Geological characteristics and sweet spot selection of Permian organic-rich sedimentary tuff series in northern Fuling, Chongqing
-
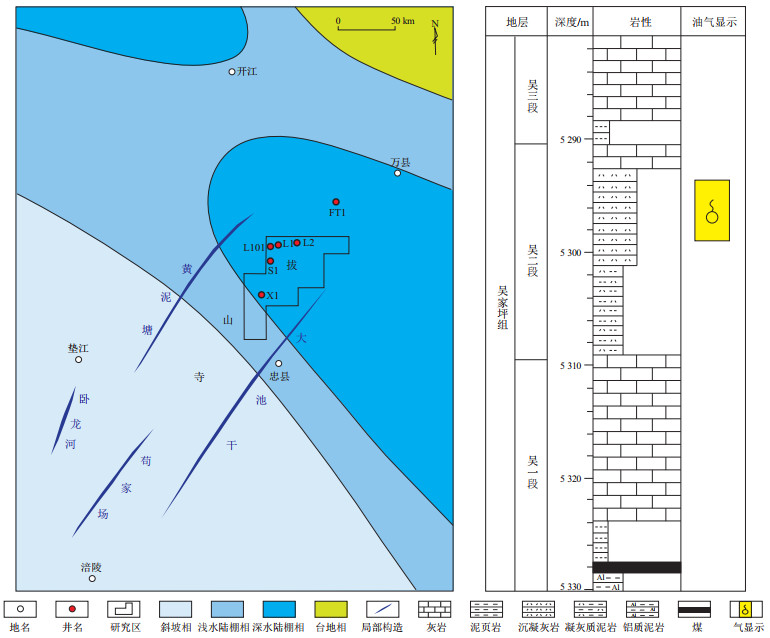
摘要: 重庆涪陵北部二叠系吴家坪组二段(吴二段)沉凝灰岩是一种新型富有机质烃源岩,是非常规气藏勘探的新领域。明确吴二段沉凝灰岩层系关键甜点参数的分布是勘探评价的首要问题。通过钻测录井、实验分析及地震等资料,从沉凝灰岩层系的有机地球化学特征、岩性特征、厚度分布、地层压力及裂缝发育等成藏富集地质条件入手,聚焦岩性品质及可压缝网两个关键因素,优中选优,评价目标甜点区。研究结果表明:涪陵北部吴二段沉凝灰岩层系处于深水陆棚相,有机质丰度高,TOC含量主要为5%~6%,Ro为1.90%~2.44%,有机质类型以Ⅰ和Ⅱ型为主,TOC含量大于4%的优质沉凝灰岩段厚度在15~20 m之间,分布面积广;优质沉凝灰岩段储集空间多样,孔隙度较高,脆性矿物含量较高,地层压力系数为高—超高压级别,同时转折端发育小型—微型裂缝带,体现了良好的“自生自储”含气勘探潜力;涪陵北部吴二段沉凝灰岩层系气藏具有优质控富、超压控藏及缝网控甜的规律。结合主控因素初步建立吴二段沉凝灰岩层系甜点评价标准,优选出3个目标甜点区,面积达186.4 km2,其中研究区西北部L2-L1井区油气显示良好,可以作为近期勘探的有利目标。Abstract: The sedimentary tuff in the second member of Permian Wujiaping Formation in the northern Fuling area of Chongqing is a new type of organic-rich source rock, which is a new field of unconventional gas reservoir exploration. Clarifying the distribution of key sweet spot parameters of the sedimentary tuff series in the second member of Wujiaping Formation is a primary issue in exploration and evaluation. Based on drilling, logging, experimental analysis and seismic data, this paper evaluated the target sweet spot starting from the sedimentary tuff series' organic geochemistry, lithological characteristics, thickness distribution, formation pressure, fracture development and other geological conditions for reservoir formation and enrichment, and focusing on the two key factors of lithology quality and compressible fracture network. The results show that: (1) The sedimentary tuff series in the second member of Wujiaping Formation in the northern Fuling area is in the deep-water shelf facies, with high organic matter abundance. The TOC content is mainly 5%-6%, the Ro value ranges 1.90%-2.44%, the organic matter types are mainly Ⅰ and Ⅱ, and the thickness of high-quality sedimentary tuff section (TOC≥4%) is 15-20 m, with a wide distribution area. (2) The reservoir space of the high-quality sedimentary tuff section is diversified, the porosity is high, the brittle mineral content is high, the formation pressure coefficient is high to ultra high pressure level, and small-micro fracture zone is developed at the hinge zone, reflecting a good gas exploration potential of "self-generation and self-storage". (3) The sedimentary tuff gas reservoir in the second member of Wujiaping Formation in the northern Fuling area has the laws of high quality control of enrichment, overpressure control of reservoir and fracture network control of sweet spot. The sweet spot evaluation criteria for sedimentary tuff series in the second member of Wujiaping Formation are preliminarily established in combination with the main control factors, and three target sweet spots are selected, with an area of 186.4 km2. The L2-L1 well area in the northwest of the exploration area has good oil and gas shows, which can be a favorable target for recent exploration.
-
图 3 重庆涪陵北部FT1井吴家坪组二段沉凝灰岩层系储集空间特征
据参考文献[16]修改。
Figure 3. Reservoir space characteristics of sedimentary tuff series in second member of Wujiaping Formation in FT1 well in northern Fuling, Chongqing
表 1 重庆涪陵北部及周缘地区吴家坪组二段沉凝灰岩层系有机地化特征
Table 1. Geochemical characteristics of sedimentary tuff series in second member of Wujiaping Formation in northern Fuling of Chongqing and its surrounding areas
