Sedimentary microfacies and environment of Paleogene carbonate-rich shale in Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin
-
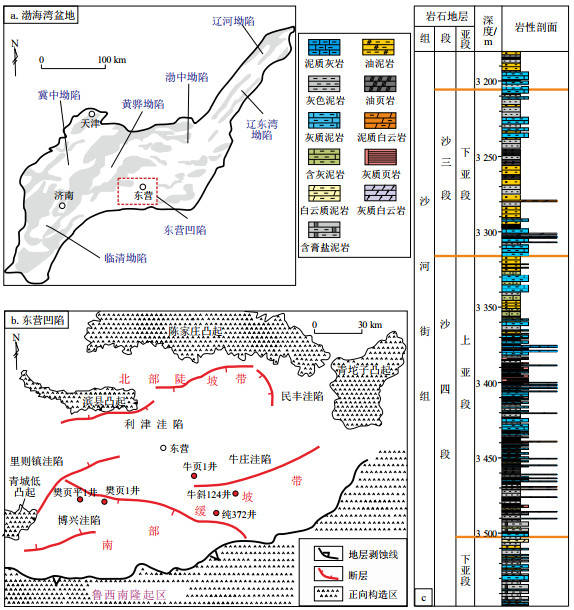
摘要: 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷富碳酸盐页岩的微相特征识别、划分及其组合方式研究,是揭示相关沉积物沉积成因和空间结构的基础。基于岩心和岩石薄片资料,利用X射线衍射、扫描电镜分析等测试分析技术,通过高分辨率的岩心取样和测试,对东营凹陷斜坡带富碳酸盐页岩开展了岩石矿物学和古生物学等方面的分析。结果表明,该区富碳酸盐页岩内部可以划分出藻席微相、介壳页岩微相等10种微相类型,各类微相通过不同方式叠加构成一系列微相组合,并显示出米级尺度的页岩相变特征。对应于东营凹陷咸水湖泊演化的不同阶段,可划分出浅水蒸发岩微相组合、震荡半深水页岩微相组合和震荡深水页岩微相组合等3种岩石微相组合,这些组合通常由高频振荡背景下湖平面升降旋回控制。东营凹陷沙河街组四段上亚段自下而上,伴随气候的湿热、风化增强、湖平面上升、湖泊盐度降低,震荡深水页岩微相组合占比逐渐增加,浅水蒸发岩微相组合逐渐降低,一系列向上水体变深的沉积旋回记录了东营凹陷中始新世持续沉降和生物—环境协同演化的特点。Abstract: The identification, classification, and integration of microfacies characteristics of carbonate-rich shale in the Dongying Sag of the Bohai Bay Basin are fundamental for understanding the sedimentary origin and spatial structure of related sediments. Leveraging core and rock thin section data, along with analytical techniques such as X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy, high-resolution core sampling and testing were conducted to analyze the rock mineralogy and paleontology of the carbonate-rich shale in the slope zone of the Dongying Sag. The research findings identified the presence of 10 types of microfacies within the carbonate-rich shale, including algal mat microfacies and shell shale microfacies. These microfacies combined in various ways to form a spectrum of microfacies combinations, exhibiting shale phase transition characteristics on a meter scale. Corresponding to the different stages of saline lake evolution in the Dongying Sag, three types of rock microfacies combinations emerged: shallow water evaporite microfacies combination, oscillatory semi-deep water shale microfacies combination, and oscillatory deep water shale microfacies combination. These combinations were typically controlled by the cyclical rise and fall of lake levels against a backdrop of high-frequency oscillations. In the upper submember of the fourth member of the Shahejie Formation, from bottom to top, as the climate became more humid and hot, weathering intensified, lake levels rose and lake salinity decreased, the proportion of oscillatory deep water shale microfacies combinations gradually increased, while that of shallow water evaporite microfacies combinations decreased. This series of upward-deepening depositional cycles recorded the continuous subsidence and co-evolution of biology and environment during the middle Eocene in the Dongying Sag.
