Reservoir-forming rules and main controlling factors of Archean buried hill reservoir of middle to northern Liaoxi Uplift in Liaodong Bay area in Bohai Bay Basin
-
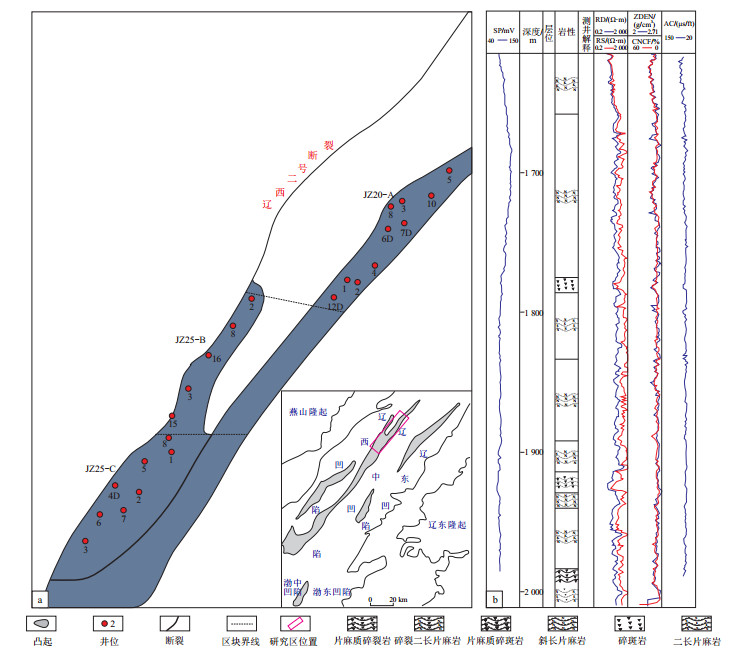
摘要: 渤海湾盆地是我国潜山油气资源勘探的重点地区之一,为了打开该区太古宇潜山勘探新局面,对辽东湾地区太古宇潜山成储规律及主控因素进行了研究。基于薄片、测井、地震等钻井资料,分析了辽西凸起中北段太古宇潜山岩石学特征、岩石展布特征、储层特征、构造演化和裂缝特征。研究表明,辽东湾地区辽西凸起太古宇潜山由片麻岩类、变质花岗岩类和碎裂岩类等组成,并以片麻岩为主;现今构造呈南高北低特征,北部地层保存相对完好,南部地层上部具剥蚀迹象,岩浆岩比例自北向南逐渐增高。该区太古宇变质岩以裂缝型储层为主,岩石中暗色矿物含量与岩石脆性呈反比关系;构造变形导致裂缝发育,太古宇潜山发育三组构造裂缝,即燕山早期受到NE向强剪切和SN向强挤压的应力方向发育NNE向剪裂缝和SN向张裂缝,喜马拉雅早期受到NW向强伸展和NE向弱剪切的应力方向发育NE向剪裂缝和北东向张裂缝,喜马拉雅晚期受到NE向强剪切和NW向弱伸展的应力方向发育EW向张裂缝及NE向和NW向共轭剪裂缝,区域构造差异活动程度控制了裂缝的有效性;燕山运动是变质岩储层主要造缝期,喜马拉雅期裂缝以方解石充填、半充填为主,后期经溶蚀可构成有效裂缝。Abstract: The Bohai Bay Basin is one of the key areas for the exploration of buried hill oil and gas resources in China. In order to create a new prospect for the exploration of the Archaean buried hills in this area, the reservoir-forming laws and main controlling factors of the Archaean buried hill reservoir in the Liaodong Bay area were studied. Based on drilling data such as stratum, logging, and seismic data, this paper classified the lithology and distribution patterns of Archean buried hills in the Liaodong Bay area, and analyzed the dominant reservoir space types and controlling factors. The results show that the Archean buried hills in the Liaodong Bay area are composed of schist, metamorphic granite and cataclastic rocks, with schist being the predominant lithology. The current structure is high in the south and low in the north. The strata are relatively intact in the north, while the upper part of the strata in the south shows evidence of denudation. The proportion of igneous rocks increases gradually from north to south. The metamorphic rocks are dominated by fracture reservoirs. The content of mafic minerals is inversely correlated with the brittleness of rocks. Tectonic deformation led to fracture development. Three sets of structural fractures were developed in the Archean buried hills of the Bohai Bay Basin, i.e., NNE shear fractures and SN tensile fractures were developed in the stress directions of NE strong shear and SN strong compression in the early Yanshanian period, NE shear fractures and NE tensile fractures were developed in the stress directions of NW strong extension and NE weak shear in the early Himalayan period, and EW tensile fractures and NE and NW conjugate shear fractures were developed in the stress directions of NE strong shear and NW weak extension in the late Himalayan period. The degree of regional tectonic activity controlled the effectiveness of the fractures. The Yanshanian movement was the main stage of fracture formation in metamorphic rock reservoirs. During the Himalayan period, fractures were mainly filled and semi-filled with calcite, and effective fractures could be formed through dissolution in the later stage.
