Characteristics and genetic mechanism of salt structure in Fuxingchang anticline, Jiangling Sag, Jianghan Basin
-
摘要: 复兴场盐背斜是江汉盆地江陵凹陷重要的含油构造,其构造演化及成因机制认识不清,制约了精细勘探。因此,对复兴场盐背斜构造演化及形成机制的分析,不仅有助于理解盐层在不同应力背景下的流动对背斜形成演化的影响,对理解油气成藏过程也有重要意义。通过对三维地震资料的精细解析,结合关键构造层的平衡恢复技术及生长地层分析技术,研究复兴场背斜的构造特征及成因机制。结果显示,复兴场背斜为一构造特征走向上变化显著,受多期次断层改造、多种变形机制复合而成的盐背斜;背斜初始于早始新世新沟咀组沉积期—晚始新世早期的正断层作用,形成滚筒状褶皱并造成盐层的聚集;在晚始新世晚期—渐新世,沉积地层的差异负载作用驱使盐层自西向东流动,造成构造整体西倾,形成单斜构造,并在渐新世晚期抬升剥蚀;背斜定型于新近纪—第四纪,发生构造反转,演化为一挤压型盐背斜,伴生逆断层和膝折构造。复兴场背斜的形成和演化受区域应力背景、沙市组盐层、东倾正断层及盐下古构造等因素的综合作用。复兴场盐背斜形成的构造圈闭略早于烃源岩的主要排油期,并且在主要排油期,构造处于拗陷阶段,断层活动弱,有利于早期圈闭油气的成藏。Abstract: The Fuxingchang salt anticline is an important oil-bearing structure in the Jiangling Sag of the Jianghan Basin, while its structural evolution and formation mechanism are unclear, which restricts the delicate exploration of oil and gas. Therefore, the analysis of structural evolution and formation mechanism of the Fuxingchang salt anticline is not only helpful to understand the influence of salt bed flow under different stress backgrounds on the formation and evolution of the anticline, but also important to understand the process of petroleum accumulation. The structural characteristics and genetic mechanism of Fuxingchang anticline were studied by analyzing 3D seismic data and combining with the techniques of balance restoration of key structural layers and growth strata analysis. The results show that the Fuxingchang anticline is a salt anticline with significant structural features that vary along strike, resulting from multiple stages of fault reconstruction and complex deformation mechanisms. The anticline was initially formed during normal faulting in the sedimentary period from Early Eocene Xingouzui Formation to the early period of Late Eocene, which formed roller fold and caused the accumulation of salt layer. From the late period of Late Eocene to Oligocene, the differential loading of sedimentary strata drove salt beds to flow from west to east, resulting in the westward dip of the whole structure and the formation of monoclinal structure, which was uplifted and denudated in the late period of Oligocene. The anticline was finalized from Neogene to Quaternary, and evolved into a compressional salt anticline, associated with reverse faults and kink-band structures. The formation and evolution of Fuxingchang anticline are influenced by the combined effects of regional stress background, salt layer of Shashi Formation, the east-dipping normal faults, sub-salt paleostructures, etc. The structural trap formed by Fuxingchang salt anticline occurred slightly earlier than the main oil expulsion period of source rocks, and during the main oil expulsion period, the structure was in the depression stage, with weak fault activity, which was conducive to the early accumulation of trapped oil and gas.
-
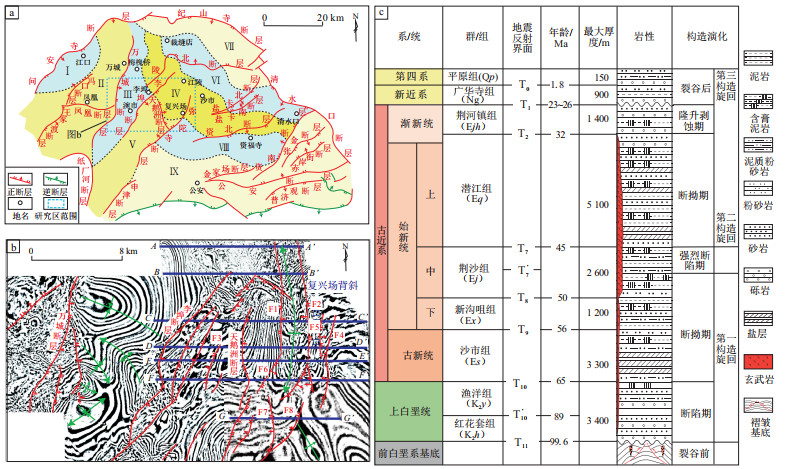
图 1 江汉盆地江陵凹陷研究区构造和地层综合柱状图
a.江陵凹陷构造纲要;b.复兴场三维地震数据时间剖面(2 200 ms)构造;c.江陵凹陷地层综合柱状图,修改自文献[9]。
Ⅰ.枝口洼陷;Ⅱ.万城断裂带;Ⅲ.万城洼陷;Ⅳ.荆州背斜带;Ⅴ.弥陀寺次洼;Ⅵ.清水口次洼;Ⅶ.裁缝店洼陷;Ⅷ.资福寺洼陷;Ⅸ.公安隆起带。Figure 1. Composite structural map and stratigraphic column of study area in Jiangling Sag, Jianghan Basin
图 2 江汉盆地江陵凹陷研究区地震剖面AA’-BB’-CC’-DD’-EE’-FF’构造解释
剖面位置见图 1b。
Figure 2. Seismic interpretation of sections AA’, BB’, CC’, DD’, EE’ and FF’ of study area in Jiangling Sag, Jianghan Basin
图 3 江汉盆地江陵凹陷研究区地震剖面GG’构造解释
剖面位置见图 1b。
Figure 3. Seismic interpretation of section GG' of study area in Jiangling Sag, Jianghan Basin
图 5 不同成因机制形成的盐背斜或盐枕构造的特征
修改自文献[32]。
Figure 5. Features of salt anticlines or salt pillows formed by different genetic mechanisms
-