-
图 2 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷沙河街组四段上亚段富碳酸盐页岩沉积微相类型
a.牛斜124井,3 243.75 m,红色页岩微相;b.樊页平1井,3 470.00 m,介壳页岩微相;c.樊页1井,3 432.42 m,白云质页岩微相;d.樊页1井,3 437.30 m,生物礁滩微相;e.纯372井,2 605.90 m,颗石藻页岩微相;f.樊页1井,3 430.00 m,透镜状灰质页岩微相;g.樊页平1井,3 454.00 m,重力流水道微相;h.樊页平1井,3 468.30 m,藻席微相;i.樊页平1井,3 473.5 7 m,泥质页岩微相;j.牛55-斜4井,3 956.10 m,含盐膏页岩微相。
Figure 2. Sedimentary microfacies types of carbonate-rich shale in upper submember of fourth member of Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin
表 1 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷沙河街组四段上亚段沉积微相组合
Table 1. Sedimentary microfacies combinations of upper submember of fourth member of Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin
物源供给 微相组合 成因相 微相类型及标志 生物群落 充填方式 过补偿 震荡深水页岩微相组合 远岸生物带,风暴沉积,浊流沉积 泥质页岩微相,介壳页岩微相,重力流水道微相,含膏盐页岩微相。水平纹层 鱼类,介形虫,盘星藻,软体类 进积 平衡充填 震荡半深水页岩微相组合 泥丘,微生物席,滑塌角砾 藻席微相,透镜状灰质页岩微相,白云质页岩微相。滑塌构造,交错纹层,波状纹层,透镜状纹层,压扁纹层等 介形类,渤海藻 加积 欠补偿 浅水蒸发岩微相组合 生物礁,粒屑滩,藻席,盐沼等 颗石藻页岩微相,生物礁滩微相,白云质页岩微相,含膏盐页岩微相。鸟眼构造,干裂纹,虫孔,含植物叶片的泥晶石灰岩 有孔虫,介形类,徳弗兰藻,陆生植物化石等 退积 -
[1] LOWERY C M, CORBETT M J, LECKIE R M, et al. Foraminiferal and nannofossil paleoecology and paleoceanography of the Cenomanian- Turonian Eagle Ford shale of southern Texas[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 413: 49-65. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.07.025 [2] ELLIOT SMITH M, CARROLL A R. Stratigraphy and paleolimnology of the Green River Formation, western USA[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2015. [3] ULMISHEK G. Volga-Ural Basin, U. S. S. R. : rich petroleum systems with a single source rock[R]. Texas: AAPG, 1991: 75. [4] ZAHRER J, DREIBRODT S, BRAUER A. Evidence of the North Atlantic Oscillation in varve composition and diatom assemblages from recent, annually laminated sediments of Lake Belau, northern Germany[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2013, 50(2): 231-244. doi: 10.1007/s10933-013-9717-7 [5] CONROY J L, THOMPSON D M, COLLINS A, et al. Climate influences on water and sediment properties of Genovesa Crater Lake, Galápagos[J]. Journal of Paleolimnology, 2014, 52(4): 331-347. doi: 10.1007/s10933-014-9797-z [6] BOHACS K M, LAZAR O R, DEMKO T M. Parasequence types in shelfal mudstone strata: quantitative observations of lithofacies and stacking patterns, and conceptual link to modern depositional regimes[J]. Geology, 2014, 42(2): 131-134. doi: 10.1130/G35089.1 [7] LIANG Chao, JIANG Zaixing, CAO Yingchang, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and origin of lacustrine organic-rich shales in the salinized Eocene Dongying Depression[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2018, 130(1/2): 154-174. [8] 杜韫华. 一种次生的片钠铝石[J]. 地质科学, 1982, 17(4): 434-437. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX198204013.htmDU Yunhua. Secondary dawsonite in Shengli Oil Field, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1982, 17(4): 434-437. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX198204013.htm [9] 徐效平. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷古近系富碳酸盐矿物页岩储集特征及其控制因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(3): 413-421. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303413XU Xiaoping. Reservoir characteristics and controlling factors of Paleogene carbonate-rich shale in Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(3): 413-421. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202303413 [10] 陈扬, 胡钦红, 赵建华, 等. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷湖相富有机质页岩纹层特征和储集性能[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(2): 307-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202202006.htmCHEN Yang, HU Qinhong, ZHAO Jianhua, et al. Lamina characteristics and their influence on reservoir property of lacustrine organic-rich shale in the Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(2): 307-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202202006.htm [11] 王伟庆, 刘惠民, 刘雅利, 等. 东营凹陷古近系页岩碳酸盐纹层内部结构与成因[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(3): 11-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202203002.htmWANG Weiqing, LIU Huimin, LIU Yali, et al. Texture and genesis of Paleogene lacustrine shale carbonate laminae in Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depresion, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(3): 11-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202203002.htm [12] 王永诗, 唐东. 咸化断陷湖盆典型页岩剖面地质特征: 以东营凹陷为例[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2022, 12(1): 181-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202201016.htmWANG Yongshi, TANG Dong. Geological characteristics of typical shale profile in a saline lacustrine rift basin: a case study of Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2022, 12(1): 181-191. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ202201016.htm [13] 伍松柏. 