Physical simulation experiment of tuffaceous dissolution effect in sandstone reservoirs: a case study of Paleogene Wenchang Formation in Huizhou and Lufeng area, Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要: 为认识埋藏过程中酸性流体对碎屑岩储层中凝灰质的溶蚀改造效应及控制因素,选取珠江口盆地珠一坳陷惠州—陆丰地区古近系文昌组凝灰质砂岩储层,设计开展了岩心尺度的流体—岩石相互作用模拟实验。通过显微镜下观察、流体成分分析、物性表征等方法,对比分析了实验前后不同流体流速、不同凝灰质含量条件下砂岩储层的溶蚀作用和物性响应特征。结果表明,酸性流体环境中凝灰质溶蚀现象普遍,但不同实验条件下,凝灰质溶蚀强度及储层物性响应不同:成岩体系的开放性与封闭性决定凝灰质的溶蚀作用强弱。相同岩石和相同酸性流体条件下,高流速开放体系中凝灰质溶蚀量高于封闭体系,且低流速相对封闭体系中溶蚀产物趋于沉淀,溶蚀作用增孔效应有限。凝灰质含量显著影响溶蚀效应,富凝灰质砂岩中溶蚀作用有限,含凝灰质砂岩和贫凝灰质砂岩能够溶蚀增孔,且含凝灰质砂岩的溶蚀增孔效率更高。凝灰质含量相对中等—较低的储层中,中浅层埋藏阶段的开放成岩流体体系最有利于粒间凝灰质溶孔的发育。经历晚期酸性流体溶蚀改造后,较易形成次生溶蚀型优质储层,这一认识有助于不同地区的溶蚀型储层甜点预测。Abstract: Tuffaceous sandstone reservoirs of Paleogene Wenchang Formation in Huizhou and Lufeng area of Zhu I Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin were selected, and core-scale fluid-rock interaction simulation experiments were designed and carried out to explore the dissolution and modification effect of acidic fluid on tuffaceous components in clastic reservoirs during burial process and its controlling factors. The dissolution characteristics and physical property response characteristics of sandstone reservoirs under different fluid flow rates and tuffaceous contents before and after the experiments were compared and analyzed through microscope observation, fluid composition analysis, physical property characterization and other methods. The results showed that tuffaceous dissolution was common in acidic fluid environment, but the intensity of tuffaceous dissolution and the response of reservoir physical properties were different under different experimental conditions. Among them, the openness and closure of diagenetic system determined the intensity of tuffaceous dissolution. Under the same rock and acidic fluid conditions, the amount of tuffaceous dissolution in the high flow rate open system was higher than that in the closed system, and the dissolution products in the closed system tended to precipitate, which was not conducive to the preservation of dissolution pores. In addition, the content of tuffaceous components significantly affected dissolution effect, the tuffaceous-rich sandstone would not be conducive to dissolution porosity, while the tuffaceous-containing sandstone and tuffaceous-poor sandstone could increase dissolution porosity, and tuffaceous-containing sandstone has higher dissolution efficiency. Overall, in the reservoirs with relatively moderate to low contents of tuffaceous components, the open diagenetic system in the shallow-middle burial stage is most conducive to the development of dissolution pores of tuffaceous components. After the late stage of acidic fluid dissolution and modification, it is easier to form secondary dissolution-type high-quality reservoirs. This study is of great significance for the prediction of dissolution-type reservoir sweet spots in different areas.
