Main controlling factors of shale oil enrichment in second member of Paleogene Funing Formation in Gaoyou Sag of Subei Basin
-
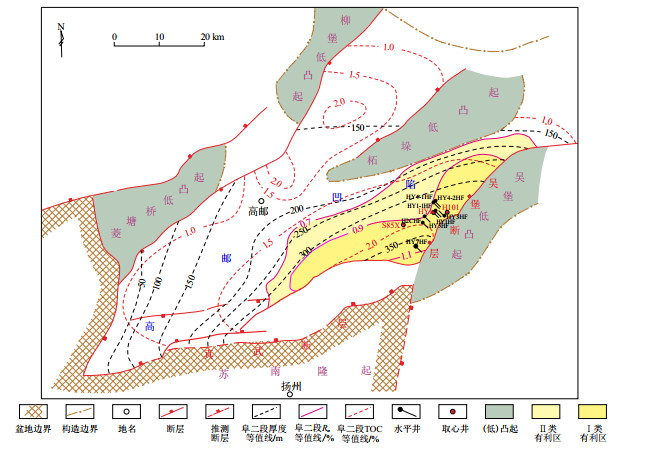
摘要: 高邮凹陷古近系阜宁组二段是苏北盆地页岩油勘探的重点区带和层系,已部署实施的8口页岩油水平井的成功,证实其具有非常大的页岩油勘探潜力和良好的勘探前景。针对该层段页岩油井产能存在差异、富集主控因素认识不清楚等难点问题,综合利用岩心、测录井、分析测试数据和生产动态数据等资料,对阜二段地质特征和页岩油富集主控因素进行研究。高邮凹陷阜二段泥页岩以长英质—黏土质混积岩和长英质—灰质/白云质混积岩为主,有机质丰度中等,有机质类型以Ⅰ型和Ⅱ1型为主;自下向上有机质类型由腐殖型向腐泥型逐渐转变,有机质丰度总体由低逐渐增高,具有较好的页岩油形成条件。综合岩相、生油性、含油性、储集性、可压性等多因素评价可知,高邮凹陷阜二段共发育Ⅴ-4~Ⅴ-9、Ⅳ-2~Ⅳ-7小层和Ⅱ~Ⅲ亚段三套勘探有利层段。阜二段页岩油富集具体表现为:①有利岩相组合是页岩油富集的物质基础,其中混积岩夹白云石条带是有利的源—储配置组合,页岩油产能高;②复杂的孔缝系统是页岩油富集的核心,层理缝和裂缝是页岩油流动的主要通道,有效沟通基质孔隙,提高页岩油导流能力;③较高的成熟度和良好的保存条件是页岩油高产稳产的关键,镜质体反射率(Ro)介于0.8%~0.9%时滞留油含量相对较高,远离长期活动性断层的井游离烃含量(S1)相对较高。Abstract: The second member of the Paleogene Funing Formation in the Gaoyou Sag is a key area for shale oil exploration within the Subei Basin. The successful implementation of eight horizontal shale oil wells evidences its significant potential and promising prospects of exploration. Addressing challenges such as variations in well productivity and unclear understanding of the main controlling factors of shale oil enrichment, this study utilized core data, logging data, analysis testing data, and production dynamics to investigate the geological characteristics and main controlling factors of shale oil enrichment in the second member of the Funing Formation. The results reveal that the mudstone and shale in this member predominantly consist of felsic-argillaceous mixed rocks and felsic-calcilutite/dolomitic mixed rocks, with moderate organic matter abundance and mainly TypeⅠand TypeⅡ1 organic matter. From bottom to top, the organic matter type gradually transitions from humus to sapropelic, with an overall increase in organic matter abundance, providing favorable conditions for shale oil formation. A comprehensive evaluation of lithofacies, oil generation potential, oil content, reservoir characteristics, and compressibility identified three favorable exploration layers in the second member of the Funing Formation: Ⅴ-4 to Ⅴ-9, Ⅳ-2 to Ⅳ-7, and Ⅱ to Ⅲ.Shale oil enrichment in the second member of the Funing Formation is characterized by the following factors: (1) Favorable lithofacies combinations, particularly mixed rocks interbedded with dolomite bands, form the material basis for shale oil enrichment, resulting in high shale oil productivity. (2) A complex pore and fracture system is central to shale oil enrichment, with laminar fractures and cracksserving as the main pathways for shale oil flow, effectively connecting matrix pores and enhancing shale oil conductivity. (3) Higher maturity and favorable preservation conditions are crucial for high and stable shale oil production, with vitrinite reflectance (Ro) between 0.8% and 0.9%, indicating relatively higher retained oil content. Wells located away from long-term active faults exhibit relatively higher free hydrocarbon (S1) content.
