫描电镜;d.菱铁矿胶结物,S131,2 699.5 m,QEMSCAN;e.岩石矿物及孔隙分布特征,S131,2 699.5 m,QEMSCAN;f.硅质胶结发育,S131,2 701.1 m,铸体薄片;g.黄铁矿胶结物,S150,2 377.6 m,扫描电镜;h.棕黄色凝灰质杂基充填孔隙,S75,2 099.7 m,铸体薄片;i.杂基溶孔及高岭石晶间孔,S75,2 097.6 m,铸体薄片;j.喉道及杂基溶孔特征,S108,2 192.5 m,铸体薄片;k.杂基混杂堆积,无固定晶形,S75,2 099.7 m,扫描电镜;l.伊利石胶结物与单晶石英共生,S107,2 075.5 m,扫描电镜;m.喷发岩岩屑溶孔及残余斑晶,S20,1 982.6 m,铸体薄片;n.杂基蚀变形成高岭石晶间孔及岩屑溶孔,S107,2 075.5 m,铸体薄片;o.片状喉道及杂基溶孔特征,S150,2 377.6 m,铸体薄片;p.残余粒间孔,S20,1 989.9 m,扫描电镜。
Figure 3. Microscopic characteristics of Taiyuan Formation reservoir in Shenmu Gas Field, Ordos Basin
表 1 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田太原组储层填隙物统计
Table 1. Statistics of reservoir interstitials in Taiyuan Formation of Shenmu Gas Field in Ordos Basin
样品编号 深度/m 碎屑颗粒/% 填隙物/% 胶结物/% 杂基/% 黏土矿物 碳酸盐矿物 泥铁质 硅质 黄铁矿 其他 伊利石 高岭石 绿泥石 铁方石 铁白石 白云石 菱铁矿 S20 1 981.8 81.8 18.2 5.0 1.0 0.5 0.5 0.0 0.2 1.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 8.0 S20 1 989.2 75.5 24.5 6.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.5 0.0 7.0 2.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 7.5 SH83 2 455.2 84.0 16.0 7.0 0.5 0.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 4.0 1.0 0.5 1.0 0.0 0.0 S75 2 097.2 70.5 29.5 9.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 4.0 0.0 0.0 0.5 2.0 0.0 0.0 12.0 S75 2 098.0 67.8 32.2 15.0 1.0 0.0 0.2 5.0 1.0 2.0 5.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 3.0 S131 2 699.5 60.4 39.6 11.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 4.0 0.0 7.0 0.0 1.0 0.5 0.1 15.0 SH153 2 482.0 78.5 21.5 12.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 3.0 0.5 0.0 2.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 SH153 2 473.9 83.0 17.0 8.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 6.0 S107 2 076.3 76.5 23.5 7.5 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.5 0.0 1.5 3.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 9.0 S108 2 195.7 73.0 27.0 10.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 0.5 1.0 0.0 0.5 1.0 0.0 12.0 S108 2 202.8 79.8 20.2 8.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 3.0 0.5 0.0 0.2 8.5 S108 2 187.5 73.0 27.0 10.0 0.5 0.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 0.5 0.0 0.5 0.5 0.0 13.0 SH175 2 414.0 77.8 22.2 8.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 0.0 0.2 0.0 2.0 4.0 0.0 0.0 6.0 SH175 2 406.0 81.0 19.0 12.0 0.0 0.5 0.0 2.5 0.0 3.0 0.0 0.5 0.5 0.0 0.0 SH175 2 411.0 86.0 14.0 6.0 2.5 0.2 0.8 0.0 0.5 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 2.0 平均含量/% 76.4 23.6 9.0 0.7 0.1 0.3 1.7 0.2 1.9 1.3 1.1 0.3 0.1 6.8 表 2 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田太原组砂岩孔隙演化定量计算方法
Table 2. Quantitative calculation method for pore evolution of sandstone in Taiyuan Formation of Shenmu Gas Field in Ordos Basin
孔隙恢复 孔隙演化定量计算公式 原始孔隙度Φ1 Φ1= 20.91 +(22.9/ S0),式中:S0为Trask分选系数,S0=(Q1/ Q3)1/2,其中Q1、Q3为粒度概率累计曲线25%和75%处的粒径大小 压实作用后剩余孔隙度Φ2 Φ2=(粒间孔面孔率+填隙物溶孔面孔率)×物性分析孔隙度/总面孔率+填隙物含量 胶结作用后剩余孔隙度Φ3 Φ3=粒间孔面孔率×物性分析孔隙度/总面孔率 溶蚀作用增加孔隙度Φ4 Φ4=溶蚀孔面孔率×物性分析孔隙度/总面孔率 计算目前孔隙度Φ5 Φ5 = Φ3 + Φ4 误差δ δ=(计算目前孔隙度-实测物性孔隙度)/实测物性孔隙度 注:公式来源参见参考文献[31-33]。 表 3 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田太原组储层孔隙演化统计
Table 3. Reservoir pore evolution statistics of Taiyuan Formation in Shenmu Gas Field, Ordos Basin
样品号 原始孔隙度Φ1/% 杂基充填残余孔隙/% 压实作用后剩余孔隙度Φ2/% 胶结作用剩余孔隙度Φ3/% 溶蚀作用增加孔隙度Φ4/% 计算现今孔隙度Φ5/% 实测现今孔隙度/% 误差δ/% S3-1 37.8 31.1 13.2 2.3 4.5 6.8 7.1 -4.2 S3-2 38.2 30.3 12.3 1.9 3.6 5.5 5.7 -3.5 S102-1 36.5 28.2 11.5 3.6 5.3 8.9 8.5 4.7 S102-2 37.2 26.6 14.2 4.2 6.8 11.0 10.6 3.8 S30-1 34.5 29.2 10.3 2.5 7.1 9.6 9.3 3.2 S30-2 33.2 28.4 14.8 2.9 3.8 6.7 6.8 -1.5 S102-1 37.6 28.0 18.2 2.7 5.5 8.2 8.6 -4.7 S102-2 34.1 29.5 12.8 3.6 6.9 10.5 10.5 0.0 SH15-1 35.9 27.0 14.1 4.1 4.8 8.9 9.1 -2.2 SH15-2 38.6 29.1 16.3 2.8 6.8 9.6 9.3 3.2 SH8-1 36.9 30.8 12.6 1.7 6.1 7.8 7.9 -1.3 SH8-2 37.8 33.0 16.3 2.3 5.8 8.1 8.0 1.3 SH8-3 36.1 26.4 15.4 4.6 4.1 8.7 8.7 0.0 SH44-1 38.2 32.5 13.9 5.1 2.9 8.0 7.6 5.3 SH44-2 37.6 31.4 9.6 2.3 3.8 6.1 6.3 -3.2 SH49-1 37.3 33.2 15.2 1.9 6.8 8.7 8.4 3.6 SH49-2 34.1 27.9 14.6 3.3 7.1 10.4 10.1 3.0 SH49-3 35.3 31.5 13.6 2.1 5.8 7.9 7.6 3.9 平均/范围 36.5 29.7 13.8 3.0 5.4 8.4 8.3 -4.7~5.3 -