砂岩储层不同产状自生高岭石成因机制及其储层改造意义: 以东营凹陷沙河街组为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(5): 12-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202305002.htmWU Songbai. Genetic mechanism of authigenic kaolinite with different occurrence in sandstone reservoirs: a case of Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(5): 12-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS202305002.htm [14] ZACHOS J, PAGANI M, SLOAN L, et al. Trends, rhythms, and aberrations in global climate 65 Ma to present[J]. Science, 2001, 292(5517): 686-693. [15] CRAMWINCKEL M J. Trends and transients in climate and environment during the Eocene[D]. Utrecht: Utrecht University, 2019. [16] 刘传联, 成鑫荣. 渤海湾盆地早第三纪非海相钙质超微化石的锶同位素证据[J]. 科学通报, 1996, 41(10): 908-910. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199610012.htmLIU Chuanlian, CHENG Xinrong. Strontium isotope evidence from Early Tertiary non-marine calcareous nanofossils in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1996, 41(10): 908-910. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199610012.htm [17] ZIMMERLE W. The encyclopedia of sedimentology: R.W. Fairbridge and J. Bourgeois (Editors). Dowden, Hutchinson & Ross, Stroudsburg, Pa., 1978, 901 pp. U.S. $ 65.00 or 42.25 (distributed by Academic Press, New York, N.Y.)[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1979, 24(3/4): 328-329. [18] 彭军, 于乐丹, 许天宇, 等. 湖相泥页岩地层米氏旋回测井识别及环境响应特征: 以渤海湾盆地济阳坳陷东营凹陷樊页1井Es4scs为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(4): 957-969. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202204017.htmPENG Jun, YU Ledan, XU Tianyu, et al. Logging identification of Milankovitch cycle and environmental response characteristics of lacustrine shale: a case study on Es4scs in well Fanye 1, Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(4): 957-969. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202204017.htm [19] FLVGEL E. Microfacies of carbonate rocks: analysis, interpretation and application[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2013. [20] THOMPSON D L, STILWELL J D, HALL M. Lacustrine carbonate reservoirs from Early Cretaceous rift lakes of western Gondwana: pre-salt coquinas of Brazil and west Africa[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 28(1): 26-51. [21] 何青芳. 山东东营凹陷下第三系介形类化石分布特征[J]. 内江科技, 2011, 32(5): 15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJNJ201105130.htmHE Qingfang. Distribution characteristics of ostracod fossils in Paleogene in Dongying Depression in Shandong[J]. Nei Jiang Science & Technology, 2011, 32(5): 15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJNJ201105130.htm [22] 李国山, 王永标, 卢宗盛, 等. 山东东营凹陷古近纪湖相藻礁群落结构及古生态特征[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2011, 36(6): 1044-1052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201106010.htmLI Guoshan, WANG Yongbiao, LU Zongsheng, et al. Community structure and paleoecology of Paleogene lacustrine cladosiphonia reefs in the Dongying Depression, Shandong Province, China[J]. Earth Science(Journal of China University of Geosciences), 2011, 36(6): 1044-1052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201106010.htm [23] 钟筱春, 钟石兰, 费轩冬, 等. 渤海湾盆地沙河街组一段颗石藻类化石及其沉积环境[J]. 微体古生物学报, 1988, 5(2): 145-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT198802002.htmZHONG Xiaochun, ZHONG Shilan, FEI Xuandong, et al. Calcareous nannofossils from the Oligocene Shahejie-1 Member in the Bohai Basin and their sedimentary environment[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 1988, 5(2): 145-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT198802002.htm [24] SCHIEBER J, SOUTHARD B J. Bedload transport of mud by floccule ripples: direct observation of ripple migration processes and their implications[J]. Geology, 2009, 37(6): 483-486. [25] 陈世悦, 张顺, 刘惠民, 等. 湖相深水细粒物质的混合沉积作用探讨[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(2): 271-284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201702008.htmCHEN Shiyue, ZHANG Shun, LIU Huimin, et al. Discussion on mixing of fine-grained sediments in lacustrine deep water[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2017, 19(2): 271-284. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201702008.htm [26] DUPRAZ C, REID R P, BRAISSANT O, et al. Processes of carbonate precipitation in modern microbial mats[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2008, 96(3): 141-162. [27] 颜佳新, 孟琦, 王夏, 等. 碳酸盐工厂与浅水碳酸盐岩台地: 研究进展与展望[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(2): 232-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201902004.htmYAN Jiaxin, MENG Qi, WANG Xia, et al. Carbonate factory and carbonate platform: progress and prospects[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2019, 21(2): 232-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201902004.htm [28] 徐金鲤, 潘照仁, 杨育梅, 等. 山东胜利油区早第三纪沟鞭藻类和疑源类[M]. 东营: 石油大学出版社, 1997.XU Jinli, PAN Zhaoren, YANG Yumei, et al. Early Tertiary dinoflagellates and acritarchs in Shengli Oilfield, Shandong[M]. Dong-ying: University of Petroleum Press, 1997. -





 下载:
下载:




 苏公网安备32021102000780号
苏公网安备32021102000780号