ω (TOC) /% Ro/% δ13C 划分范围 频率 平均 划分范围 频率 平均 划分范围/‰ 频率/% 平均/‰ <2.0 <1.3 -26.0~-23.0 17.64 2.0~4.0 9.6 6.05 1.3~2.0 2 2.3 -28.0~-26.0 50.12 -27.55 >4.0 90.4 >2.0 98 -31.0~-28.0 32.24 表 2 重庆涪陵北部钻井优质沉凝灰岩段厚度预测误差
Table 2. Prediction errors of high-quality sedimentary tuff section thickness in typical wells in northern Fuling, Chongqing
井名 X1 S1 L2 优质沉凝灰岩段预测厚度/m 14.8 17.1 17.3 优质沉凝灰岩段实际厚度/m 15.0 16.6 16.8 厚度误差/m 0.2 0.5 0.5 -
[1] 熊伟, 王越, 熊峥嵘, 等. 准噶尔盆地石北凹陷岛弧环境下火山—沉积建造特征及源储发育模式: 以石炭系姜巴斯套组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 656-666. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304656XIONG Wei, WANG Yue, XIONG Zhengrong, et al. Characteristics of volcanic-sedimentary formations and developmental patterns of source and reservoir rocks in an island arc environment of Shibei Sag, Junggar Basin: taking the Carboniferous Jiangbasitao Formation as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 656-666. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304656 [2] 张啸, 陈国军, 李俊飞, 等. 准噶尔盆地石西凸起风化型火山岩储层相态发育模式[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(3): 47-55.ZHANG Xiao, CHEN Guojun, LI Junfei, et al. Phase development pattern of weathered volcanic reservoirs in Shixi high, Junggar Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(3): 47-55. [3] 夏文谦, 朱祥, 金民东, 等. 川北地区上二叠统吴家坪组火山碎屑岩油气藏储层特征及主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(2): 307-316. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302307XIA Wenqian, ZHU Xiang, JIN Mindong, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of volcanic clastic rock reservoirs in Wujiaping Formation of Upper Permian in northern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(2): 307-316. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302307 [4] 连志刚, 常智勇, 李路路, 等. 玛东地区二叠系火山岩成藏特征及勘探潜力[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(5): 57-65.LIAN Zhigang, CHANG Zhiyong, LI Lulu, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics and exploration potential of Permian volcanic rocks in Madong area[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(5): 57-65. [5] 向芳, 肖倩, 喻显涛, 等. 四川盆地元坝地区上二叠统海相凝灰沉积储层特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(4): 889-901.XIANG Fang, XIAO Qian, YU Xiantao, et al. Reservoir characteristics of the Upper Permian marine tuffaceous deposits in Yuanba area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(4): 889-901. [6] 张本健, 王宇峰, 裴森奇, 等. 川西北地区上二叠统吴家坪组沉积演化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(12): 1709-1720. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2019.12.007ZHANG Benjian, WANG Yufeng, PEI Senqi, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Upper Permian Wujiaping Formation in the northwestern Sichuan[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(12): 1709-1720. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2019.12.007 [7] 梁西文, 李乐. 鄂西渝东区上二叠统吴家坪组页岩气地质条件及勘探潜力[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(3): 386-394. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103386LIANG Xiwen, LI Le. Geological conditions and exploration potential for shale gas in Upper Permian Wujiaping Formation in the region of western Hubei-eastern Chongqing[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(3): 386-394. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103386 [8] 王良军, 杨诚, 王庆波, 等. 