-
Key words:
- main controlling factor /
- reservoir /
- buried hill /
- Archean /
- Liaoxi Uplift /
- Bohai Bay Basin
-
图 3 渤海湾盆地辽东湾地区辽西凸起太古宇岩心特征
a.JZ25-C-2井,2 020.25~2 020.38 m,二长片麻岩;b.JZ25-C-2井,1 751.44 m,斜长片麻岩;c.JZ25-C-5井,1 801.60~1 801.75 m,花岗片麻岩;d.JZ25-C-2井,1 751.14~1 751.34 m,角闪花岗片麻岩;e.JZ25-B-2井,2 165~2 170 m,碎裂花岗岩;f.JZ20-A-3井,2 697.69 m,花岗质碎裂岩,颗粒破碎,裂缝发育;g.JZ20-A-3井,2 214.9 m,混合岩化片麻岩;h.JZ20-A-4井,2 668.7 m,混合岩;i.JZ20-A-5井,2 346.6 m,碱长混合片麻岩;j.JZ25-B-1井,2 923.1 m,混合花岗岩;k.JZ25-C-2井,2 020.51 m,碎裂化二长花岗岩;l.JZ20-A-5井,2 350.65 m,黑云二长花岗岩;m.JZ20-A-5井,2 351.41 m,变质花岗岩;n.JZ20-A-12D井,2 798.2~2 800 m,辉绿岩。
Figure 3. Core characteristics of Archean buried hills in Liaoxi Uplift, Liaodong Bay area, Bohai Bay Basin
图 5 渤海湾盆地辽东湾地区辽西凸起太古宇储集空间及裂缝叠加特征
a.JZ25-B-2,1 956 m,碎裂岩裂缝发育,黑云母和钙质充填;b.JZ25-B-2,1 954 m,长英质裂缝均为钙质(先)和硅质(后) 充填;c.JZ25-B-2,1 960 m,裂缝钙质充填,云母溶蚀孔;d.JZ20-A-3井,2 102.62 m,斑状花岗岩;e.JZ20-A-7D井,2 691.57 m,花岗质碎裂岩;f.JZ20-A-4井,2 957.11 m,碎裂混合片麻岩。
Figure 5. Characteristics of Archean reservoir space and superposition of fractures in Liaoxi Uplift, Liaodong Bay area, Bohai Bay Basin
-
[1] 穆龙新. 裂缝储层地质模型的建立[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1995, 22(6): 78-82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1995.06.010MU Longxin. Establishment of the geological model of fractured reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1995, 22(6): 78-82. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1995.06.010 [2] WALTERS R F. Oil production from fractured pre-Cambrian basement rocks in central Kansas[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1953, 37(2): 300-313. [3] 胡见义, 童晓光, 徐树宝. 渤海湾盆地古潜山油藏的区域分布规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1981(5): 1-9.HU Jianyi, TONG Xiaoguang, XU Shubao. Regional distribution law of the paleo-Qianshan oil reservoir in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1981(5): 1-9. [4] 李军, 刘丽峰, 赵玉合, 等. 古潜山油气藏研究综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2006, 21(3): 879-887. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2006.03.028LI Jun, LIU Lifeng, ZHAO Yuhe, et al. A review of study on ancient buried hill reservoir[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2006, 21(3): 879-887. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2006.03.028 [5] 叶涛, 韦阿娟, 祝春荣, 等. 渤海海域基底"改造型火山机构"特征及油气成藏意义[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(11): 1370-1380. doi: 10.7623/syxb201611005YE Tao, WEI Ajuan, ZHU Chunrong, et al. Characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation significance of reformed volcanic edifice in the basement of Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(11): 1370-1380. doi: 10.7623/syxb201611005 [6] 周心怀, 项华, 于水, 等. 渤海锦州南变质岩潜山油藏储集层特征与发育控制因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(6): 17-20. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.06.004ZHOU Xinhuai, XIANG Hua, YU Shui, et al. Reservoir characteristics and development controlling factors of JZS Neo-Archean metamorphic buried hill oil pool in Bohai Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(6): 17-20. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.06.004 [7] 宋柏荣, 胡英杰, 边少之, 等. 辽河坳陷兴隆台潜山结晶基岩油气储层特征[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(1): 77-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2011.01.013SONG Bairong, HU Yingjie, BIAN Shaozhi, et al. Reservoir characteristics of the crystal basement in the Xinglongtai buried-hill, Liaohe Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(1): 77-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2011.01.013 [8] 郭子南. 兴隆台潜山基岩油藏储层分类评价[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(2): 64-71.GUO Zinan. Classification and evaluation of bedrock reservoirs in Xinglongtai buried hill[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(2): 64-71. [9] 杨晓利, 王政军, 高文中, 等. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷深层碳酸盐岩潜山地质特征与勘探实践[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(3): 425-432. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202203425YANG Xiaoli, WANG Zhengjun, GAO Wenzhong, et al. Geolo-gical characteristics and exploration practice of deep carbonate buried hills in Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geo-logy & Experiment, 2022, 44(3): 425-432. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202203425 [10] 童凯军, 赵春明, 吕坐彬, 等. 渤海变质岩潜山油藏储集层综合评价与裂缝表征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(1): 56-63.TONG Kaijun, ZHAO Chunming, LÜ Zuobin, et al. Reservoir evaluation and fracture characterization of the metamorphic buried hill reservoir in Bohai Bay[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(1): 56-63. [11] NGUYEN T B N, BAE W, NGUYEN L A, et al. A new method for building porosity and permeability models of a fractured granite basement reservoir[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2014, 32(15): 1886-1897. doi: 10.1080/10916466.2010.551241 [12] 薛罗, 马轮, 史忠生, 等. 