[1] 田昌炳, 罗凯, 朱怡翔. 低效气藏资源特征及高效开发战略思考[J]. 天然气工业, 2004, 24(1): 4-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2004.01.002TIAN Changbing, LUO Kai, ZHU Yixiang. Resources characte-ristics of low beneficial gas reservoirs and strategic thoughts of high profitable development[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2004, 24(1): 4-6. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0976.2004.01.002 [2] 田昌炳, 于兴河, 徐安娜, 等. 我国低效气藏的地质特征及其成因特点[J]. 石油实验地质, 2003, 25(3): 235-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2003.03.002TIAN Changbing, YU Xinghe, XU Anna, et al. Geological characte-ristics and origin peculiarities of low efficiency gas reservoirs in China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2003, 25(3): 235-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2003.03.002 [3] 蒙晓灵, 张宏波, 刘志军, 等. 神木气田太原组气藏开发低效性主控因素[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 27(1): 7-10.MENG Xiaoling, ZHANG Hongbo, LIU Zhijun, et al. Dominant factors of the low-efficiency development of the gas reservoir in Taiyuan Formation in Shenmu Gasfield[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 27(1): 7-10. [4] 蒙晓灵, 张宏波, 冯强汉, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田二叠系太原组天然气成藏条件[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(1): 37-41.MENG Xiaoling, ZHANG Hongbo, FENG Qianghan, et al. Gas accumulation conditions of the Permian Taiyuan Formation in Shenmu Gas Field, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2013, 34(1): 37-41. [5] 孙靖, 尤新才, 张全, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖地区深层致密砾岩储层发育特征及成因[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2023, 34(2): 240-252.SUN Jing, YOU Xincai, ZHANG Quan, et al. Development characteristics and genesis of deep tight conglomerate reservoirs of Mahu area in Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 34(2): 240-252. [6] 屈凯旋, 郭少斌. 南华北盆地太康隆起太原组砂岩储层致密成因及天然气充注特征[J]. 石油科学通报, 2022, 7(3): 294-308.QU Kaixuan, GUO Shaobin. Tightening genesis and gas charging characteristics of the Taiyuan Formation sandstone reservoir in the Taikang uplift, southern North China Basin[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2022, 7(3): 294-308. [7] 王小娟, 洪海涛, 吴长江, 等. 四川盆地川中地区侏罗系沙溪庙组致密砂岩储层特征及成因[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2022, 52(4): 1037-1051.WANG Xiaojuan, HONG Haitao, WU Changjiang, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanisms of tight sandstone reservoirs in Jurassic Shaximiao Formation, central of Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2022, 52(4): 1037-1051. [8] 徐宁宁, 张守鹏, 王永诗, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部二叠系下石盒子组致密砂岩成岩作用及孔隙成因[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(2): 422-434.XU Ningning, ZHANG Shoupeng, WANG Yongshi, et al. Diagenesis and pore formation of the Upper Paleozoic tight sandstone in the northern area of the Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(2): 422-434. [9] 曹尚, 李树同, 党海龙, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部长7段页岩孔隙特征及其控制因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(1): 11-17.CAO Shang, LI Shutong, DANG Hailong, et al. Pore characteristics and controlling factors of Chang 7 shale in southeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(1): 11-17. [10] 付强, 肖冬生. 胜北洼陷三间房组致密砂岩气藏有利储层特征与成岩相[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(1): 9-16.FU Qiang, XIAO Dongsheng. Favorable reservoir characteristics and diagenetic facies of tight sandstone gas reservoir of Sanjianfang Formation in Shengbei Subsag[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2023, 30(1): 9-16. [11] 罗腾跃, 米乃哲, 王念喜, 等. 延145—延128井区致密储层单砂体分布特征及开发潜力[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(3): 43-49.LUO Tengyue, MI Naizhe, WANG Nianxi, et al. Distribution characteristics and development potential of single sand bodies in tight reservoirs in well blocks Yan 145-Yan 128, Yangtze region[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(3): 43-49. [12] 高照普. 鄂尔多斯盆地北缘什股壕气区盒2+3段沉积微相及其含气性研究[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2022, 12(2): 292-301.GAO Zhaopu. Sedimentary micro-facies and gas bearing property of He2+3 Member in Shiguhao gas area, northern margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2022, 12(2): 292-301. [13] 吴云飞, 刘成林, 冯小龙, 等. 