[1] 贾承造, 赵文智, 魏国齐, 等. 盐构造与油气勘探[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(2): 17-19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2003.02.003JIA Chengzao, ZHAO Wenzhi, WEI Guoqi, et al. Salt structures and exploration of oil and gas[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(2): 17-19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2003.02.003 [2] 汤良杰, 余一欣, 陈书平, 等. 含油气盆地盐构造研究进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2005, 12(4): 375-383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.04.006TANG Liangjie, YU Yixin, CHEN Shuping, et al. Major developments of research on salt tectonics in oil-gas-bearing basins[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2005, 12(4): 375-383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.04.006 [3] 王莉, 吴珍云, 尹宏伟, 等. 含盐沉积盆地挤压盐构造及其对油气成藏的意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 136-150.WANG Li, WU Zhengyun, YIN Hongwei, et al. Compressional salt structures of salt-bearing sedimentary basins and its significance to hydrocarbon accumulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 136-150. [4] 彭伟, 黄华, 杜学斌, 等. 基于多元统计方法的油气成藏关键因素筛选与分析: 以江陵凹陷新沟嘴组岩性油藏为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(2): 295-302. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201902295PENG Wei, HUANG Hua, DU Xuebin, et al. Analysis of main controls of stratigraphic reservoirs in Xingouzui Formation of Jiangling Sag based on a multivariate statistical method[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(2): 295-302. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201902295 [5] 赵文芳. 巴西坎波斯盆地A区块盐下构造特征及其对油气分布的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(2): 233-240. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202002233ZHAO Wenfang. Tectonic controls on the pre-salt hydrocarbon distribution in block A of Campos Basin, Brazil[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(2): 233-240. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202002233 [6] 杨长清. 江陵凹陷盐构造及与油气聚集的关系[J]. 断块油气田, 2004, 11(3): 4-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8907.2004.03.002YANG Changqing. Salt structure and its relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation in Jiangling Sag[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2004, 11(3): 4-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8907.2004.03.002 [7] 王春连, 刘成林, 胡海兵, 等. 江汉盆地江陵凹陷南缘古新统沙市组四段含盐岩系沉积特征及其沉积环境意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2012, 14(2): 165-175.WANG Chunlian, LIU Chenglin, HU Haibing, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and its environmental significance of salt-bearing strata of the member 4 of Paleocene Shashi Formation in southern margin of Jiangling Depression, Jianghan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2012, 14(2): 165-175. [8] 黄华, 袁娟梅. 江陵凹陷荆州背斜带形成演化及成藏特征[J]. 断块油气田, 2013, 20(3): 301-304.HUANG Hua, YUAN Juanmei. Evolutionary process and accumulation feature of Jingzhou anticlinal belt in Jiangling Sag[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2013, 20(3): 301-304. [9] WU Lulu, MEI Lianfu, LIU Yunsheng, et al. Multiple provenance of rift sediments in the composite basin-mountain system: constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology and heavy mine-rals of the Early Eocene Jianghan Basin, Central China[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2017, 349: 46-61. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.12.003 [10] WU Lulu, MEI Lianfu, PATON D A, et al. Late Cretaceous-Cenozoic intraplate extension and tectonic transitions in Eastern China: implications for intraplate geodynamic origin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 117: 104379. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104379 [11] 杨飞, 刘雅博. 江陵凹陷盐隆构造体系对富钾卤水储层分布特征的影响[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(10): 1847-1854.YANG Fei, LIU Yabo. Study on the influence of salt structural system on the distribution characteristics of potassium-rich brine reservoirs in Jiangling Depression[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(10): 1847-1854. [12] 杨长清, 陈孔全, 程志强, 等. 江陵凹陷形成演化与勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2003, 23(6): 51-54.YANG Changqing, CHEN Kongquan, CHENG Zhiqiang, et al. Constituent evolution and exploration potential in Jiangling Depression[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2003, 23(6): 51-54. [13] 卢明国, 童小兰, 王必金. 江汉盆地江陵凹陷油气成藏期分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2004, 26(1): 28-30. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200401028LU Mingguo, TONG Xiaolan, WANG Bijin. Analysis of reservoir formation periods, the Jiangling Depression of the Jianghan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2004, 26(1): 28-30. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200401028 [14] 刘俊, 卢明国, 童小兰, 等. 江陵凹陷构造演化与含油气系统关系研究[J]. 地球学报, 2008, 29(1): 89-94.LIU Jun, LU Mingguo, TONG Xiaolan, et al. Correlation between structure evolution and petroleum system of the Jiangling Depression[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2008, 29(1): 89-94. [15] 沈尚峰. 江汉盆地江陵凹陷的构造格架和演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2008.SHEN Shangfeng. Tectonic framework and evolution of Qianjiang Depression in Jianghan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2008. [16] 张黎. 江陵凹陷资福寺洼陷构造特征研究[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2012.ZHANG Li. A study on tectonic characteristics in the Zifusi Sag Jiangling Depression[D]. Jingzhou: Changjiang University. 2012. [17] 蒋卫明, 李建华. 江陵凹陷复兴场地区地质结构与油气成藏规律[J]. 江汉石油职工大学学报, 2005, 18(2): 4-5.JIANG Weiming, LI Jianhua. Geologic framework and forming laws of hydrocarbon reservoir in Fuxingchang area of Jiangling Depression[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum University of Staff and Workers, 2005, 18(2): 4-5. [18] 宿赛, 张晓程, 王慧, 等. 江陵凹陷复兴场—李家台构造演化特征[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2014(21): 189.SU Sai, ZHANG Xiaocheng, WANG Hui, et al. The structural features of Fuxingchang-Lijiatai in Jiangling Depression[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2014(21): 189. [19] 周舟. 江陵凹陷荆州背斜带典型构造解析[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2018.ZHOU Zhou. Structural analysis of typical tectonics in Jingzhou anticlinal belt, Jiangling Sag[D]. Jingzhou: Changjiang University, 2018. [20] 刘建党, 兰正凯, 贾超. 江陵凹陷断层封闭性评价及勘探潜力[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(3): 36-42.LIU Jiandang, LAN Zhengkai, JIA Chao. Fault trap evaluation and exploration potential in Jiangling Sag[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(3): 36-42. [21] DAHLSTROM C D A. Balanced cross sections[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1969, 6(4): 743-757. [22] 蒋录全, 刘光炎. 平衡剖面技术综述[J]. 南方油气地质, 1995, 1(3): 39-46.JIANG Luquan, LIU Guangyan. Review of balanced cross section technique[J]. South China Petroleum Geology, 1995, 1(3): 39-46. [23] 陈书平, 汤良杰. 盐构造剖面的分层合并复原方法及应用[J]. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 23(3): 32-37.CHEN Shuping, TANG Liangjie. Layer-by-layer restoring technique of salt tectonics and its application[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 23(3): 32-37. [24] 胡望水, 曾涛, 周亚丽, 等. 含滑脱层剖面的分层平衡恢复技术在川东北构造演化研究中的运用[J]. 现代地质, 2011, 25(5): 896-901.HU Wangshui, ZENG Tao, ZHOU Yali, et al. Applying balanced-restoring technique with detachment horizon profile to study the tectonic evolution of northeastern Sichuan[J]. Geoscience, 2011, 25(5): 896-901. [25] SUPPE J, CHOU G T, HOOK S C. Rates of folding and faulting determined from growth strata[M]//MCCLAY K R. Thrust tectonics. Dordrecht: Springer, 1992: 105-121. [26] XIAO Hongbin, SUPPE J. Origin of rollover[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1992, 76(4): 509-529. [27] CHEN Hanlin, ZHANG Yuqing, CHENG Xiaogan, et al. Using migrating growth strata to confirm a ~230-km-long detachment thrust in the southern Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2022, 154: 104488. [28] BISHOP D J, BUCHANAN P G, BISHOP C J. Gravity-driven thin-skinned extension above Zechstein Group evaporites in the western central North Sea: an application of computer-aided section restoration techniques[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 1995, 12(2): 115-135. [29] GROSHONG R H. 3-D structural geology[M]. 2nd ed. Heidelberg: Springer, 2006. [30] JACKSON M P A, HUDEC M R. Salt tectonics: principles and practice[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017. [31] PICHEL L M, JACKSON C A L, PEEL F, et al. Base-salt relief controls salt-tectonic structural style, São Paulo Plateau, Santos Basin, Brazil[J]. Basin Research, 2020, 32(3): 453-484. [32] HUDEC M R, JACKSON M. The salt mine[M]. University of Texas at Austin. Bureau of Economic geology. Annua (99), 2011: 1-324. -





 下载:
下载:





 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号