-
图 3 溶蚀反应前后粒间凝灰质溶蚀差异
a.HZ-1井,3 777.13 m,富凝灰质砂岩,反应前,粒间孔中被凝灰质完全充填,无显孔,仅发育少量凝灰质收缩缝;b.HZ-1井,3 777.13 m,富凝灰质砂岩,封闭体系中反应后,粒间凝灰质未发生明显溶蚀作用;c.HZ-1井,3 777.13 m,富凝灰质砂岩,开放体系中反应后,粒间凝灰质未发生明显溶蚀作用,局部产生凝灰质收缩缝;d.HZ-2井,3 856.14 m,含凝灰质砂岩,反应前,粒间凝灰质晶间微孔发育,长石溶孔及粒间凝灰质溶孔不发育,少量原生孔隙;e.HZ-2井,3 856.14 m,含凝灰质砂岩,封闭体系中反应后,凝灰质溶孔不发育,仍以晶间孔为主;f.HZ-2井,3 856.14 m,开放体系中反应后,粒间凝灰质溶孔较发育;g.LF-1井,3 666 m,贫凝灰质砂岩,反应前,凝灰质含量较少,孔隙类型以原生孔隙为主;h.LF-1井,3 666 m,贫凝灰质砂岩,封闭体系中反应后,粒间溶蚀残余变少,未见明显自生矿物沉淀;i.LF-2井,3 503.5 m,贫凝灰质砂岩,开放体系中反应后,粒间溶孔增多,粒间溶蚀残余变少;j.LF-2井,3 483 m,含凝灰质砂岩,反应前,粒间凝灰质晶间微孔发育,长石溶孔及粒间凝灰质溶孔不发育,少量原生孔隙;k.LF-2井,3 483 m,含凝灰质砂岩,低温开放体系中反应后,粒间凝灰质溶孔发育,溶蚀孔中含有凝灰质溶蚀残余;l.LF-2井,3 483 m,含凝灰质砂岩,低温开放体系中反应后,粒间凝灰质溶蚀孔发育,未见自生矿物沉淀。
Figure 3. Difference of intergranular tuffaceous dissolution before and after dissolution reaction
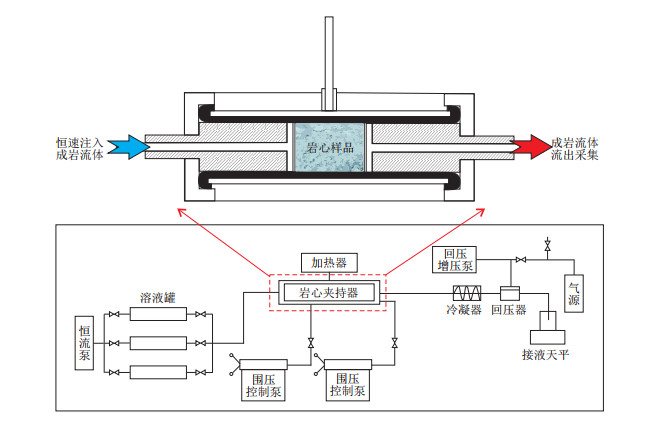
表 1 溶蚀模拟实验样品信息
Table 1. Information of experiment samples for dissolution simulation
井号 深度/m 类型 石英/% 长石/% 岩屑/% 凝灰质/% 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 HZ-1 3 777.13 富凝灰质砂岩 13 14 73 20 5.78 0.42 HZ-1 3 777.13 富凝灰质砂岩 13 14 73 20 5.73 0.36 HZ-2 3 856.14 含凝灰质砂岩 12.5 13.75 73.75 8 9.66 0.51 HZ-2 3 856.14 含凝灰质砂岩 12.5 13.75 73.75 8 9.62 0.40 LF-2 3 483.00 含凝灰质砂岩 75 13.5 11.5 7 15.77 0.68 LF-1 3 666.00 贫凝灰质砂岩 62.5 34.5 3 2 13.56 2.45 LF-2 3 503.50 贫凝灰质砂岩 76 17 7 2 19.63 1.71 表 2 珠江口盆地惠州—陆丰地区研究区凝灰质柱塞样实验前后物性特征
Table 2. Physical properties of tuffaceous plug samples before and after experiments in Huizhou and Lufeng area, Pearl River Mouth Basin
凝灰质含量 流体体系 反应前 反应后 孔隙度变化率/% 渗透率变化率/% 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 贫凝灰质 高温开放 19.63 1.71 21.29 2.43 8.46 42.11 含凝灰质 9.66 0.51 20.88 8.05 116.15 1 478.43 富凝灰质 5.78 0.42 6.52 0.18 12.80 -57.14 贫凝灰质 高温封闭 13.56 2.45 14.33 2.97 5.68 21.22 含凝灰质 9.62 0.40 10.97 0.72 14.03 80.00 富凝灰质 5.73 0.36 3.00 0.06 -47.64 -83.33 含凝灰质 低温开放 15.77 0.68 16.37 1.87 3.67 63.64 -
[1] 蒙启安, 李军辉, 李跃, 等. 海拉尔—塔木察格盆地中部富油凹陷高含凝灰质碎屑岩储层成因及油气勘探意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(2): 569-578.MENG Qi'an, LI Junhui, LI Yue, et al. Genetic mechanism of high content tuffaceous clastic rock reservoir in Hailar-Tamucage Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2020, 50(2): 569-578. [2] 田立新. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷古近系规模性砂砾岩储层凝灰质成因及其油气地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(2): 452-463.TIAN Lixin. Genesis mechanism of tuffaceous materials in Paleogene large-scale glutenite reservoirs and implications for hydrocarbon exploration in the Huizhou Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(2): 452-463. . [3] 刘晓健, 王清斌, 代黎明, 等. 凝灰质砂砾岩复合型储集空间特征及其成因: 以莱州湾南斜坡沙河街组为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(3): 48-58.LIU Xiaojian, WANG Qingbin, DAI Liming, et al. Characteristics and genesis of compound reservoir space in tuffaceous glutenite: a case from Shahejie Formation on the south slope of Laizhou Sag[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(3): 48-58. [4] 魏巍, 朱筱敏, 朱世发, 等. 湖相富火山物质复杂储层的岩石学特征及成岩作用: 以二连盆地阿南凹陷下白垩统腾一段为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(2): 147-158.WEI Wei, ZHU Xiaomin, ZHU Shifa, et al. Petrologic and diagenetic characteristics of the lacustrine volcanic-siliciclastic tight reservoir: an example from the first member of the Tenggeer Formation in the Lower Cretaceous, Anan Sag, Erlian Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(2): 147-158. [5] 贾珍臻, 林承焰, 任丽华, 等. 苏德尔特油田低渗透凝灰质砂岩成岩作用及储层质量差异性演化[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(6): 1624-1636.JIA Zhenzhen, LIN Chengyan, REN Lihua, et al. Diagenesis and reservoir quality evolution of low permeability tuffaceous sandstones in suderte oilfield[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2016, 46(6): 1624-1636. [6] 朱世发, 朱筱敏, 刘学超, 等. 油气储层火山物质蚀变产物及其对储集空间的影响: 以准噶尔盆地克—夏地区下二叠统为例[J]. 