致密砂岩储层微观结构特征及分类评价: 以鄂尔多斯盆地南梁油田长9储层为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(2): 246-253.WU Yunfei, LIU Chenglin, FENG Xiaolong, et al. Microstructural characteristics and classification evaluation of tight sandstone reservoirs: a case study of the Chang 9 reservoir in the Nanliang Oilfield of the Ordos Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2023, 30(2): 246-253. [14] 杜贵超, 杨兆林, 尹洪荣, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部长73段泥页岩储层有机质发育特征及富集模式[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(6): 1-11.DU Guichao, YANG Zhaolin, YIN Hongrong, et al. Developmental characteristics of organic matter and its enrichment model in shale reservoirs of Chang73 Member in Yanchang Formation of southeast Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(6): 1-11. [15] 段志强, 夏辉, 王龙, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地庆阳气田山1段储集层特征及控制因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(3): 285-293.DUAN Zhiqiang, XIA Hui, WANG Long, et al. Reservoir characteristics and controlling factors of Shan 1 member in Qingyang gas field, Ordos Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(3): 285-293. [16] 兰朝利, 张君峰, 陶维祥, 等. 神木气田石千峰组储层沉积微相与成岩作用[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 26(1): 28-33.LAN Chaoli, ZHANG Junfeng, TAO Weixiang, et al. Study on sedimentary micro-facies and diageneses of Shiqianfeng Formation, Shenmu Gasfield, northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 26(1): 28-33. [17] 兰朝利, 张永忠, 张君峰, 等. 神木气田太原组储层特征及其控制因素[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 25(1): 7-11.LAN Chaoli, ZHANG Yongzhong, ZHANG Junfeng, et al. Reservoir characteristics of Upper Carboniferous Taiyuan Formation in Shenmu Gasfield and their controlling factors[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 25(1): 7-11. [18] 彭磊, 石磊, 朱玉杰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东部神木地区太原组微观储层特征及其产能影响因素分析[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 58(4): 451-457.PENG Lei, SHI Lei, ZHU Yujie, et al. Micropore structure and impact factors of the productivity of the Taiyuan Formation in Shenmu area, eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2022, 58(4): 451-457. [19] 仇明慧. 神木地区双三区块储渗单元评价[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2019.QIU Minghui. Evaluation of reservoir-permeability unit of Shuang3 block in Shenmu area[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University, 2019. [20] 李浩. 鄂尔多斯盆地古生界气藏成藏模式及优势储层预测[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(2): 57-63.LI Hao. Accumulation pattern and favorable reservoir prediction of Paleozoic gas reservoirs in Ordos Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(2): 57-63. [21] 赵子丹, 乔向阳, 周进松, 等. 砂岩储层致密化及其与油气充注成藏的耦合关系: 以鄂尔多斯盆地延安气田上古生界为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(3): 363-371.ZHAO Zidan, QIAO Xiangyang, ZHOU Jinsong, et al. The densification of sandstone reservoir and its coupling relationship with hydrocarbon charging and accumulation: a case study of the Upper Paleozoic in Yan'an Gas Field, Ordos Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2023, 30(3): 363-371. [22] 李芙蓉, 刘文汇, 王晓锋, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地古生界天然气地球化学特征与成因[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 809-820. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304809LI Furong, LIU Wenhui, WANG Xiaofeng, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of Paleozoic natural gas in the Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 809-820. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304809 [23] 徐延勇, 申建, 张兵, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中东部上古生界致密气成藏条件差异性分析[J]. 断块油气田, 2022, 29(5): 577-583.XU Yanyong, SHEN Jian, ZHANG Bing, et al. Analysis on differences of tight gas accumulation conditions of Upper Paleozoic in central and eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2022, 29(5): 577-583. [24] 单俊峰, 吴炳伟, 金科, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地宜川—黄龙地区上古生界储层特征及其对天然气成藏的影响[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(6): 29-38.SHAN Junfeng, WU Bingwei, JIN Ke, et al. Characteristics of Upper Paleozoic reservoirs and its influence on natural gas accumulation in Yichuan-Huanglong area, Ordos Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reserviors, 2022, 29(6): 29-38. [25] 杨涛. 