四川盆地涪陵地区茅口组热液白云岩储层预测[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2018, 40(3): 298-305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2018.03.03WANG Liangjun, YANG Cheng, WANG Qingbo, et al. Hydrothermal dolomite reservoir prediction for Maokou Formation in Fuling area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 40(3): 298-305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2018.03.03 [9] 王红岩, 刘德勋, 蔚远江等. 大面积高丰度海相页岩气富集理论及地质评价技术进展与应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(3): 69-81.WANG Hongyan, LIU Dexun, WEI Yuanjiang, et al. Enrichment theory of large area and high abundance marine shale gas and its geological evaluation technology progress and application[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(3): 69-81. [10] 李俊, 卢和平, 胡象辉, 等. 川东红星地区二叠系吴家坪组海相页岩气钻井实践[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(6): 1189-1195. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2023061189LI Jun, LU Heping, HU Xianghui, et al. Drilling practice of marine shale gas in Permian Wujiaping Formation in Hongxing area of eastern Sichuan[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(6): 1189-1195. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2023061189 [11] 刘光祥, 金之钧, 邓模, 等. 川东地区上二叠统龙潭组页岩气勘探潜力[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(3): 481-487.LIU Guangxiang, JIN Zhijun, DENG Mo, et al. Exploration potential for shale gas in the Upper Permian Longtan Formation in eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(3): 481-487. [12] 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等. 中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 37(6): 641-653.ZOU Caineng, DONG Dazhong, WANG Shejiao, et al. Geological characteristics, formation mechanism and resource potential of shale gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(6): 641-653. [13] 郭旭升, 郭彤楼, 魏志红, 等. 中国南方页岩气勘探评价的几点思考[J]. 中国工程科学, 2012, 14(6): 101-105, 112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2012.06.014GUO Xusheng, GUO Tonglou, WEI Zhihong, et al. Thoughts on shale gas exploration in southern China[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2012, 14(6): 101-105, 112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1742.2012.06.014 [14] 李敏, 刘雅利, 冯动军, 等. 中国海相页岩气资源潜力及未来勘探方向[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(6): 1097-1108. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2023061097LI Min, LIU Yali, FENG Dongjun, et al. Potential and future exploration direction of marine shale gas resources in China[J]. Petro-leum Geology and Experiment, 2023, 45(6): 1097-1108. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2023061097 [15] 郭少斌, 王子龙, 马啸. 中国重点地区二叠系海陆过渡相页岩气勘探前景[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(3): 377-385, 414. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103377GUO Shaobin, WANG Zilong, MA Xiao. Exploration prospect of shale gas with Permian transitional facies of some key areas in China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(3): 377-385, 414. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202103377 [16] 温思宇, 张兵, 姚永君, 等. 川东地区二叠系吴家坪组页岩中黄铁矿形态及其对大洋缺氧事件的指示意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(5): 71-80.WEN Siyu, ZHANG Bing, YAO Yongjun, et al. Pyrite morphology in shale of Permian Wujiaping Formation in eastern Sichuan Basin and its indicative significance to oceanic anoxic events[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(5): 71-80. [17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 页岩气地质评价方法: GB/T 31483-2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015: 1-11.