石油学报, 2014, 35(2): 276-285.ZHU Shifa, ZHU Xiaomin, LIU Xuechao, et al. Alteration pro-ducts of volcanic materials and their influence on reservoir space in hydrocarbon reservoirs: evidence from Lower Permian strata in Ke-Xia region, Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2014, 35(2): 276-285. [7] 朱世发, 朱筱敏, 吴冬, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘下二叠统油气储层中火山物质蚀变及控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(1): 77-85.ZHU Shifa, ZHU Xiaomin, WU Dong, et al. Alteration of volcanics and its controlling factors in the Lower Permian reservoirs at northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(1): 77-85. [8] KARIG D E. Reconsolidation tests and sonic velocity measurements of clay-rich sediments from the Nankai Trough[J]. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 1993, 131: 247-260. [9] EHRENBERG S N. Preservation of anomalously high porosity in deeply buried sandstones by grain-coating chlorite: examples from the Norwegian Continental Shelf[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(7): 1260-1286. [10] ZHU Shifa, ZHU Xiaomin, WANG Xulong, et al. Zeolite diagenesis and its control on petroleum reservoir quality of Permian in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin, China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(3): 386-396. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4314-y [11] 王剑, 高崇龙, 白雷, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘西段白垩系清水河组储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 632-645. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304632WANG Jian, GAO Chonglong, BAI Lei, et al. Diagenesis and pore evolution of Cretaceous Qingshuihe Formation reservoir in western section of southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 632-645. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304632 [12] 付小东, 张天付, 吴健平, 等. 二连盆地阿南凹陷白垩系腾格尔组致密油储层特征及主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(1): 64-76. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202101064FU Xiaodong, ZHANG Tianfu, WU Jian, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of tight oil reservoirs in Cretaceous Tengger Formation, A'nan Sag, Erlian Basin[J]. Petroleum Geo-logy & Experiment, 2021, 43(1): 64-76. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202101064 [13] 熊伟, 王越, 熊峥嵘, 等. 准噶尔盆地石北凹陷岛弧环境下火山—沉积建造特征及源储发育模式: 以石炭系姜巴斯套组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4): 656-666. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304656XIONG Wei, WANG Yue, XIONG Zhengrong, et al. Characteristics of volcanic-sedimentary formations and developmental patterns of source and reservoir rocks in an island arc environment of Shibei Sag, Junggar Basin: taking the Carboniferous Jiangbasitao Formation as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4): 656-666. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202304656 [14] 孙林, 邹信波, 李旭光, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷火山岩酸化可行性[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(2): 145-154.SUN Lin, ZOU Xinbo, LI Xuguang, et al. Feasibility study on acidification of volcanic rocks in Huizhou Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(2): 145-154. [15] 王韬, 徐倩, 李永军, 等. 车排子油田南部火山岩地质时代及成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(2): 160-168.WANG Tao, XU Qian, LI Yongjun, et al. Geological age and petrogenesis of volcanic rocks in southern Chepaizi oilfield[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(2): 160-168. [16] 连志刚, 常智勇, 李路路, 等. 玛东地区二叠系火山岩成藏特征及勘探潜力[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(5): 57-65.LIAN Zhigang, CHANG Zhiyong, LI Lulu, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics and exploration potential of Permian volcanic rocks in Madong area[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(5): 57-65. [17] 丁琳, 李晓艳, 周凤娟, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷古近系优质储层差异发育特征及主控因素: 以陆丰地区和惠州地区文昌组为例[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2022, 41(1): 75-86.DING Lin, LI Xiaoyan, ZHOU Fengjuan, et al. Differential deve-lopment characteristics and main controlling factors of the Paleogene high-quality reservoirs from the Zhu I Depression in the Pearl River Mouth Basin: a case on Wenchang Formation at Lufeng area and Huizhou area[J]. Acta Petrologica et Minera-logica, 2022, 41(1): 75-86. [18] 杨威, 谢武仁, 俞凌杰, 等. 