神木—双山地区太原组储层砂岩成岩作用演化及其成藏特征研究[D]. 荆州: 长安大学, 2010.YANG Tao. Research on diagenetic evolution of sandstone reservoirs and gas accumulation of Taiyuan Formation in Shenmu-Shuangshan area[D]. Jingzhou: Chang'an University, 2010. [26] 申博恒, 沈树忠, 吴琼, 等. 华北板块石炭纪—二叠纪地层时间框架[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2022, 52(7): 1181-1212.SHEN Boheng, SHEN Shuzhong, WU Qiong, et al. Time frame of Carboniferan-Permian strata in North China Plate[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2022, 52(7): 1181-1212. [27] 朱筱敏. 沉积岩石学[M]. 4版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008.ZHU Xiaomin. Sedimentary petrology[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008. [28] 陈朝兵, 赵振宇, 付玲, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区延长组6段深水致密砂岩填隙物特征及对储层发育的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(5): 1098-1111.CHEN Zhaobing, ZHAO Zhenyu, FU Ling, et al. Interstitial matter and its impact on reservoir development in Chang 6 deepwater tight sandstone in Huaqing area, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(5): 1098-1111. [29] 吕大炜, 高志武, 李增学, 等. 华北石炭—二叠系火山事件沉积研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(2): 9-18.LÜ Dawei, GAO Zhiwu, LI Zengxue, et al. Study progress on volcanic event deposits of Permo-Carboniferous in North China[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(2): 9-18. [30] 李道品. 低渗透砂岩油田开发[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997.LI Daopin. The development of the low permeability sandstone oil field[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1997. [31] 刘金, 王剑, 张宝真, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组微—纳米孔隙页岩油原位赋存特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(2): 270-278. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202202270LIU Jin, WANG Jian, ZHANG Baozhen, et al. In situ occurrence of shale oil in micro-nano pores in Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(2): 270-278. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202202270 [32] GOU Qiyang, XU Shang, HAO Fang, et al. Full-scale pores and micro-fractures characterization using FE-SEM, gas adsorption, nano-CT and micro-CT: a case study of the Silurian Longmaxi Formation shale in the Fuling area, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Fuel, 2019, 253: 167-179. [33] LI Changzhi, WANG Haihong, WANG Lianguo, et al. Characteristics of tight oil sandstone reservoirs: a case study from the Upper Triassic Chang 7 member in Zhenyuan area, Ordos Basin, China[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2020, 13(2): 78. [34] YANG Bo, QU Hongjun, PU Renhai, et al. Controlling effects of tight reservoir micropore structures on seepage ability: a case study of the Upper Paleozoic of the eastern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2020, 94(2): 322-336. [35] 王剑, 周路, 靳军, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油储层孔隙结构、烃类赋存及其与可动性关系[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(6): 941-948. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202106941WANG Jian, ZHOU Lu, JIN Jun, et al. Pore structure, hydrocarbon occurrence and their relationship with shale oil production in Lucaogou Formation of Jimsar Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(6): 941-948. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202106941 [36] 吴琼. 中国和北美二叠纪高精度火山灰锆石U-Pb年代学研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2020.WU Qiong. High-precision zircon U-Pb geochronological studies of the Permian ash beds from China and North America[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2020. [37] 桑树勋, 刘焕杰, 贾玉如. 华北中部太原组火山事件层与煤岩层对比: 火山事件层的沉积学研究与展布规律(Ⅰ)[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 1999, 28(1): 46-49.SANG Shuxun, LIU Huanjie, JIA Yuru. Volcanic event strata and correlation of coals and rocks of Taiyuan Formation in central North China: sedimentary study of volcanic event strata and their distribution(Ⅰ)[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 1999, 28(1): 46-49. [38] 周安朝. 