-
表 1 苏北盆地高邮凹陷古近系阜宁组二段不同岩性泥页岩参数统计
Table 1. Statistics of shale parameters of different lithology in second member of Paleogene Funing Formation, Gaoyou Sag, Subei Basin
页岩岩性 ω(TOC)/% S1/(mg/g) Φ/% 长英质—灰质/白云质混积岩 1.07 1.56 5.30 长英质—黏土质混积岩 1.42 3.11 4.94 黏土质长英细粒岩 1.77 3.07 5.05 长英细粒岩 0.86 1.78 5.37 长英质碳酸盐岩 1.45 1.54 4.33 碳酸盐岩 1.44 2.59 5.17 -
[1] 张金川, 林腊梅, 李玉喜, 等. 页岩油分类与评价[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(5): 322-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205032.htmZHANG Jinchuan, LIN Lamei, LI Yuxi, et al. Classification and evaluation of shale oil[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(5): 322-331. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205032.htm [2] EIA. Technically recoverable shale oil and shale gas resources: an assessment of 137 shale formations in 41 countries outside the United States[R]. Washington: U.S. Energy Information Administration, 2013. [3] 杨雷, 金之钧. 全球页岩油发展及展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5): 553-559. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201905002.htmYANG Lei, JIN Zhijun. Global shale oil development and prospects[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5): 553-559. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY201905002.htm [4] 周庆凡, 金之钧, 杨国丰, 等. 美国页岩油勘探开发现状与前景展望[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(3): 469-477. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201903004.htmZHOU Qingfan, JIN Zhijun, YANG Guofeng, et al. Shale oil exploration and production in the U.S.: status and outlook[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3): 469-477. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201903004.htm [5] 邹才能, 潘松圻, 荆振华, 等. 页岩油气革命及影响[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202001001.htmZOU Caineng, PAN Songqi, JING Zhenhua, et al. Shale oil and gas revolution and its impact[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202001001.htm [6] 邓舟舟. 美国页岩油分布规律及主控因素研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019.DENG Zhouzhou. Study of distribution and main control factors of shale oil in USA[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2019. [7] 李倩文, 马晓潇, 高波, 等. 美国重点页岩油区勘探开发进展及启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(5): 630-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202105019.htmLI Qianwen, MA Xiaoxiao, GAO Bo, et al. Progress and enlightenment of exploration and development of major shale oil zones in the USA[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(5): 630-640. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202105019.htm [8] 杨阳, 郑兴范, 肖毓祥, 等. 中国石油中高成熟度页岩油勘探开发进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2023, 28(3): 23-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202303003.htmYANG Yang, ZHENG Xingfan, XIAO Yuxiang, et al. Progress in exploration and development of high-mature shale oil of Petro-China[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2023, 28(3): 23-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTSY202303003.htm [9] 郭秋麟, 米石云, 张倩, 等. 中国页岩油资源评价方法与资源潜力探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 402-412. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303402GUO Qiulin, MI Shiyun, ZHANG Qian, et al. Assessment methods and potential of shale oil resources in China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 402-412. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303402 [10] 文家成, 胡钦红, 杨升宇, 等. 渤海湾盆地沧东凹陷孔二段页岩储层特征及页岩油可动性评价[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(4): 63-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202304008.htmWEN Jiacheng, HU Qinhong, YANG Shengyu, et al. Shale reservoir characteristics and shale oil mobility in member 2 of Kongdian Formation of Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(4): 63-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ202304008.htm [11] 徐君, 杨春, 孟朋飞. 吐哈探区非常规油气资源开发策略[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 314-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202303007.htmXU Jun, YANG Chun, MENG Pengfei. Development strategies for unconventional oil and gas resources in Turpan-Hami exploration area[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(3): 314-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202303007.htm [12] 罗安湘, 喻建, 刘显阳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中生界石油勘探实践及主要认识[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(3): 253-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202203001.htmLUO Anxiang, YU Jian, LIU Xianyang, et al. Practices and cognitions of petroleum exploration in Mesozoic, Ordos Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(3): 253-260. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD202203001.htm [13] 赵俊峰, 刘池洋, 张东东, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘铜川地区三叠系延长组长7段剖面及其油气地质意义[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2022, 12(1): 233-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202201020.htmZHAO Junfeng, LIU Chiyang, ZHANG Dongdong, et al. Description and its hydrocarbon geological implications of outcrop sections of Triassic Chang-7 Member in southern Ordos Basin[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2022, 12(1): 233-245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202201020.htm [14] 彭艳霞, 杜玉山, 蒋龙, 等. 济阳坳陷缓坡带页岩油储层微观孔隙结构及分形特征[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(4): 535-544. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202304002.htmPENG Yanxia, DU Yushan, JIANG Long, et al. Micropore structure and fractal characteristics of shale oil reservoir in gentle slope zone of Jiyang Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2023, 30(4): 535-544. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202304002.htm [15] 李洪波, 吴智超, 张敏, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油地球化学特征与运聚意义[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(4): 579-585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202304008.htmLI Hongbo, WU Zhichao, ZHANG Min, et al. The geochemical characteristics and migration-accumulation significances of shale oil in Lucaogou Formation of Jimsar Sag[J]. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 2023, 30(4): 579-585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT202304008.htm [16] 于燕, 林刚, 卓龙成, 等. 浅谈页岩油效益开发[J]. 复杂油气藏, 2023, 16(2): 144-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ202302004.htmYU Yan, LIN Gang, ZHUO Longcheng, et al. Discussion on the benefit development of shale oil[J]. Complex Hydrocarbon Reser-voirs, 2023, 16(2): 144-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FZYQ202302004.htm [17] 翟光明. 中国石油地质志卷八: 苏浙皖闽油气区[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1992: 215.ZHAI Guangming. Petroleum geology of China, Vol. 8[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1992: 215. [18] 昝灵, 白鸾羲, 印燕铃等. 苏北盆地溱潼凹陷古近系阜宁组二段页岩油基本特征及成因分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(2): 356-365. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302356ZAN Ling, BAI Luanxi, YIN Yanling, et al. Basic characteristics and genesis analysis of shale oil in the second member of Paleogene Funing Formation in Qintong Sag, Subei Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(2): 356-365. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202302356 [19] 马晓鸣. 高邮凹陷构造特征研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2009.MA Xiaoming. Research of structural characteristics of Gaoyou Depression[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2009. [20] 许中杰, 程日辉, 张莉, 等. 华南陆缘晚三叠—早、中侏罗世海平面相对升降与古气候演化的地球化学记录[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2012, 37(1): 113-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201201015.htmXU Zhongjie, CHENG Rihui, ZHANG Li, et al. The geochemistry records of sea-level relative movement and paleoclimatic evolution of the South China continental margin in Late Triassic-Early-Middle Jurassic[J]. Editorial Committee of Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2012, 37(1): 113-124. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201201015.htm [21] 胡涛, 庞雄奇, 姜福杰, 等. 陆相断陷咸化湖盆有机质差异富集因素探讨: 以东濮凹陷古近系沙三段泥页岩为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(1): 140-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202101010.htmHU Tao, PANG Xiongqi, JIANG Fujie, et al. Factors controlling differential enrichment of organic matter in saline lacustrine rift basin: a case study of third member Shahejie Fm in Dongpu Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(1): 140-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202101010.htm [22] 张林晔, 包友书, 李钜源, 等. 湖相页岩油可动性: 以渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷东营凹陷为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(6): 641-649. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201406001.htmZHANG Linye, BAO Youshu, LI Juyuan, et al. Movability of lacustrine shale oil: a case study of Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(6): 641-649. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201406001.htm [23] JARVIE D M. Shale resource systems for oil and gas: part 2: shale-oil resource systems[M]//BREYER J A. Shale reservoirs—giant resources for the 21st century. Tulsa, Oklahoma: AAPG, 2012: 89-119. [24] LEYTHAEUSER D, SCHAEFER R G, RADKE M. SP2 on the primary migration of petroleum[C]//Paper Presented at the 12th World Petroleum Congress. Houston, 1987: 227-236. [25] LEYTHAEUSER D, RADKE M, WILLSCH H. Geochemical effects of primary migration of petroleum in Kimmeridge source rocks from Brae Field area, North Sea. Ⅱ: Molecular composition of alkylated naphthalenes, phenanthrenes, benzo- and dibenzo thiophenes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1988, 52(12): 2879-2891. [26] 陈建平, 孙永革, 钟宁宁, 等. 地质条件下湖相烃源岩生排烃效率与模式[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(11): 2005-2032. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201411001.htmCHEN Jianping, SUN Yongge, ZHONG Ningning, et al. The efficiency and model of petroleum expulsion from the lacustrine source rocks within geological frame[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(11): 2005-2032. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201411001.htm [27] 付晓飞, 石海东, 蒙启安, 等. 构造和沉积对页岩油富集的控制作用: 以松辽盆地中央坳陷区青一段为例[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2020, 39(3): 56-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202003006.htmFU Xiaofei, SHI Haidong, MENG Qi'an, et al. Controlling effects of the structure and deposition on the shale oil enrichment: taking formation qn_1 in the central depression of Songliao Basin as an instance[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2020, 39(3): 56-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQSK202003006.htm [28] 孙彪. 苏北盆地海安凹陷古近系阜二段页岩油地质甜点评价研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2021.SUN Biao. Evaluation of geological sweet spot of shale oil: a case study of the second member of Funing Formation in Haian Sag, Subei Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2021. [29] 芮晓庆, 周圆圆, 李志明, 等. 苏北盆地阜宁组源储特征及页岩油勘探方向探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40 (6): 133-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202006012.htmRUI Xiaoqing, ZHOU Yuanyuan, LI Zhiming, et al. Characteristics of source rocks and reservoirs of the Funing Formation in the Subei Basin and their bearing on future shale oil exploration[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(6): 133-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ202006012.htm -





 下载:
下载:









 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号