四川盆地上三叠统须家河组致密砂岩溶蚀实验及地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(4): 655-663. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202104655YANG Wei, XIE Wuren, YU Lingjie, et al. Dissolution experiments and geological implications of tight sandstones in the Xujiahe Formation of Upper Triassic, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(4): 655-663. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202104655 [19] CHARDON E S, LIVENS F R, VAUGHAN D J. Reactions of feldspar surfaces with aqueous solutions[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2006, 78(1/2): 1-26. [20] BIEHL B C, REUNING L, SCHOENHERR J, et al. Do CO2-charged fluids contribute to secondary porosity creation in deeply buried carbonates?[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 76: 176-186. [21] BJØRLYKKE K, JAHREN J. Open or closed geochemical systems during diagenesis in sedimentary basins: constraints on mass transfer during diagenesis and the prediction of porosity in sandstone and carbonate reservoirs[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(12): 2193-2214. [22] BJØRLYKKE K. Relationships between depositional environments, burial history and rock properties. Some principal aspects of diagenetic process in sedimentary basins[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2014, 301: 1-14. [23] YUAN Guanghui, CAO Yingchang, ZHANG Yongchao, et al. Diagenesis and reservoir quality of sandstones with ancient "deep" incursion of meteoric freshwater: an example in the Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 82: 444-464. [24] YUAN Guanghui, CAO Yingchang, GLUYAS J, et al. Feldspar dissolution, authigenic clays, and quartz cements in open and closed sandstone geochemical systems during diagenesis: typical examples from two sags in Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2015, 99(11): 2121-2154. [25] 彭威龙, 胡国艺, 刘全有, 等. 热模拟实验研究现状及值得关注的几个问题[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(9): 1252-1263.PENG Weilong, HU Guoyi, LIU Quanyou, et al. Research status on thermal simulation experiment and several issues for concerns[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(9): 1252-1263. [26] 佘敏, 蒋义敏, 胡安平, 等. 碳酸盐岩溶蚀模拟实验技术进展及应用[J]. 海相油气地质, 2020, 25(1): 12-21.SHE Min, JIANG Yimin, HU Anping, et al. The progress and application of dissolution simulation of carbonate rock[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2020, 25(1): 12-21. [27] 赵姗姗, 张哨楠, 万友利. 塔中顺托果勒低隆区柯坪塔格组长石溶蚀及对储层的影响[J]. 石油实验地质, 2015, 37(3): 293-299. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201503293ZHAO Shanshan, ZHANG Shaonan, WAN Youli. Feldspar dissolution and its effect on reservoir in Kepingtage Formation, Shun-tuoguole Low Uplift, central Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2015, 37(3): 293-299. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201503293 [28] 郭欣欣, 刘立, 曲希玉, 等. 碱性地层水对火山碎屑岩改造作用的实验研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(3): 314-319. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201303314GUO Xinxin, LIU Li, QU Xiyu, et al. Experimental study on reformation of volcanic clastic rocks by alkaline formation water[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2013, 35(3): 314-319. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201303314 [29] 曲希玉, 刘立, 蒙启安, 等. 大气水对火山碎屑岩改造作用的研究: 以塔木查格盆地为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2012, 34(3): 285-290. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201203285QU Xiyu, LIU Li, MENG Qian, et al. Reformation effect of atmospheric water on volcanic clastic rocks: a case study in Tamtsag Basin, Mongolia[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2012, 34(3): 285-290. doi: 10.11781/sysydz201203285 [30] 张庆玉, 季少聪, 曾韬, 等. 四川盆地北部中二叠统茅口组碳酸盐岩溶蚀模拟实验与岩溶层组特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(1): 175-184. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202301175ZHANG Qingyu, JI Shaocong, ZENG Tao, et al. Experimental dissolution and karst strata association of Middle Permian Maokou carbonate rocks in the northern part of Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(1): 175-184. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202301175 [31] 葛家旺, 朱筱敏, 潘荣, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷文昌组砂岩孔隙定量演化模式: 以HZ-A地区辫状河三角洲储层为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(1): 183-193.GE Jiawang, ZHU Xiaomin, PAN Rong, et al. A quantitative porosity evolution model of sandstone for Wenchang Formation in Huizhou Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin: a case study for braided fluvial delta reservoir of HZ-A area[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(1): 183-193. [32] 龙更生, 施和生, 郑荣才, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州凹陷深部储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2011, 30(4): 665-673.LONG Gengsheng, SHE Hesheng, ZHENG Rongcai, et al. Diagenesis and porosity evolution of deep reservoirs in Huizhou Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2011, 30(4): 665-673. [33] 马梓珂. LF14-4油田文昌组储层地质特征及注水储层保护技术研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2019.MA Zike. Study on Reservoir geological characteristics and water injection reservoir protection technology of Wenchang Formation in LF14-4 Oilfield[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2019. [34] 王宏语, 张晓龙, 段志勇, 等. 苏德尔特地区南一段凝灰质砂岩储层微观非均质性及其主控因素[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 2011, 35(4): 30-37.WANG Hongyu, ZHANG Xiaolong, DUAN Zhiyong, et al. Tuffaceous sandstone reservoir's microcosmic heterogeneity and major controlling factors of the Nantun-Ⅰ formation in Suderte area, Hailar Basin[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute, 2011, 35(4): 30-37. [35] 王宏语, 樊太亮, 肖莹莹, 等. 凝灰质成分对砂岩储集性能的影响[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(3): 432-439.WANG Hongyu, FAN Tailiang, XIAO Yingying, et al. Effect of tuffaceous components on physical property of sandstone reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 432-439. [36] 杨华, 杨奕华, 石小虎, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地周缘晚古生代火山活动对盆内砂岩储层的影响[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(4): 526-534.YANG Hua, YANG Yihua, SHI Xiaohu, et al. Influence of the Late Paleozoic volcanic activity on the sandstone reservoir in the interior of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(4): 526-534. [37] 远光辉, 操应长, 葸克来, 等. 东营凹陷北带古近系碎屑岩储层长石溶蚀作用及其物性响应[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(5): 853-866.YUAN Guanghui, CAO Yingchang, XI Kelai, et al. Feldspar dissolution and its impact on physical properties of Paleogene clastic reservoirs in the northern slope zone of the Dongying Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(5): 853-866. [38] 刘明洁, 季永承, 唐青松, 等. 成岩体系对致密砂岩储层质量的控制: 以四川盆地中台山地区须二段为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(4): 826-840.LIU Mingjie, JI Yongcheng, TANG Qingsong, et al. Diagenetic system control of tight sandstone reservoir quality: case study of Xu2 member, Xujiahe Formation, in Zhongtaishan area, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(4): 826-840. [39] 万琼华, 刘伟新, 罗伟, 等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷A油田储层质量差异及低渗储层主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(3): 551-560.WAN Qionghua, LIU Weixin, LUO Wei, et al. Reservoir quality differences and major factors controlling low-permeability reservoirs of Oilfield A in the Lufeng Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2017, 38(3): 551-560. [40] GUO Zhengfu, WILSON M, DINGWELL D B, et al. India-Asia collision as a driver of atmospheric CO2 in the Cenozoic[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3891. [41] 夏文谦, 朱祥, 金民东, 等. 川北地区上二叠统吴家坪组火山碎屑岩油气藏储层特征及主控因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(2): 307-316. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302307XIA Wenqian, ZHU Xiang, JIN Mindong, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of volcanic clastic rock reservoirs in Wujiaping Formation of Upper Permian in northern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(2): 307-316. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302307 -





 下载:
下载:




 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号