华北地块北缘晚古生代盆地演化及盆山耦合关系[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2000.ZHOU Anchao. The evolution of Late Paleozoic Basins in north margin of North China block and the coupling relationship between basin and range[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2000. [39] 张拴宏, 赵越, 刘建民, 等. 华北地块北缘晚古生代: 早中生代岩浆活动期次、特征及构造背景[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 824-842.ZHANG Shuanhong, ZHAO Yue, LIU Jianmin, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry and tectonic setting of the Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic magmatism in the northern margin of the North China Block: a preliminary review[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2010, 29(6): 824-842. [40] LI Yong, GAO Xiangdong, MENG Shangzhi, et al. Diagenetic sequences of continuously deposited tight sandstones in various environments: a case study from Upper Paleozoic sandstones in the Linxing area, eastern Ordos Basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2019, 103(11): 2757-2783. [41] REN Xiaoxia, LI Aifen, FU Shuaishi, et al. Influence of micro-pore structure in tight sandstone reservoir on the seepage and water-drive producing mechanism: a case study from Chang 6 reservoir in Huaqing area of Ordos Basin[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2019, 7(3): 741-753. [42] 习丽英. 神木气田储层评价及井位优化部署[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2015.XI Liying. Reservoir evaluation & well location optimal deployment of Shenmu Gas Field[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Shiyou University, 2015. [43] 郭正权, 潘令红, 刘显阳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗系古地貌油田形成条件与分布规律[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2001, 6(4): 20-27.GUO Zhengquan, PAN Linghong, LIU Xianyang, et al. Formation conditions and distribution of Jurassic paleogeomorphic oil fields in Ordos Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2001, 6(4): 20-27. [44] 张涵冰. 深埋藏致密砂岩储层成因机理及评价: 以塔中地区志留系柯坪塔格组为例[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2017.ZHANG Hanbing. Genetic mechanism for deep buried tight sandstone reservoir and its evolution: a case study of Silurian Kepingtage Formation in Tazhong area[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2017. [45] 雒斌, 孙卫, 陶荣德, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地马岭地区长81储层成岩作用及孔隙度定量演化[J]. 地质与勘探, 2019, 55(1): 223-230.LUO Bin, SUN Wei, TAO Rongde, et al. Diagenesis and quantitative evolution of porosity in the Chang 81 reservoir in the Maling area, Ordos Basin[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2019, 55(1): 223-230. [46] 刘闯. 鄂尔多斯盆地临兴地区上古生界砂岩储层致密与成藏耦合关系[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2019.LIU Chuang. The coupling relationship between densification and accumulation of tight sandstones for the Upper Paleozoic formation in Linxing area, Ordos Basin[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2019. [47] 米敬奎. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界天然气藏的运聚特征[D]. 广州: 中国科学院研究生院(广州地球化学研究所), 2003.MI Jingkui. The migration and accumulation characters of the Upper Paleozoic gas reservoir in Ordos Basin[D]. Guangzhou: Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry), 2003. [48] 陈朝兵, 杨友运, 邵金辉, 等. 鄂尔多斯东北部致密砂岩气藏地层水成因及分布规律[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(2): 313-325.CHEN Zhaobing, YANG Youyun, SHAO Jinhui, et al. Origin and distribution of formation water in tight sandstone reservoirs in the northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(2): 313-325. [49] 杨华, 刘新社, 闫小雄, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地神木气田的发现与天然气成藏地质特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2015, 35(6): 1-13.YANG Hua, LIU Xinshe, YAN Xiaoxiong, et al. The Shenmu Gas Field in the Ordos Basin: its discovery and reservoir-forming geological characteristics[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2015, 35(6): 1-13. -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号