南苏丹Melut盆地Ruman潜山构造演化及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(2): 53-60.XUE Luo, MA Lun, SHI Zhongsheng, et al. Tectonic evolution and its influence on hydrocarbon accumulation of Ruman buried hill in Melut Basin, South Sudan[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(2): 53-60. [13] 李建红, 王延斌, 缪欢, 等. 北大港潜山滨海断层发育特征及其与上古生界二次生烃耦合成藏研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(1): 52-58.LI Jianhong, WANG Yanbin, MIAO Huan, et al. Study on developmental characteristics of coastal fault in Beidagang buried hill and its coupling with the Upper Paleozoic secondary hydrocarbon formation[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(1): 52-58. [14] THOMAS M F. Weathering and landslides in the humid tropics; a geomorphological perspective[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of China, 1997, 40(1): 1-16. [15] ZHAO J, BROMS B B, ZHOU Y, et al. A study of the weathering of the Bukit Timah granite part a: review, field observations and geophysical survey[J]. Bulletin of the International Association of Engineering Geology-Bulletin de l'Association Internationale de Géologie de l'Ingénieur, 1994, 49(1): 97-106. [16] GUPTA A S, RAO K S. Index properties of weathered rocks: inter-relationships and applicability[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 1998, 57(2): 161-172. [17] TUǦUL A, ZARIF I H. Correlation of mineralogical and textural characteristics with engineering properties of selected granitic rocks from Turkey[J]. Engineering Geology, 1999, 51(4): 303-317. [18] 黄镇国, 张伟强, 陈俊鸿, 等. 中国南方红色风化壳[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1996: 138.HUANG Zhenguo, ZHANG Weiqiang, CHEN Junhong, et al. Red weathering crust in southern China[M]. Beijing: Ocean Press, 1996: 138. [19] 杨洁. 华南沿海花岗岩风化壳岩土工程特征变化研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2004.YANG Jie. Variation of geotechnical properties of weathered granite in Southeast China[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2004. [20] 徐长贵, 于海波, 王军, 等. 渤海海域渤中19-6大型凝析气田形成条件与成藏特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1): 25-38.XU Changgui, YU Haibo, WANG Jun, et al. Formation conditions and accumulation characteristics of Bozhong 19-6 large condensate gas field in offshore Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1): 25-38. [21] 温宏雷, 杨海风, 杨波, 等. 渤海海域莱北低凸起新近系岩性油藏成藏模式及勘探实践[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(1): 102-111. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202201102WEN Honglei, YANG Haifeng, YANG Bo, et al. Exploration advances and accumulation model for Neocene lithological reservoirs in Laibei Low Uplift, Bohai Sea area[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(1): 102-111. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202201102 [22] 张波. 渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷孤北潜山下古生界油气来源及运移方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(6): 981-988. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202206981ZHANG Bo. Source and migration direction of hydrocarbon in Lower Paleozoic in Gubei buried hill, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(6): 981-988. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202206981 [23] 杨玲, 胡明. 东营凹陷太古界储层裂缝发育控制因素及油气勘探方向[J]. 特种油气藏, 2010, 17(2): 35-38.YANG Ling, HU Ming. Controlling factors of Archeozoic reservoir fractures development and hydrocarbon prospecting direction in Dongying Depression[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2010, 17(2): 35-38. [24] 陈建波, 潘玲黎, 童凯军, 等. 辽西低凸起太古宇变质岩潜山储层控制因素研究[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2016, 30(4): 30-35.CHEN Jianbo, PAN Lingli, TONG Kaijun, et al. Controlling factors analysis of Archaezoic metamorphic buried hill reservoirs in Liaoxi low salient[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2016, 30(4): 30-35. [25] 邹华耀, 赵春明, 尹志军, 等. 渤海湾盆地新太古代结晶岩潜山裂缝发育的露头模型[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(5): 879-885.ZOU Huayao, ZHAO Chunming, YIN Zhijun, et al. Fracture-occurring outcrop model in neoarchean crystalline rock-buried hill, Bohai Bay Basin, North China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(5): 879-885. [26] 徐长贵. 渤海古近系坡折带成因类型及其对沉积体系的控制作用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2006, 18(6): 365-371.XU Changgui. Genetic types of Paleogene slope-break zones and their controls on depositional system in Bohai offshore[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2006, 18(6): 365-371. -





 下载:
下载:





 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号