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. Geological evaluation methods for shale gas: GB/T 31483-2015[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015: 1-11. [18] 蒋裕强, 付永红, 谢军, 等. 海相页岩气储层评价发展趋势与综合评价体系[J]. 天然气工业, 2019, 39(10): 1-9. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.10.001JIANG Yuqiang, FU Yonghong, XIE Jun, et al. Development trend of marine shale gas reservoir evaluation and a suitable comprehensive evaluation system[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2019, 39(10): 1-9. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2019.10.001 [19] 何希鹏, 卢比, 何贵松, 等. 渝东南构造复杂区常压页岩气生产特征及开发技术政策[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(1): 224-240.HE Xipeng, LU Bi, HE Guisong, et al. Production characteristics and optimized development technologies for normal-pressure shale gas in the structurally complex areas of southeastern Chongqing[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(1): 224-240. [20] 李明诚. 石油与天然气运移[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1987: 4-11.LI Mingcheng. Oil and gas migration[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1987: 4-11. [21] 赵爽, 李曙光, 林正良. 川南深层五峰—龙马溪组页岩工程"甜点"地震预测技术[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2022, 19(4): 466-473.ZHAO Shuang, LI Shuguang, LIN Zhengliang. Seismic prediction technology for engineering "sweet spot" of deep Wufeng-Longmaxi formation shale in southern Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2022, 19(4): 466-473. [22] 王幸蒙, 姜振学, 王世骋, 等. 泥页岩天然裂缝特征及其对页岩气成藏、开发的控制作用[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(8): 34-42.WANG Xingmeng, JIANG Zhengxue, WANG Shicheng, et al. Characteristics of natural fractures in shale and their control effect on shale gas accumulation and development[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(8): 34-42. [23] 胡春锋, 梅俊伟, 李仕钊, 等. 四川盆地东部南川常压页岩气开发效果地质与工程因素分析[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2021, 11(4): 559-568.HU Chunfeng, MEI Junwei, LI Shizhao, et al. Analysis on geological and engineering factors of development effects on normal pressure shale gas in Nanchuan block, eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2021, 11(4): 559-568. [24] 姜晓宇, 张研, 甘利灯, 等. 花岗岩潜山裂缝地震预测技术[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2020, 55(3): 694-704.JIANG Xiaoyu, ZHANG Yan, GAN Lideng, et al. Seismic techniques for predicting fractures in granite buried hills[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2020, 55(3): 694-704. [25] 董大忠, 梁峰, 管全中, 等. 四川盆地五峰组—龙马溪组页岩气优质储层发育模式及识别评价技术[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(8): 96-111.DONG Dazhong, LIANG Feng, GUAN Quanzhong, et al. Deve-lopment model and identification evaluation technology of Wufeng-Longmaxi formation quality shale gas reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(8): 96-111. [26] 蔡勋育, 周德华, 赵培荣, 等. 中国石化深层、常压页岩气勘探开发进展与展望[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(6): 1039-1049. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2023061039CAI Xunyu, ZHOU Dehua, ZHAO Peirong, et al. Development progress and outlook of deep and normal pressure shale gas of SINOPEC[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(6): 1039-1049. doi: 10.11781/sysydz2023061039 -





 下载:
下载:










 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号